ACC 210 NCSU - Exam 1
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Sole Proprietorship
- simple to establish
- owner controlled
- tax advantages
Partnership
- simple to establish
- shared control
- broader skills and resources
- tax advantages
Corporation
- easier to transfer ownership
- easier to raise funds
- no personal liability
Managerial Accounting
provides information for internal users
Financial Accounting
provides information for external users
Accounting
the process of identifying, measuring, recording, and reporting business activity in monetary terms
Revenues
amounts earned from the sale of products and other sources (sales revenue, service revenue, and interest revenue)
Inventory
goods available for sale to customers
Accounts Receivable
right to receive money from a customer as a result from a sale
Expenses
cost of assets consumed or services used. (cost of goods sold, selling, marketing, administrative, interest, and income taxes expense)
Liabilities
arising from expenses include accounts payable, interest payable, wages payable, sales taxes payable, and income taxes payable.
Net income
when revenue exceeds expenses
Net loss
when expenses exceed revenues
Stockholder's Equity
summarizes the changes in stockholder's equity of a period of time
common stock (external source) + retained earnings (internal source)
Balance Sheet
presents the financial position of the company on a particular date
financial position: Resources (assets) = Claims to resources (liabilities and stockholder's equity)
Statement of Cash Flows
measures activities involving cash receipts and cash payments over an interval of time
operating activities, investing activities, financing activities
Management discussion and analysis (MD&A)
management's view on the company's ability to pay near-term obligations, its ability to fund operations and expansion, and its results of operations
Notes to the Financial Statements
notes clarify information presented in the financial statements and provide additional detail
Auditor's Report
- auditor's opinion as to the fairness of the presentation of the financial position and results of operations and their conformance with generally accepted accounting principles
- only certified public accountants (CPA) may perform audits
Role of Auditors
- help ensure that management has in fact appropriately applied GAAP in preparing the company's financial statements
