Gen Chem 2: Exam 1(Ch10 & 11)
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
INTRAmolecular forces
attractions within the molecule that keep the molecule together, like the bonds between the atoms
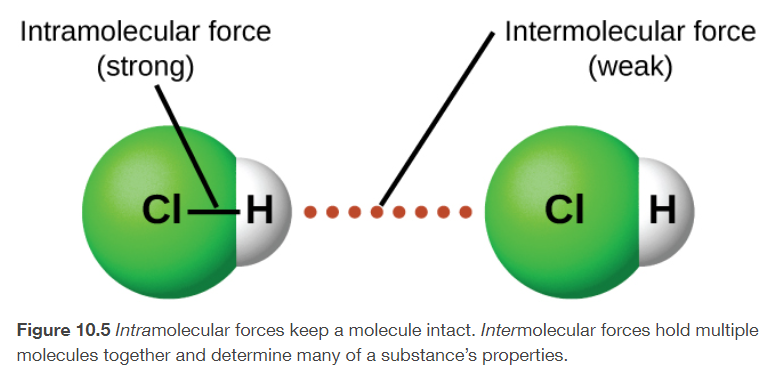
INTERmolecular forces
attractions between molecules, which determine many of the physical properties of a substance, like boiling point
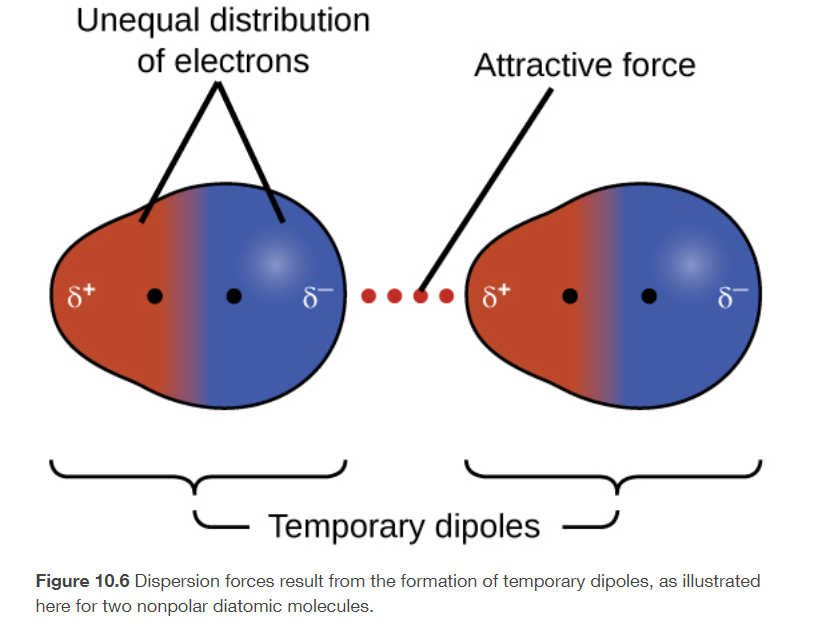
dispersion forces
temporary polarity in the molecules due to unequal electron distribution
present in ALL molecules and atoms
dipole-dipole attractions
permanent polarity in the molecules due to their structure leads to attractive forces
present in POLAR molecules
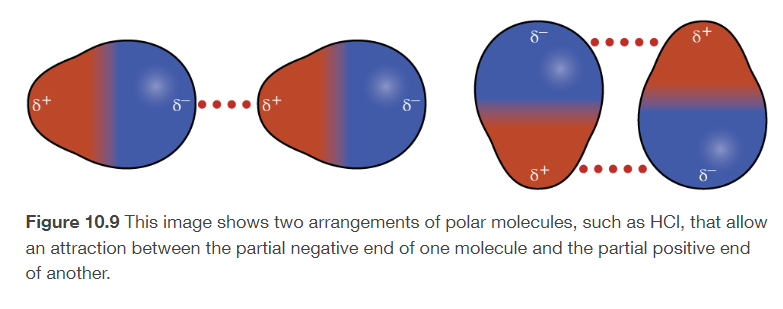
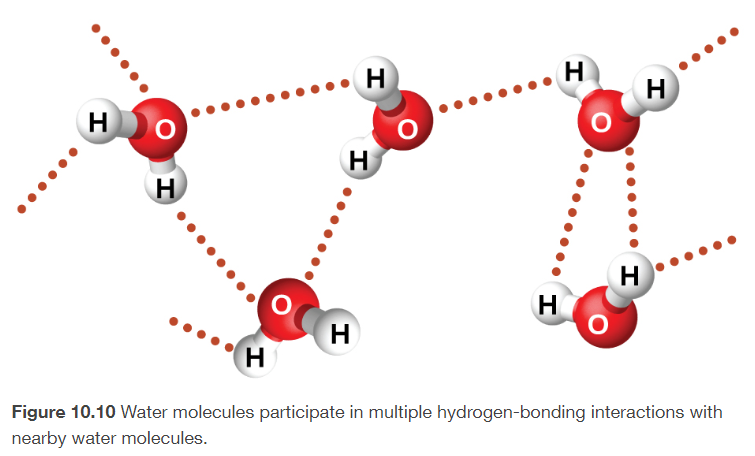
hydrogen bonds
especially strong dipole-dipole attraction that results when Hydrogen is attached to an extremely electronegative atom
H-N
H-O
