ASL 14. Deep Structures of the Neck and Head
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
posterior digastric muscle
Superficial muscle going under the jaw, makes an obtuse angle with anterior digastric muscle
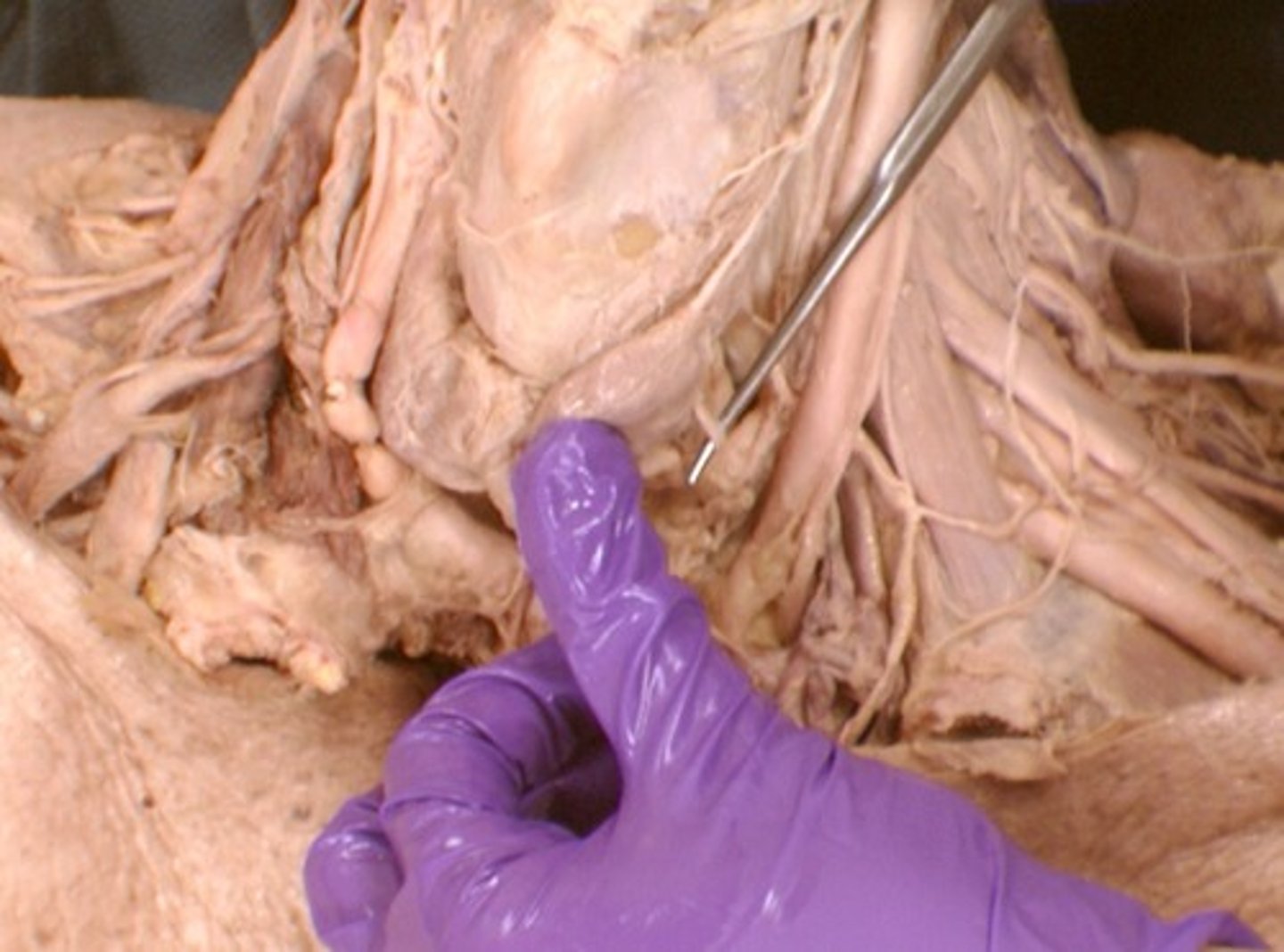
Stylopharyngeus m.
elevates and draws pharynx laterally
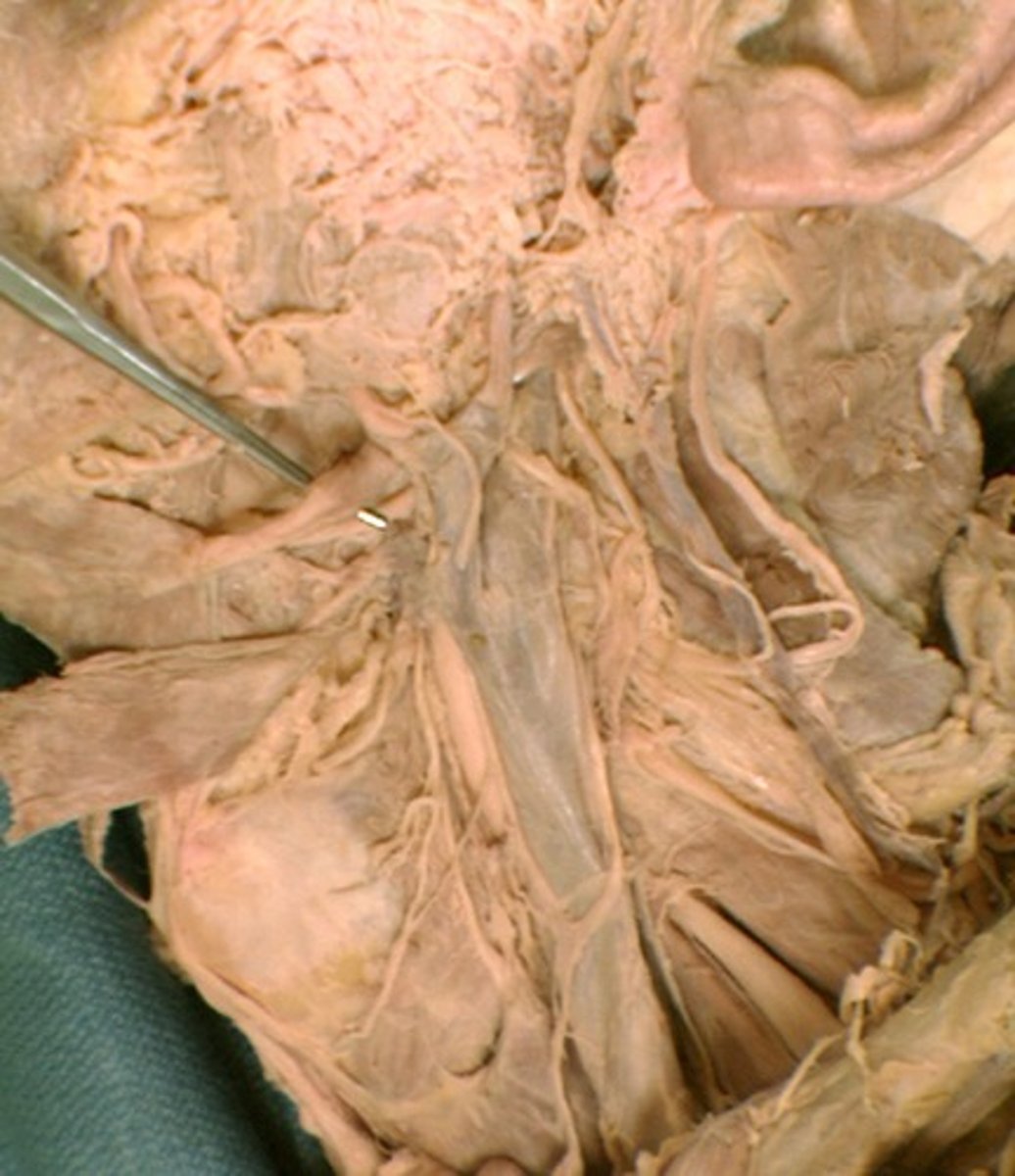
Glossopharyngeal n.
Cranial nerve IX, Both, Tongue and Pharynx (sensory), Pharynx (motor)
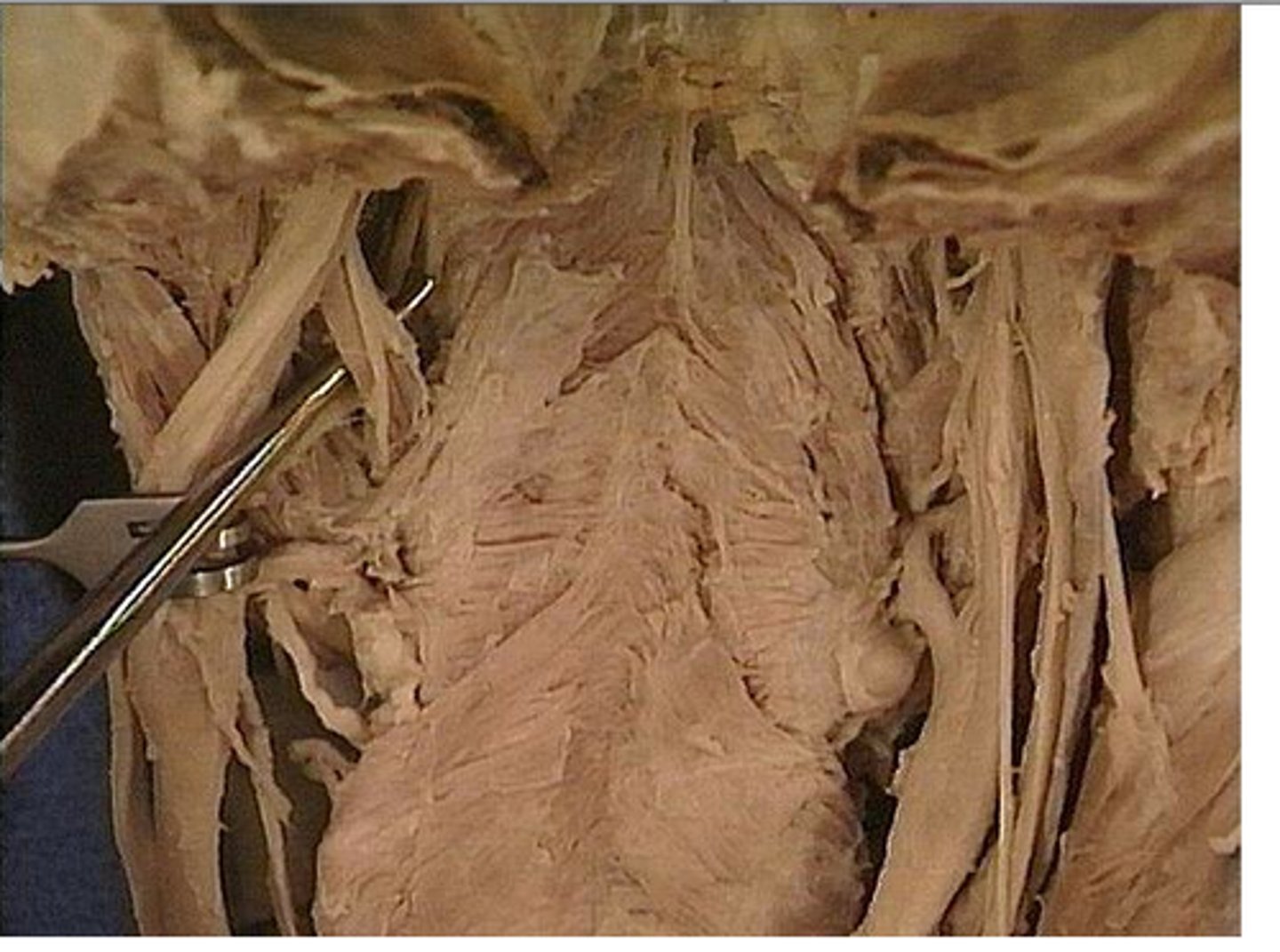
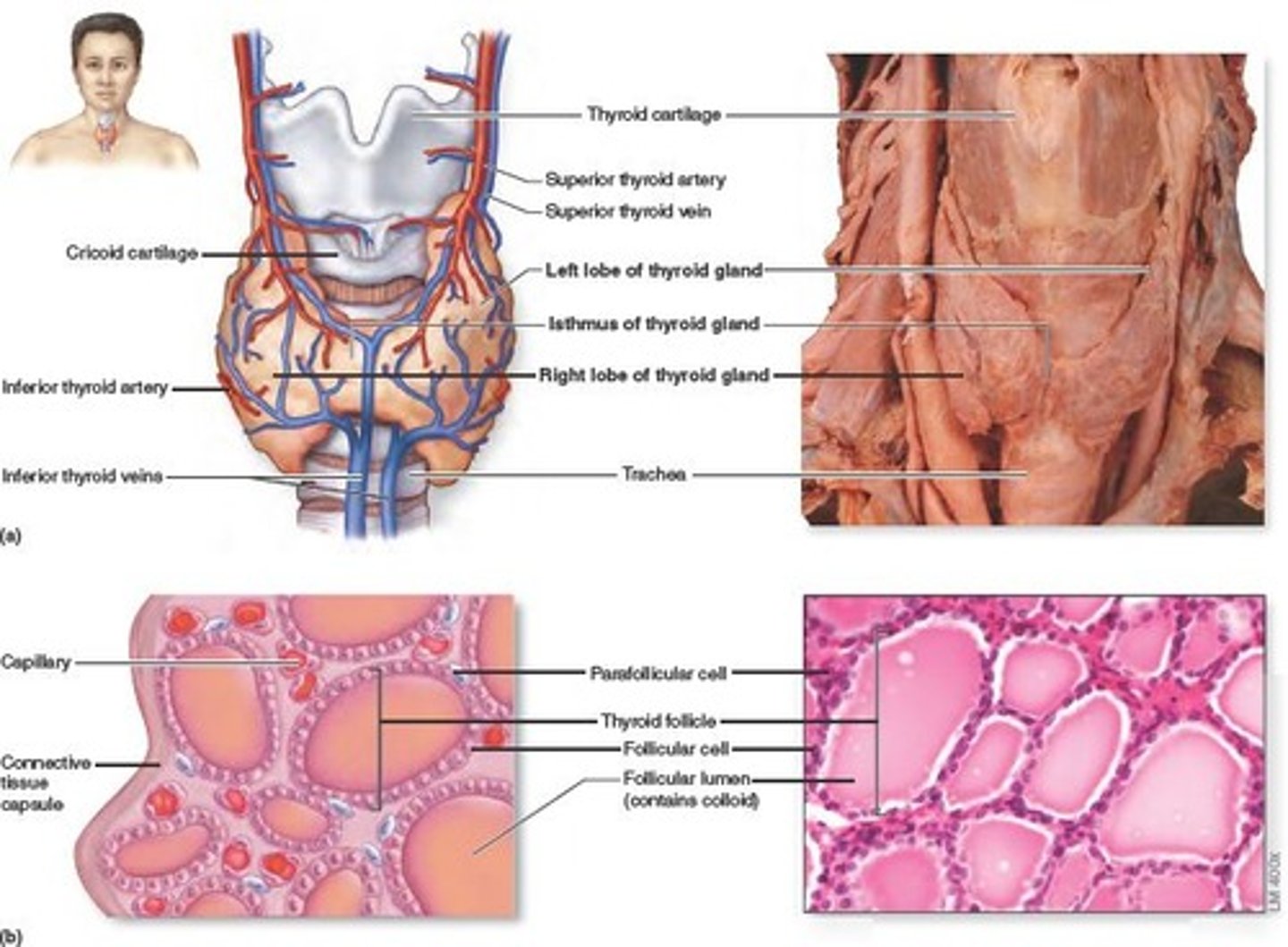
Thyroid gland
produces hormones that regulate metabolism, body heat, and bone growth
Longus colli m.
Function: unilateral contraction bends and turns cervical column to the side. Also bend the cervical spine forward
Innervation: cervical and brachial plexus (C2-C8)
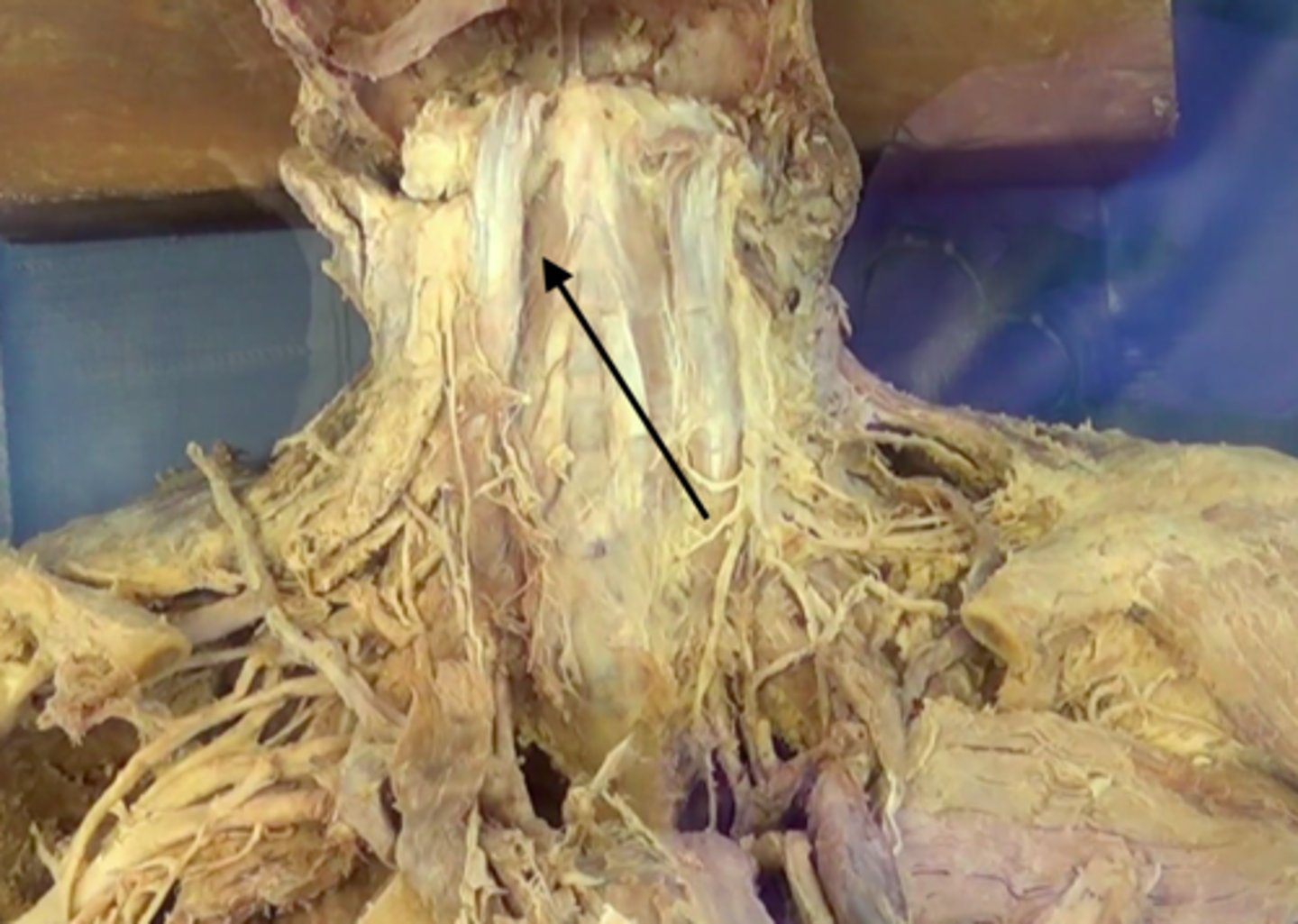
Longus capitis m.
Function: bend the head forward and unilateral action turns the head sideways
Innervation: cervical plexus (C1-C4)
Uvula
soft tissue hanging from the middle of the soft palate
Palatopharyngeal arch (fold)
muscular fold that extends from the lateral side of the soft palate to the side of the pharynx

Piriform recess
Site of aspirated lodged fishbone in the Laryngopharynx
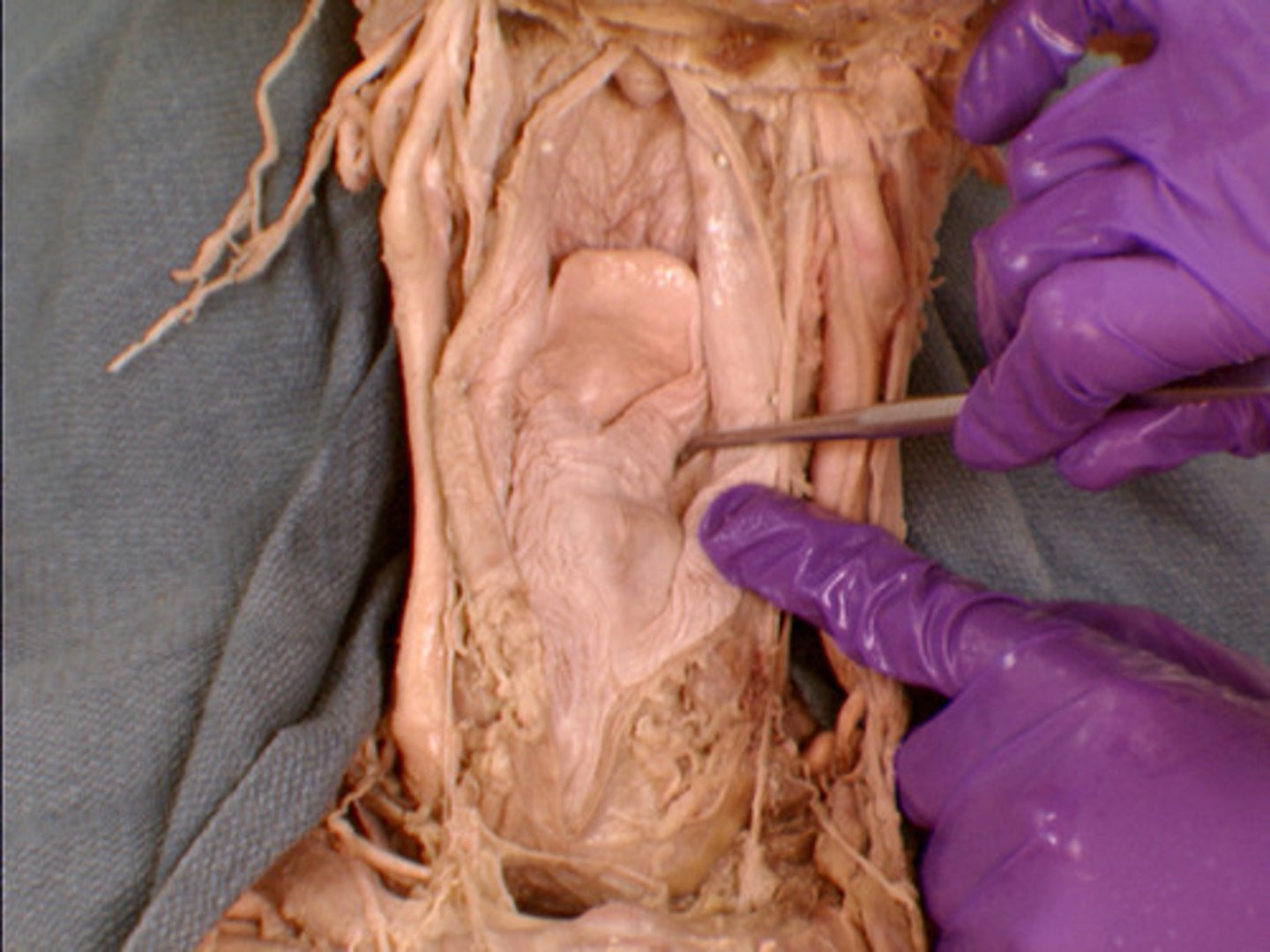
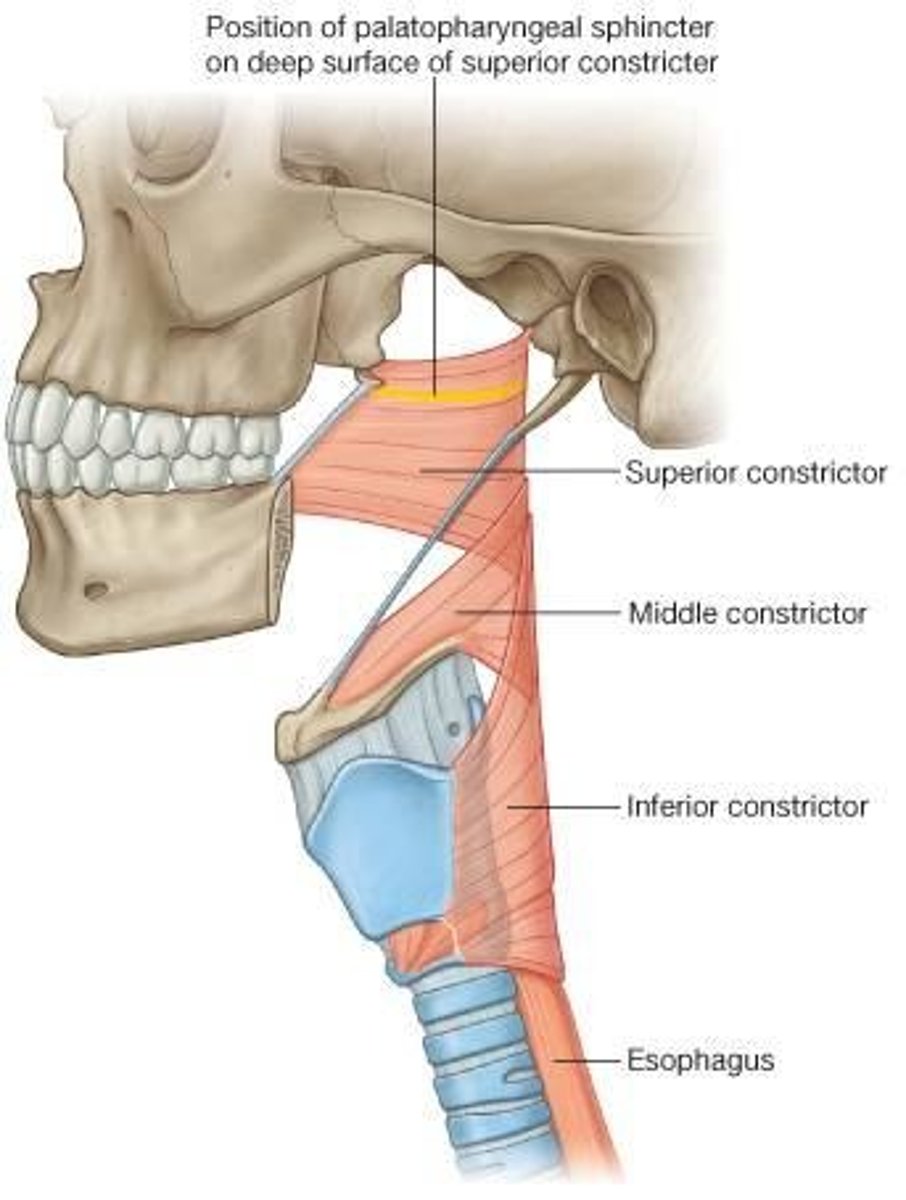
Pharyngeal constrictor mm.
The superior, middle, and inferior constrictor muscles serve to move the food during swallowing. They are innervated by the pharyngeal plexus - CNn IX, X, and the cranial root of XI.
*inferior constrictor is innervated by recurrent laryngeal nn. with contributions from CNn IX and XI
Pharyngoesophageal constriction
located at the junction of the pharynx with the oesophagus (C5 vertebral level), behind the cricoid cartilage, caused by contraction of the cricopharyngeal part of the inferior constrictor of the pharynx (upper esophageal sphincter).
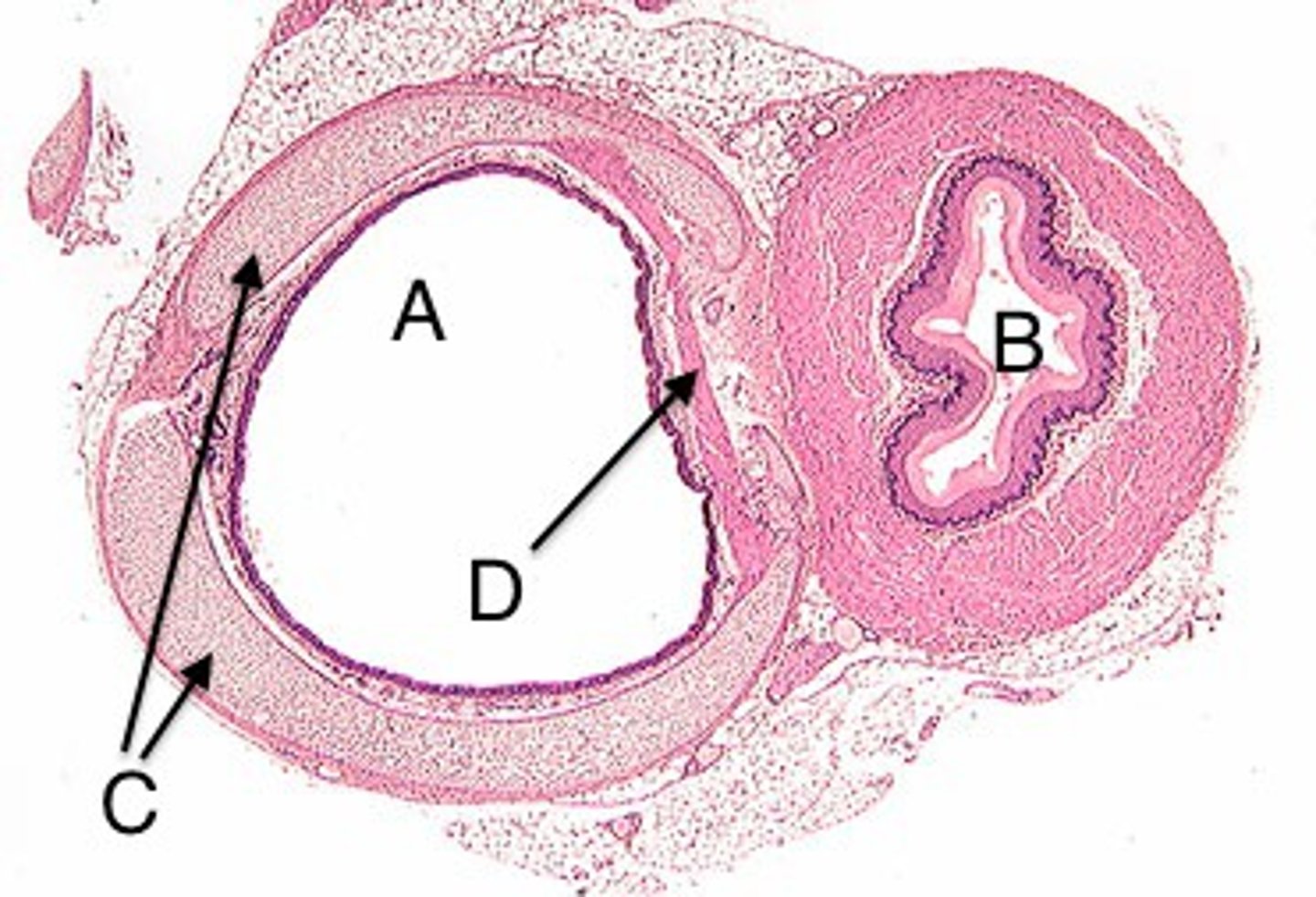
Esophagus
A muscular tube that connects the mouth to the stomach.