-help investors and creditors in their decisions by adding credibility to the financial statements
Rules of Financial Accounting
Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP)
Current Standard Setting
US - Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB): governed by the (SEC)
Global - International Accounting Standards Board (IASB)
Objectives of Financial Accounting
1. it is useful to investors and creditors in making decisions
2. helps predict cash flows
3. tells us about economic resources, claims to resources, and changes in resources and claims
Analyzing Transactions
the process of identifying the specific effects of economic events on the accounting equation
Fundamental Accounting Equation
Assets = Liabilities + Stockholders' Equity
Accounting Cycle
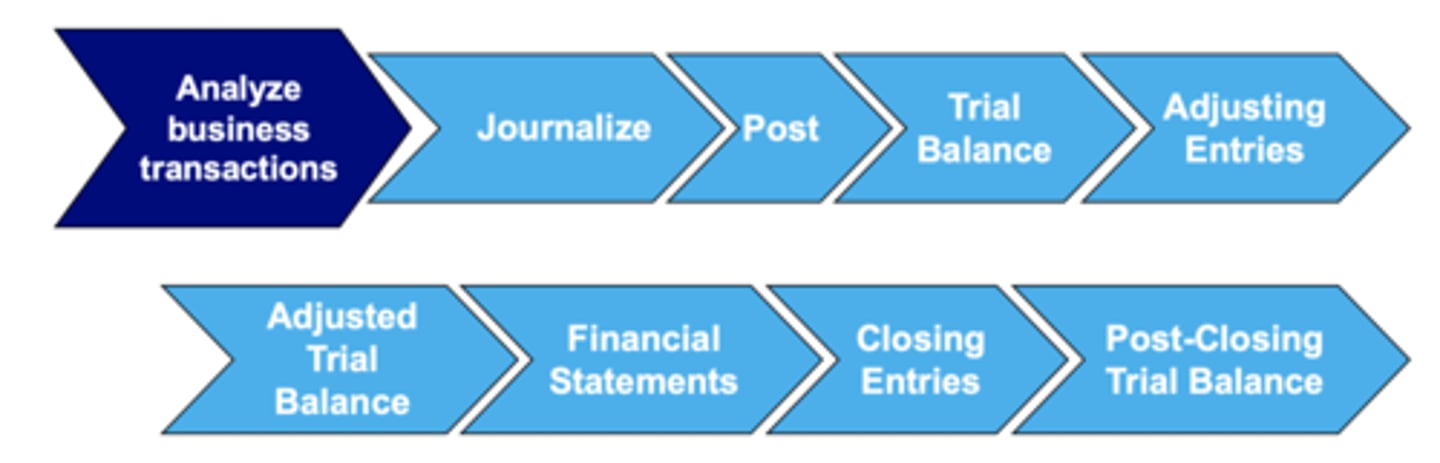
Transactions
economic events that must be captured in the Accounting Information System (and will ultimately show up in the Financial Statements)
- not all activities represent transactions—only those we can measure in US Dollars
- assets, liabilities, or stockholders' equity items change as a result of these economic events
- dual effect on the accounting equation
Expanded Fundamental Accounting Equation
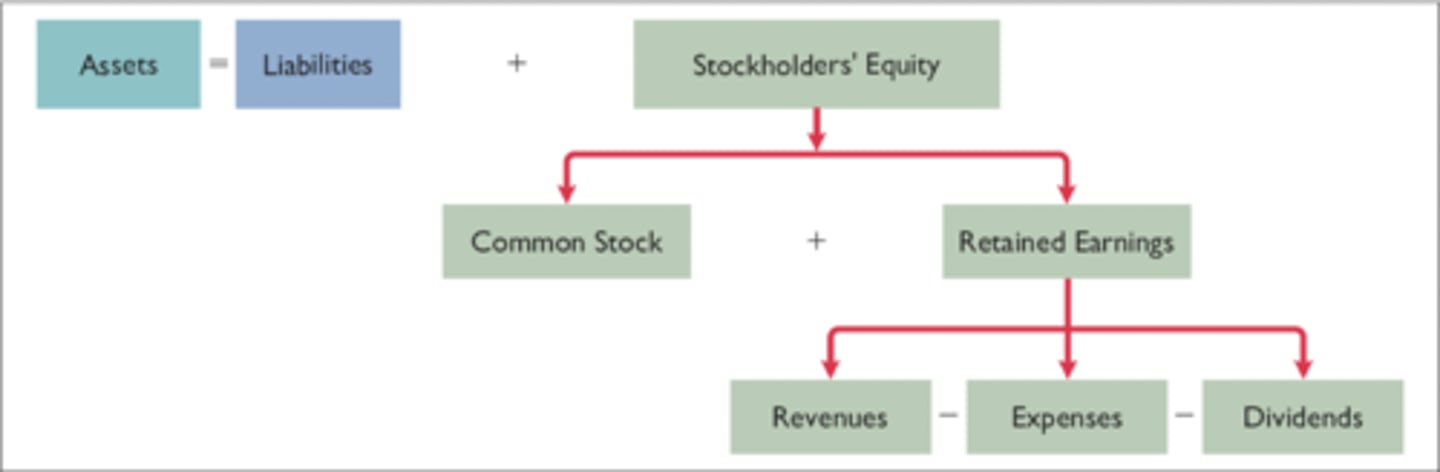
Double-entry system
- each transaction must affect two or more accounts to keep the basic accounting equation in balance
- recording done by debiting at least one account and crediting another
- DEBITS must equal CREDITS
Debit and Credit
if Debits are greater than Credits, the account will have a debit balance
if Credits are greater than Debits, the account will have a Credit balance
Assets and Liabilities
assets - Debits should exceed credits
liabilities - Credits should exceed debits
Stockholders' Equity
- investments by stockholders and revenues increase stockholders' equity (credit)
- dividends and expenses decrease stockholder's equity (debit)
DEALOR
debit balances: dividends, expenses, assets
credit balances: liabilities, owner's equity, revenue
The Recording Process
1. analyze each transaction in terms of its effect on the accounts
2. record the transaction information in the General Journal
3. periodically, transfer (post) the General Journal information to the appropriate accounts in the General Ledger
The General Journal
transactions are recorded in chronological order before they are transferred to the general ledger
- discloses the complete effects of a transaction.