H-F
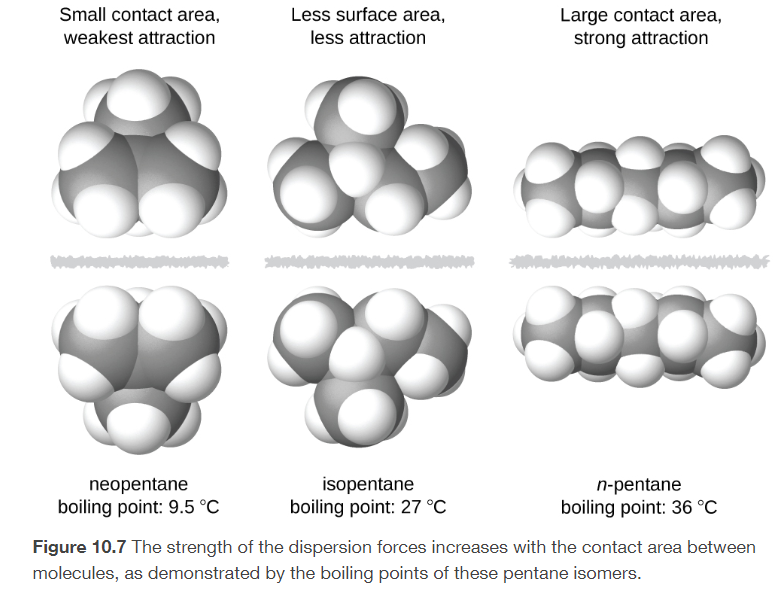
Nonpolar molecules ONLY have
london dispersion force
the stronger the IMFs
the higher the boiling point and melting point
the more surface-to-surface contact in the shape of a molecule
the stronger the IMFs, the higher the boiling and melting point
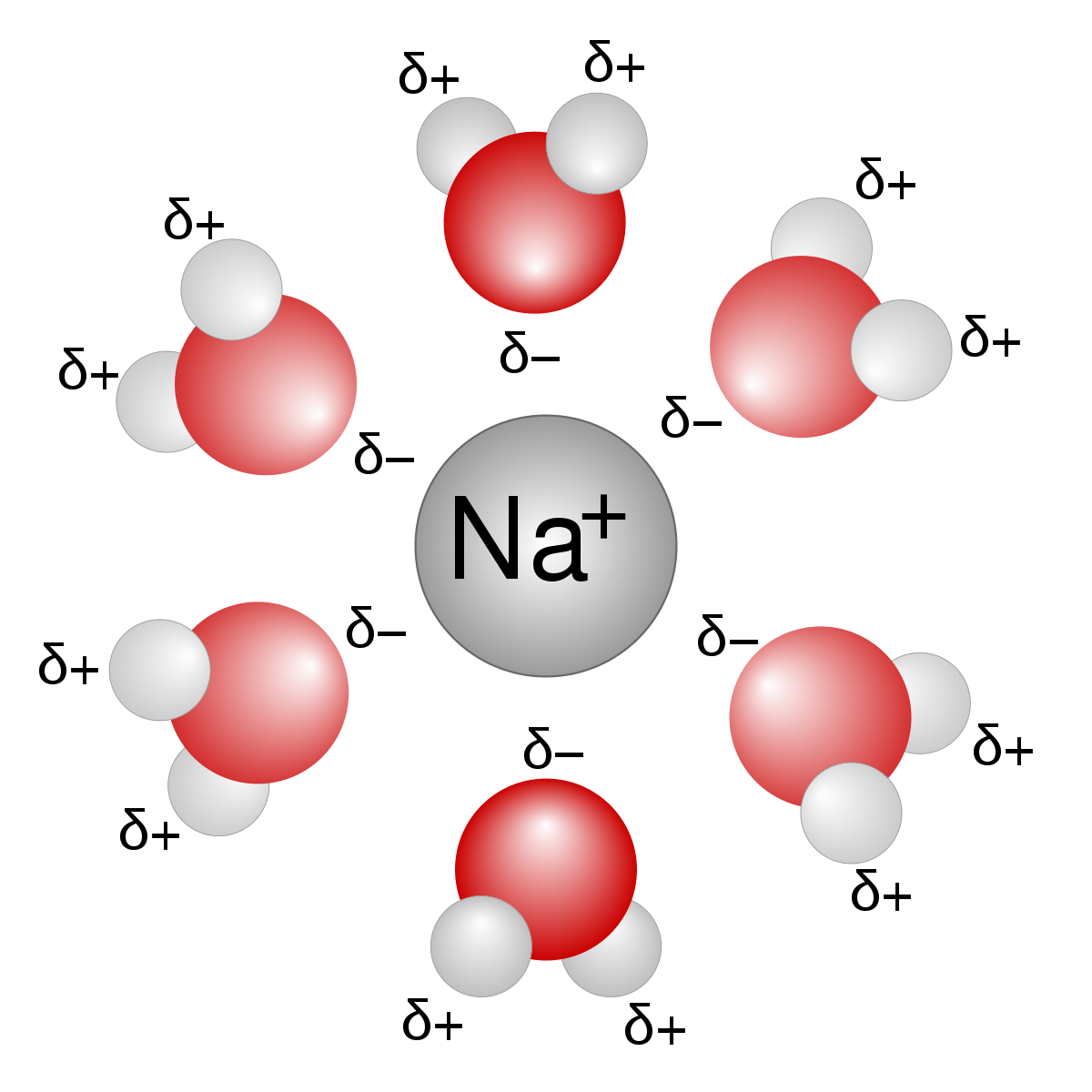
ion-dipole
mixture of ionic compound and polar molecules
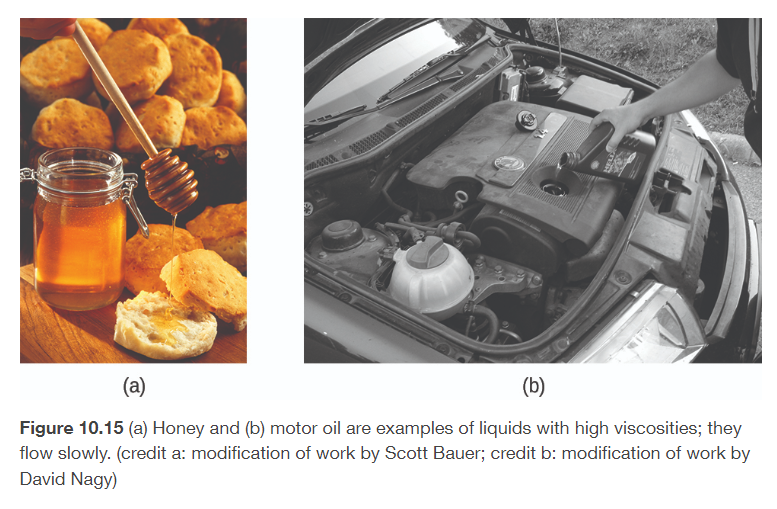
viscosity
the resistance of a liquid to flow
the stronger the IMFs, the higher the viscosity will be
the less contact surface the molecule as, the lower the viscosity will be
increase the temperature of a liquid will reduce its viscosity
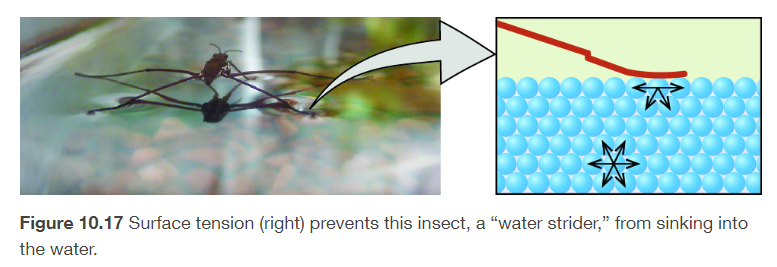
surface tension
energy required to increase the surface area of a liquid, the force required to increase the length of a liquid surface by a given amount
the stronger the IMFs, the higher the surface tension