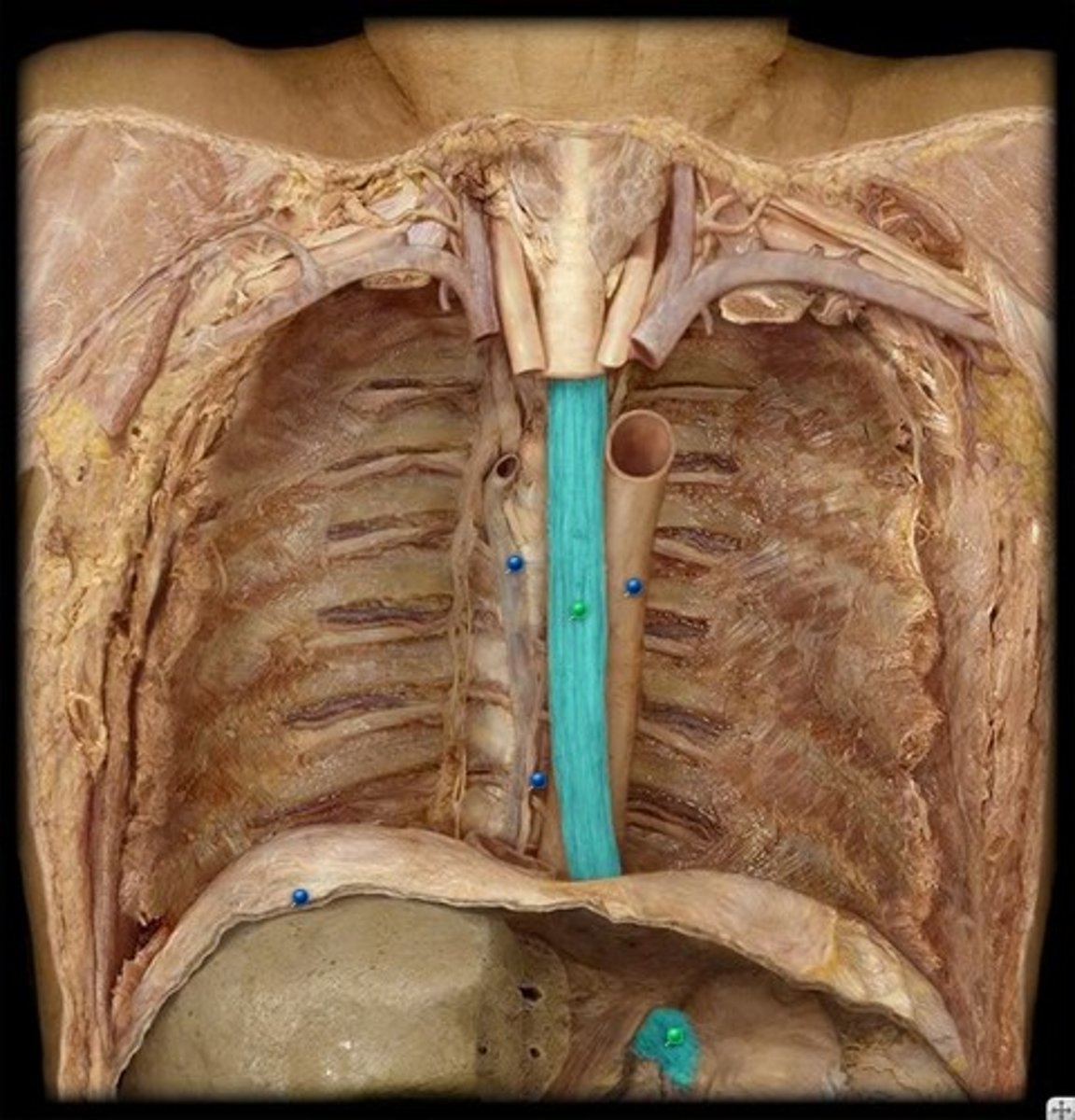
Sympathetic trunk
function: allows for preganglionic and ganglonic nerves fibers to communicate with each other
Superior cervical ganglion
one of the paravertebral ganglia of the sympathetic system that projects to the head
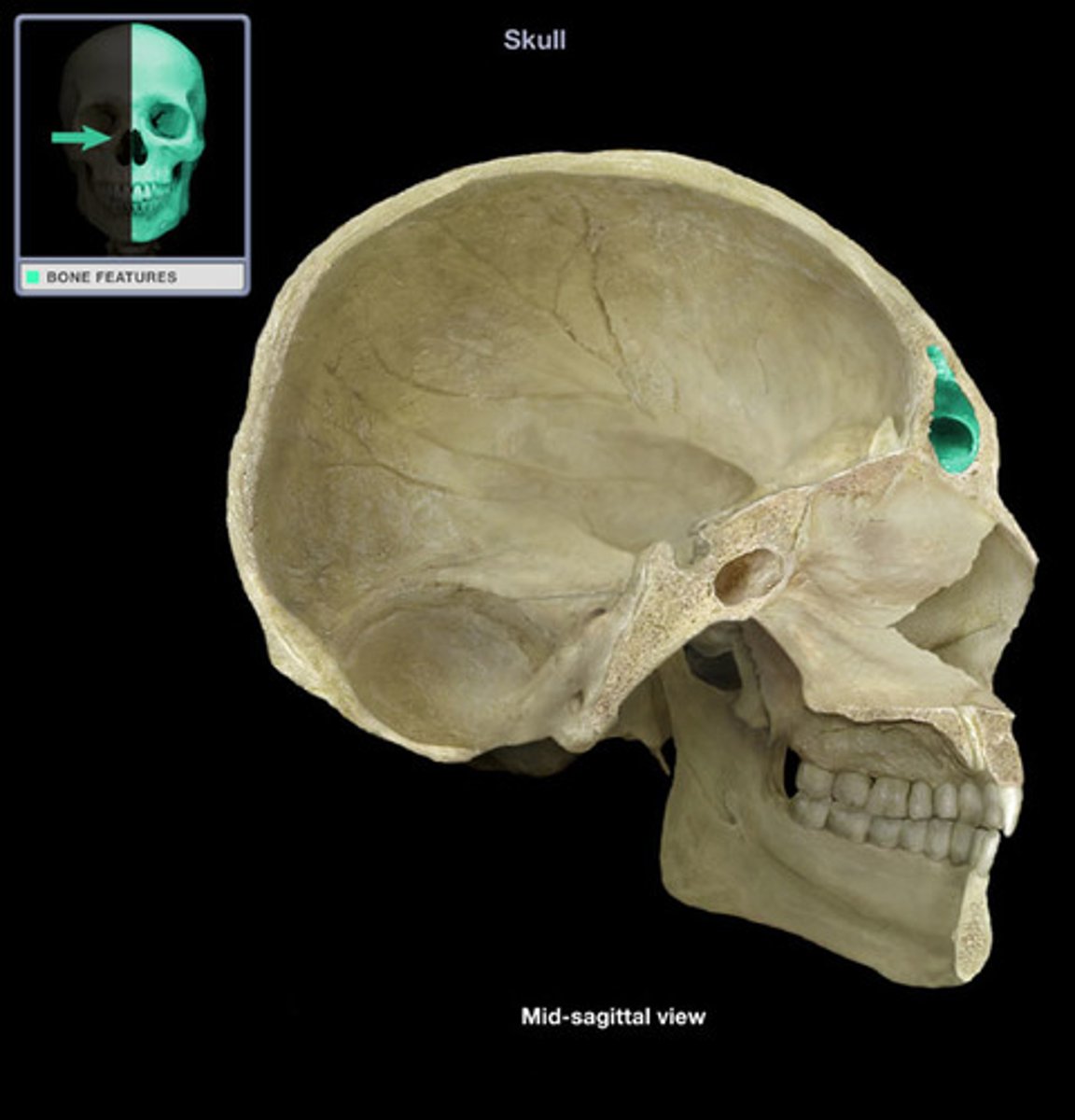
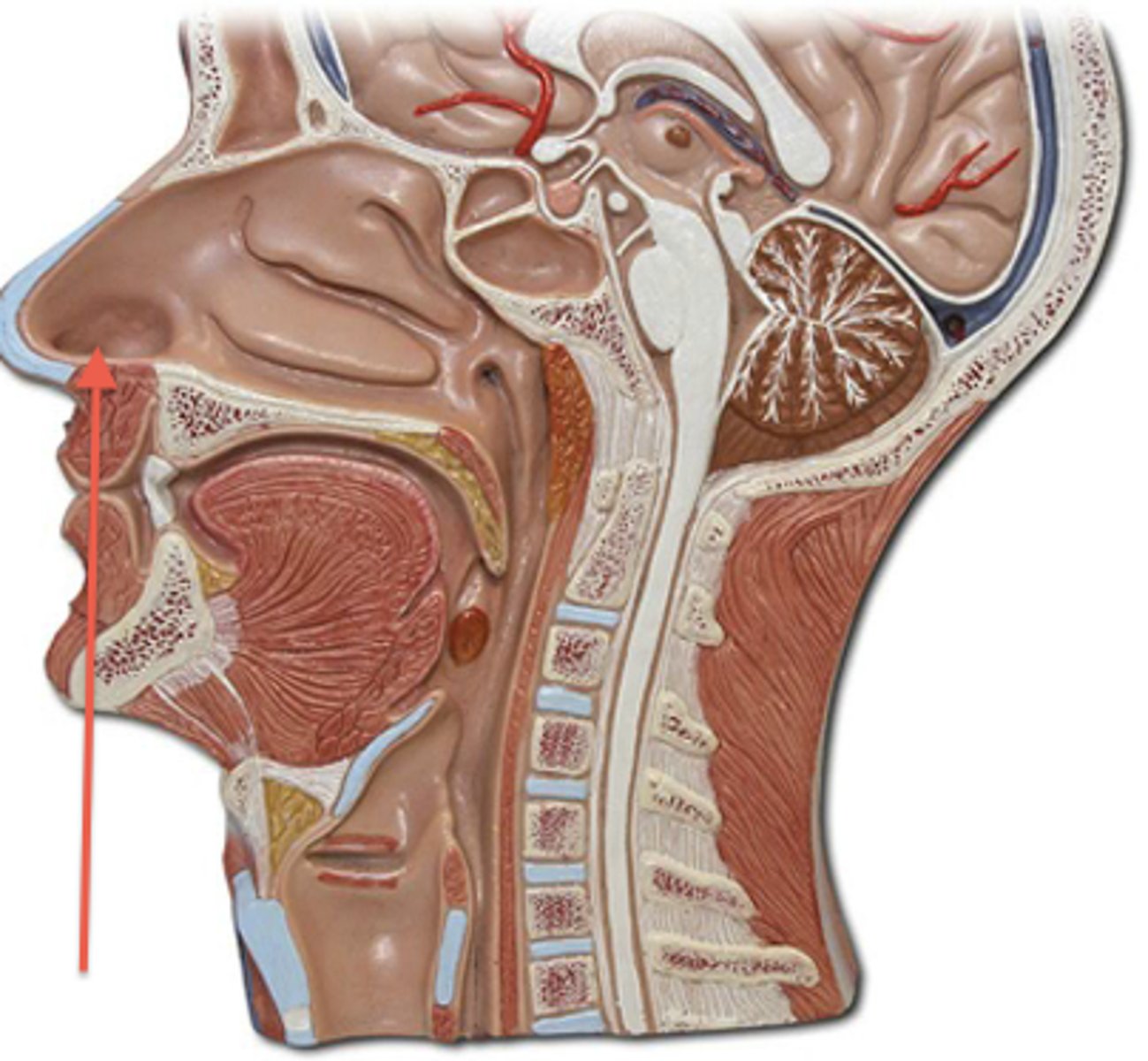
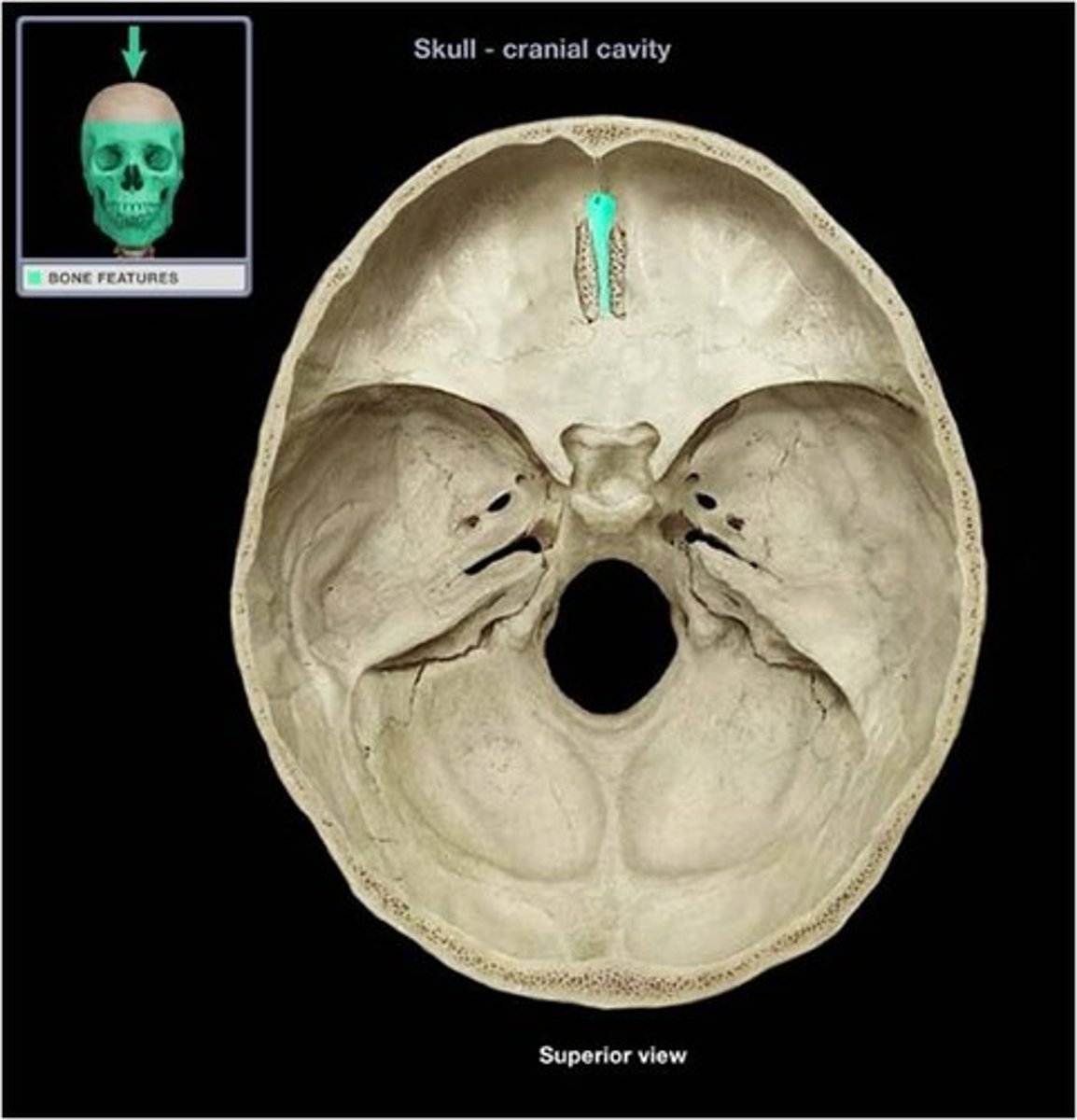
Frontal sinus
cavity within the frontal bone (forehead)
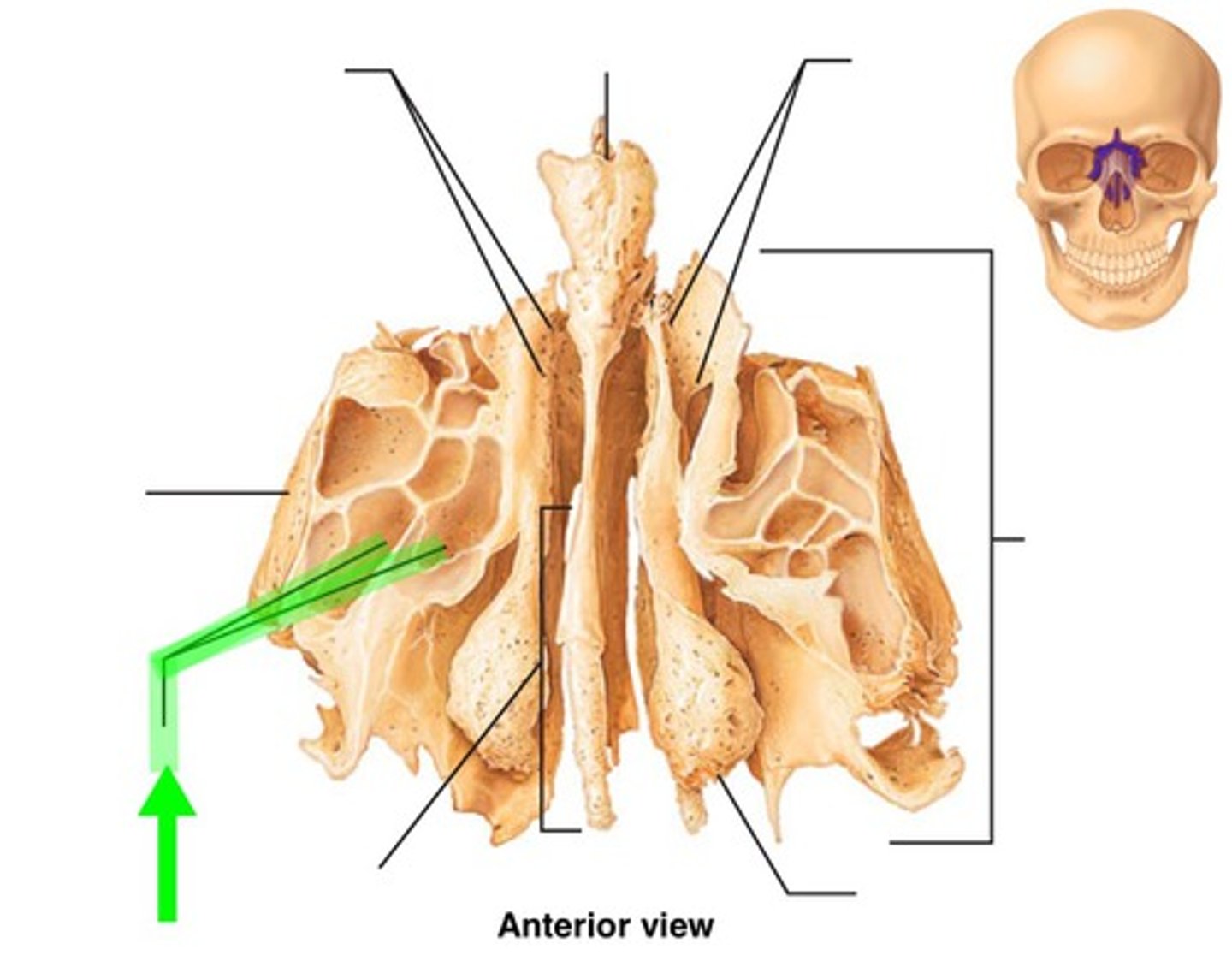
Ethmoid air cells
The ethmoid sinuses consist of many small cavities called ethmoid air
cells that separated by thin plates of bone within the ethmoid bone.
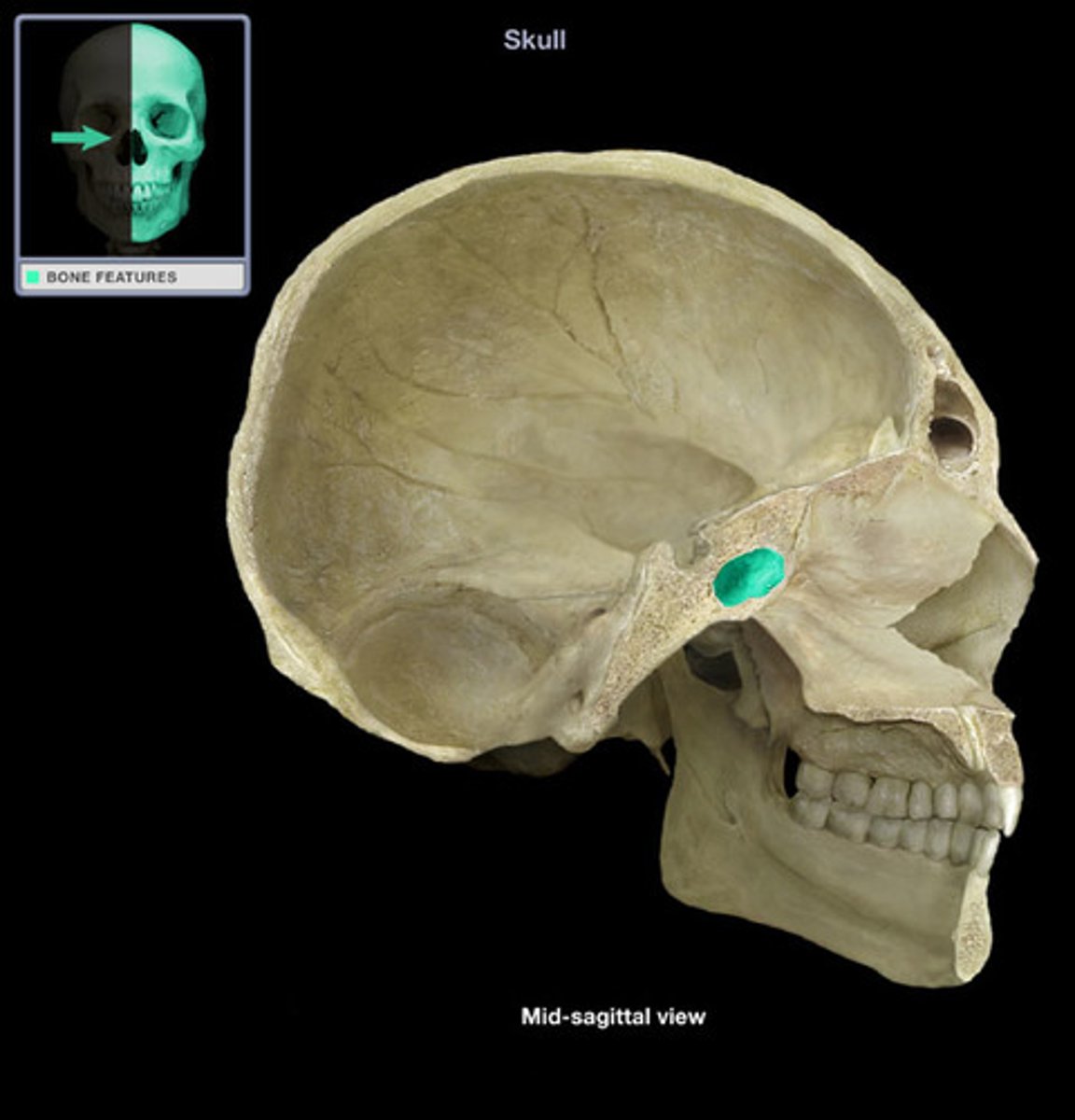
Sphenoidal sinus
paired cavity located within the sphenoid, inferior to the sella turcica
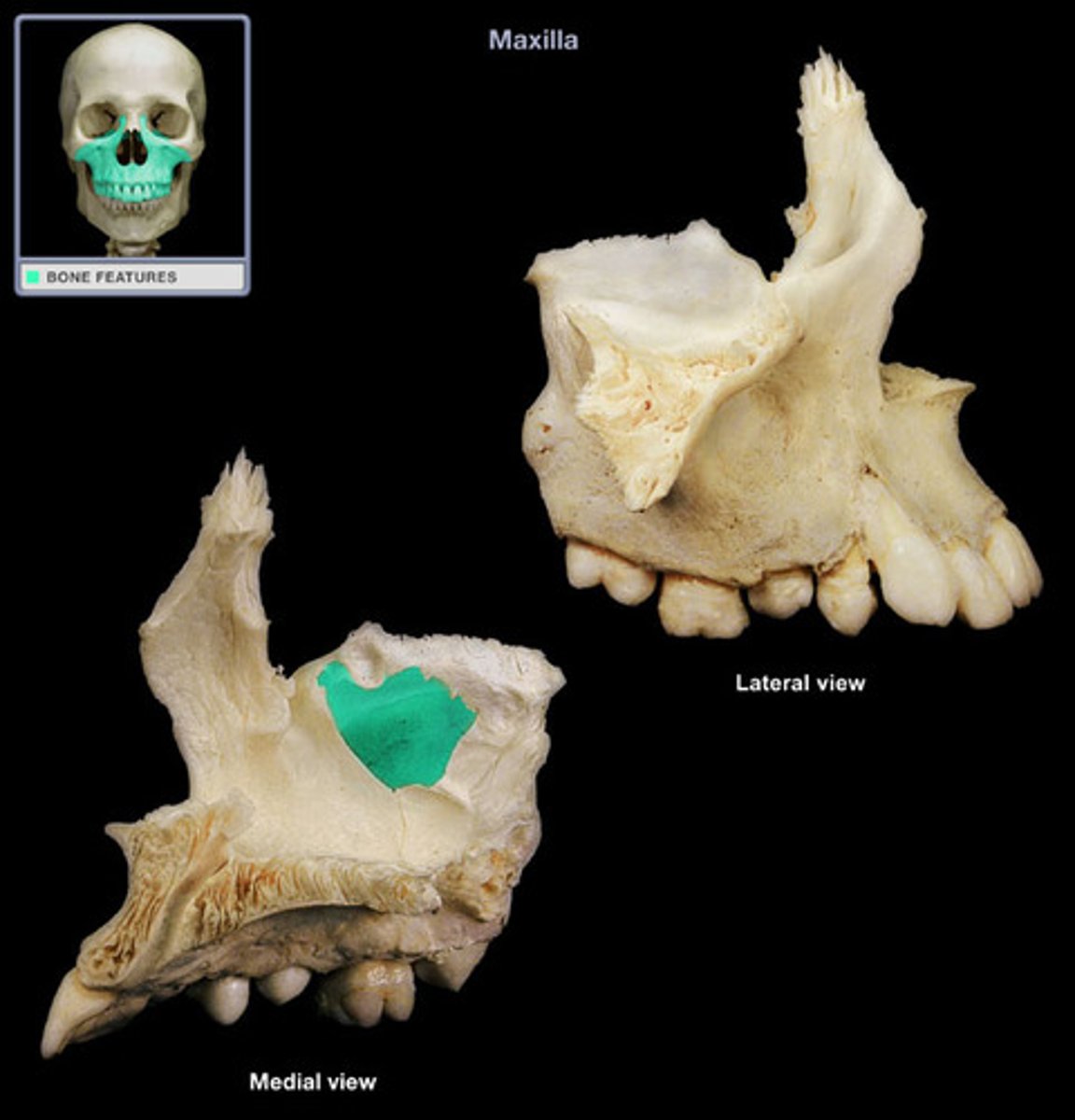
Maxillary sinus
largest paranasal sinus; pyramidal; on cheek bone lateral to nasal bone
Nares
the nostrils or the nasal passages
Ethmoid bone
forms part of the posterior portion of the nose, the orbit, and the floor of the cranium
Nasal septum
partition separating the right and left nasal cavities
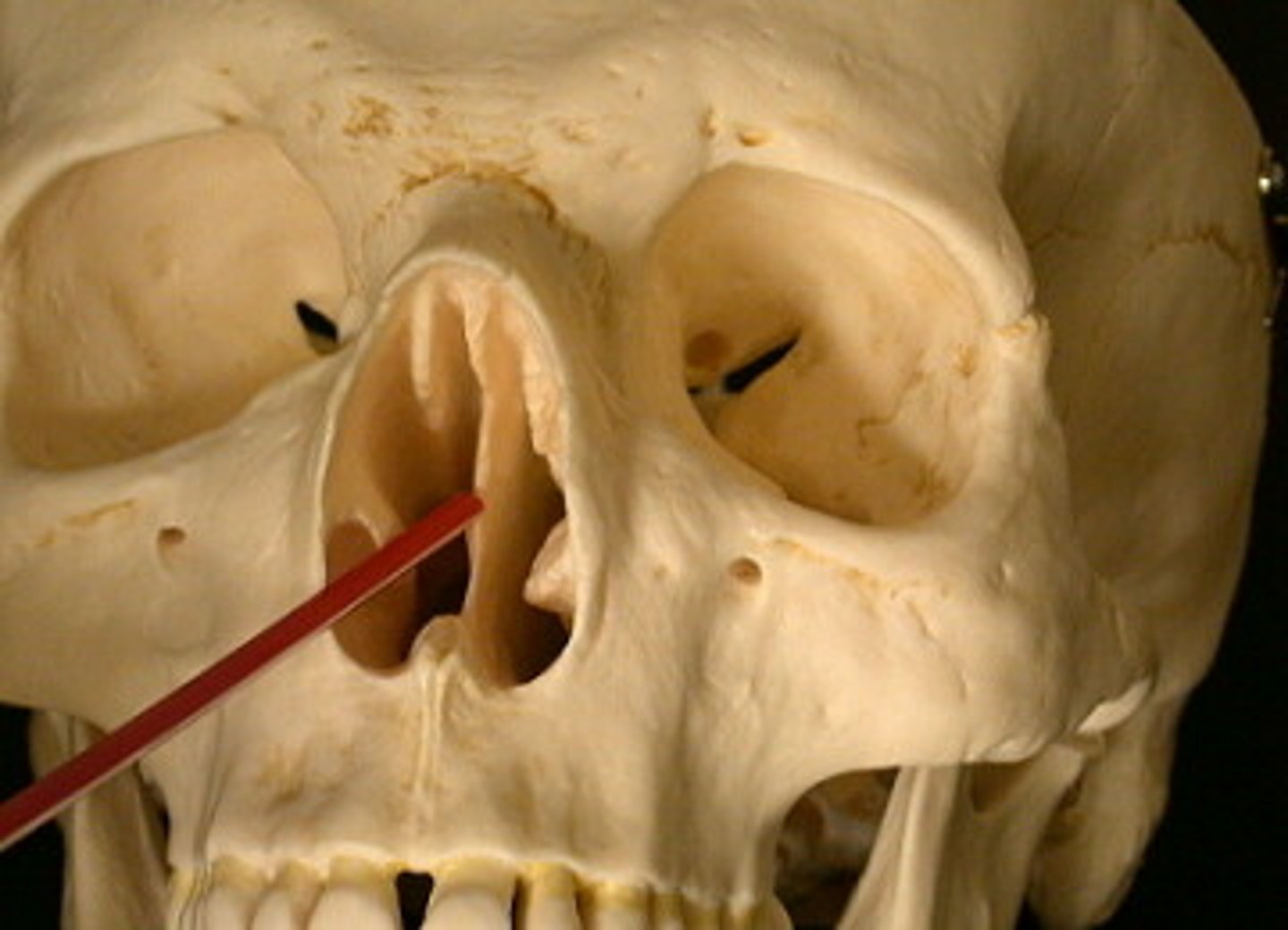
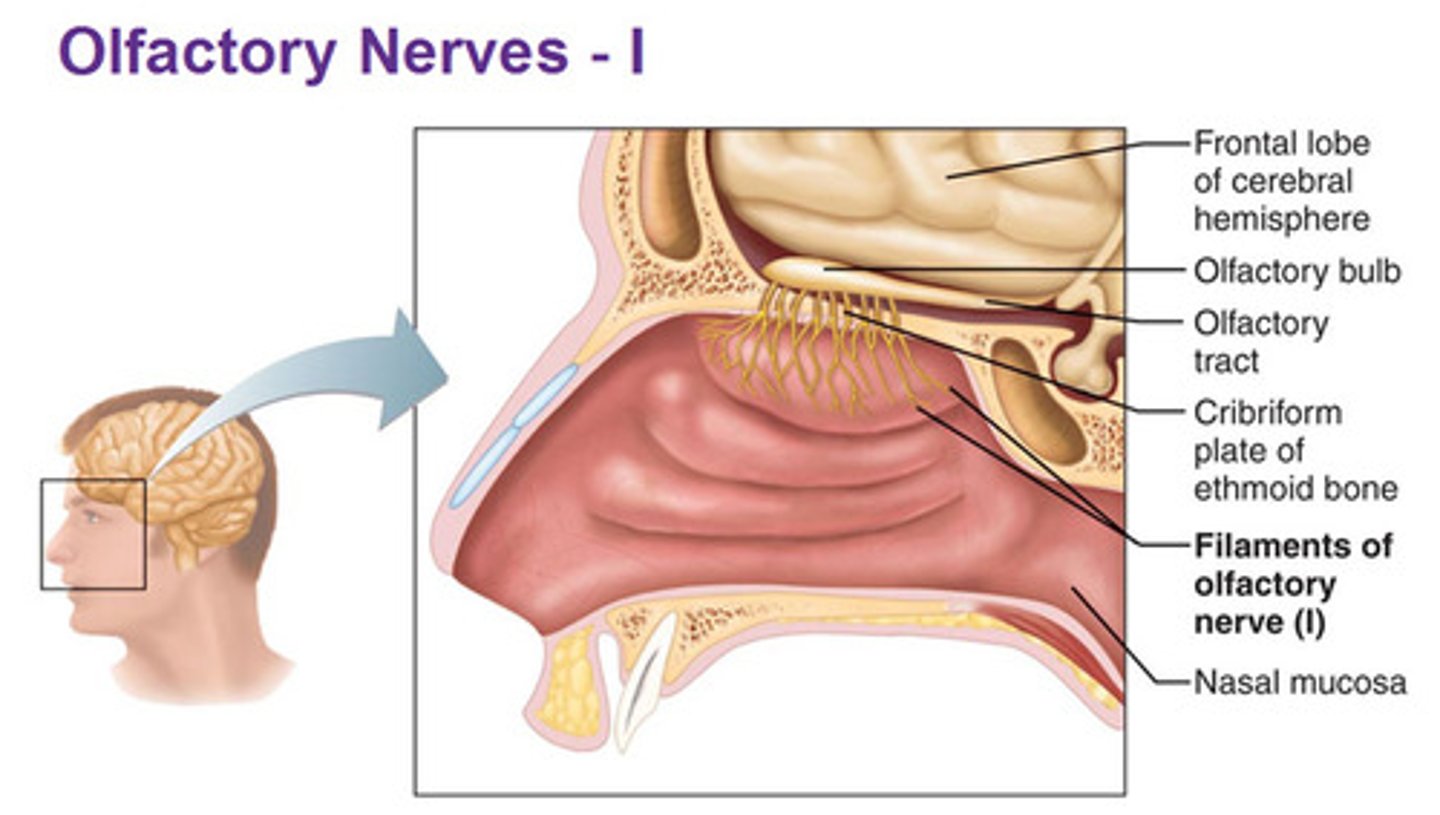
Olfactory nerve filaments
also known as olfactory fila, are among the most important structures in the olfactory system and play a key role in connecting peripheral olfactory neurons to the central nervous system.