- provides a chronological record of transactions.
- helps to prevent or locate errors because the debit and credit amounts can be easily compared
Journalizing
entering transaction data in the journal
Listing of Accounts
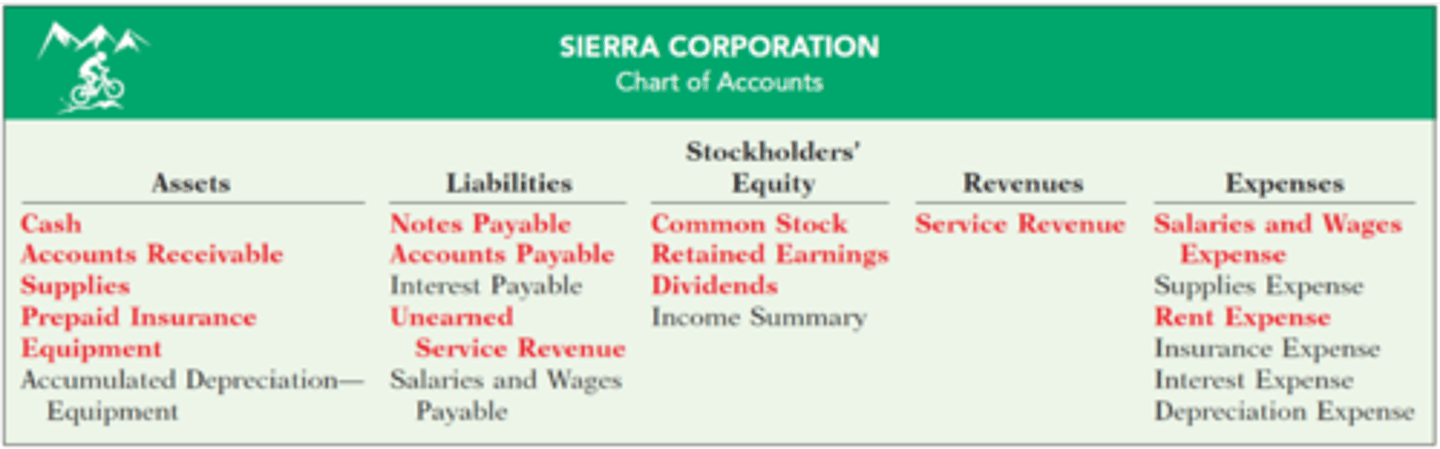
Posting
the process of transferring journal entry amounts to ledger accounts
Trial Balance
- a list of accounts and their balances at a given time
- accounts are listed in the order in which they appear in the ledger
- purpose is to prove that debits equal credits
- may also uncover errors in journalizing and posting
- useful in the preparation of financial statements.