increase the temperature of a liquid reduces its surface tension
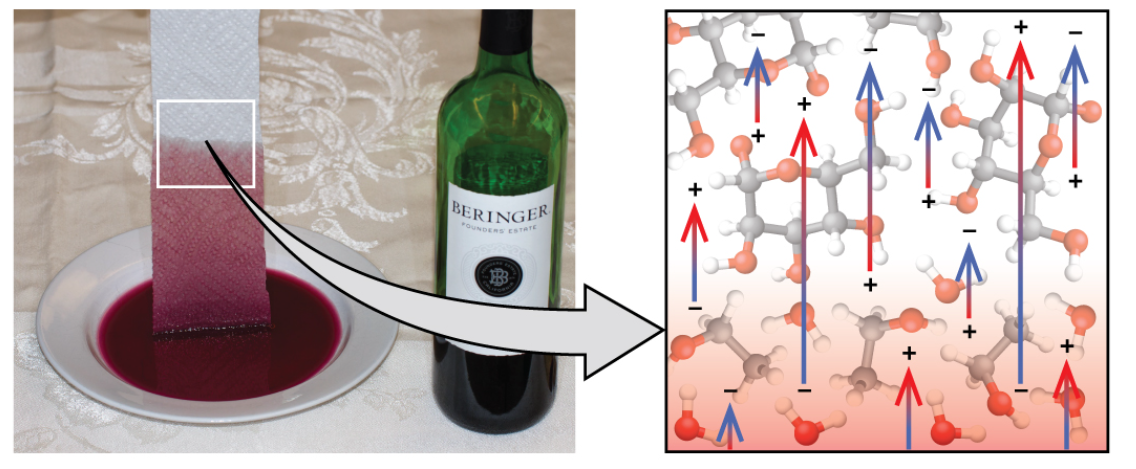
cohesive force
the IMFs between identical molecules of a substance
adhesive force
the IMFs between two different molecules
ex: water on a leaf
capillary action
The adhesive forces between the liquid and the porous material, combined with the cohesive forces within the liquid, may be strong enough to move the liquid upward against gravity
the narrower the tube, the higher the liquid rises
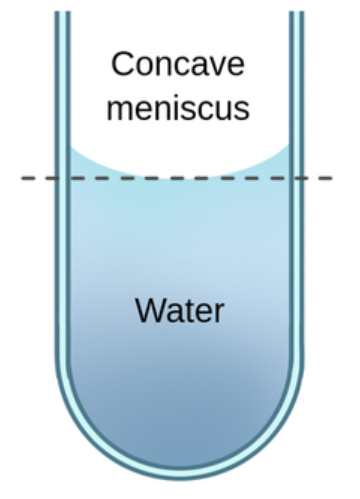
meniscus
the curving of the liquid surface in a thin tube due to the competition between cohesive and adhesive forces
concave meniscus
water’s adhesion to the glass is stronger than its cohesion for itself
water is attracted to the glass more than other water molecules
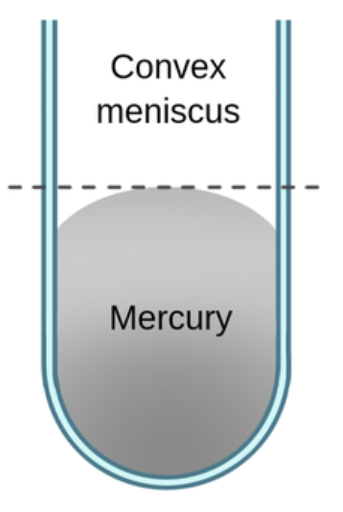
convex
mercury’s cohesion for itself is stronger than its adhesion for the glass