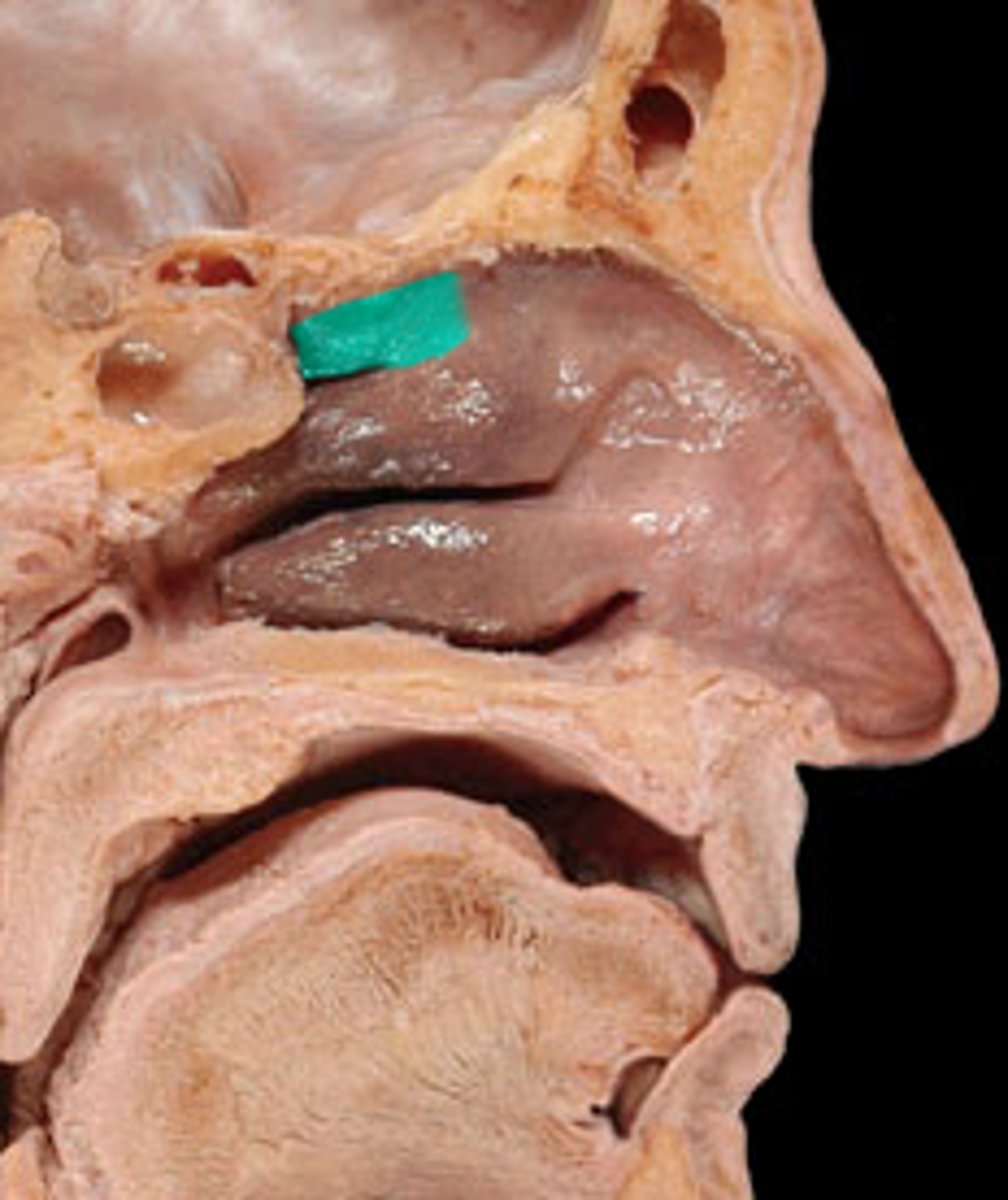
Superior nasal concha
not a named bone, but part of the ethmoid bone. Above middle nasal concha
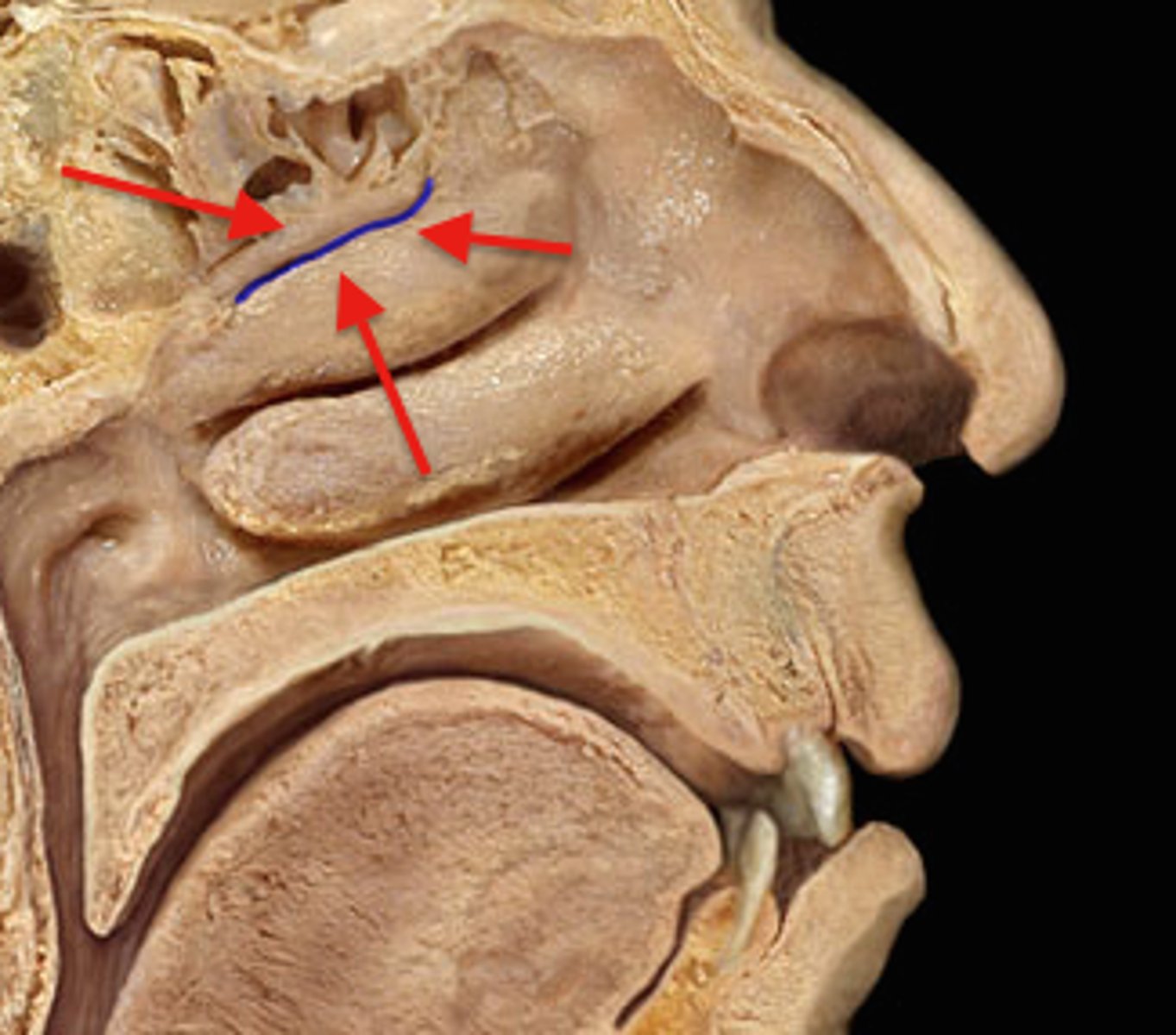
Superior (nasal) meatus
posterior ethmoid sinuses
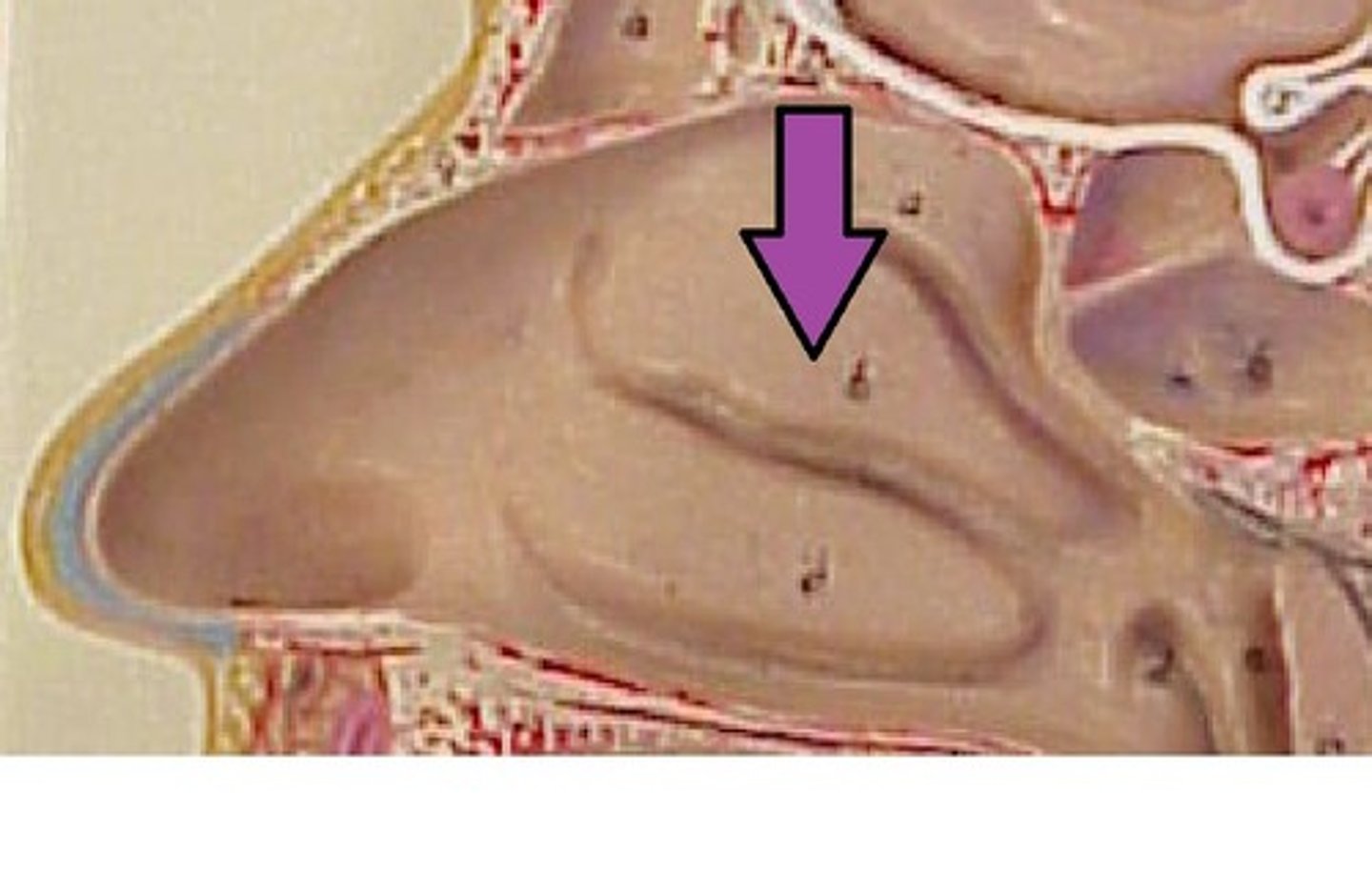
Middle nasal concha
the middle thin, spongy, bony plate with curved margins, part of the ethmoidal labyrinth, projecting from the lateral wall of the nasal cavity and separating the superior meatus from the middle meatus
Middle (nasal) meatus
frontal sinus (frontonasal duct)
anterior and middle ethmoid sinuses
maxillary sinus
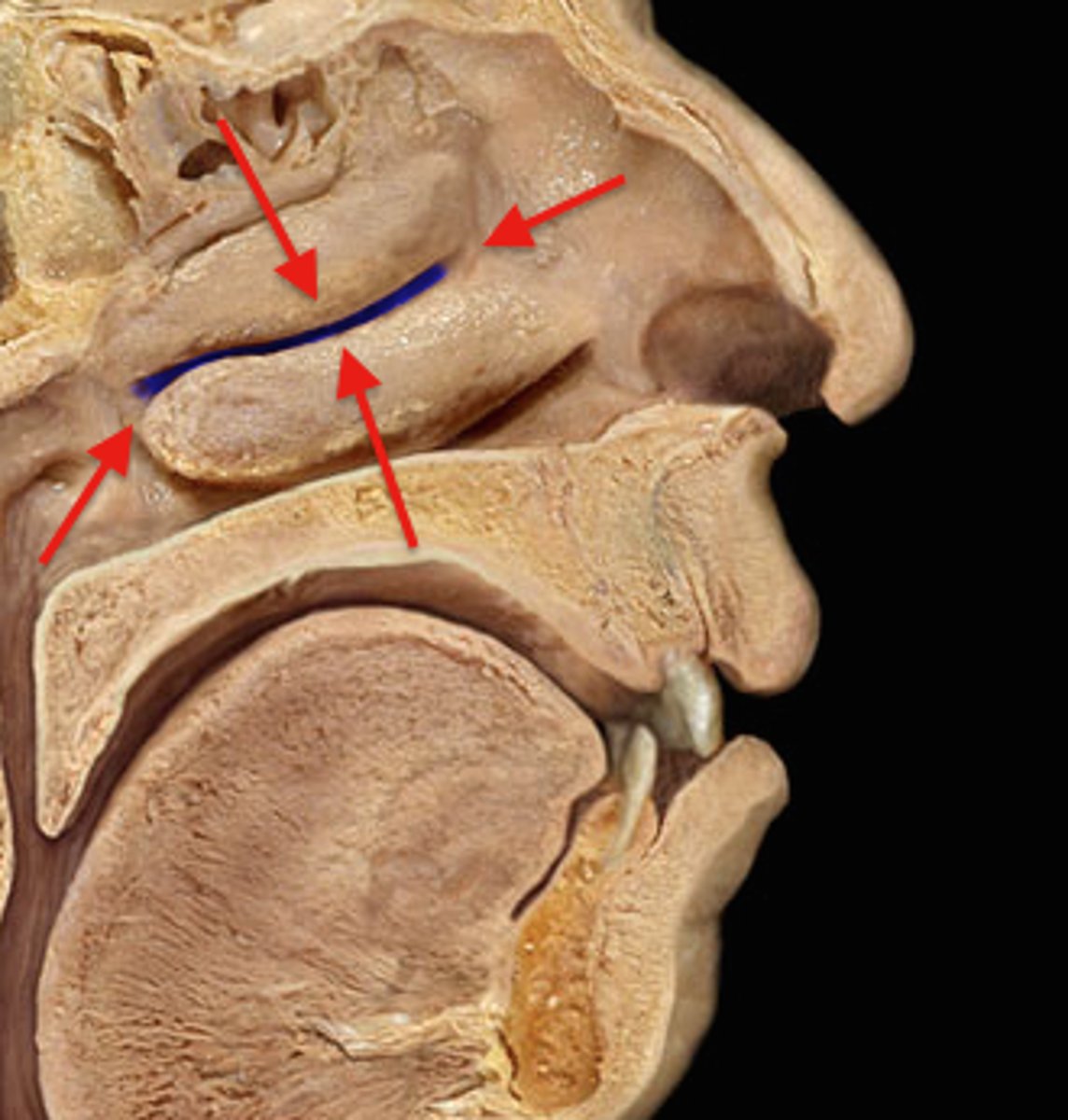
Hiatus semilunaris
cleft lying underneath the middle conchae where the maxillary sinus, frontal sinus, and anterior ethmoidal air cells drain
Ostium of maxillary sinus
-The communication between mouth and nose
-The only sinus that doesn't drain between 2nd & 3rd concha is sphenoid which drains between 1st & 2nd
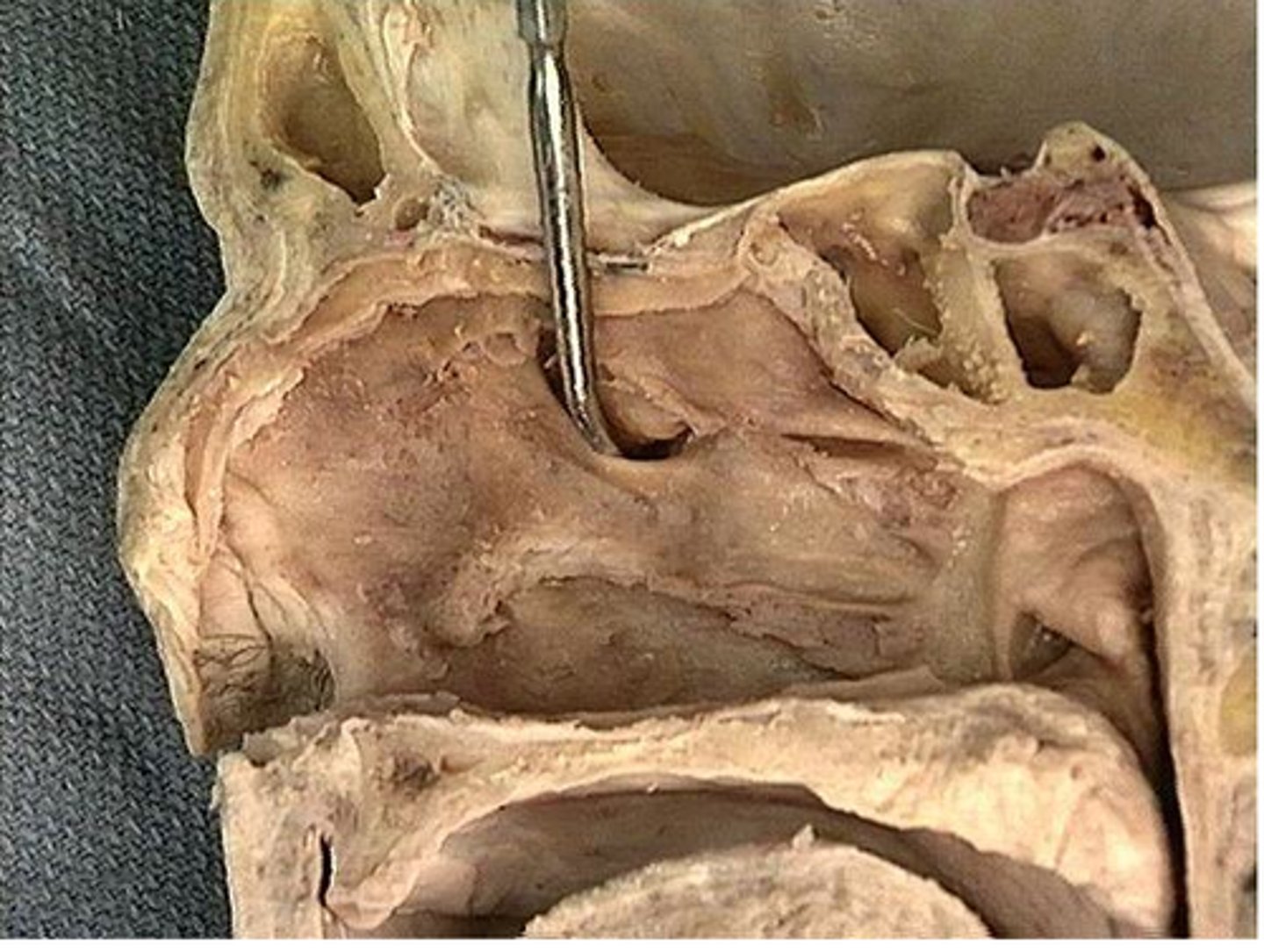
Inferior nasal concha
located on each side of the nasal septum, attached to the lateral wall of the nasal cavity; increase epithelial surface area and create turbulence in the inspired air
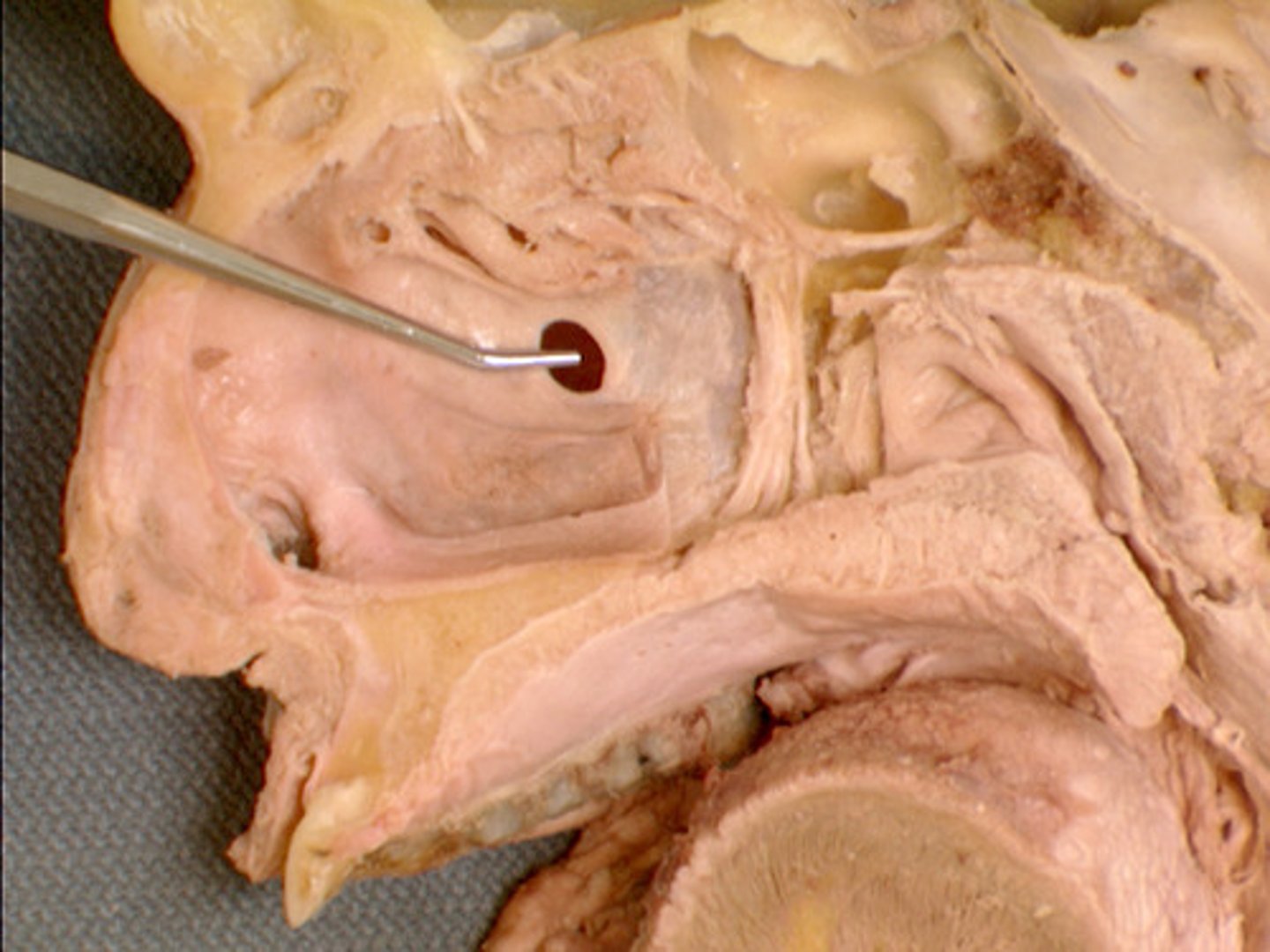
Inferior (nasal) meatus
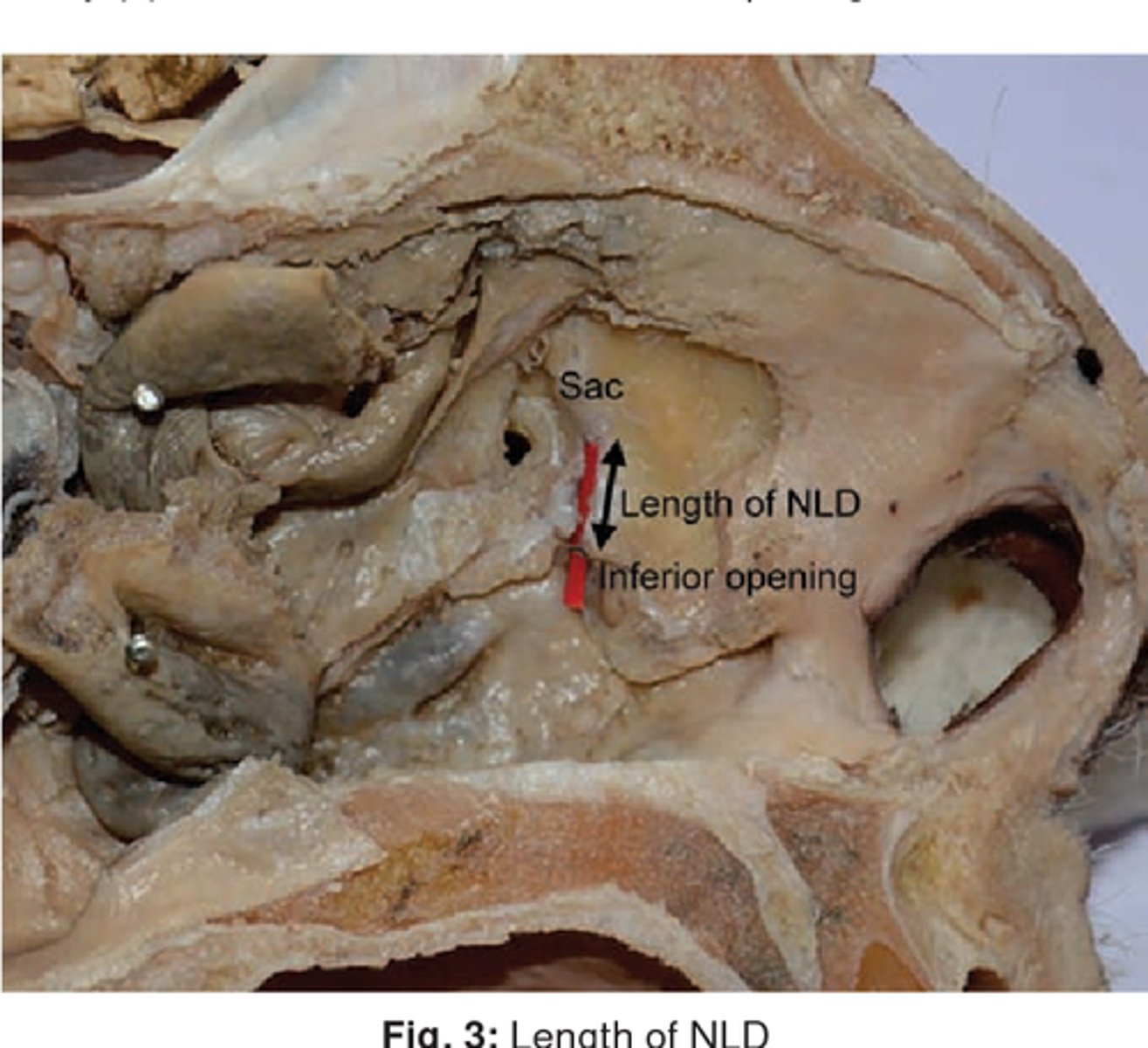
The nasolacrimal duct drains into this nasal space
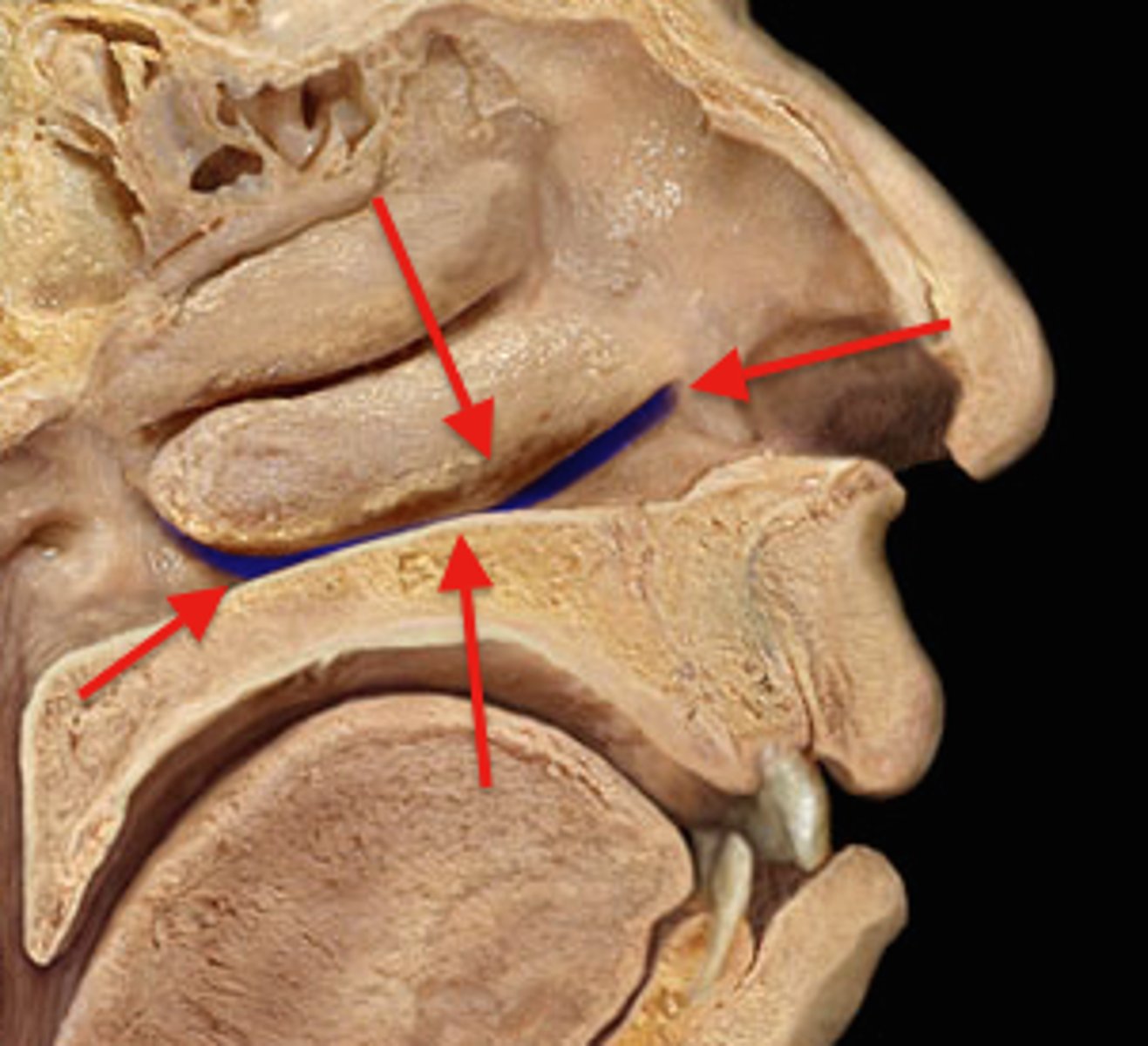
Nasal orifice of nasolacrimal duct
begins in the eye socket between the maxillary and lacrimal bones, from where it passes downwards and backwards. The opening of the _________ into the inferior nasal meatus of the nasal cavity is partially covered by a mucosal fold.