Limitations of a Trial Balance
the trial balance may balance even when:
1) a transaction is not journalized
2) a correct journal entry is not posted
3) a journal entry is posted twice
4) incorrect accounts are used in journalizing or posting
5) offsetting errors are made in recording the amount of a transaction
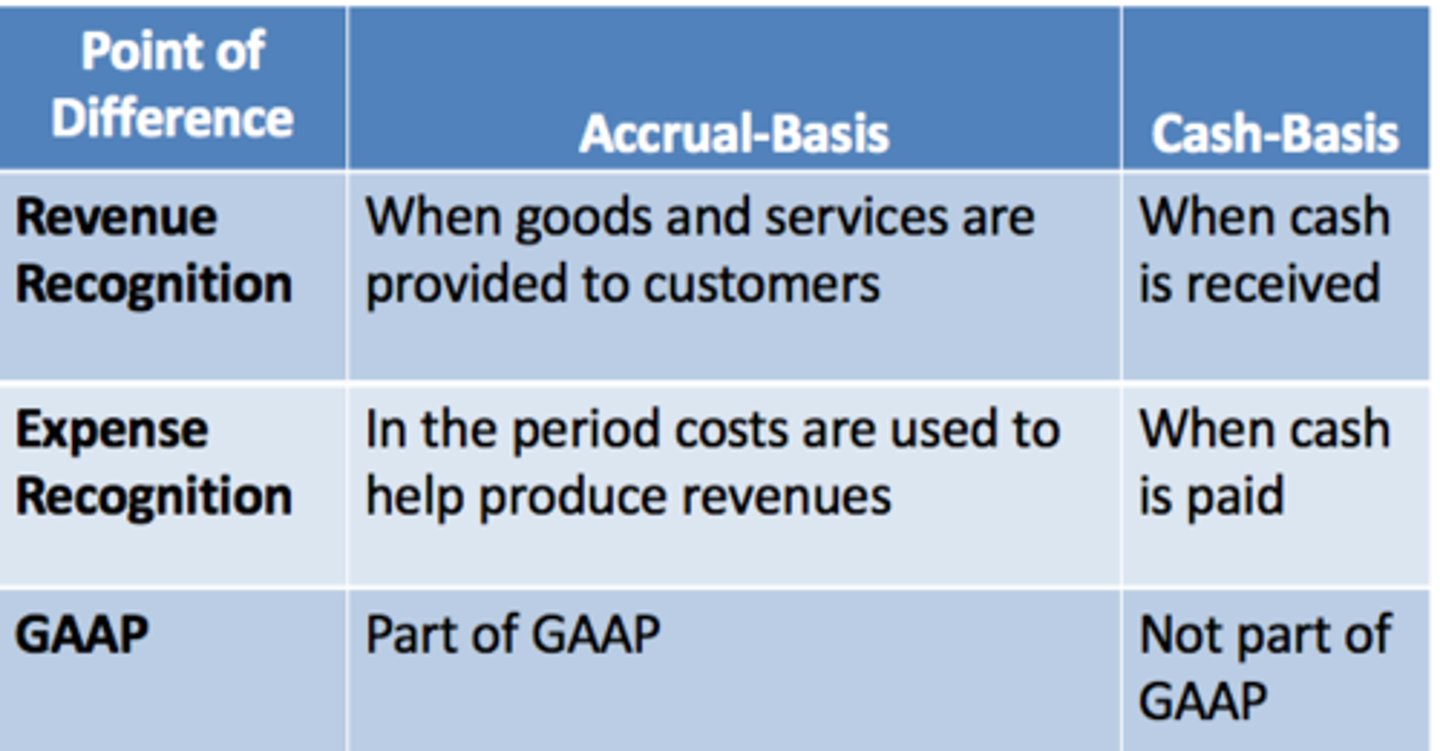
Revenue recognition
recognize revenue when it is earned—that is, when the seller has satisfied a performance obligation and has been paid (or is in possession of a receivable expected to be collected)
Expense recognition
- expenses are reported in the same period as the revenues they help to generate
-matching principle
Accrual-Basis Accounting Compared with Cash-Basis Accounting
Types of Adjusting Journal Entries
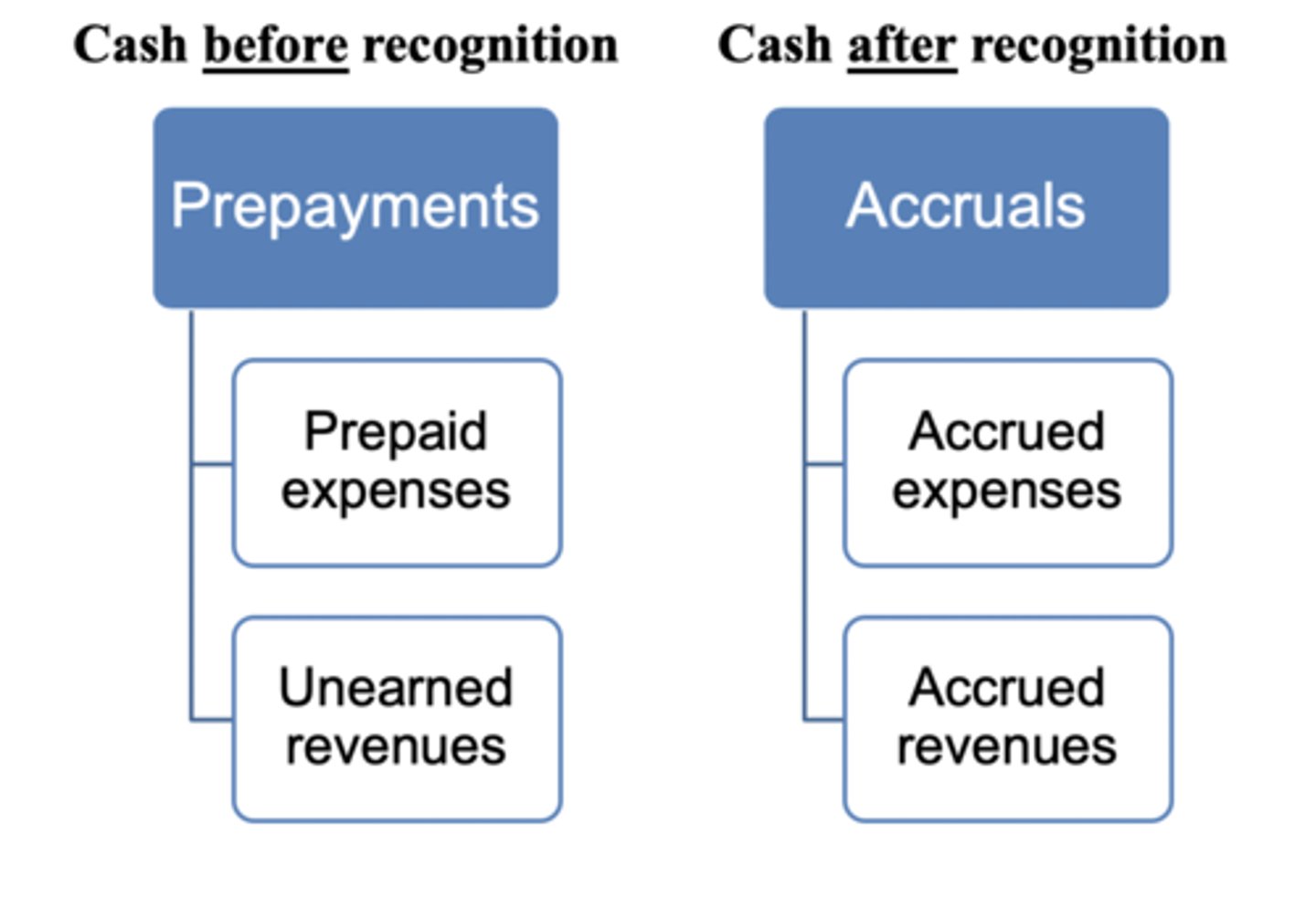
Adjusting Journal Entries
- to account for transactions that have not been recorded by the end of the period (never involve cash)
- to record revenues in the period earned and to record expenses in the period they are incurred to generate those revenues
- all adjusting entries involve one income statement account (revenue or expense) and one balance sheet account (asset or liability)
Prepare Adjusted Trial Balance
- after all adjusting entries are journalized and posted to the General Ledger accounts the company prepares another trial balance from the ledger accounts (Adjusted Trial Balance).
- the adjusted trial balance's purpose is to prove the equality of debit balances and credit balances in the ledger.
- the adjusted trial balance is the primary basis for the preparation of the financial statements.
Closing Entries
- to transfer the balances of temporary accounts (revenues, expenses, and dividends) to Retained Earnings
- to reduce the balances of these temporary accounts to zero
- posting these closing entries to the general ledger accounts will prepare the books for the next accounting period
Closing the Books
at the end of the accounting period, companies transfer the temporary account balances to the permanent stockholders' equity account—Retained Earnings
Preparing Closing Entries
in addition to updating Retained Earnings to its correct ending balance, closing entries produce a zero balance in each temporary account