IMF is stronger between mercury molecules than between mercury and the glass
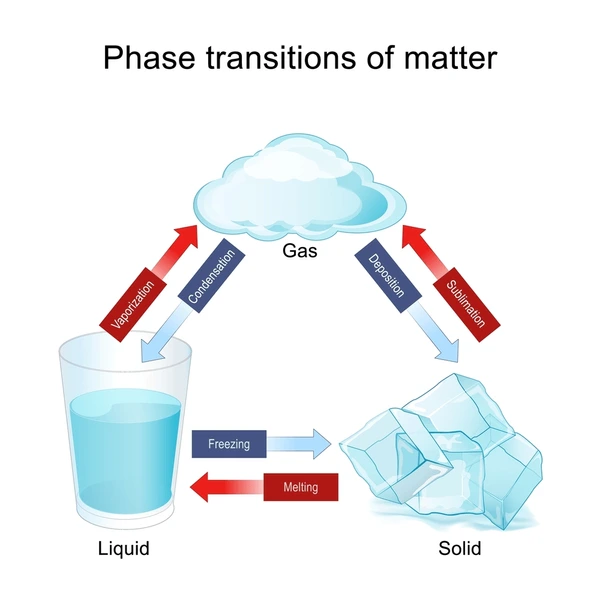
vaporization
change from liquid phase to the gas phase
condensation
change from gas phase to liquid phase

vaporization and condensation are
opposite processes
in an open container
the net result is the rate of vaporization is greater then the rate of condensation, there is a net loss of liquid
in a closed container
the net result is that at some time the rates of vaporization and condensation will equal
dynamic equilibrium
when two opposite processes reach the same rate so that is no gain or loss if material
the weaker the IMF, the ____ the rate of evaporation
faster
rate of vaporization increases with ___ temperature
increasing
rate of vaporization increases with ___ surface area
increasing
the more area exposed in an open container, the faster it will vaporize