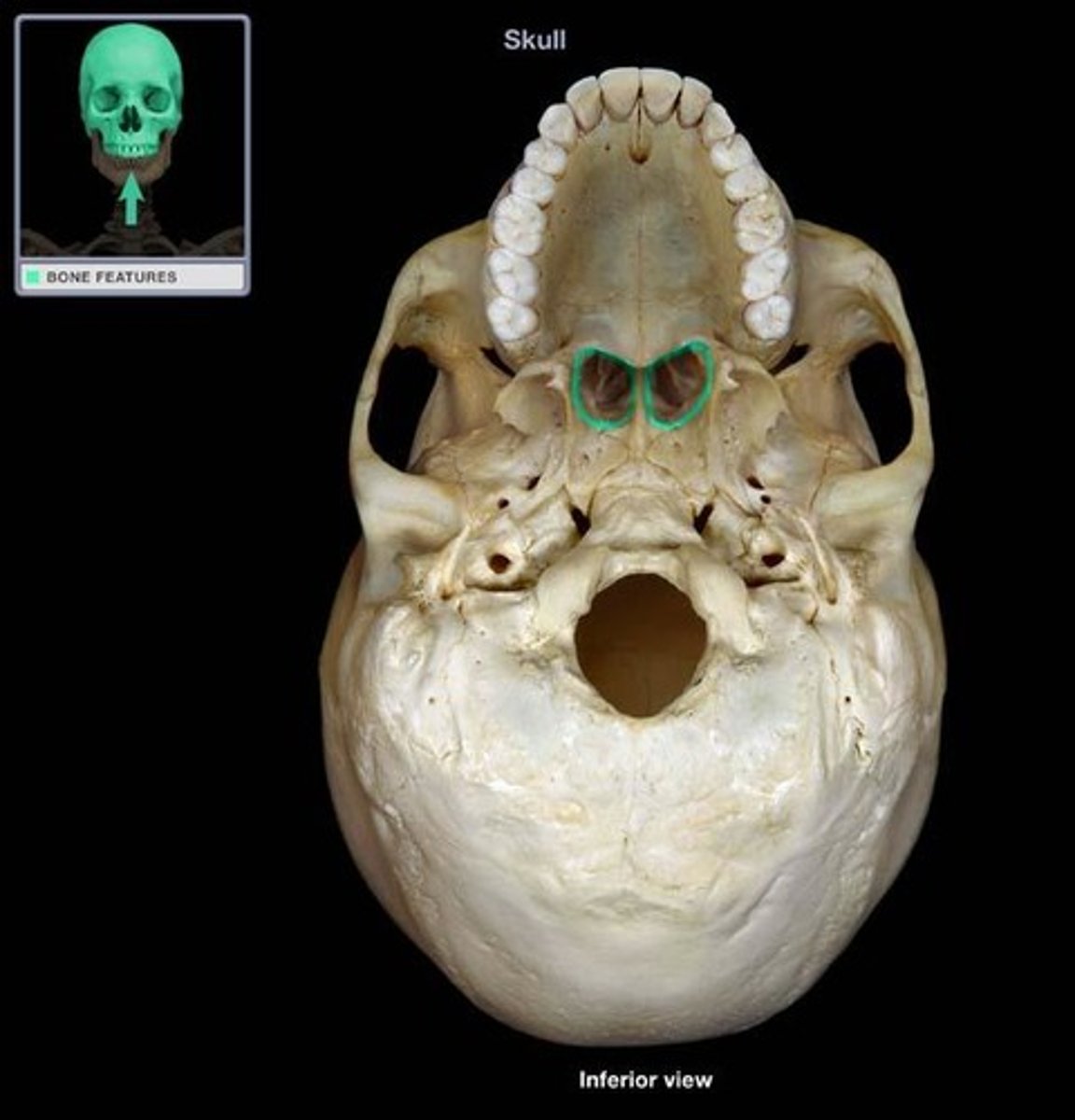
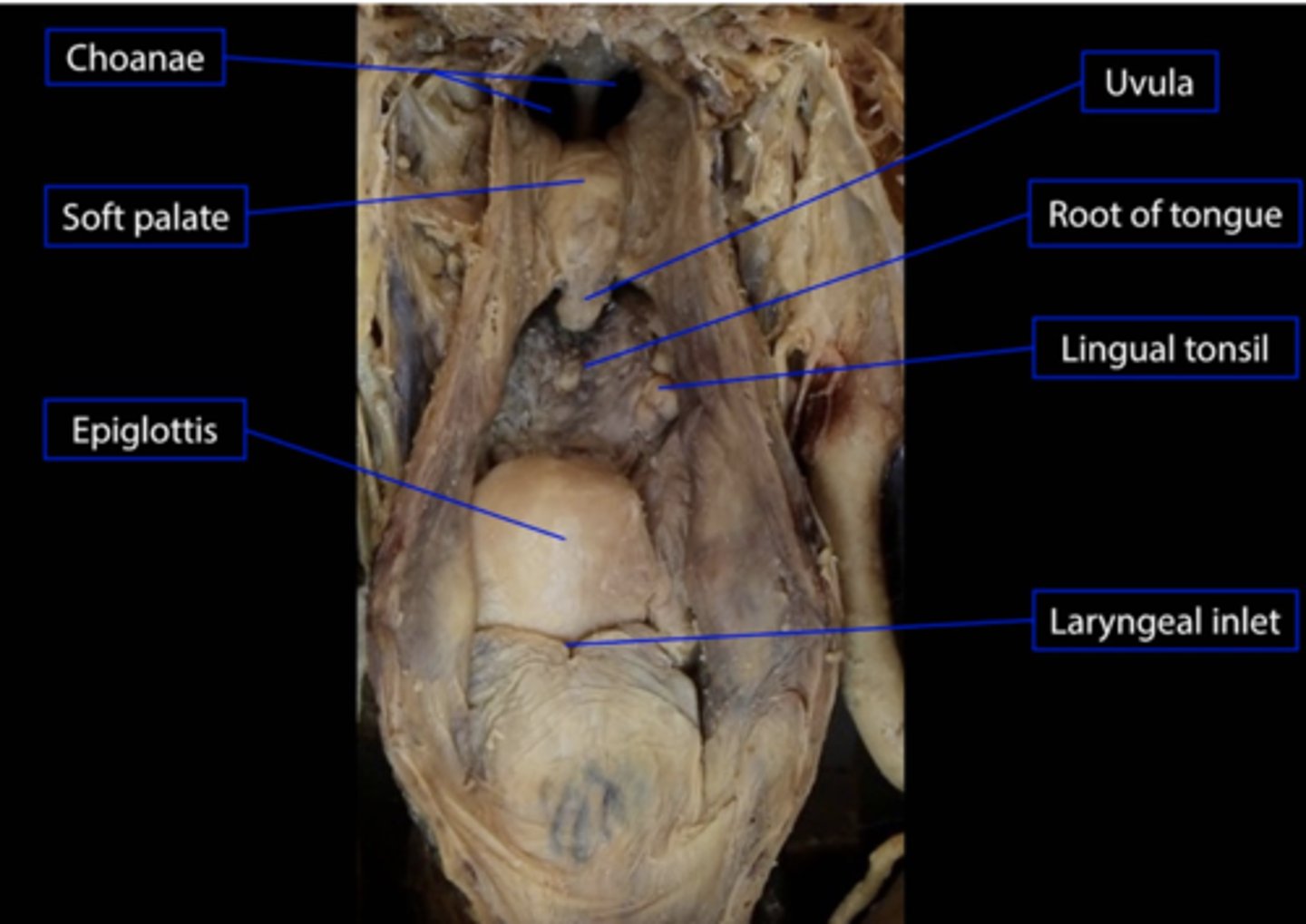
Choana
nasal opening in the hard palate
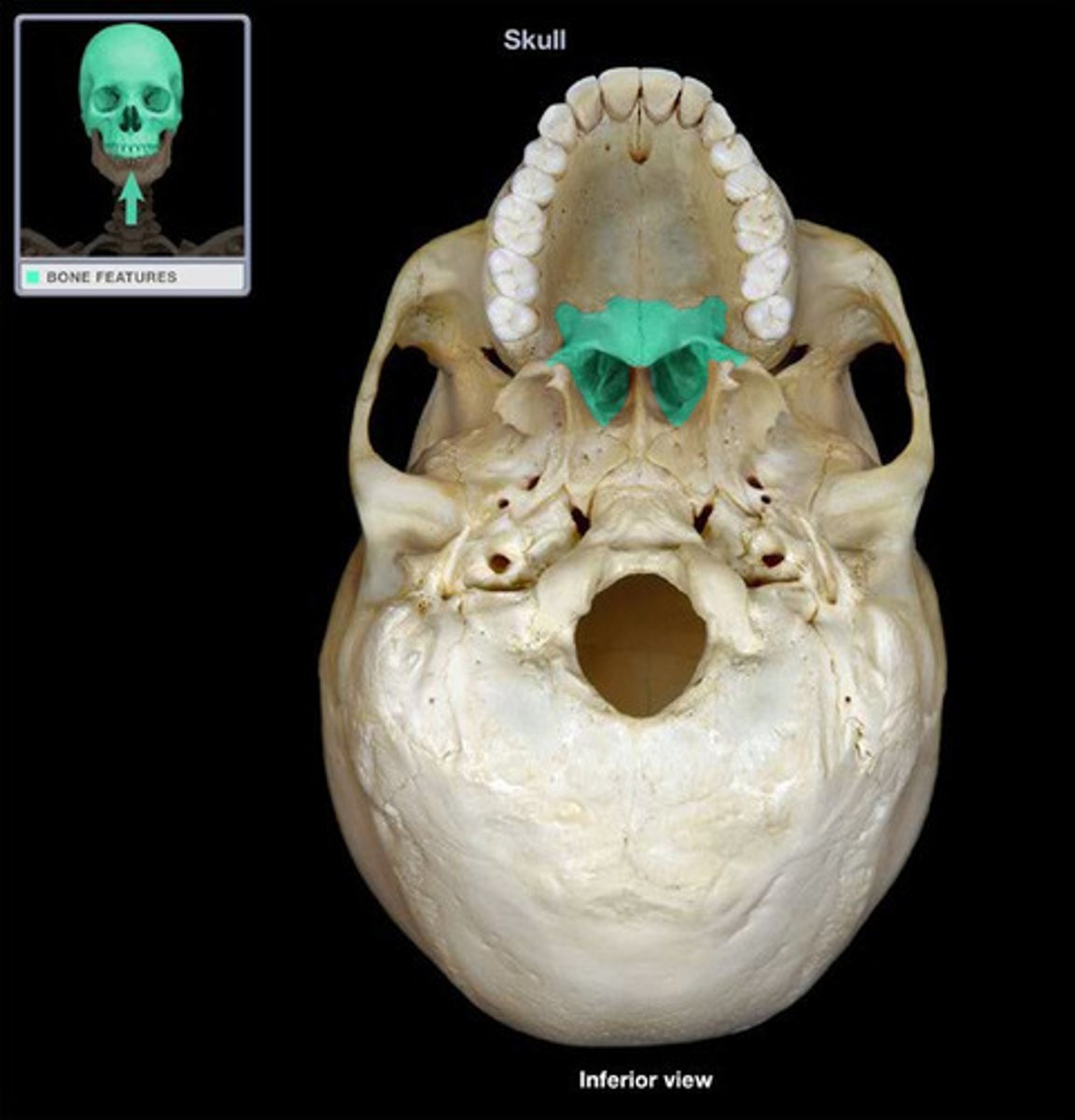
Palatine bone
either of two irregularly shaped bones that form the back of the hard palate and helps to form the nasal cavity and the floor of the orbits
Sphenopalatine a.
What artery supplies the lateral walls of the nasal cavity?
- branch of maxillary artery
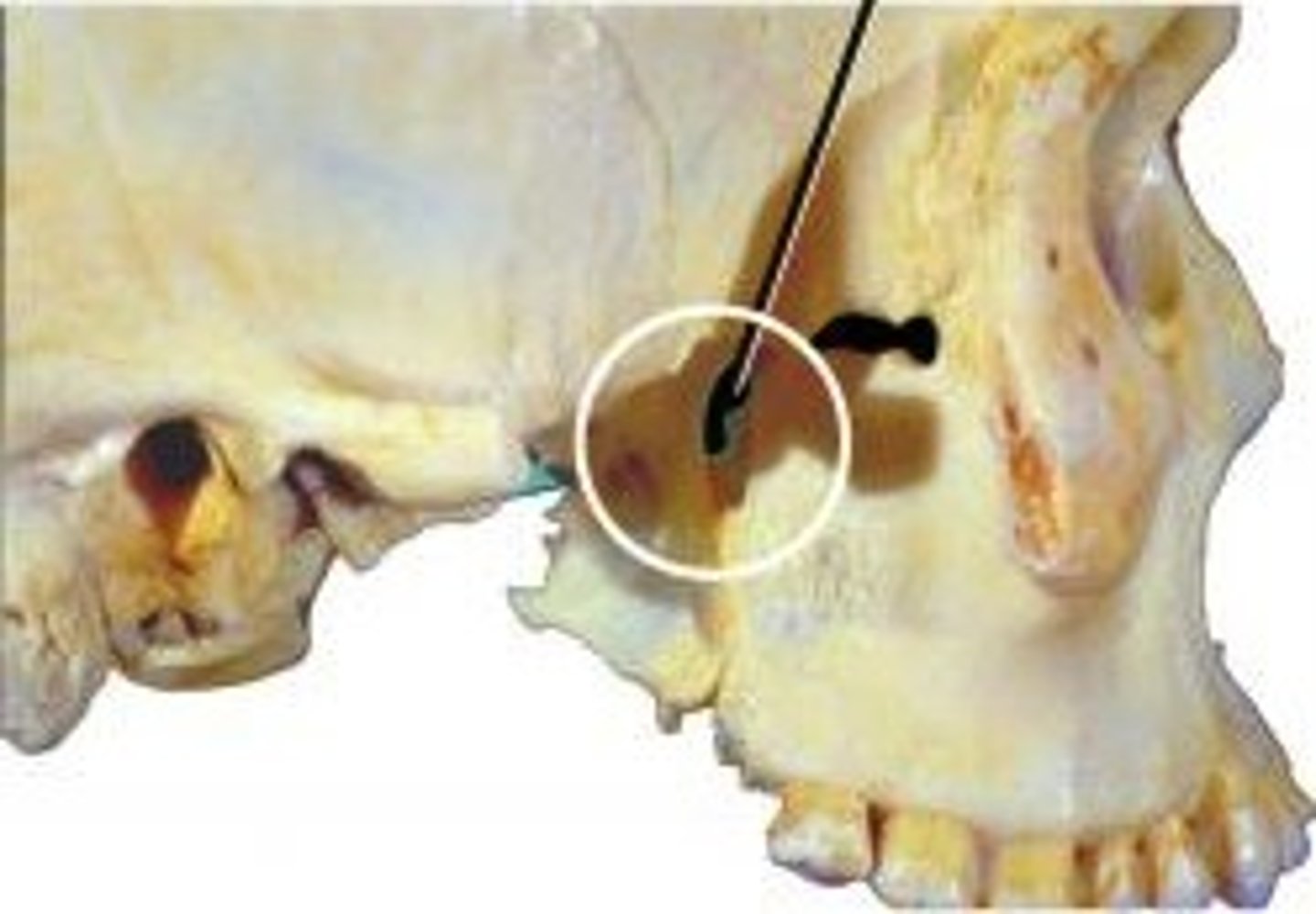
Pterygopalatine ganglion
postganglionic fibers synapse on nasal mucosa, pharynx, palate, and lacrimal glands
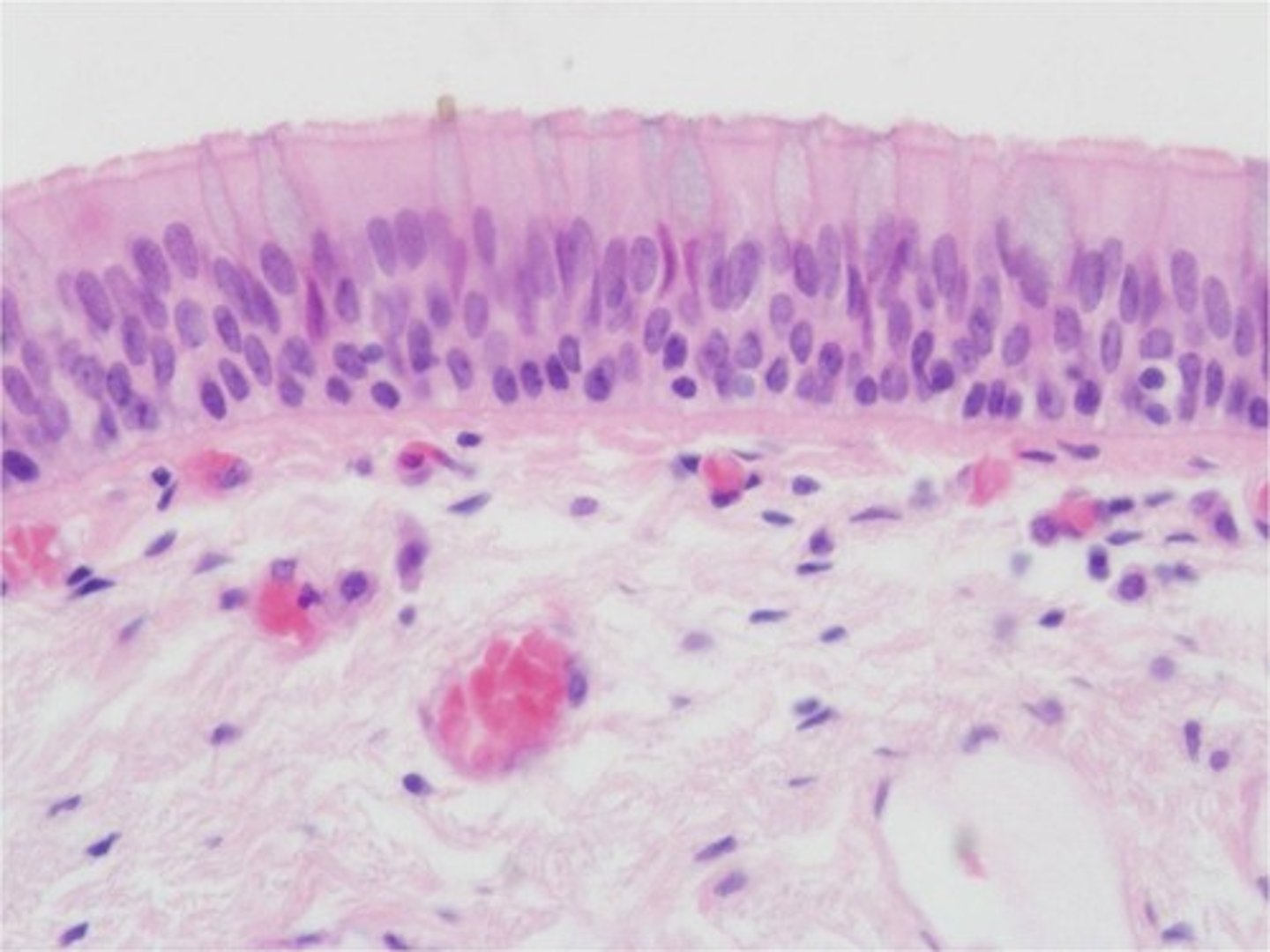
Respiratory epithelium
Pseudostratified, ciliated, columnar epithelium containing goblet cells
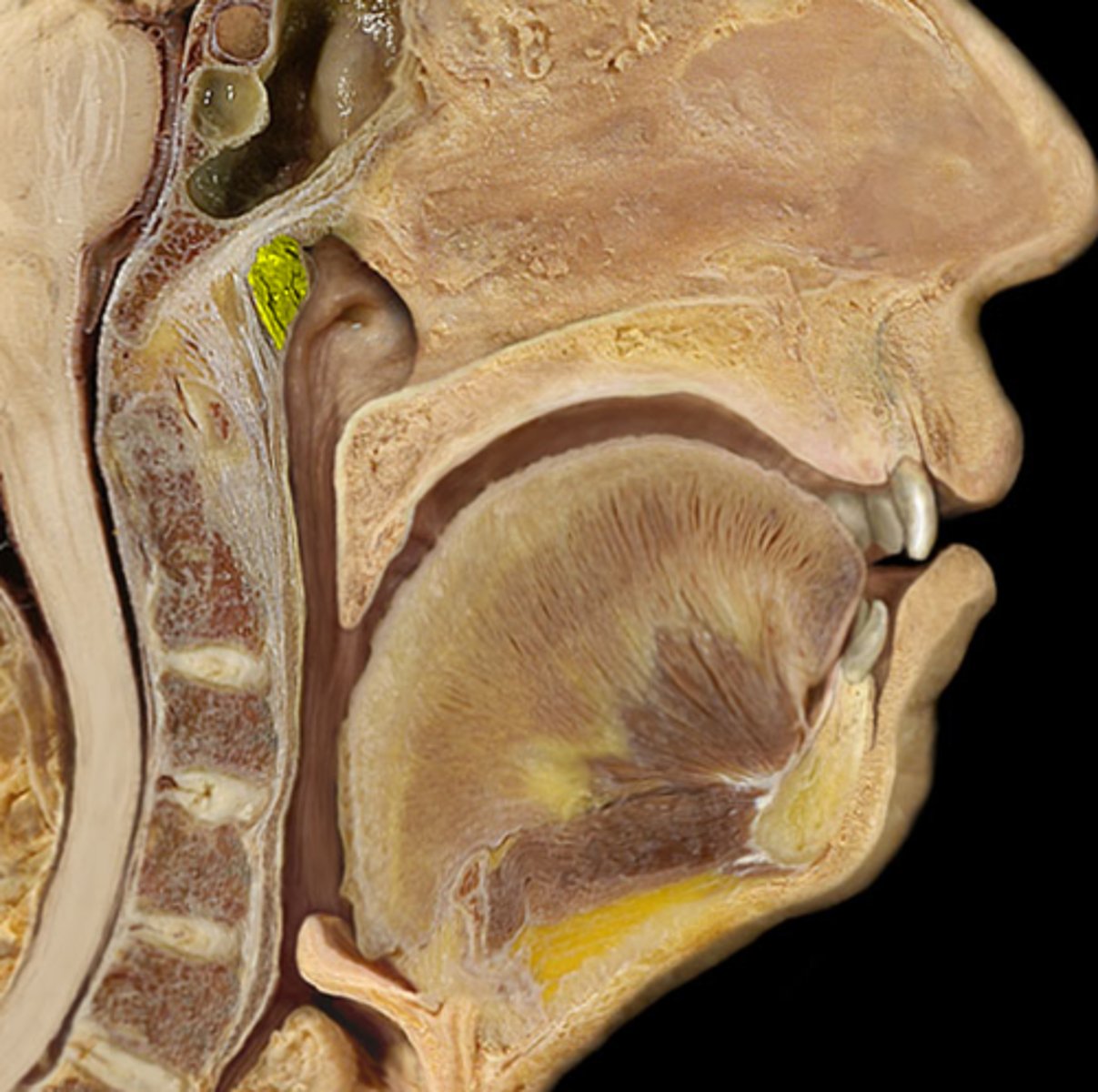
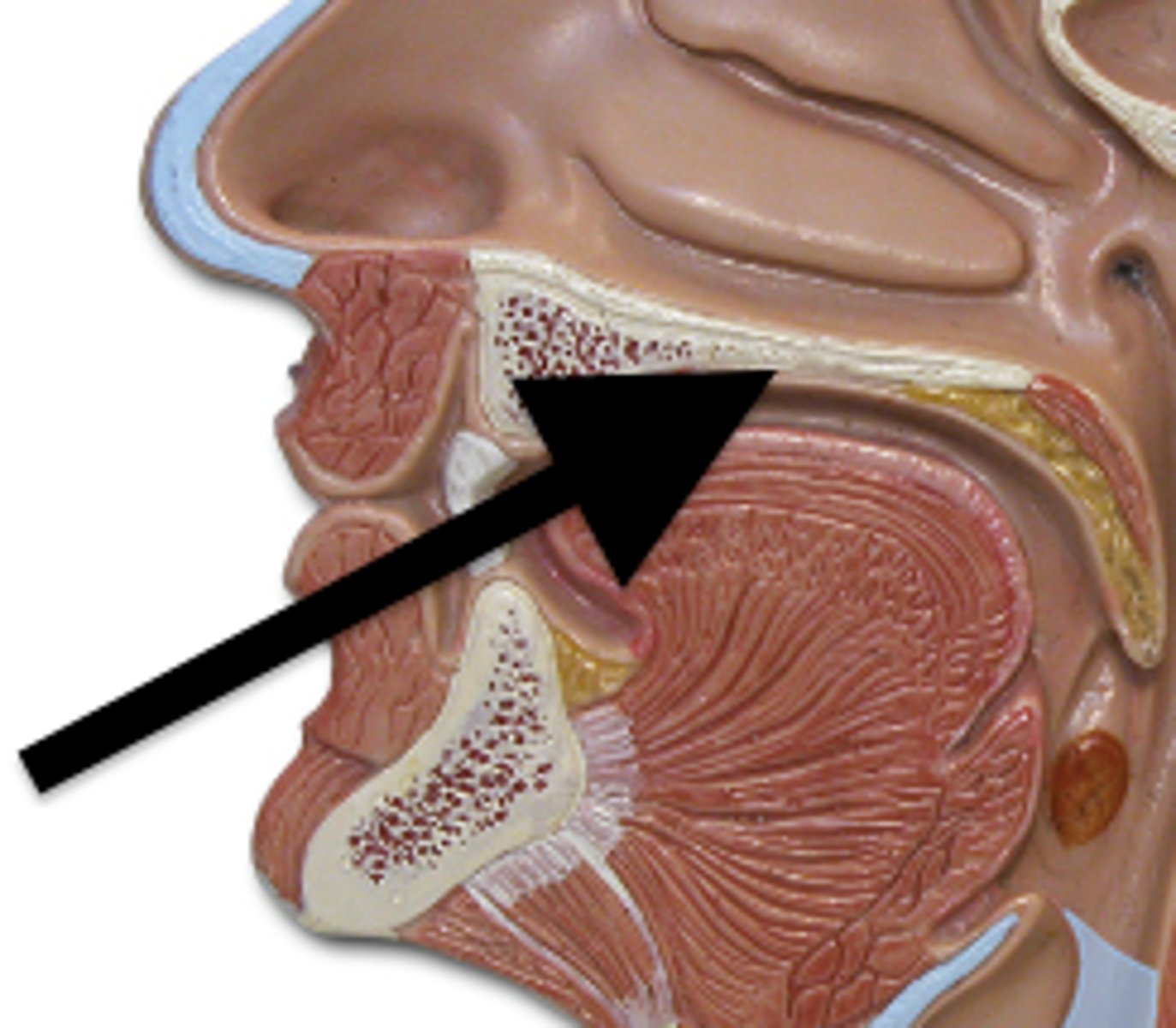
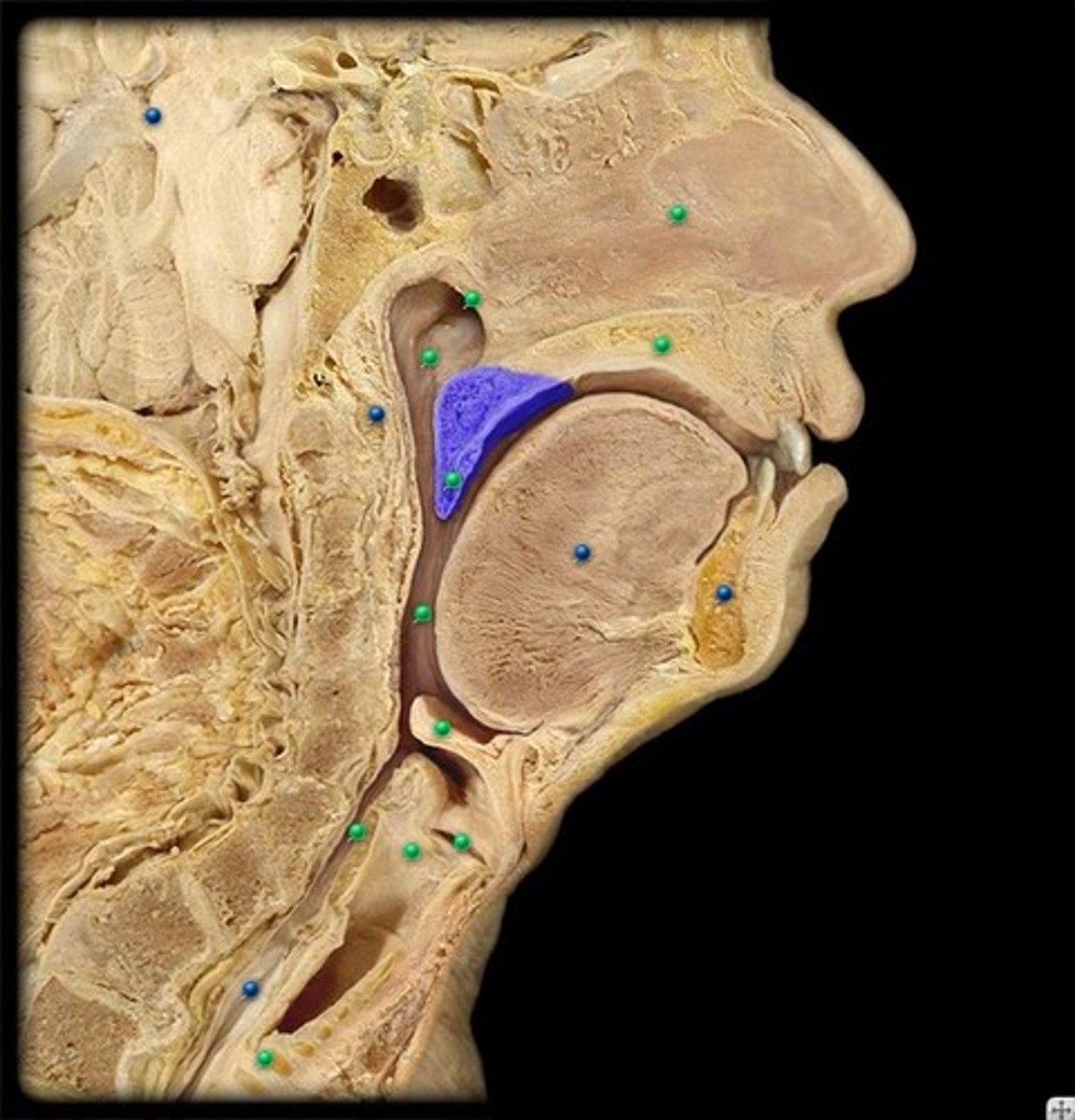
Pharyngeal tonsil
also called adenoids; located in posterior wall of nasopharynx
Torus tubarius
elevation of cartilage caused by the auditory tube in the nasopharynx
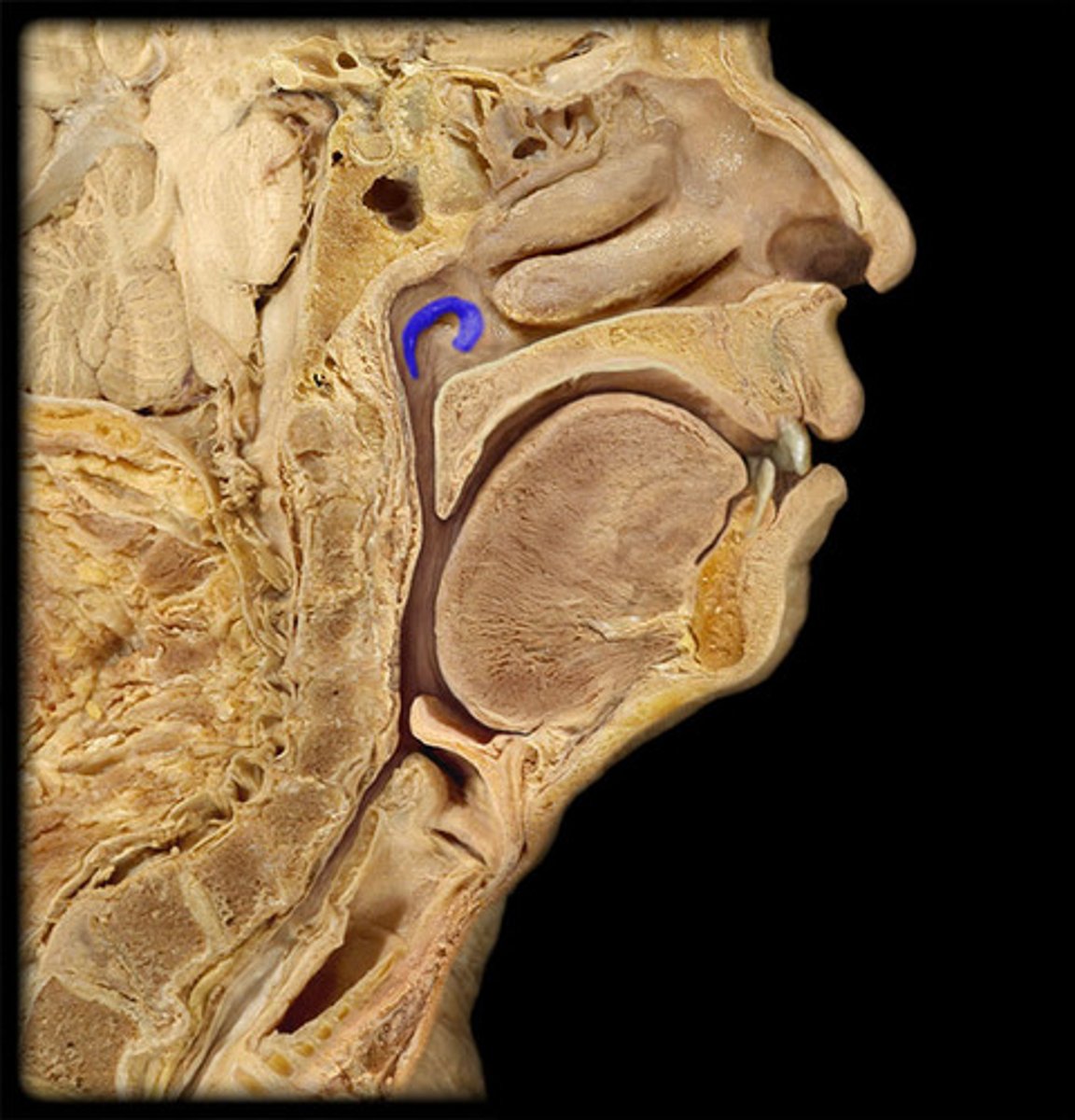
Pharyngeal orifice of auditory tube
Opens into the nasopharynx about 1.5 cm posterior to the inferior nasal concha. The unobstructed quality of this orifice is important as it is the means by which air pressure is equilibrated across the tympanic membrane. ALSO is a convenient means for the spread of infection from the nasopharynx to the middle ear.
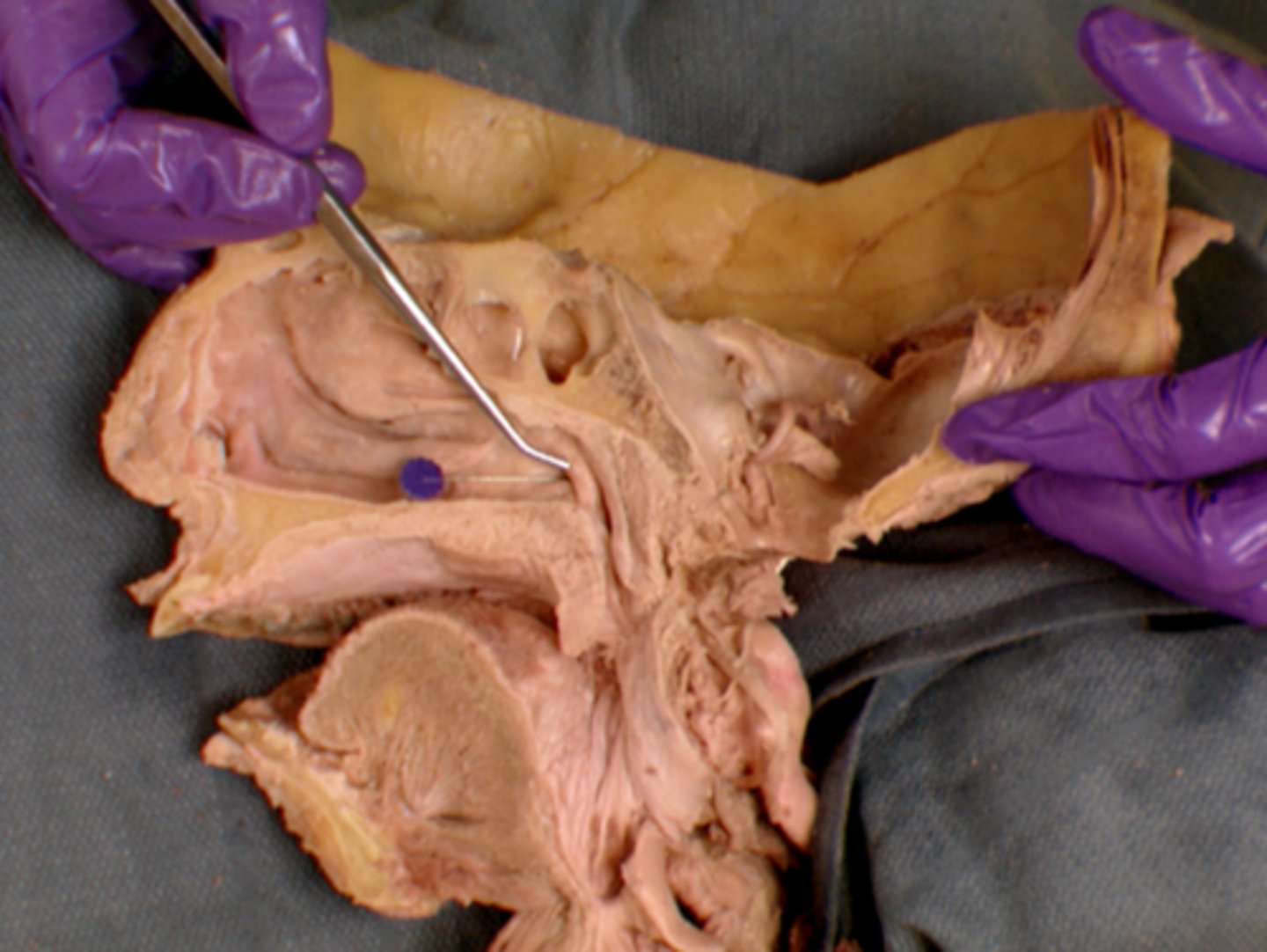
Tensor veli palatini m.
causes tension in the soft palate which helps to stop food from entering the nasopharynx while swallowing
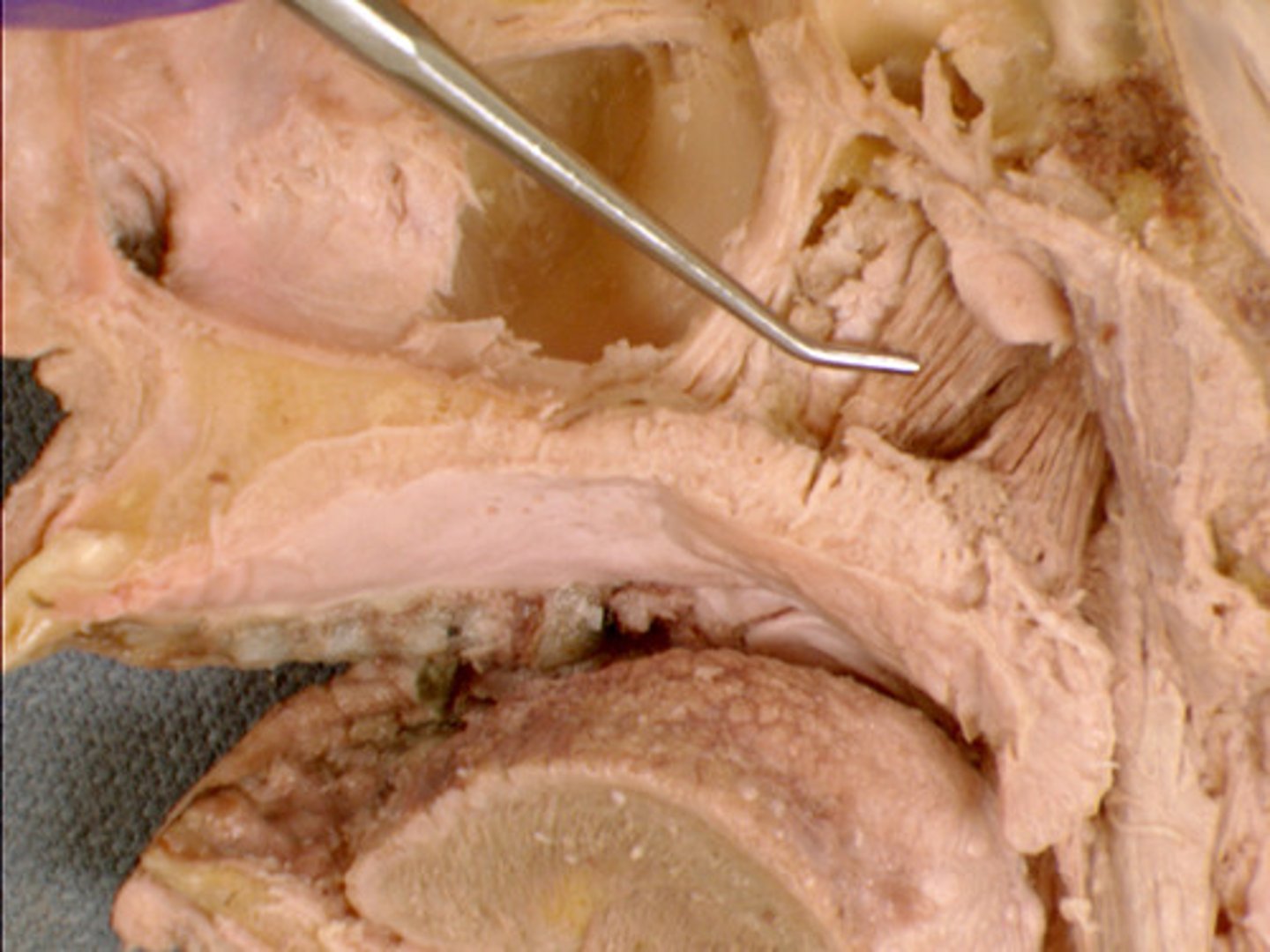
Levator veli palatini m.
Action: elevates soft palate when swallowing
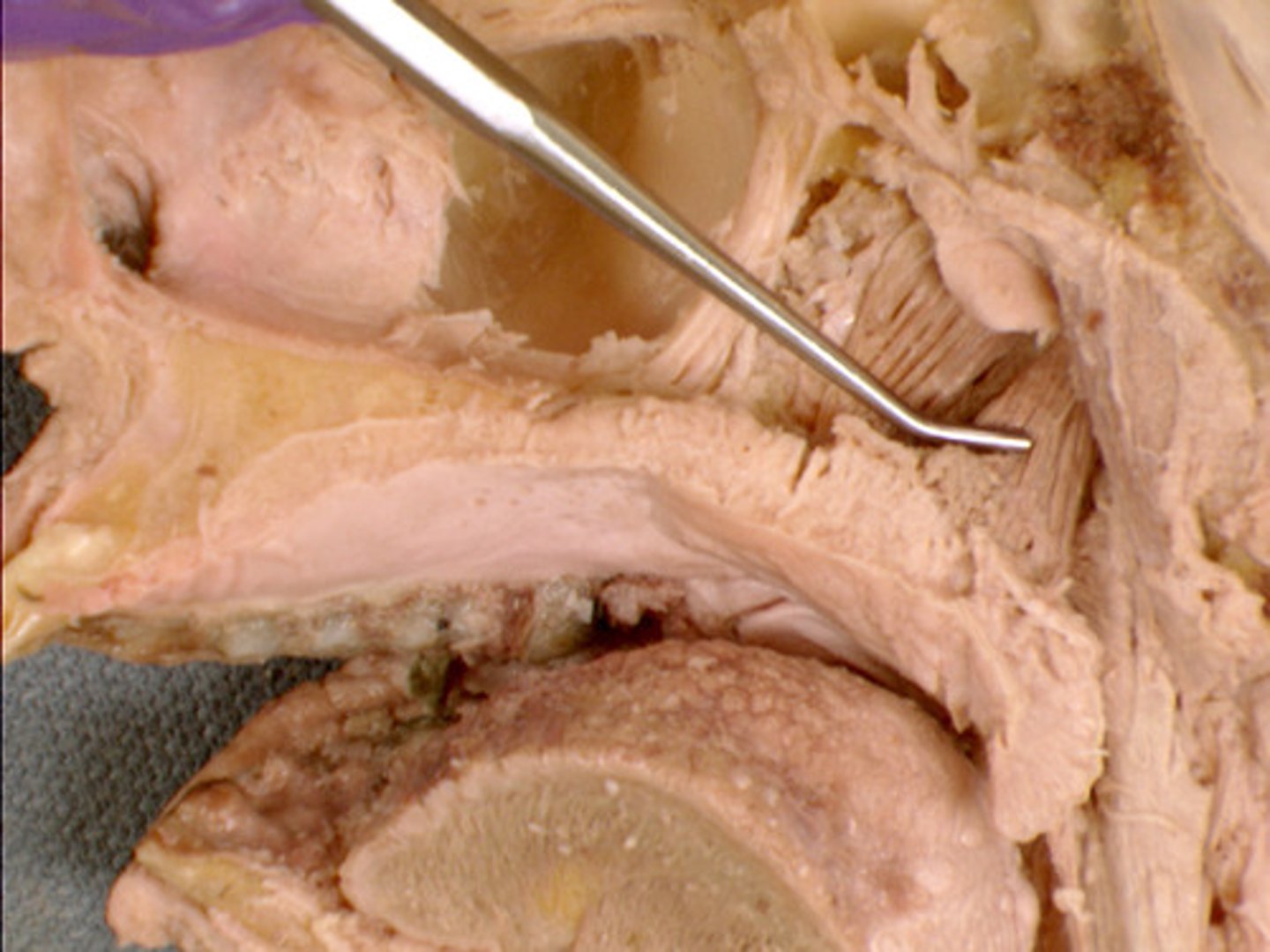
Oral vestibule
area between the teeth and lips/cheeks
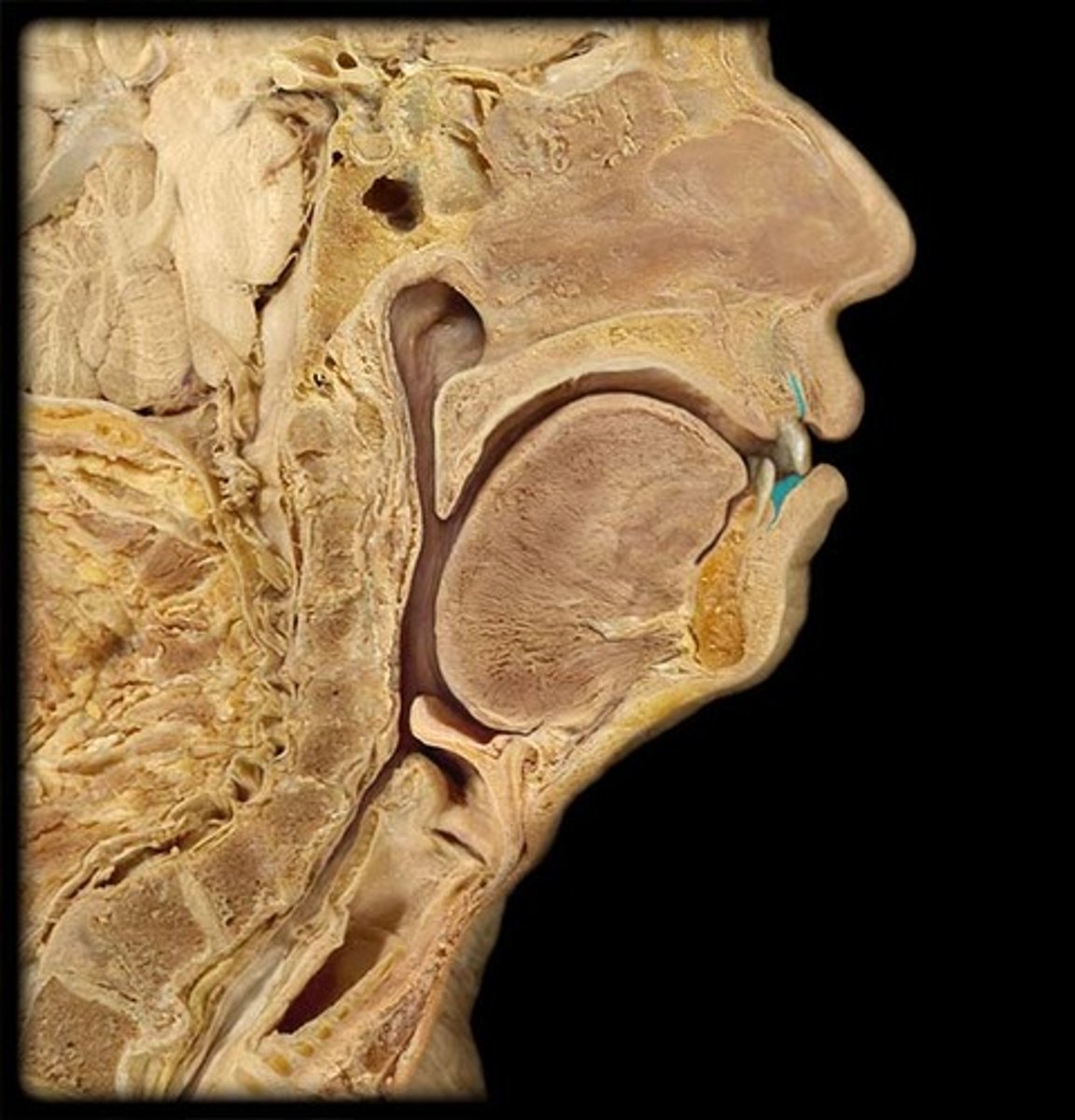
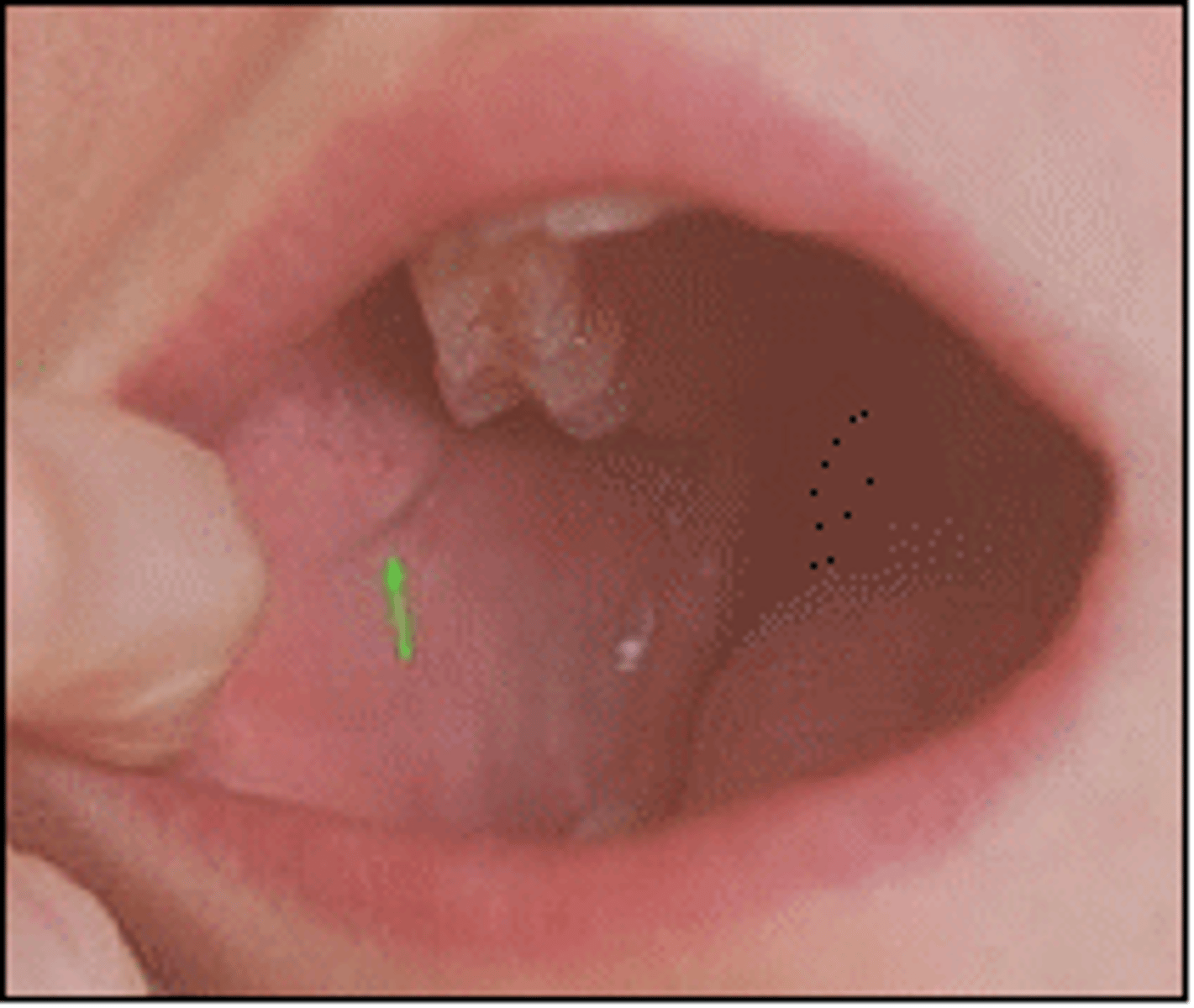
Parotid papilla
Small elevation of tissue located on the inner surface of the cheek
Hard palate
roof of the mouth, floor of the nose
Soft palate
posterior portion, not supported by bone
palatoglossal arch (fold)
muscular fold that extends from the lateral side of the soft palate to the base of the tongue
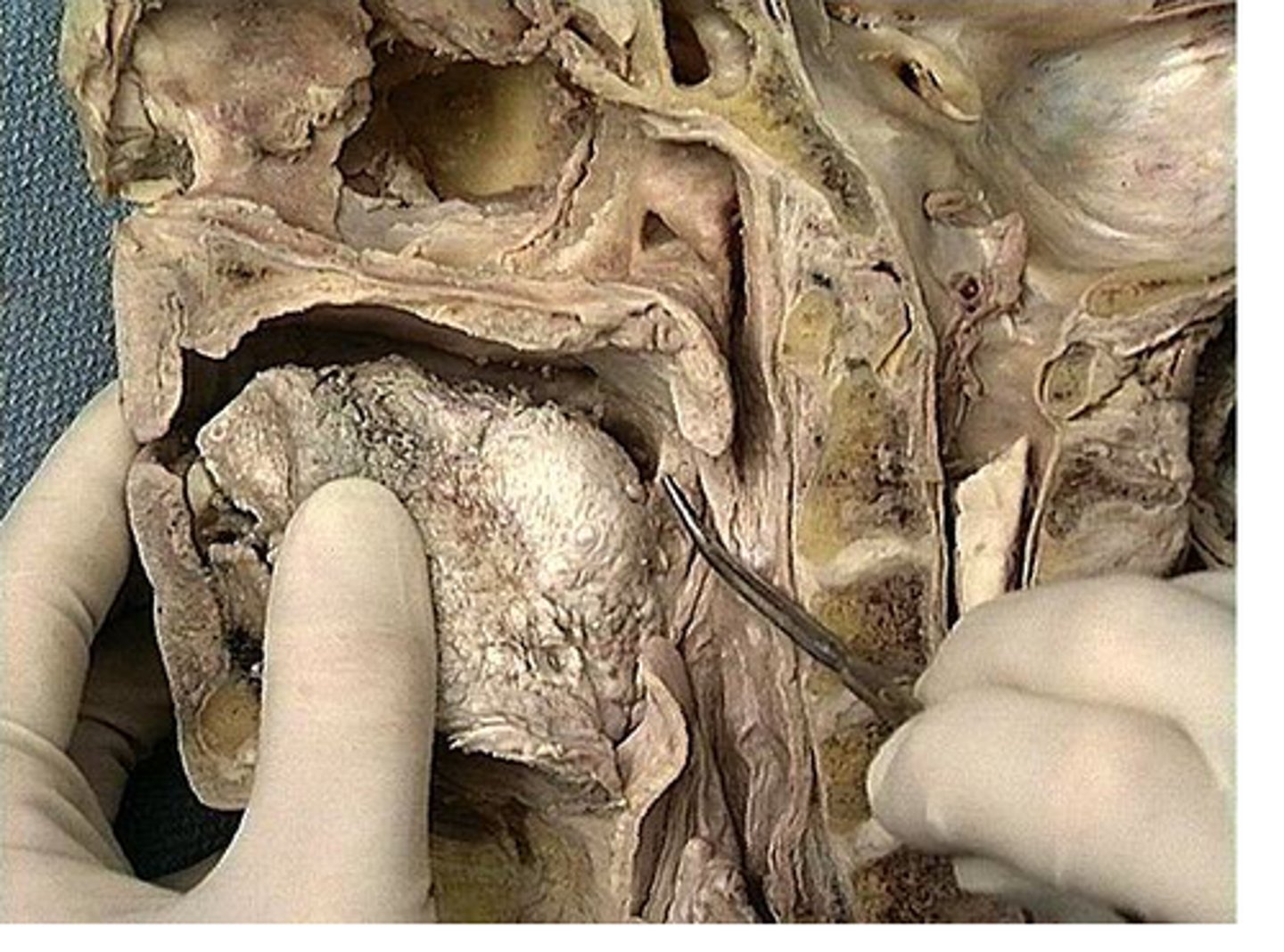
Palatine tonsil
one of a pair of almond-shaped masses of lymphatic tissue in the oropharynx
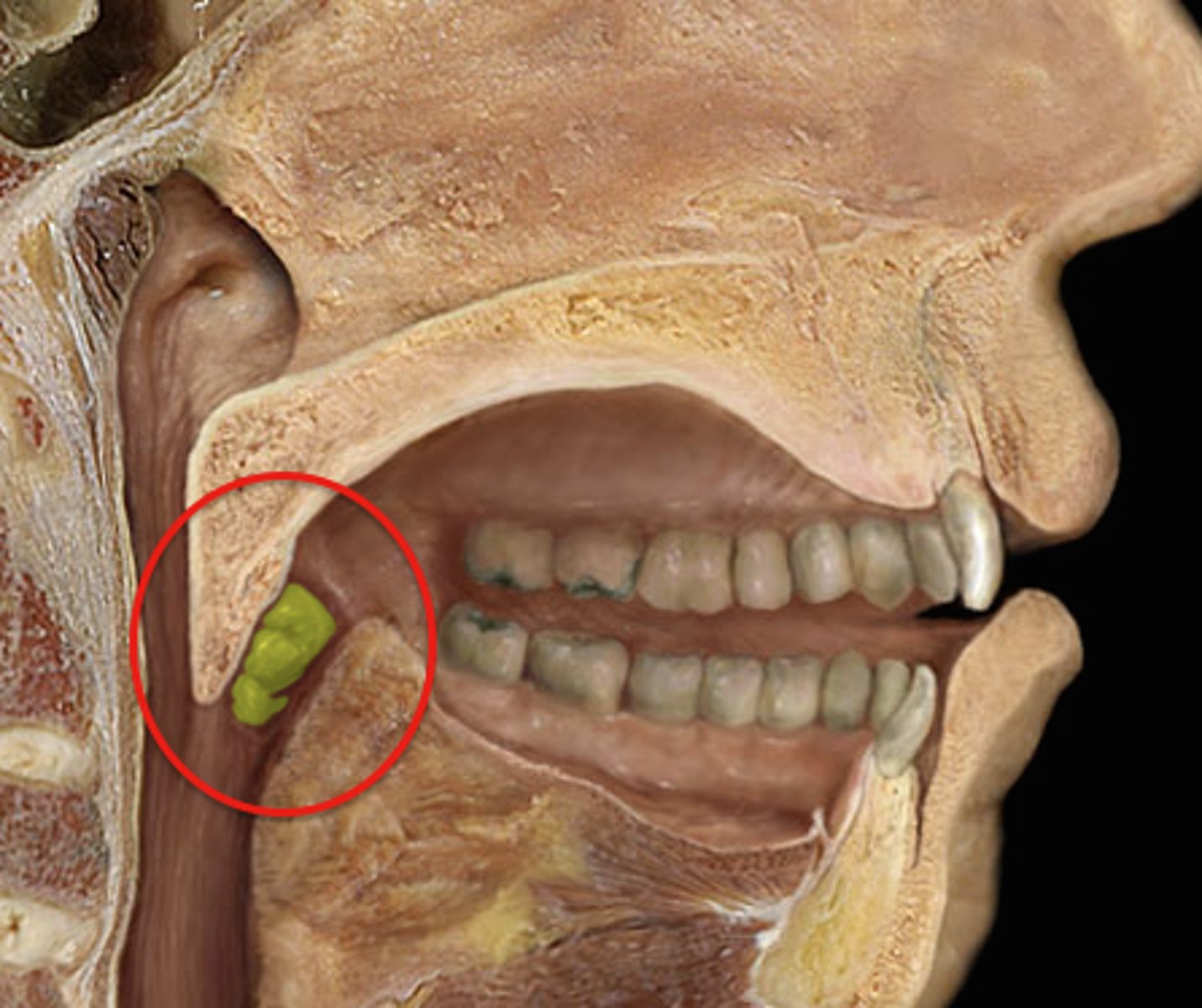
Tongue
manipulates food for chewing and swallowing; a taste organ
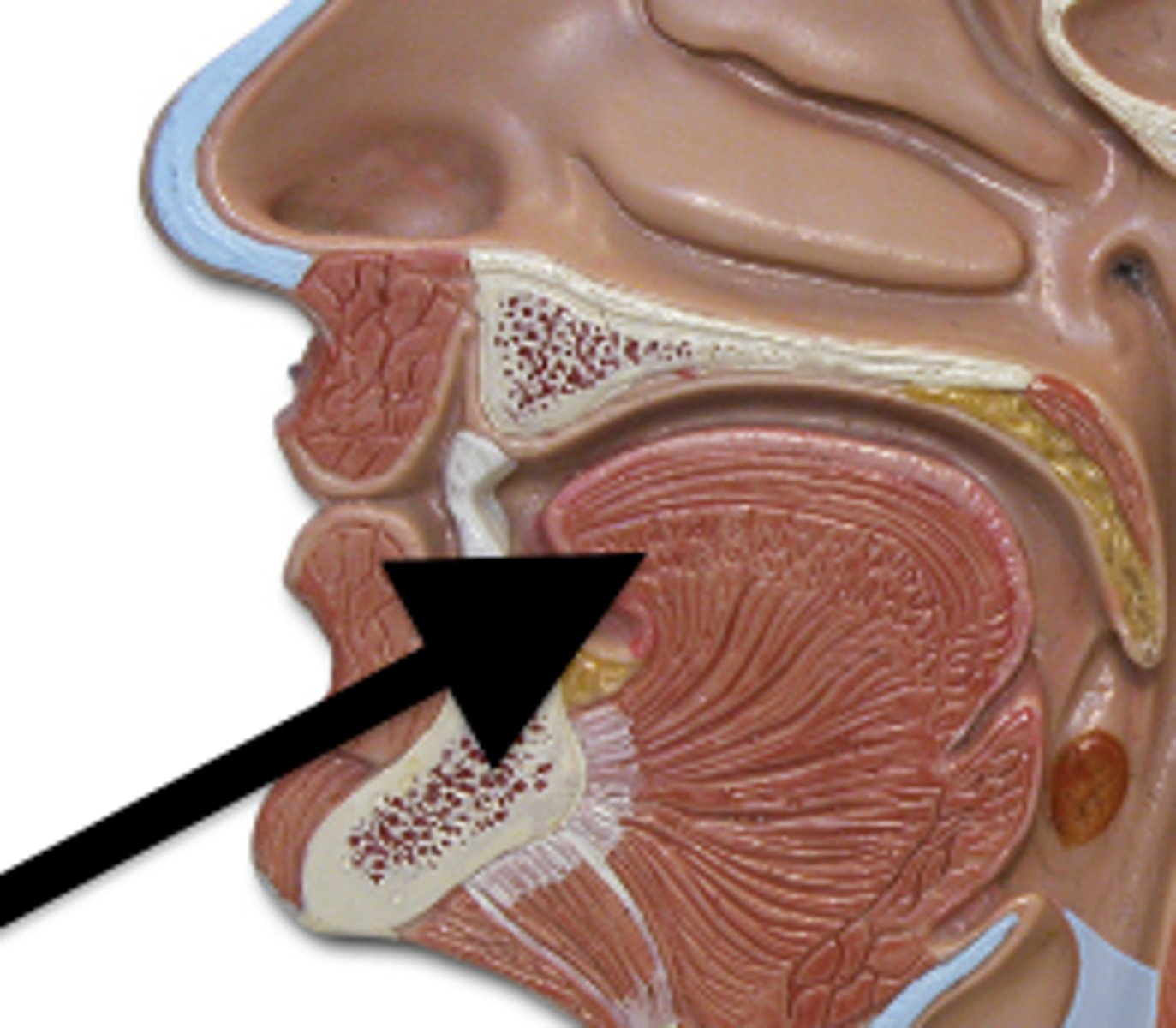
Circumvallate papillae
large papillae with taste buds- on back of tongue
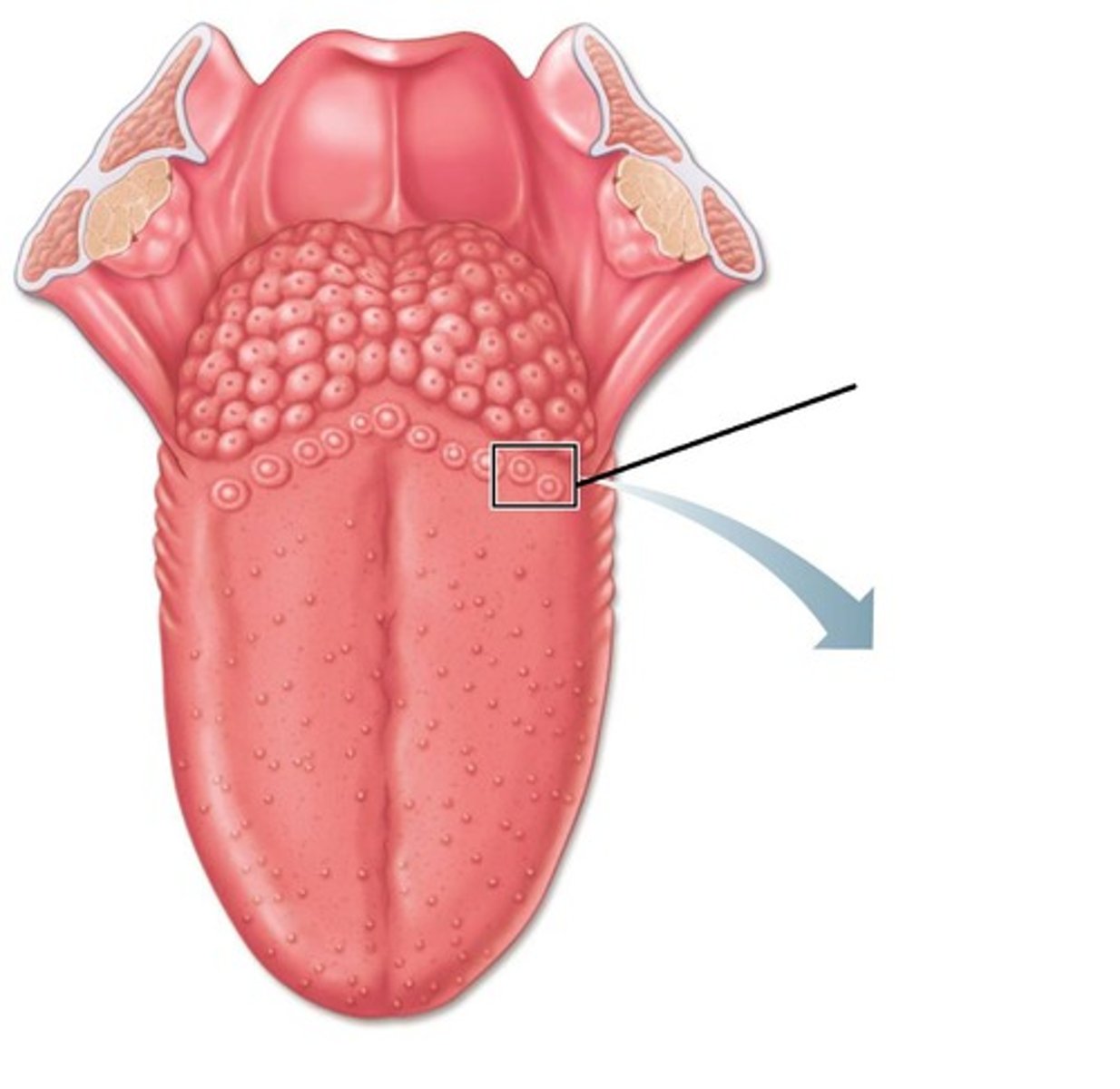
Sulcus terminalis
marks border between mouth and pharynx
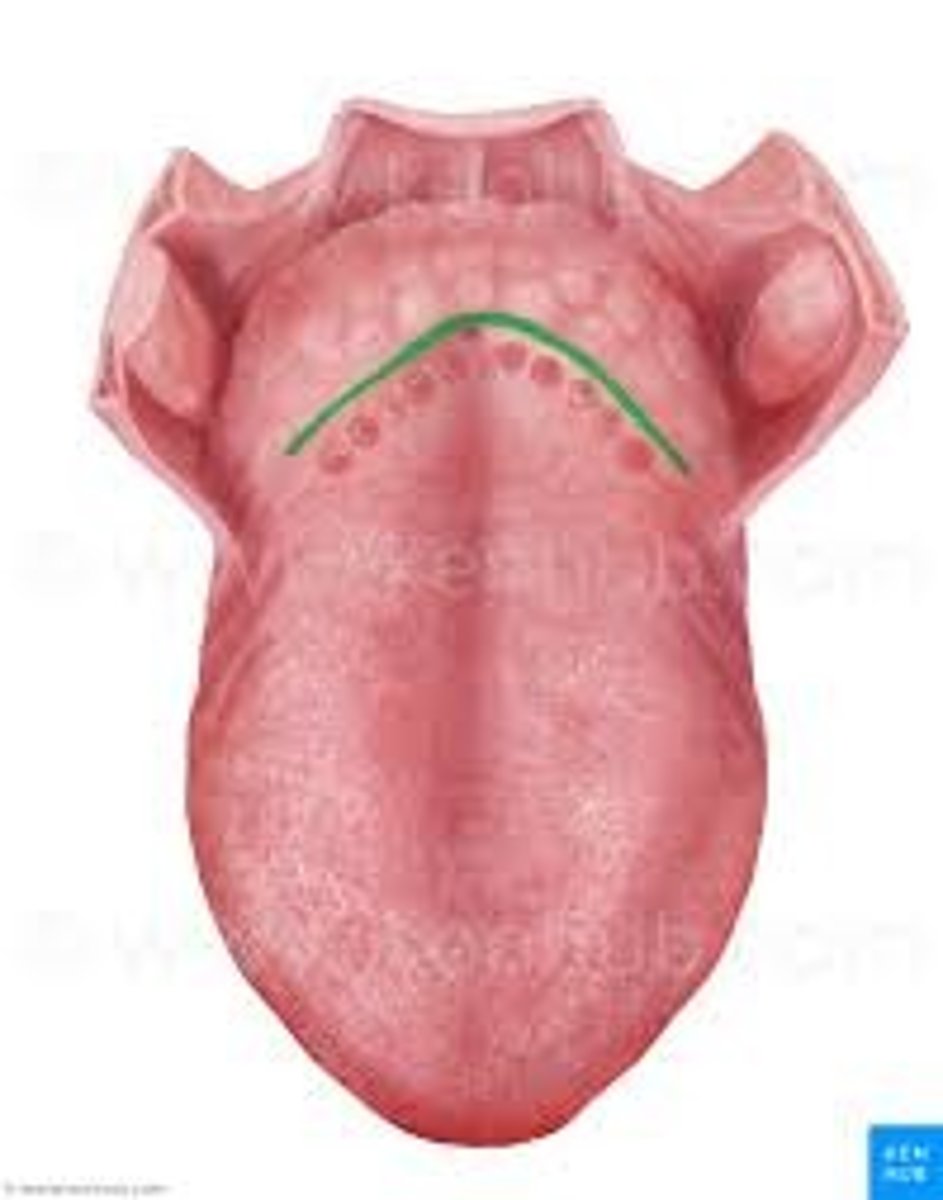
Lingual tonsil
at base of tongue anterior to the epiglottis
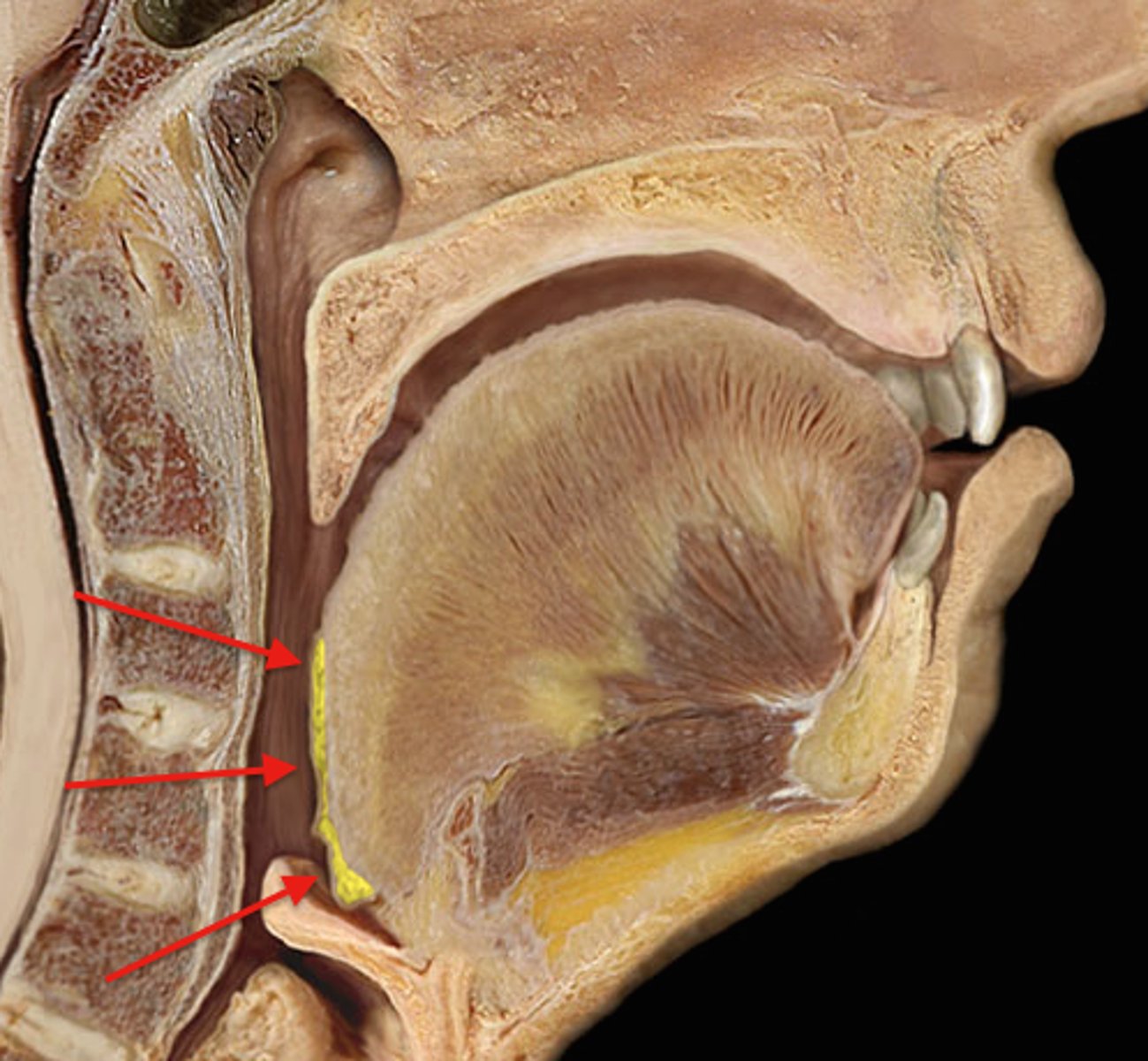
genioglossus muscle
forms the bulk of the tongue and allows it to move freely
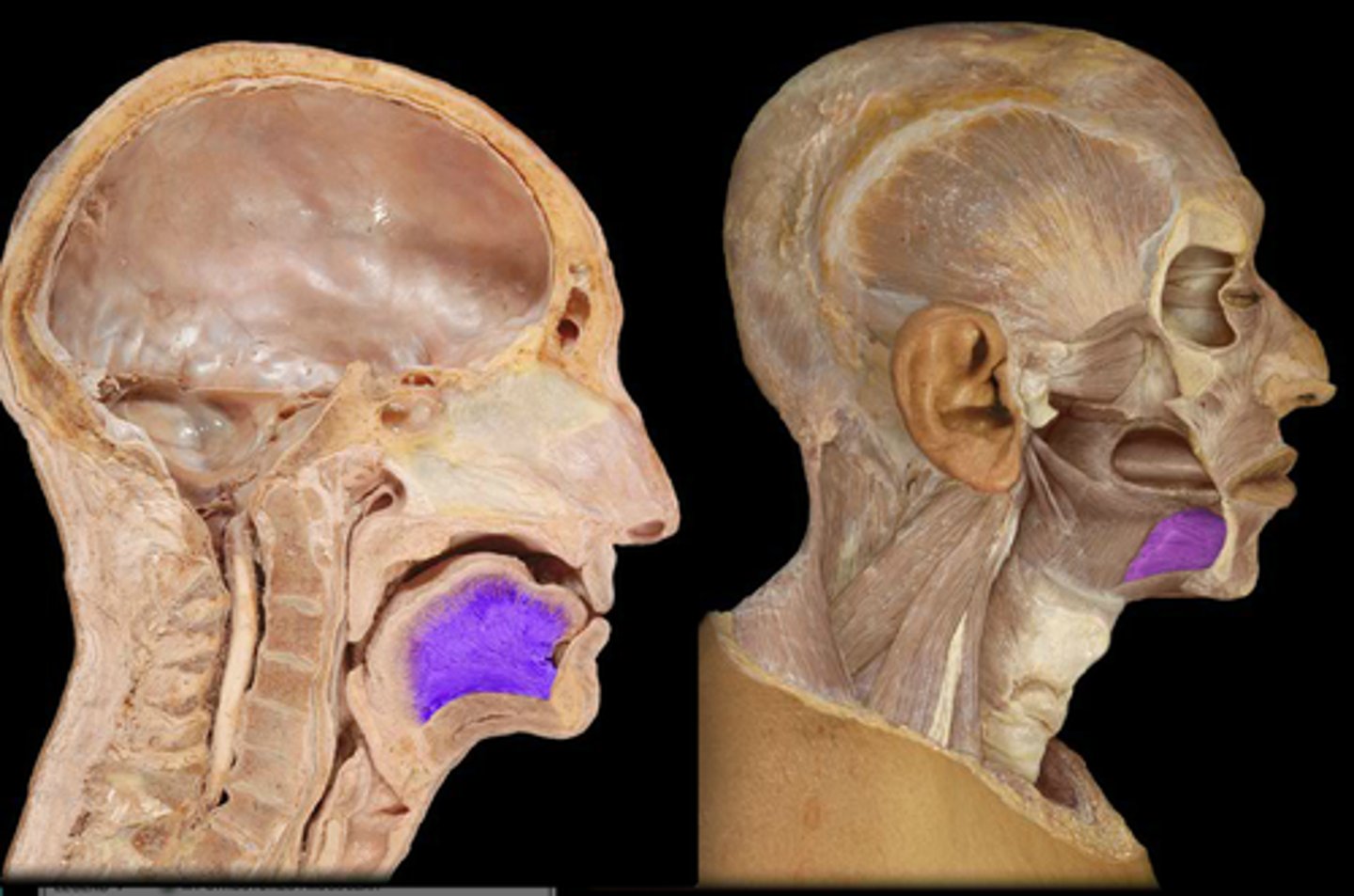
Geniohyoid m.