volatile
liquids that evaporate easily
nonvolatile
liquids that do not evaporate easily
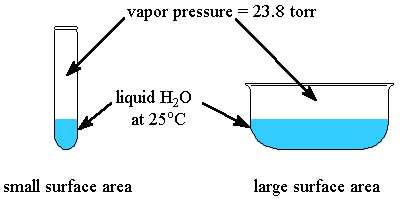
vapor pressure
the pressure exerted by the vapor when it is in dynamic equilibrium with its liquid
the higher the vapor pressure, the weaker the IMFs
the higher the vapor pressure, the ___ volatile the liquid
more
normal boiling point of a liquid
its boiling point when surrounding pressure is equal to 1 atm= 760 torr=760 mmHg
heat of vaporization(or enthalpy of vaporization)
amount of heat energy required to vaporize one mole of the liquid
it’s always endothermic, so it’s always positive
sublimation
solids transitioning directly into a gas state
deposition
gas substances condense directly into a solid state
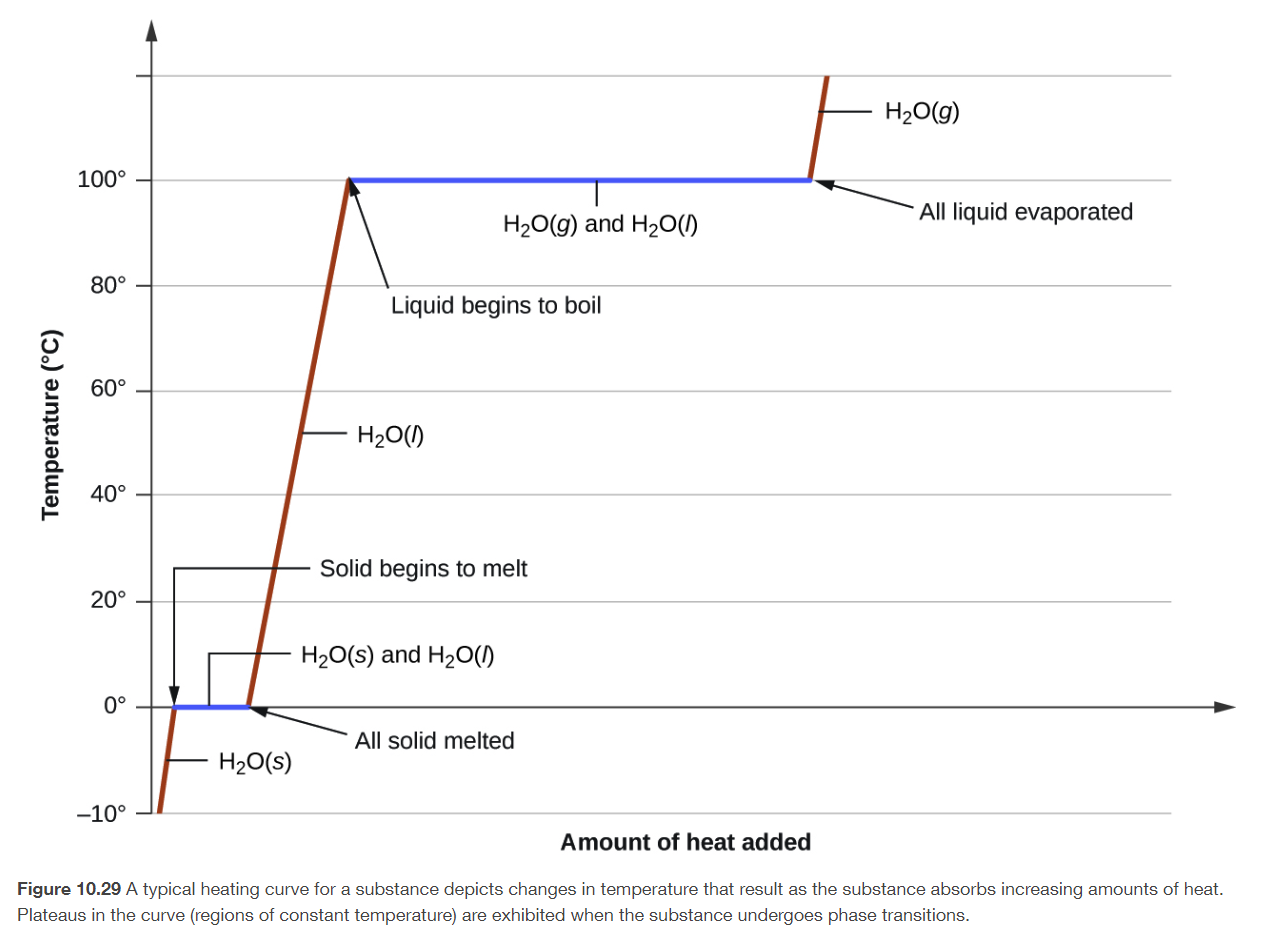
heat curve of water
water freezes at 0 degrees Celsius, and boils at 100 degrees Celsius
phase diagram