Function: pulls the hyoid anterosuperiorly, shortens floor of the mouth and widens pharynx
Innervation: C1 via hypoglossal nerve
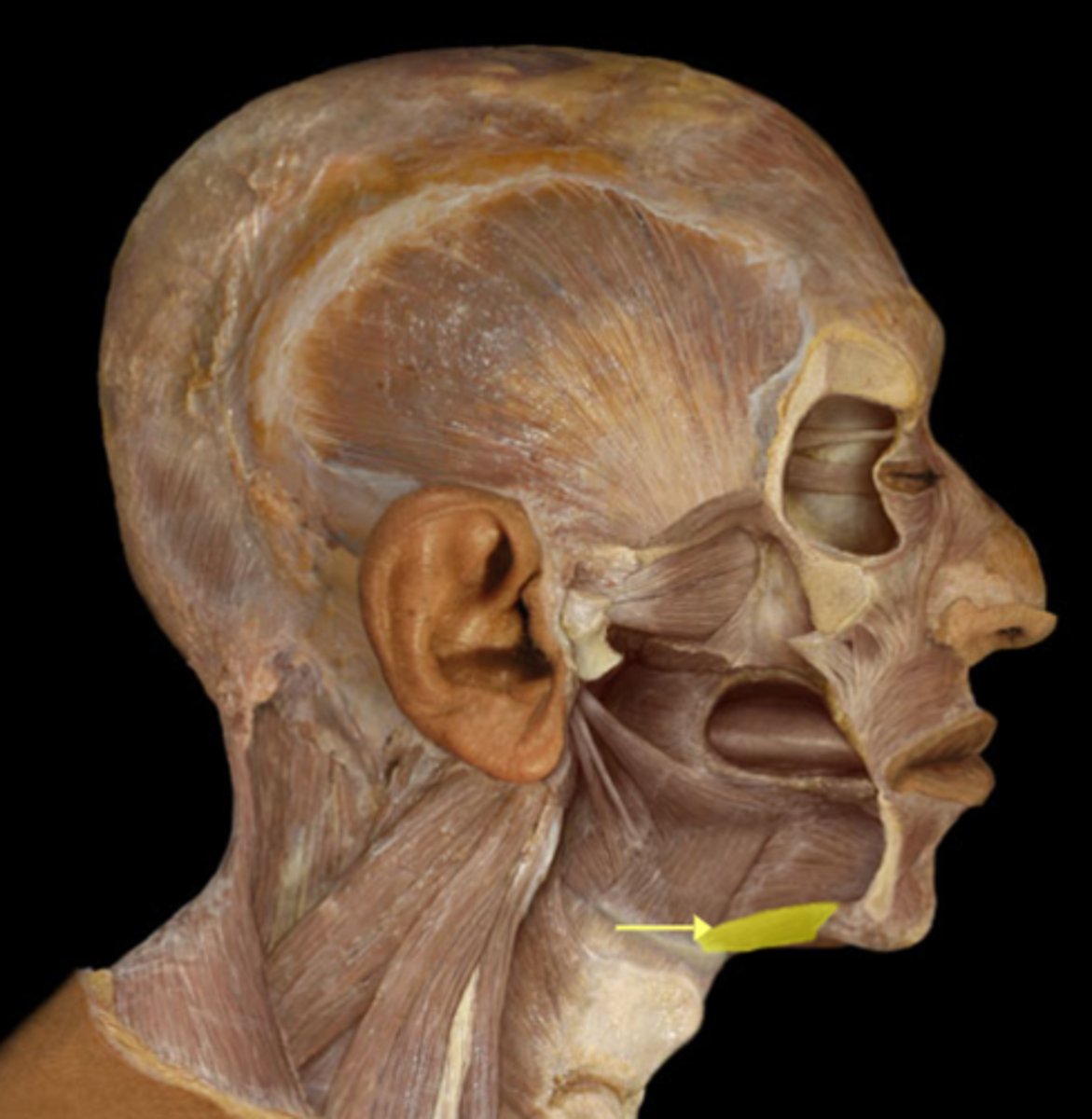
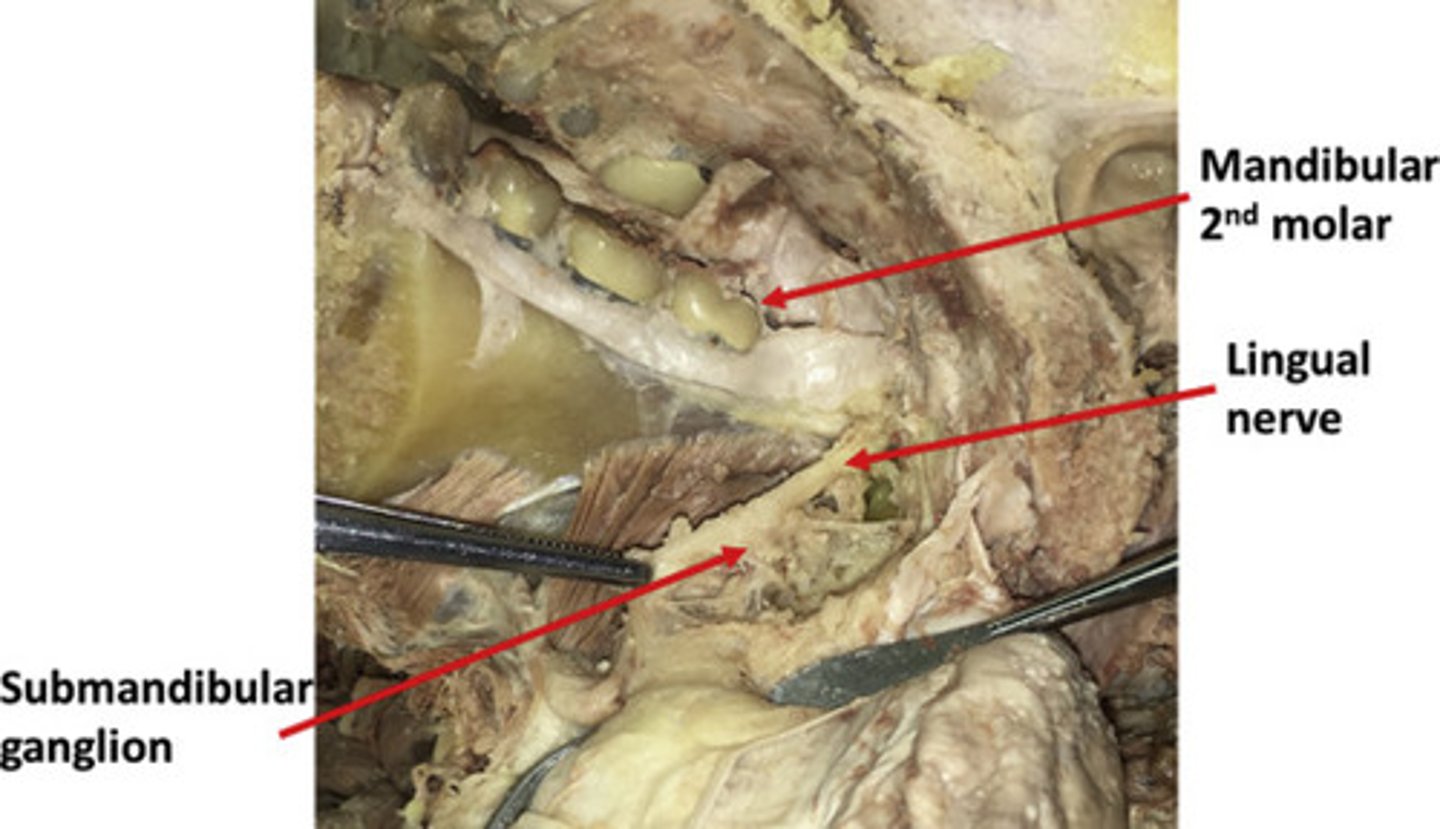
Submandibular duct
duct associated with submandibular gland
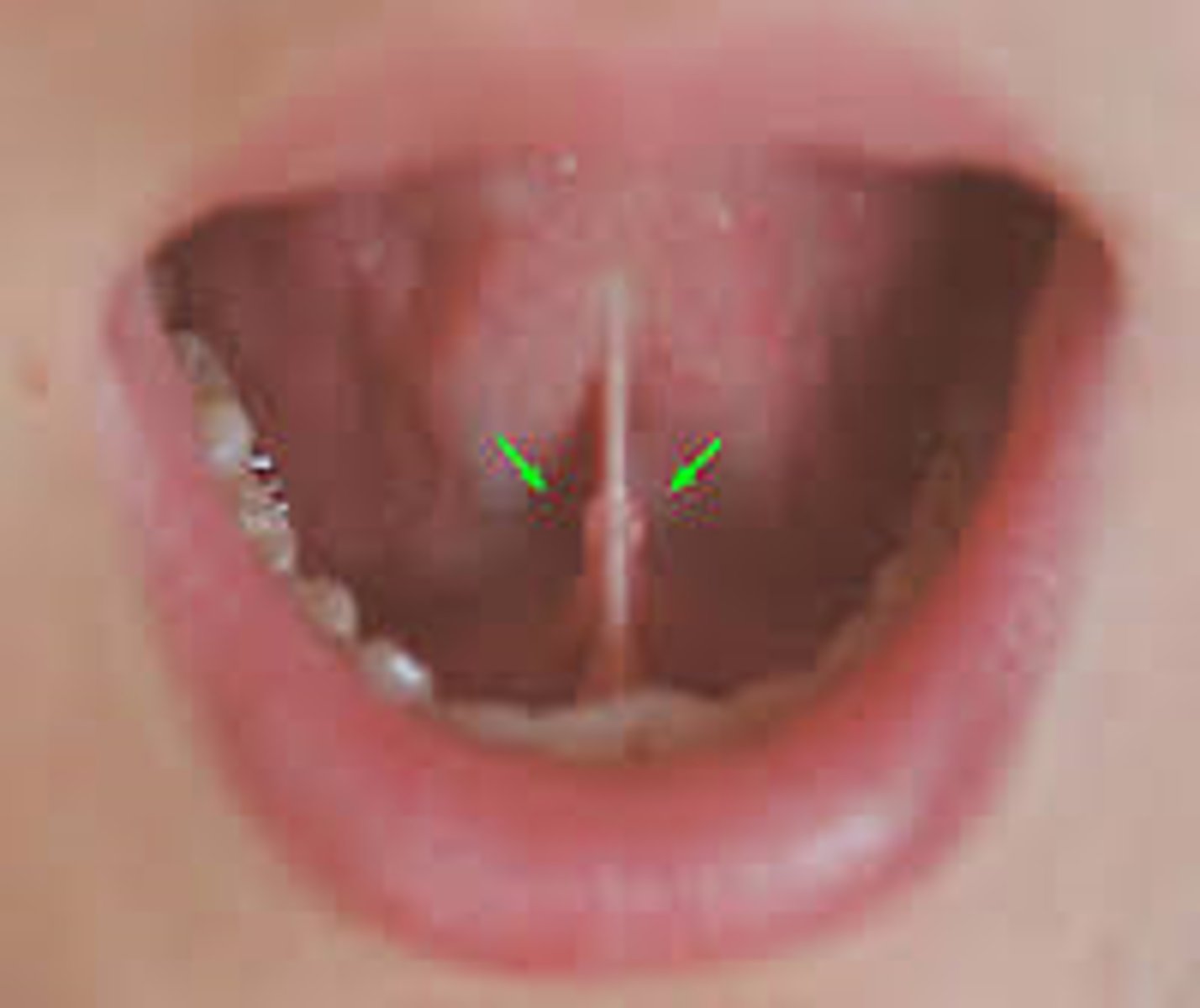
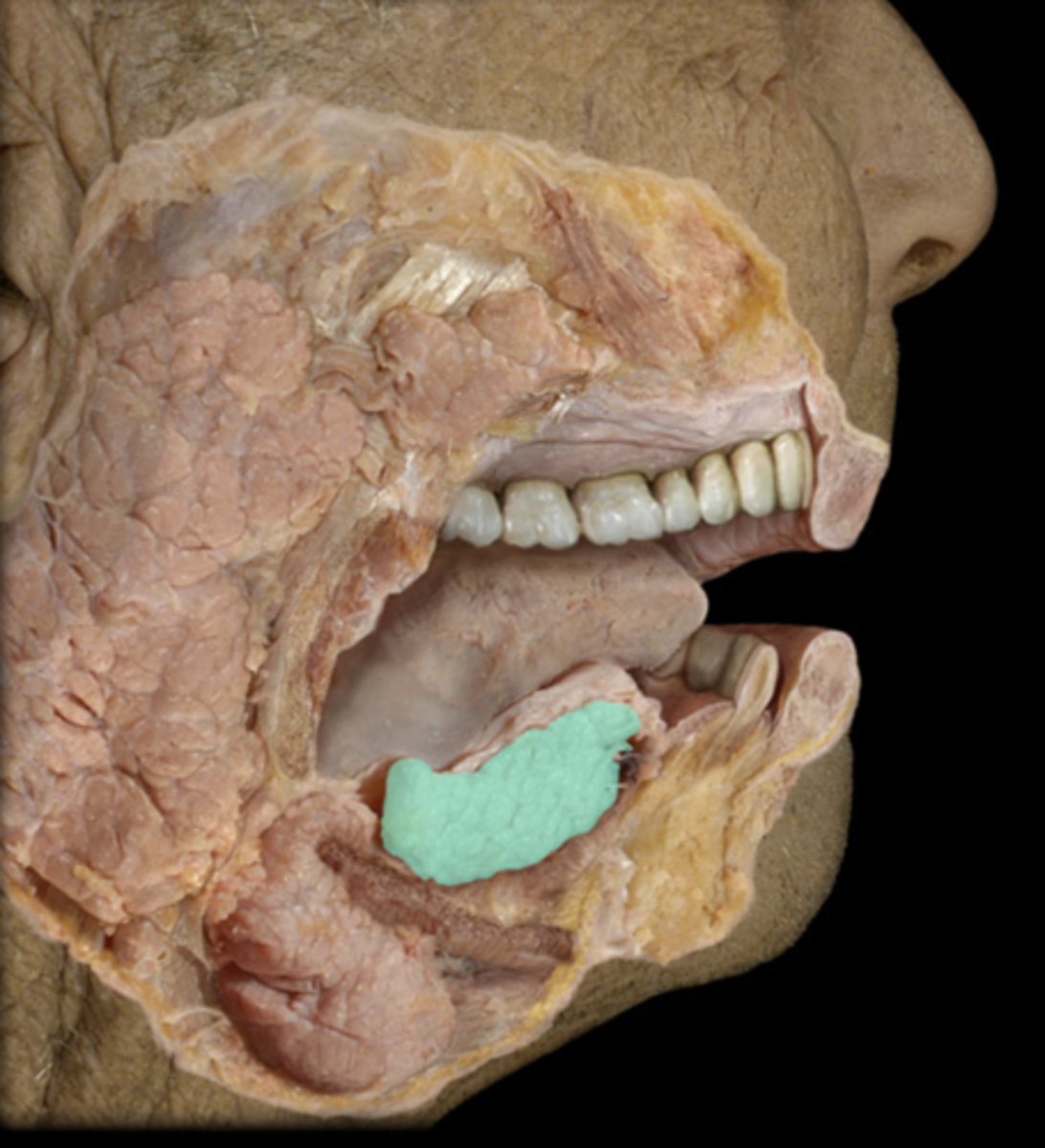
Sublingual salivary gland
under the tongue, produces mucus
Lingual nerve
supplies anterior 2/3 of the tongue
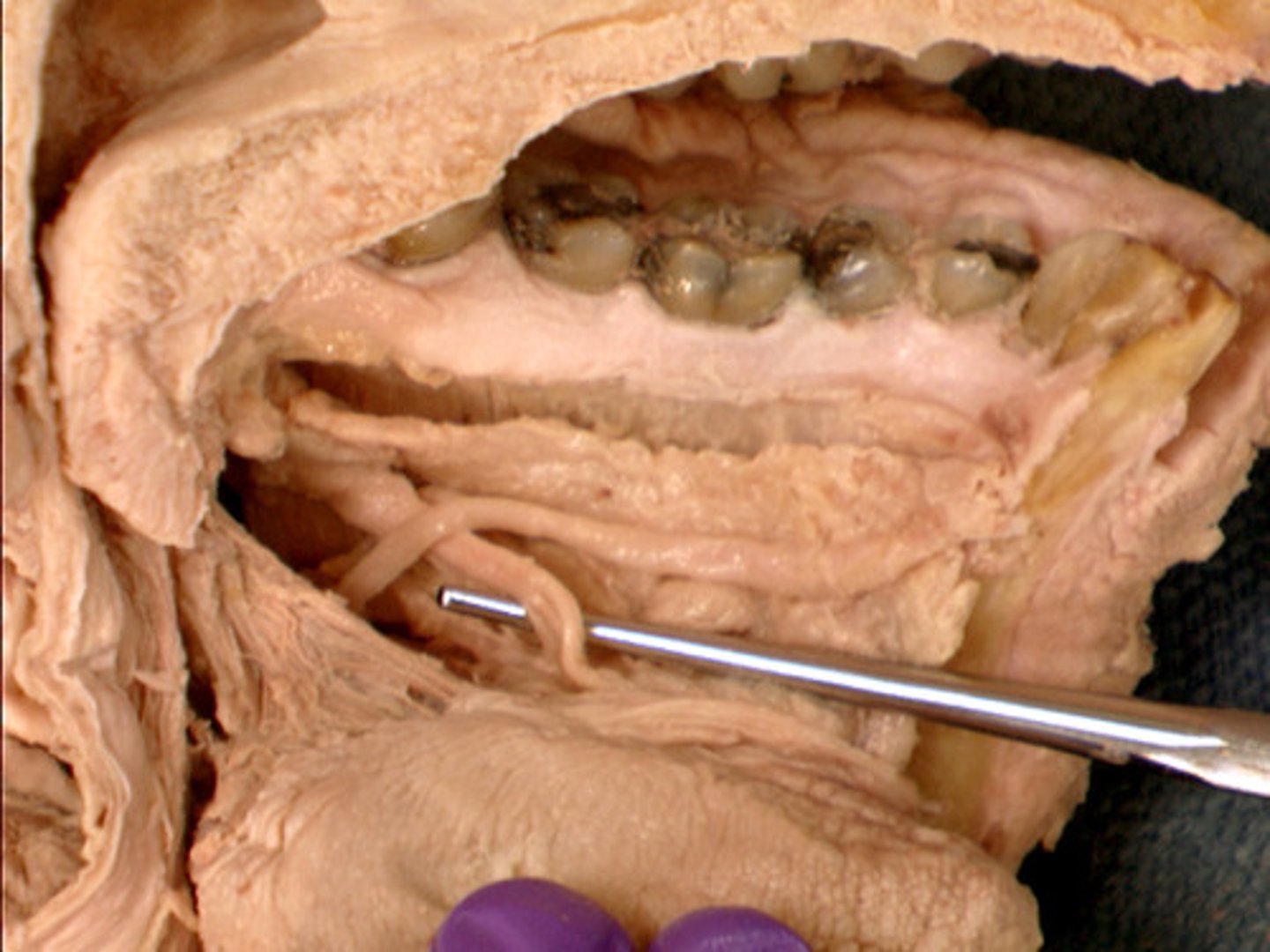
Chorda tympani n.
Nerve that provides taste to anterior 2/3 of tongue
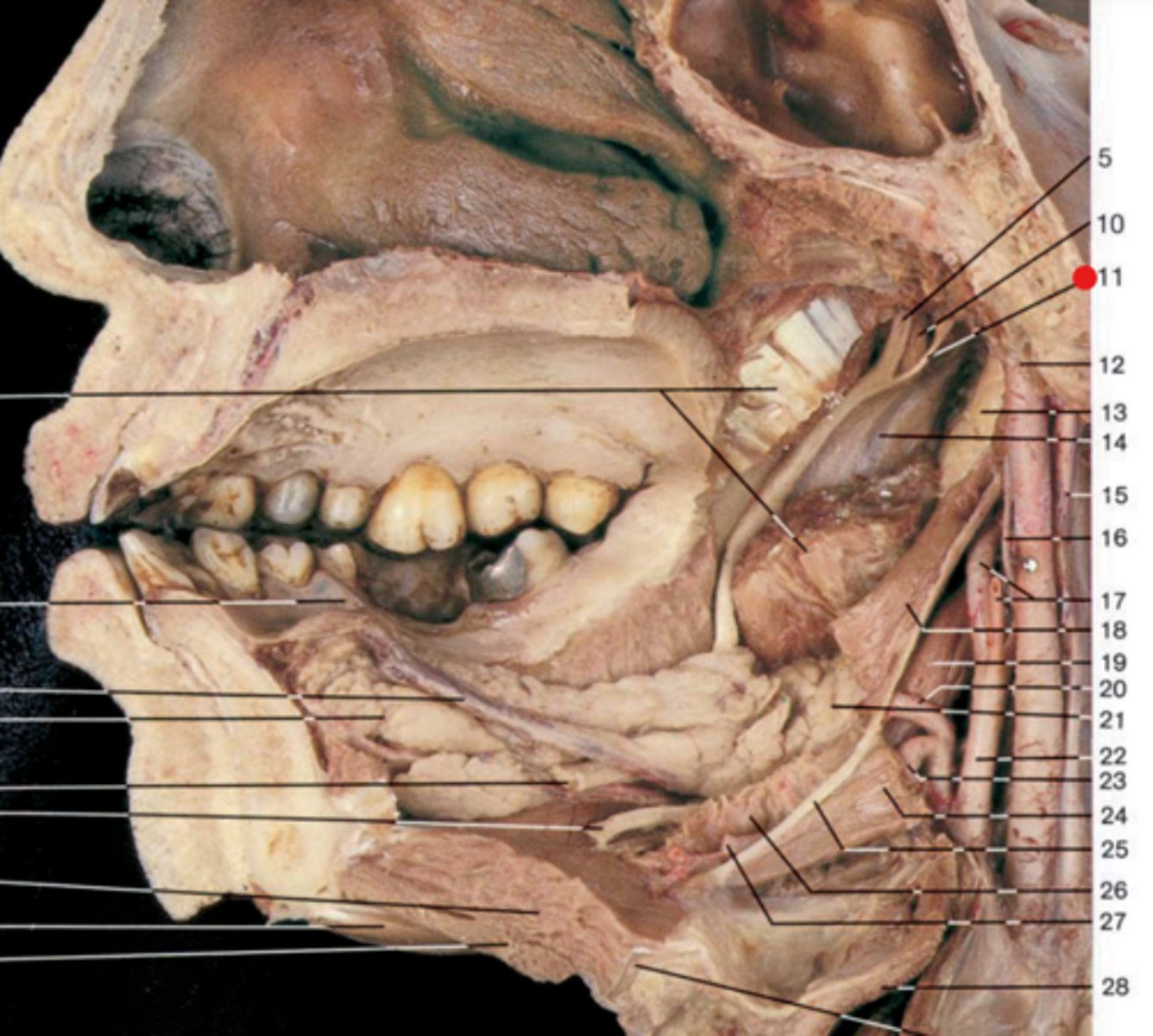
Submandibular ganglion
Postganglionic fibers synapse on salivary glands; CN VII
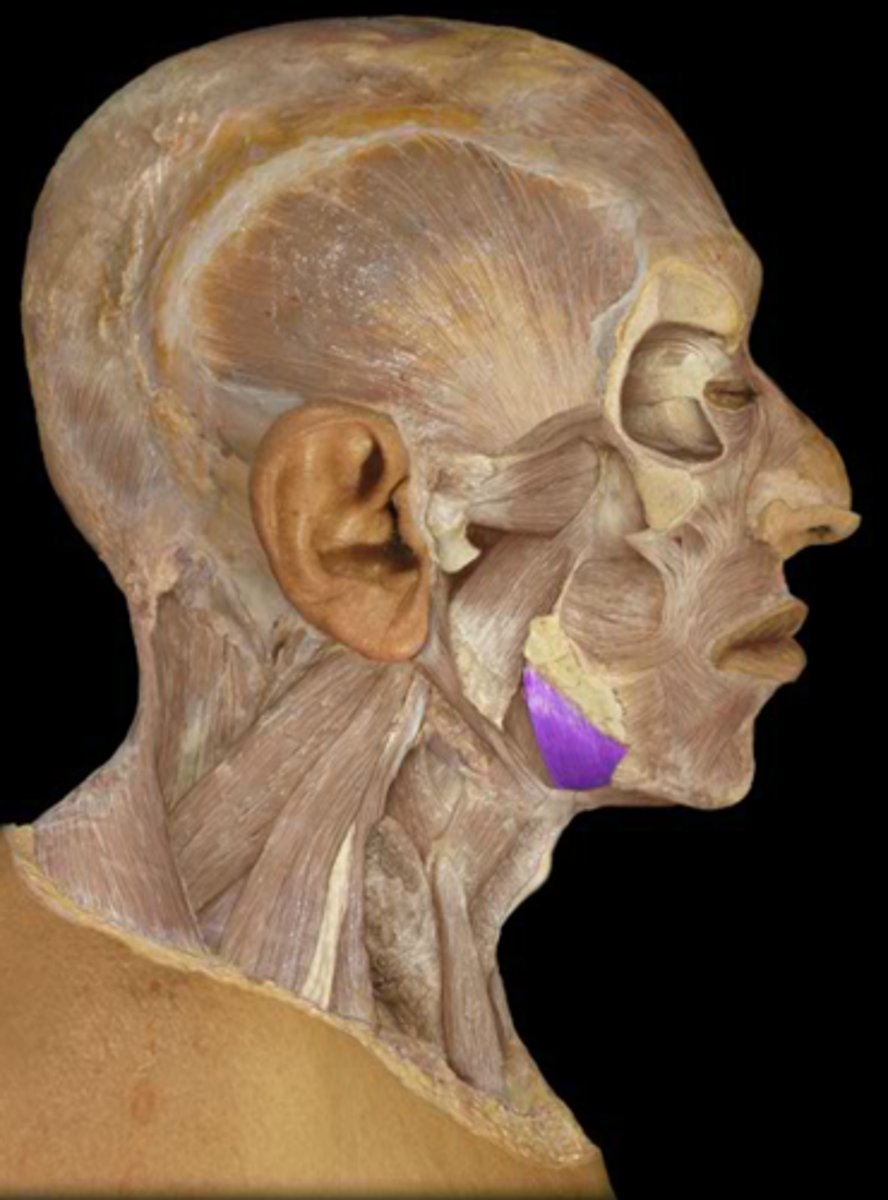
Mylohyoid m.
hyoid elevation
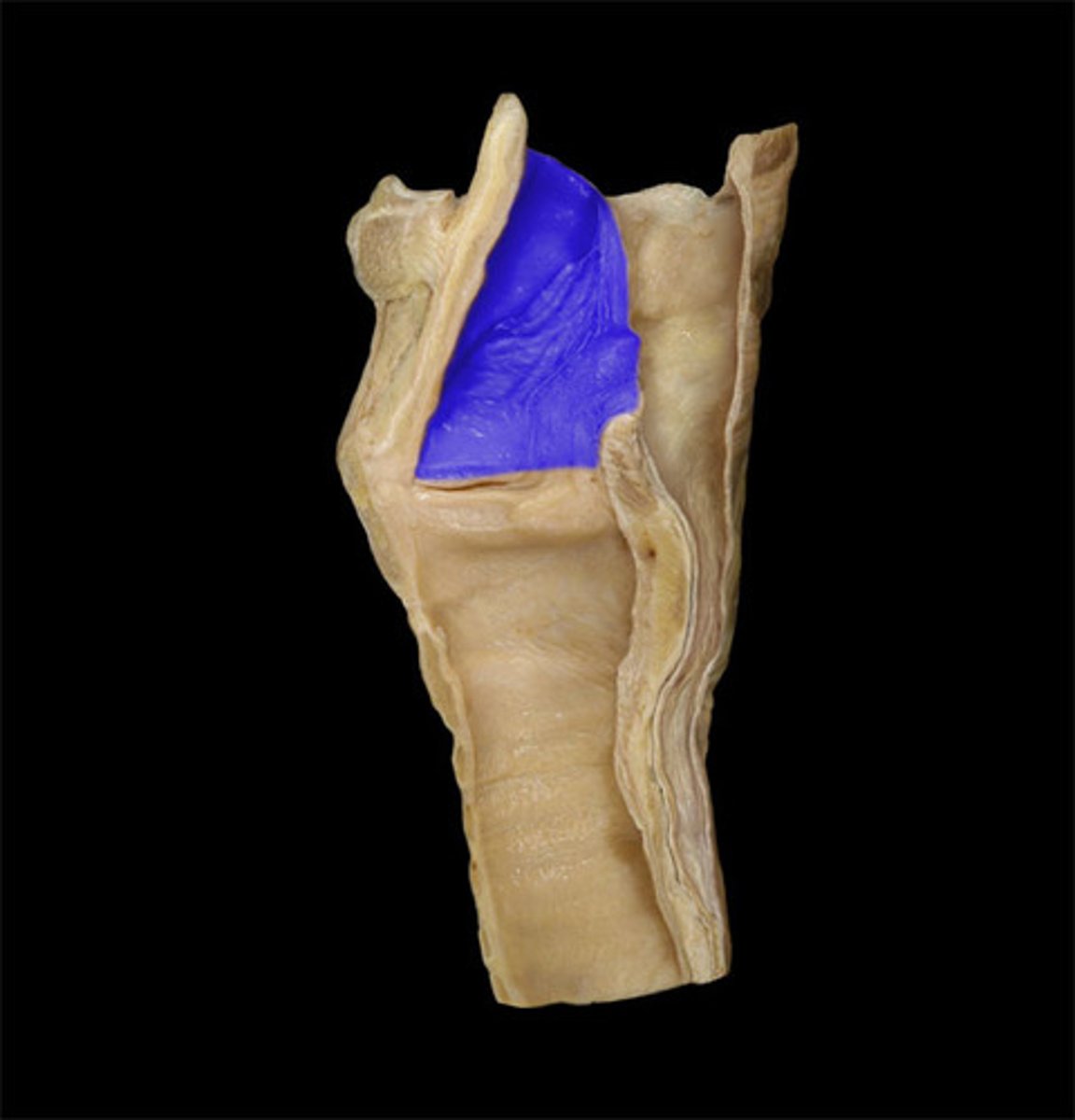
Laryngeal inlet (laryngeal orifice)
opening that connects the pharynx and larynx
Laryngeal vestibule
Opening of larynx below epiglottis and aditus but above the false vocal folds
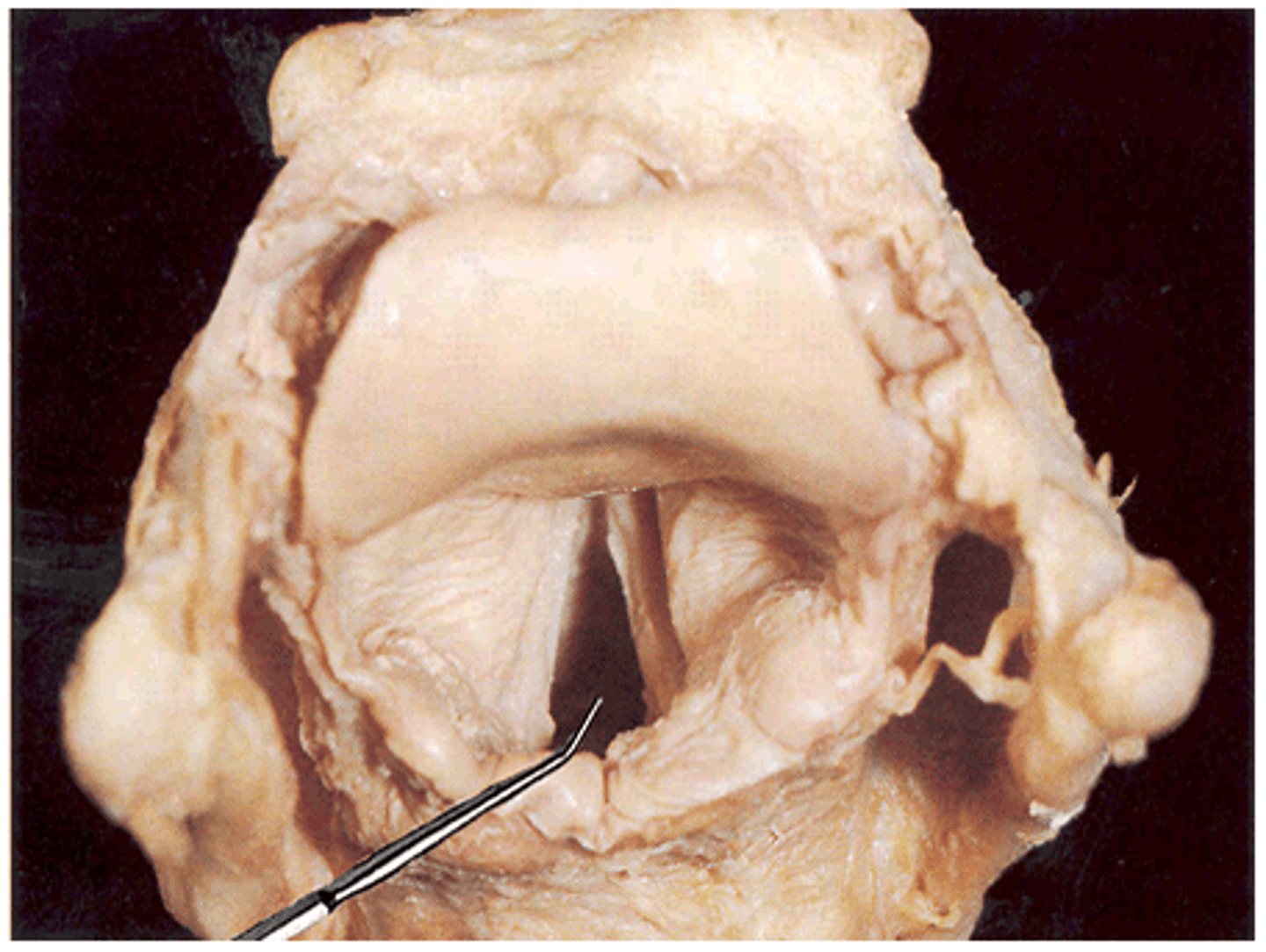
Rima vestibuli
space between false vocal folds
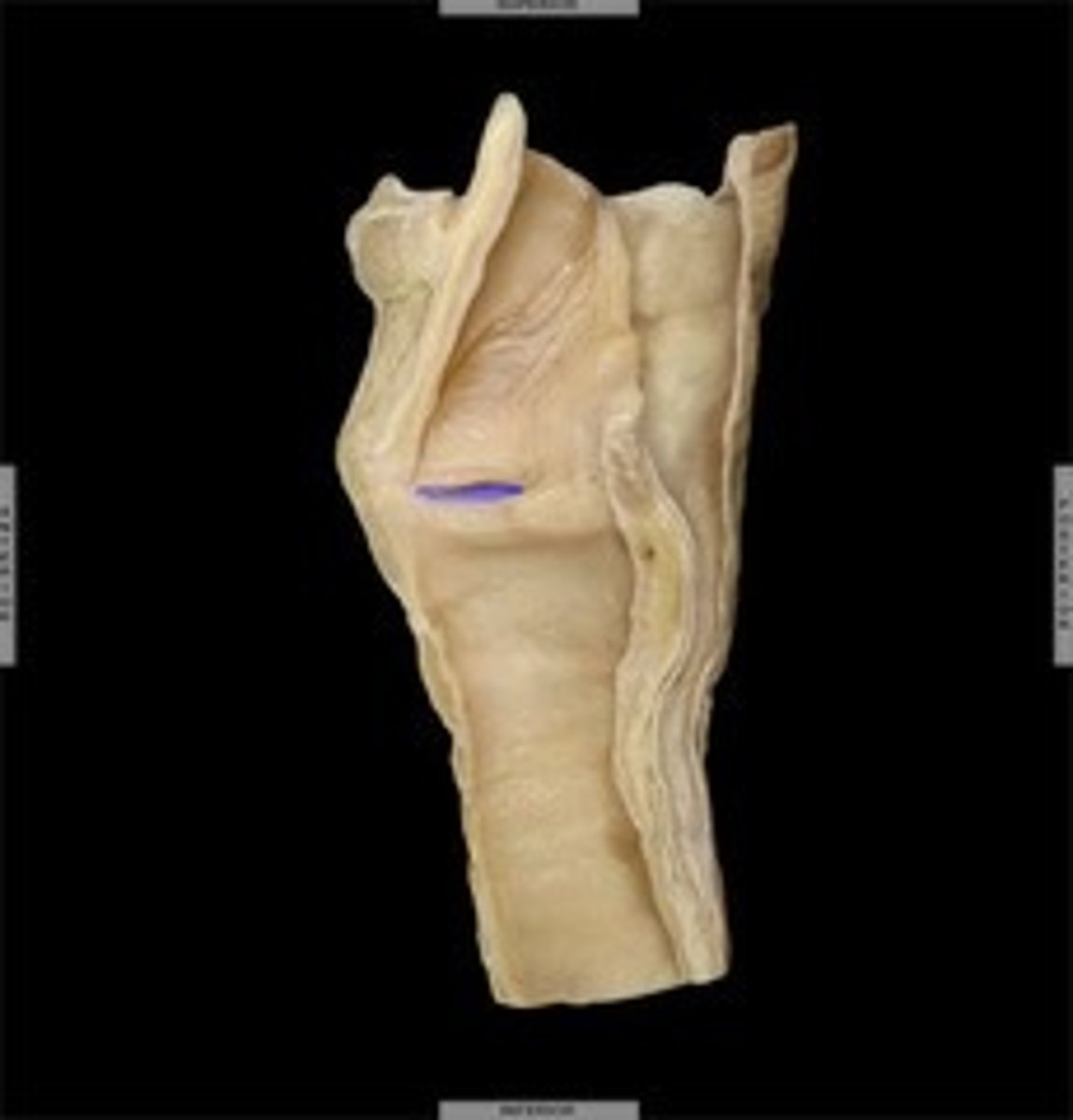
Laryngeal ventricle
space between true and false vocal folds
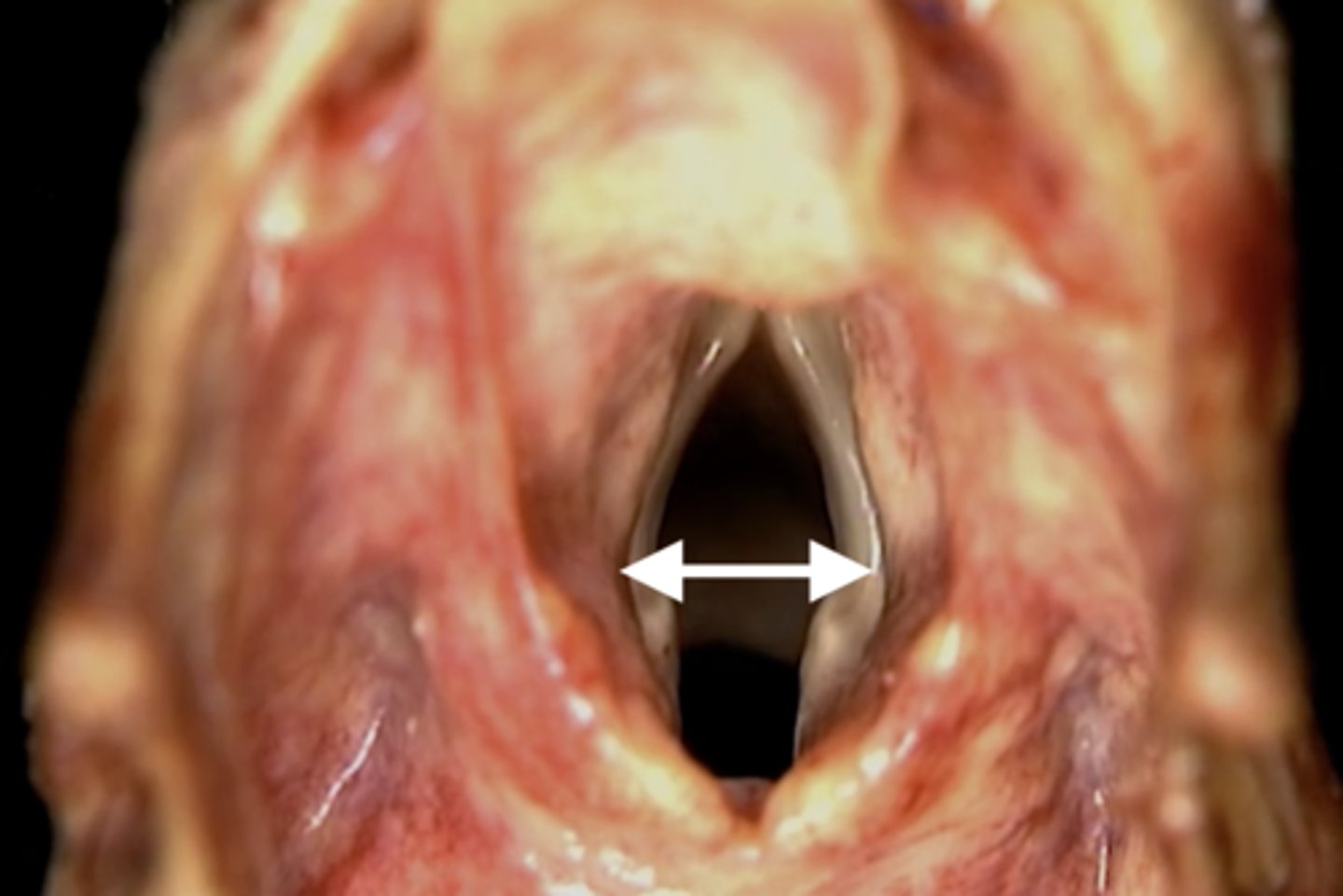
Rima glottidis
opening between vocal folds
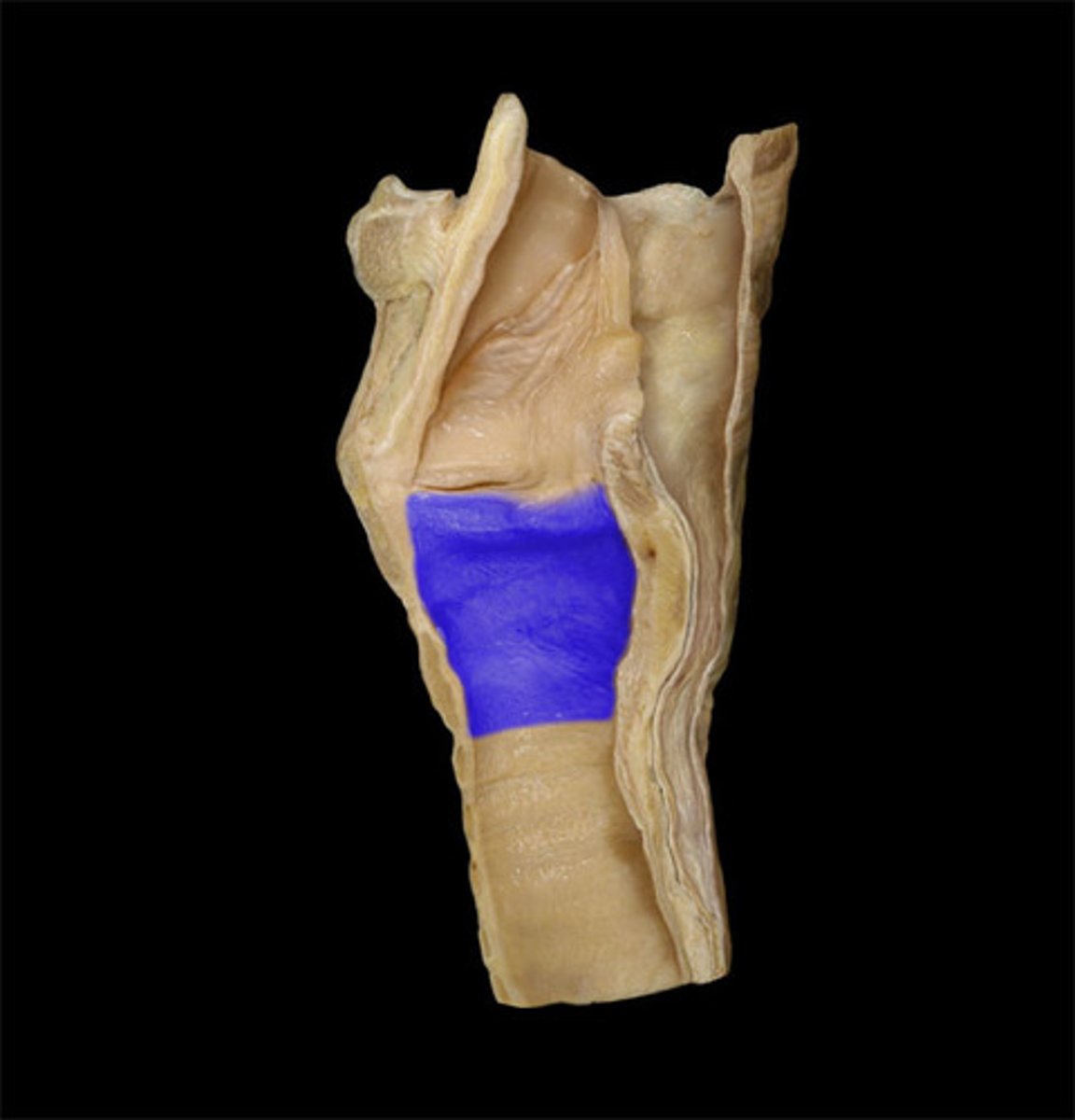
Infraglottic space
area inferior to the vocal folds
Tracheal lumen
cavity or channel within the trachea
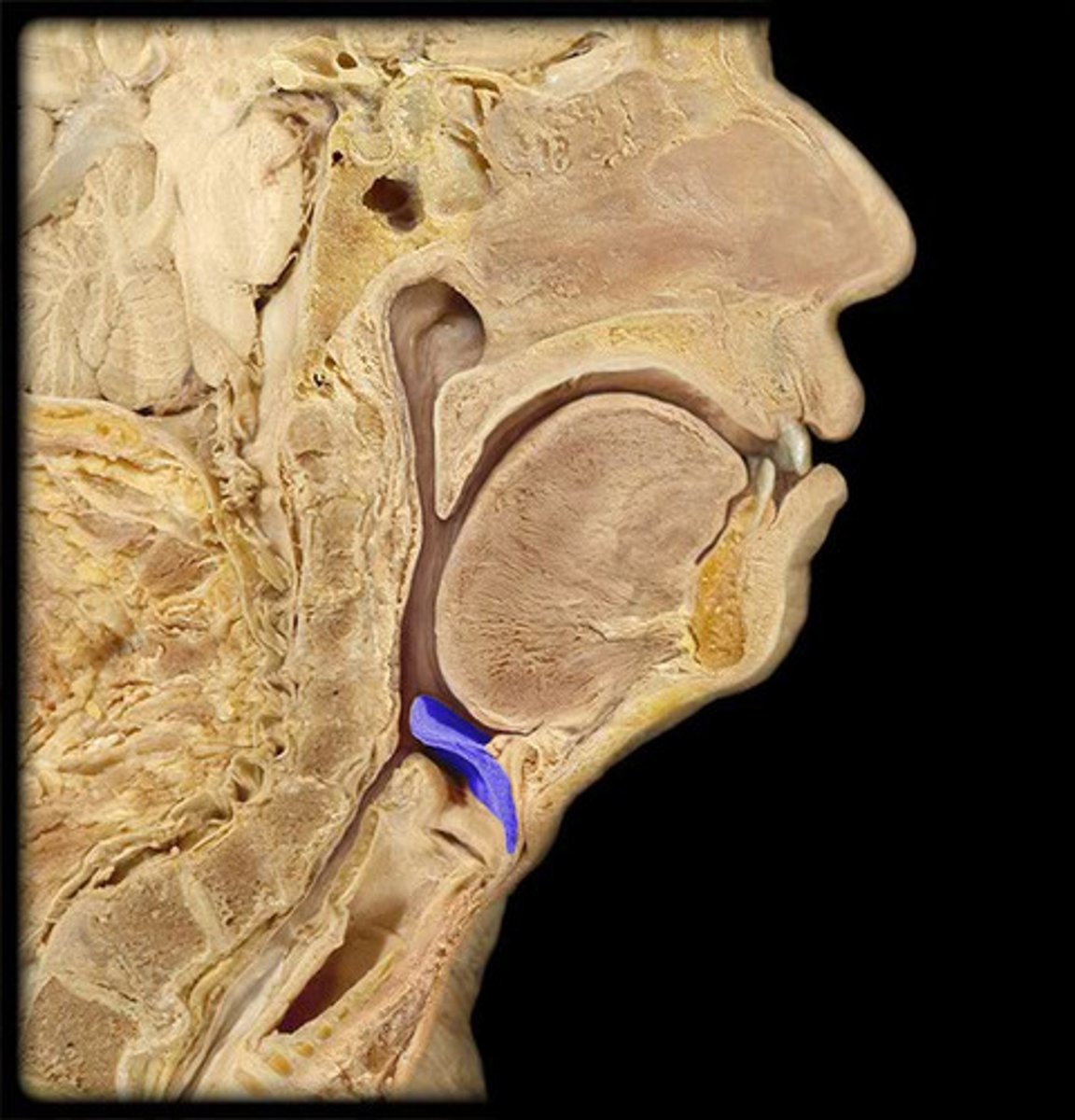
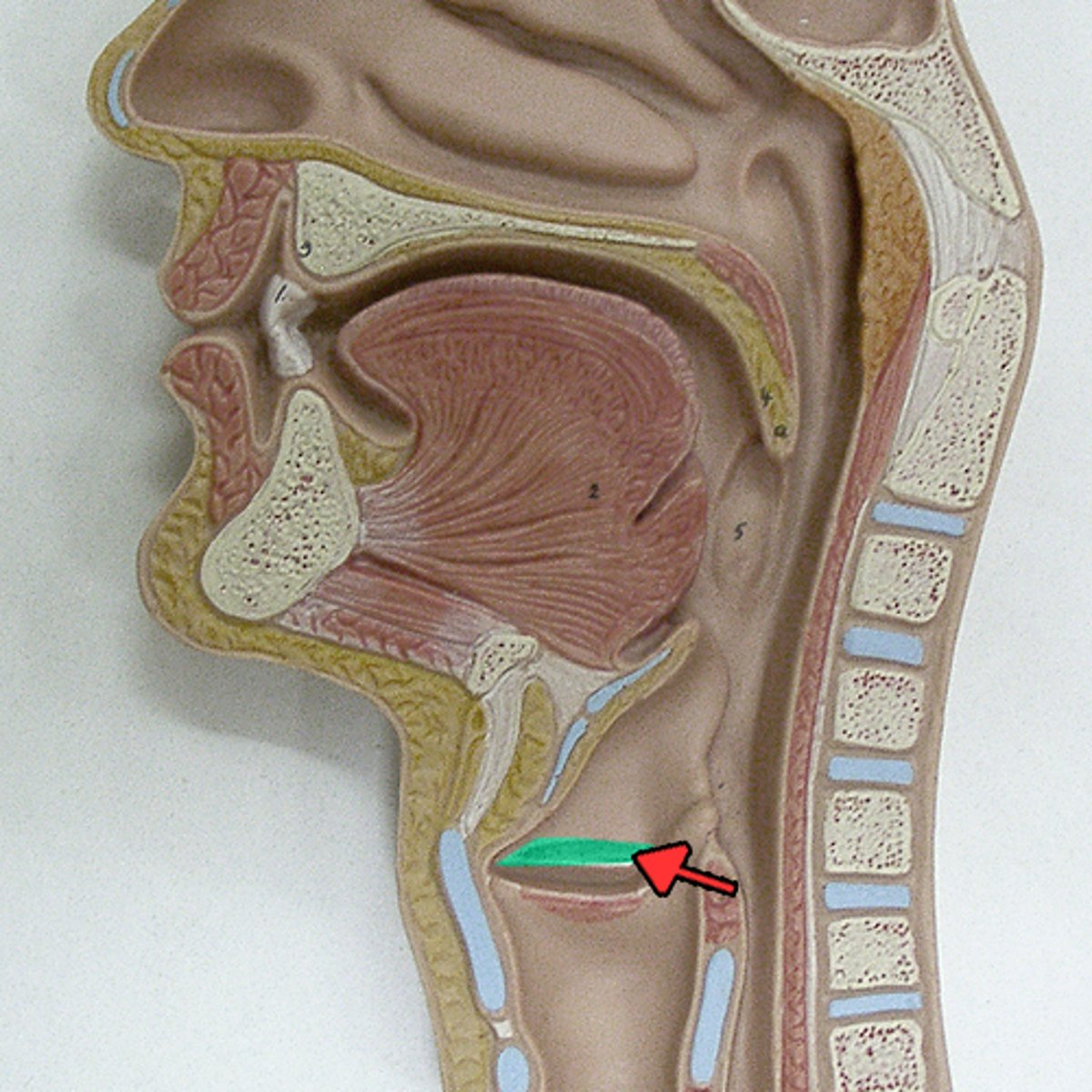
Epiglottis
A flap of tissue that seals off the windpipe and prevents food from entering.
Aryepiglottic fold
a fold of tissue that extends from the apex of the arytenoids to the epiglottis
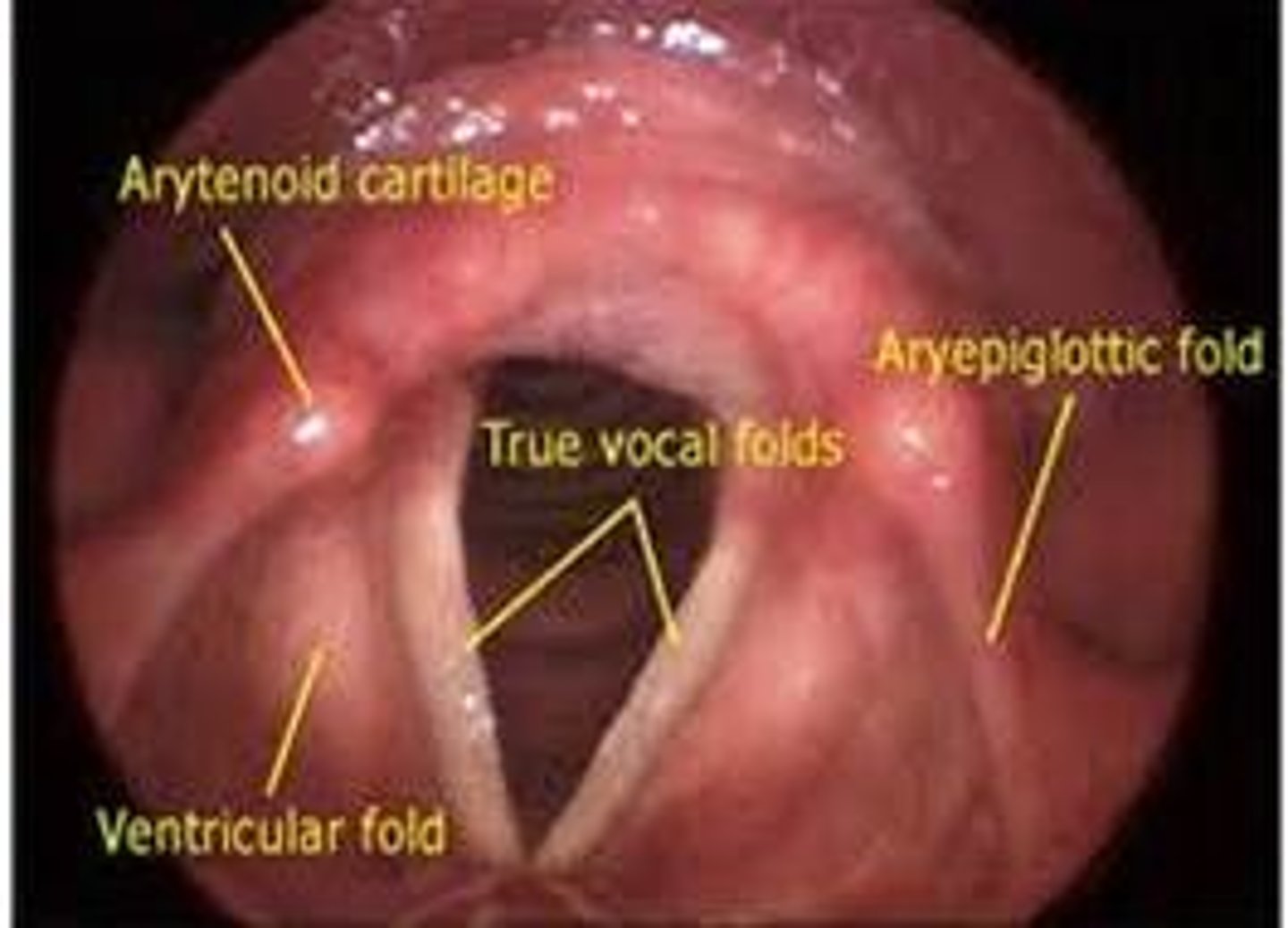
False vocal fold
vestibular fold
Arytenoid cartilage
Two small cartilages in the larynx, the movements of which abduct and adduct the vocal folds.