on the lines, both states exist simultaneously
for most substances, the freezing point increase as pressure increase
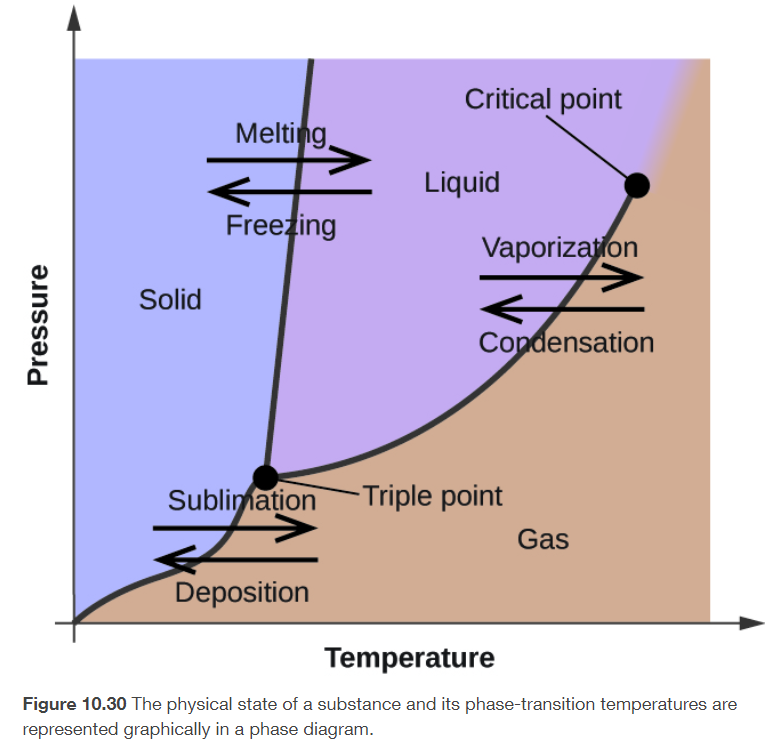
triple point
temperature and pressure at which all three phases of a substance coexists
critical point
specific temperature and pressure at which liquid and gas phases have the same density and are indistinguishable from each other
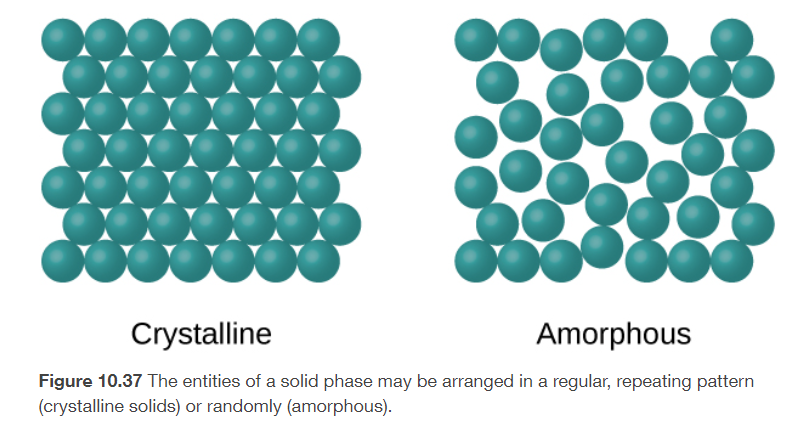
crystalline solids
its molecules, atoms, or ions are in patterns with long range and repeating order
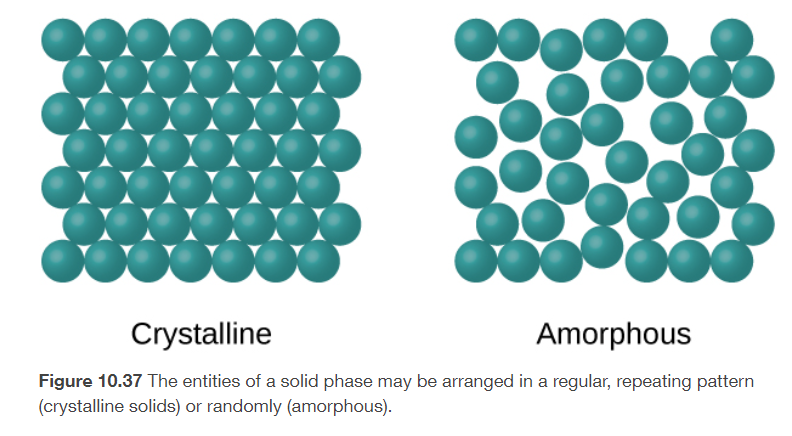
amorphous solids
its molecules, atoms, or ions do not have any long-range order
ex: glass
ionic solids
composed of positive and negative ions that are held together by electrostatic attractions
high melting points
hard, tend to be brittle
do net conduct electrivity
metallic solids
atoms held together by metallic bonding