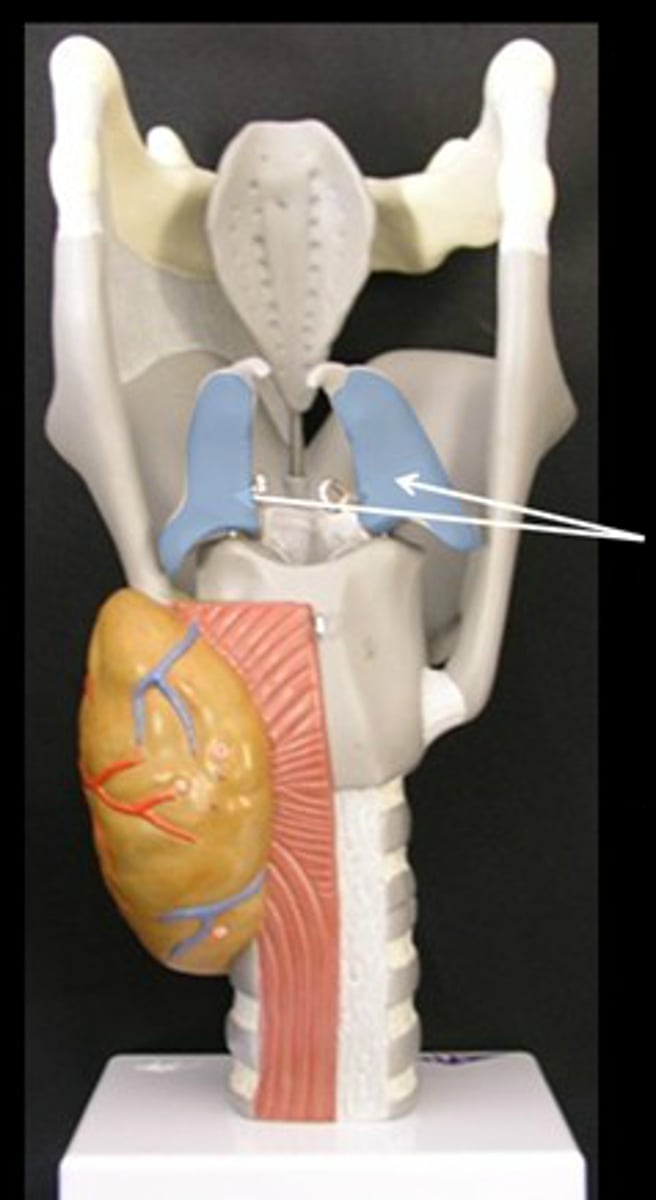
Vocal process
projection of the arytenoid cartilage to which the vocal folds attach
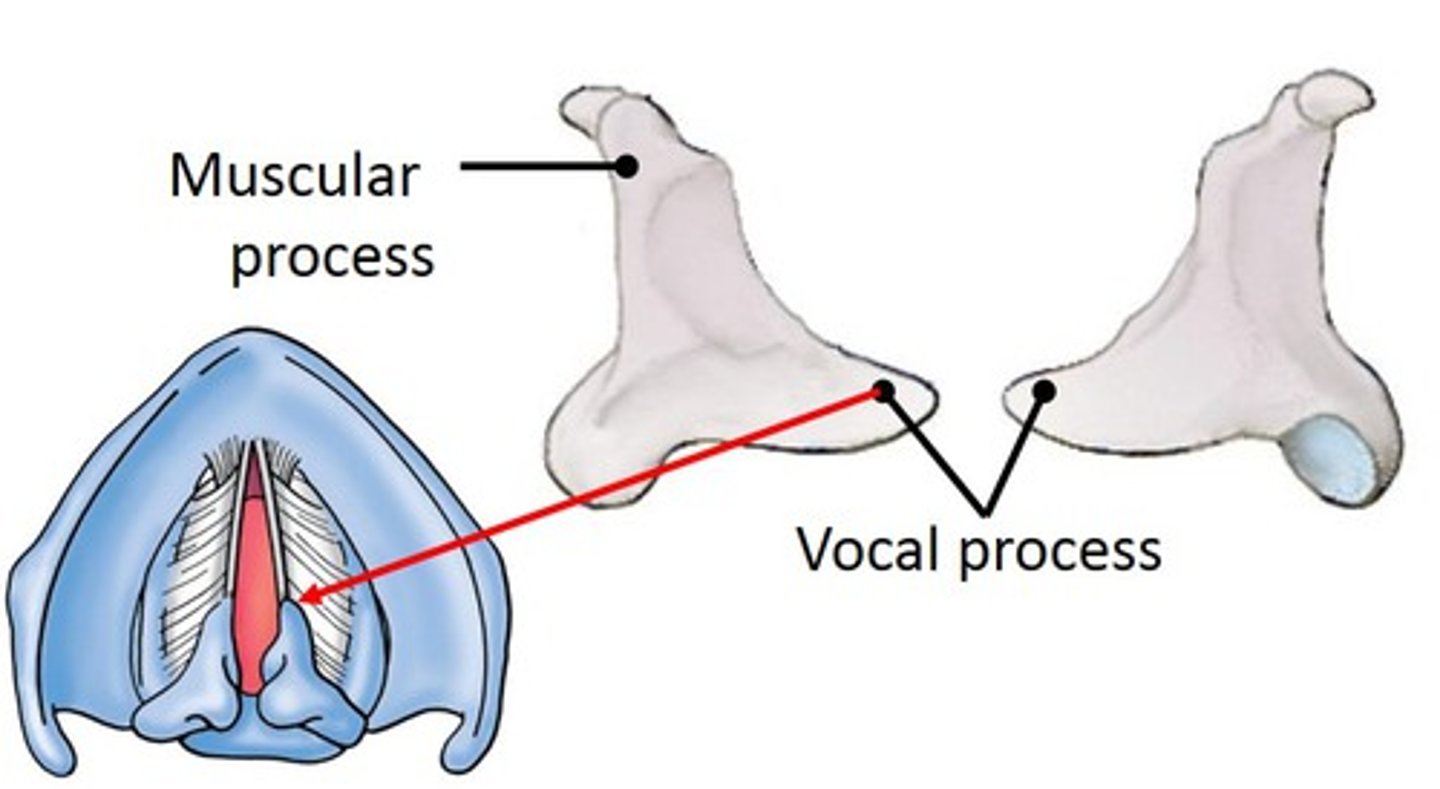
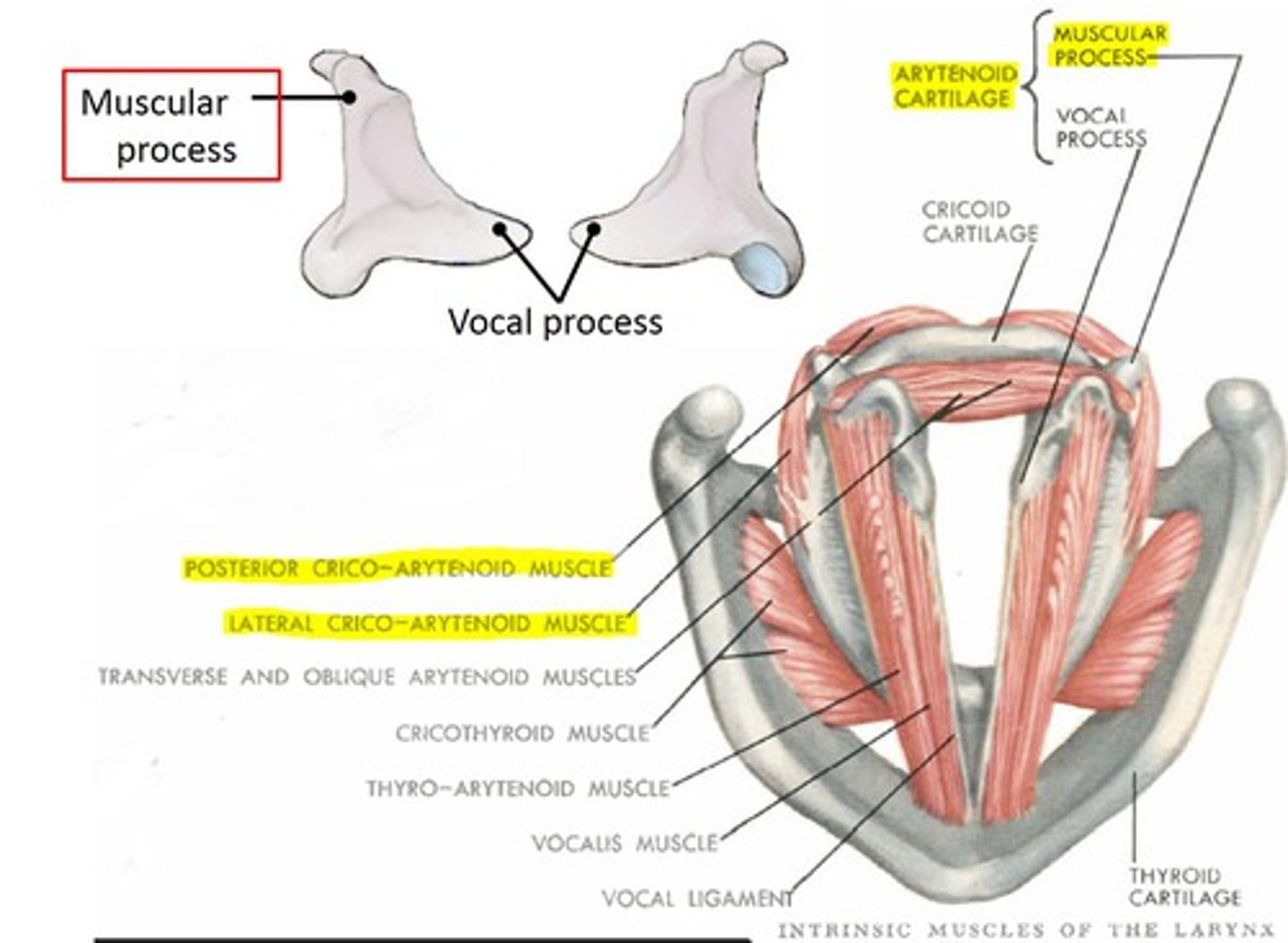
Muscular process
Lateral portion of the arytenoid. Attachment for muscles that adduct and abduct the vocal folds.
Glottis
Opening between vocal cords
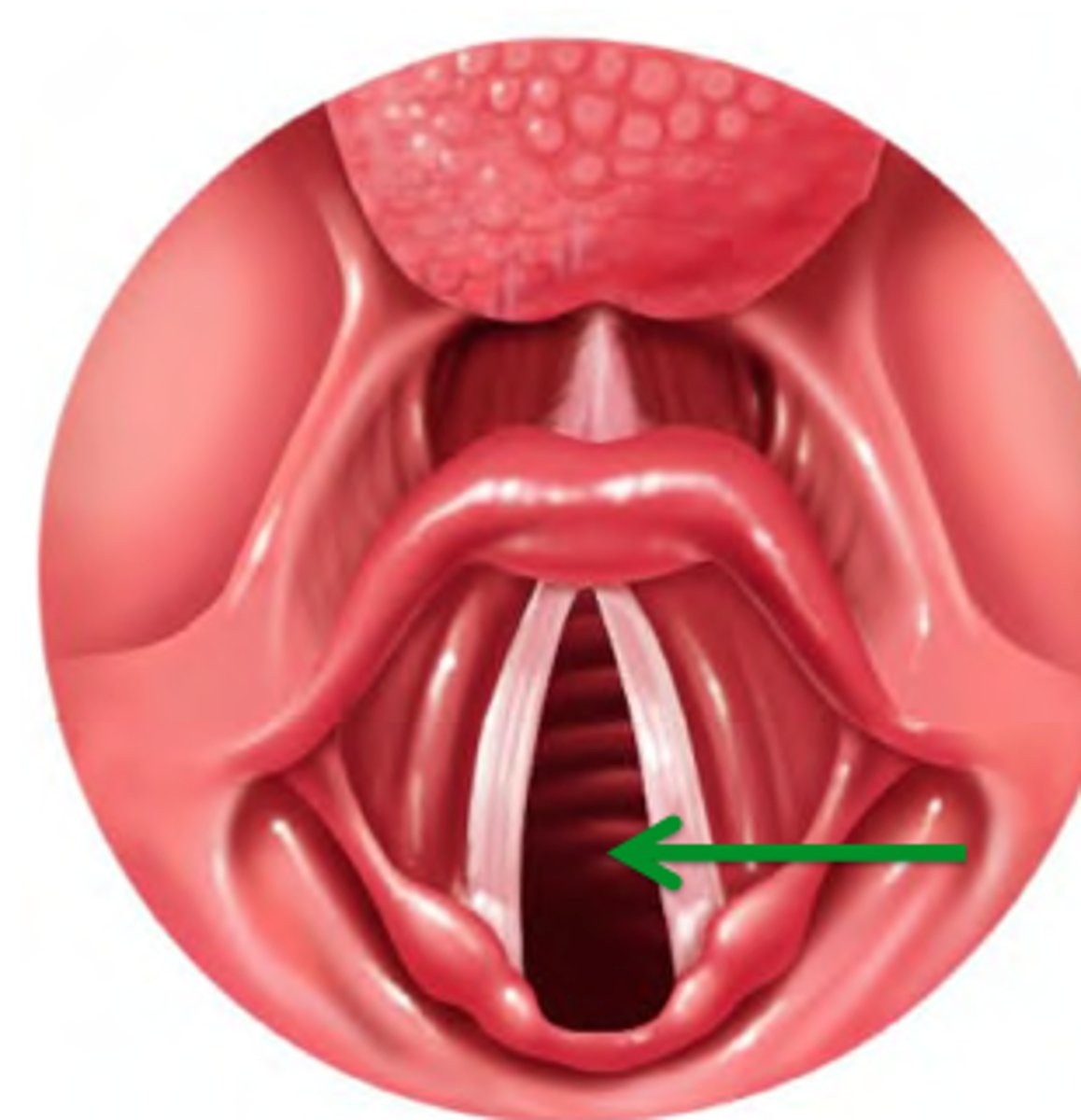
True vocal fold
Name this structure
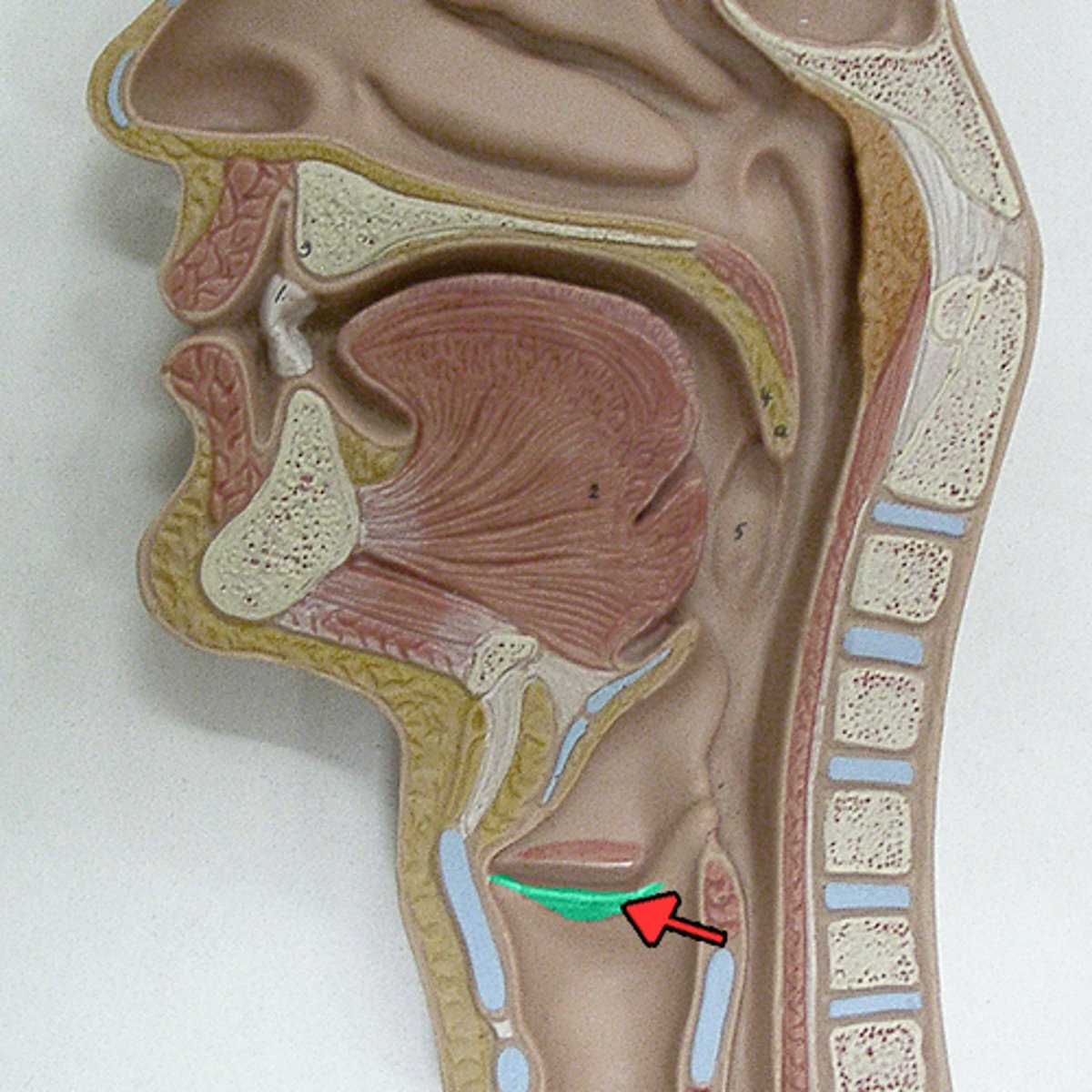
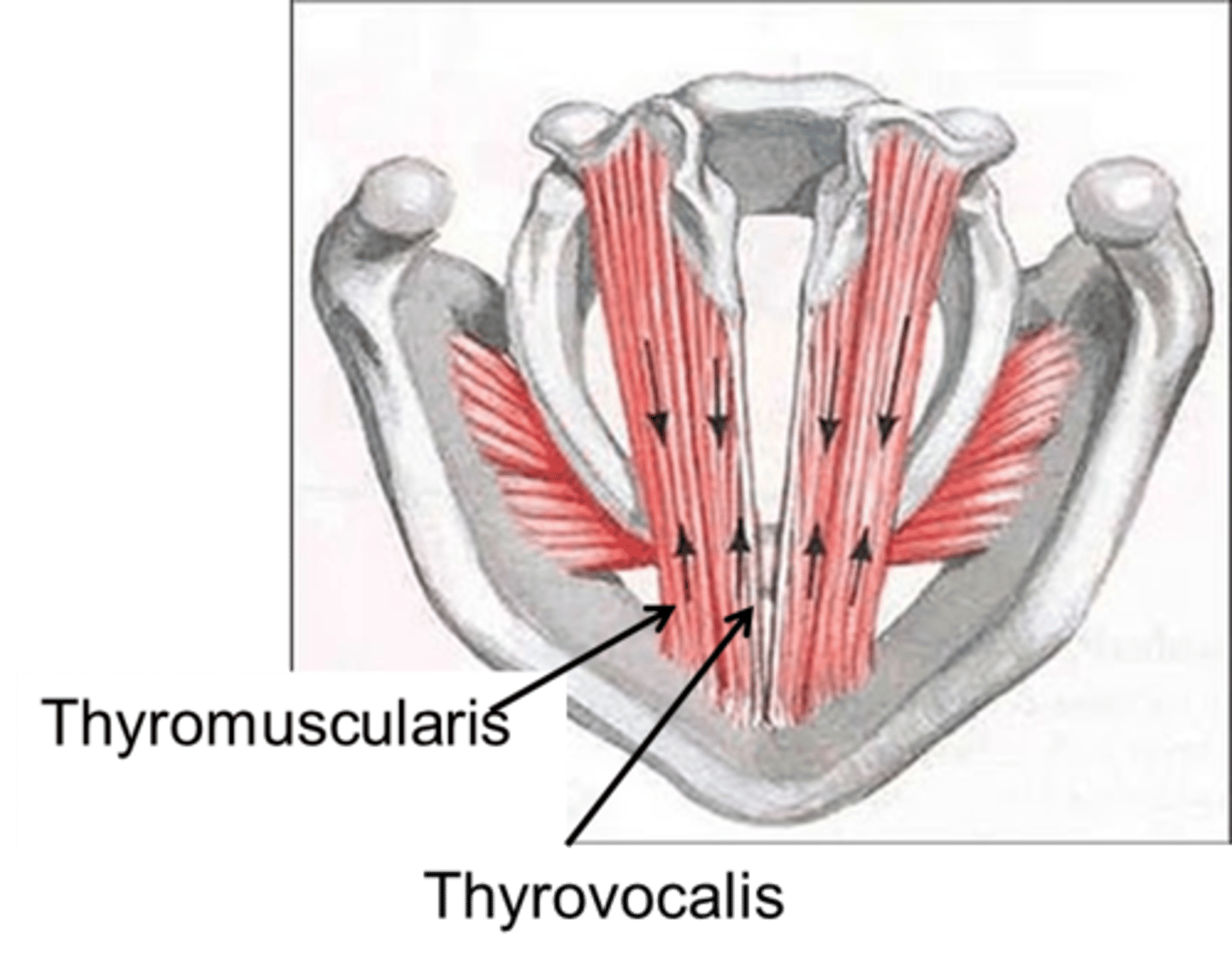
vocalis muscle (thyroarytenoid m.)
the main body of the vocal fold which may be likened to a bundle of stiff rubber bands
Cricoid cartilage
the ring-shaped structure that forms the lower portion of the larynx
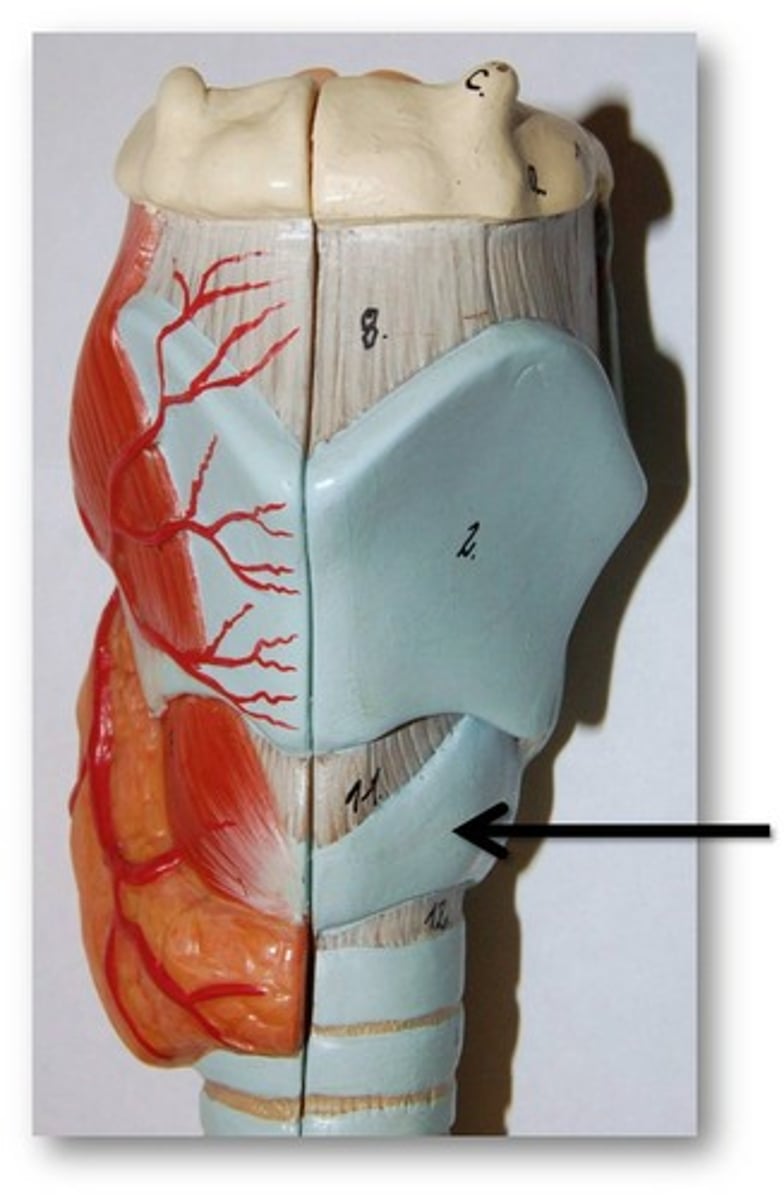
Transverse arytenoid m.
name #7, muscle behind the x
unpaired muscle
attaches to posterior surfaces of both arytenoid cartilages
slides arytenoid cartilages medially
adductor of vocal folds
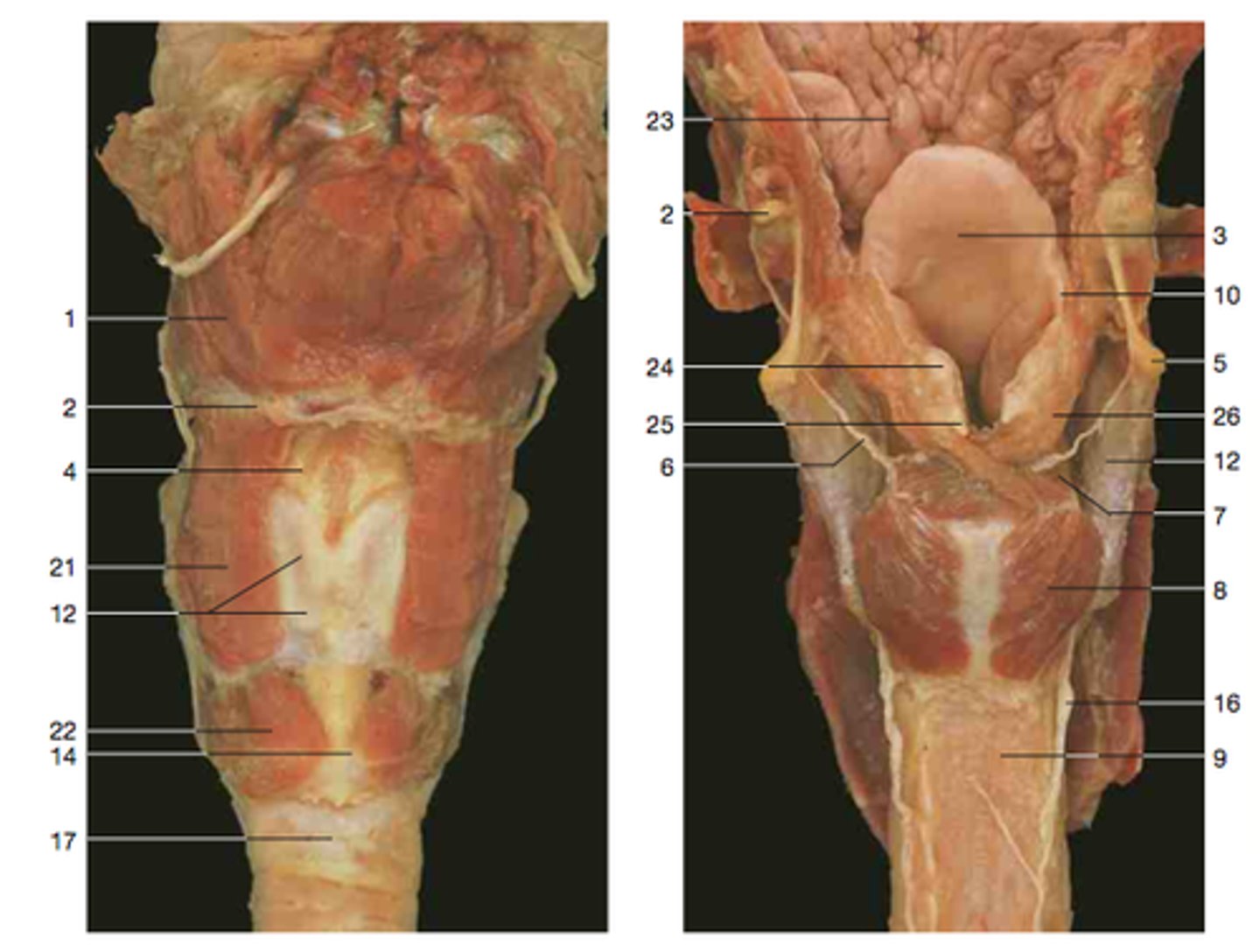
Posterior cricoarytenoid m.
abduction of vocal cords
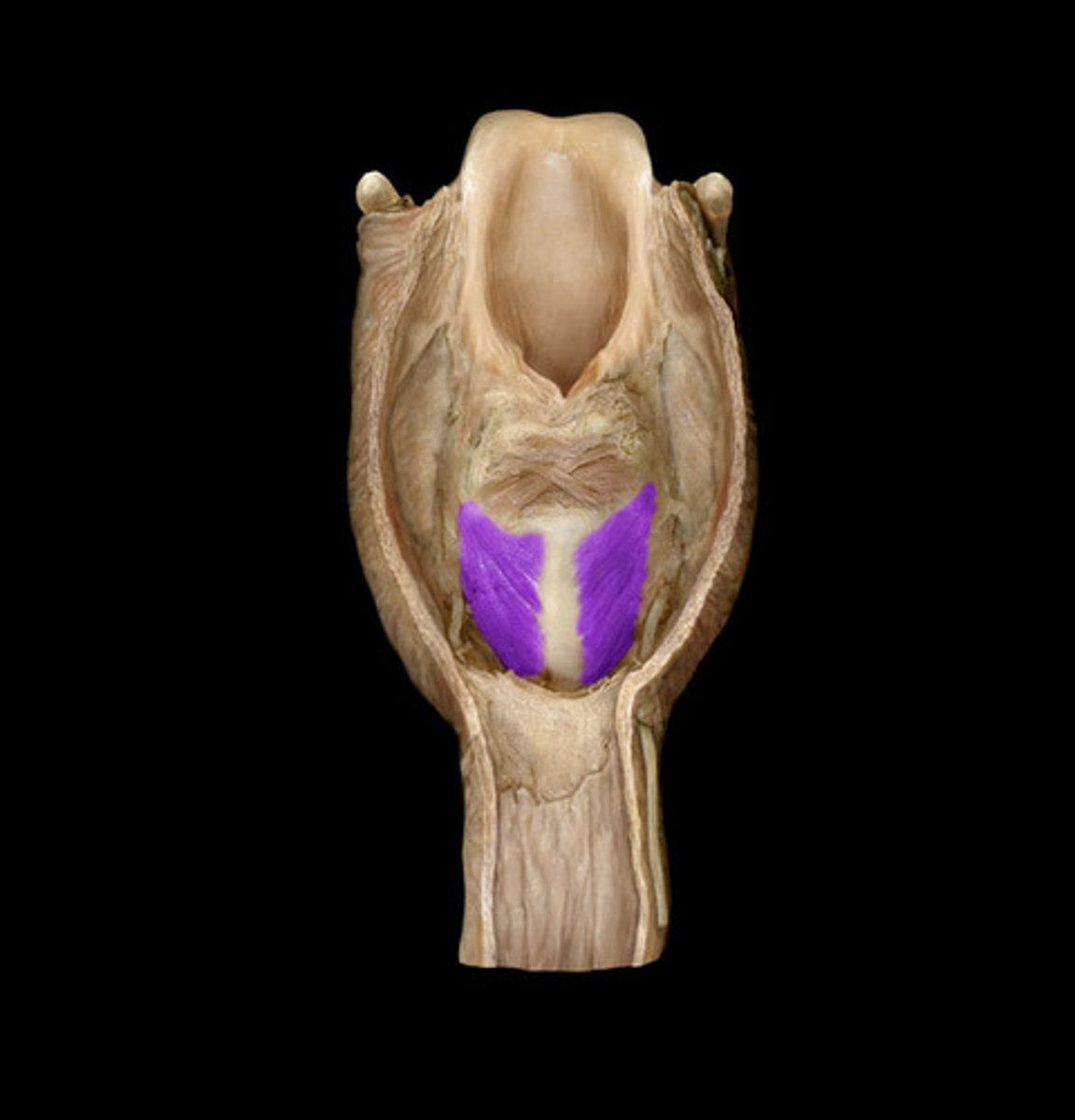
Cricothyroid m.
Identify
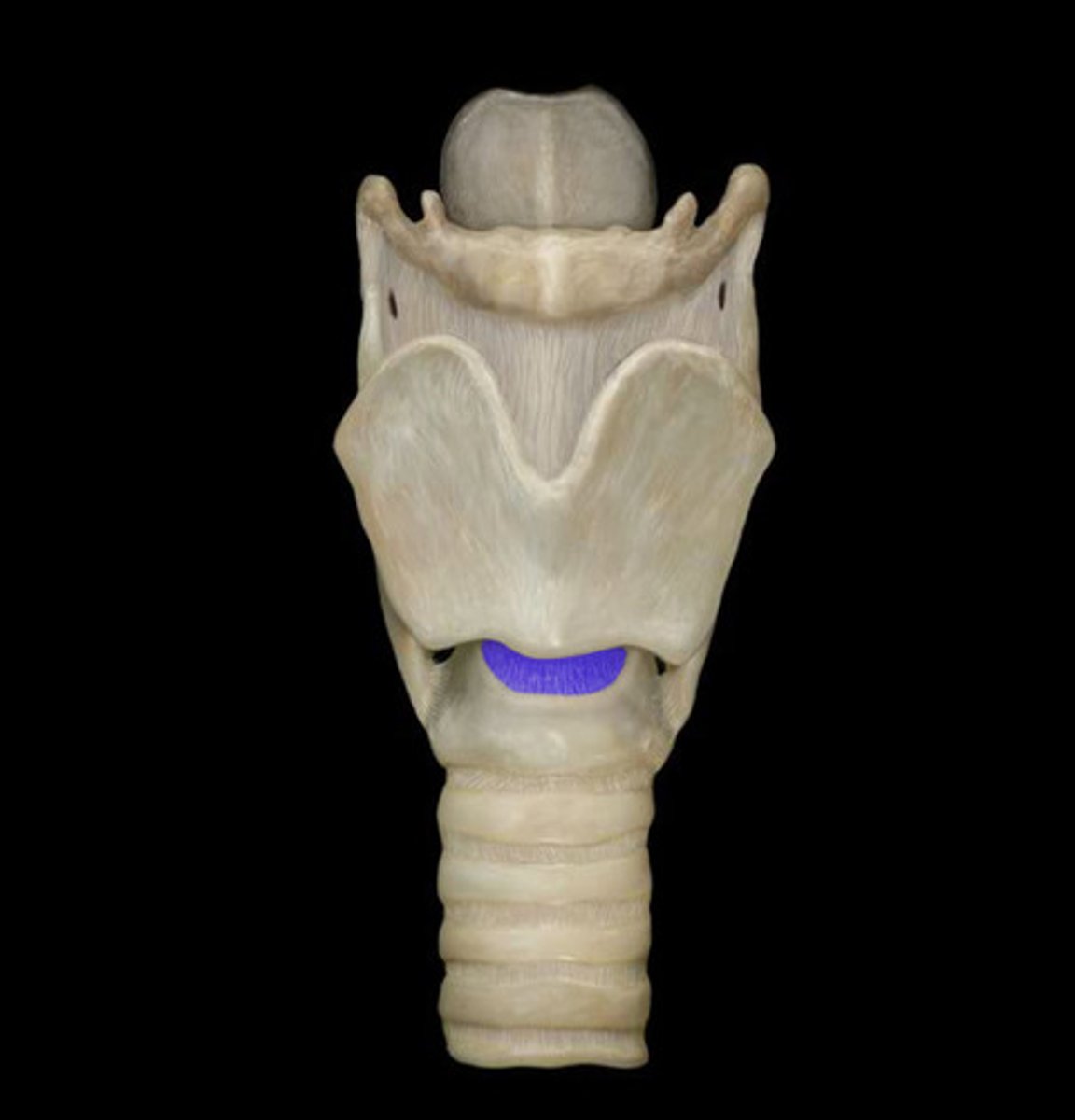
Recurrent laryngeal n.
Sensory nerve to larynx inferior to vocal cords