high thermal and electrical conductivity, metallic luster, and malleability
very hard and quite strong
melting points of the metals vary widely
covalent network solid
solids held by a network of covalent bonds
relatively strong
hardness, strength, and high melting points
not conductive
ex: diamond, SiO2, SiC
molecular solids
solids composed of neutral molecules
variable hardness
variable brittleness
not conductive
low melting points
coordination number
number of other particles each particle is in contact with
packing efficiency
the percentage of volume in a unit cell occupied by particles
“like dissolves like”
a chemical will dissolve in a solvent that has a similar structure to the solvent
polar molecules/ionic compounds will be more soluble in polar solvents
nonpolar molecules will be more soluble in nonpolar solvents
miscible
liquids will dissolve in each other, they have the same polarities
hydrophilic
likes water
OH, H2O, CHO, NH2
polar
hydrophobic
afraid of water
C-H, C-C
nonpolar
for the solvent and solute to mix you must overcome
all of the solvent-solute attractive forces or
some of the solvent-solvent attractive forces
the solubility of a solute in a particles solvent is
the maximum concentration that may be achieved under given conditions when the dissolution process is at equilibrium
saturated
a solution that has the solute and the solvent in dynamic equilibrium
unsaturated
a solution that has less solute than saturation
super saturated
a solution that has more solute than saturation
colligative properties
properties whose value depends only on the number of solute properties, and NOT on what they are
the presence of nonvolatile solutes lowers the
vapor pressure of a solution
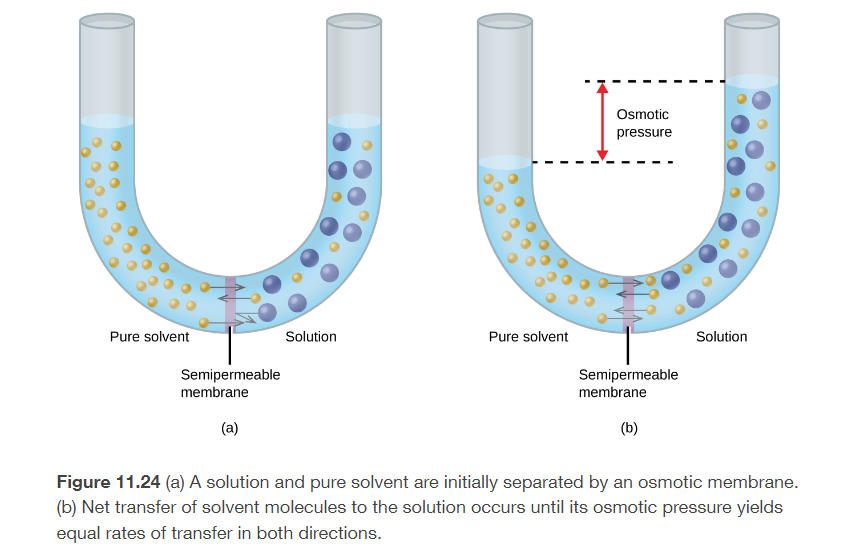
osmosis
the flow of solvent from a solution of low concentration into a solution of high concentration