Unit 4 1945-1980 DE
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
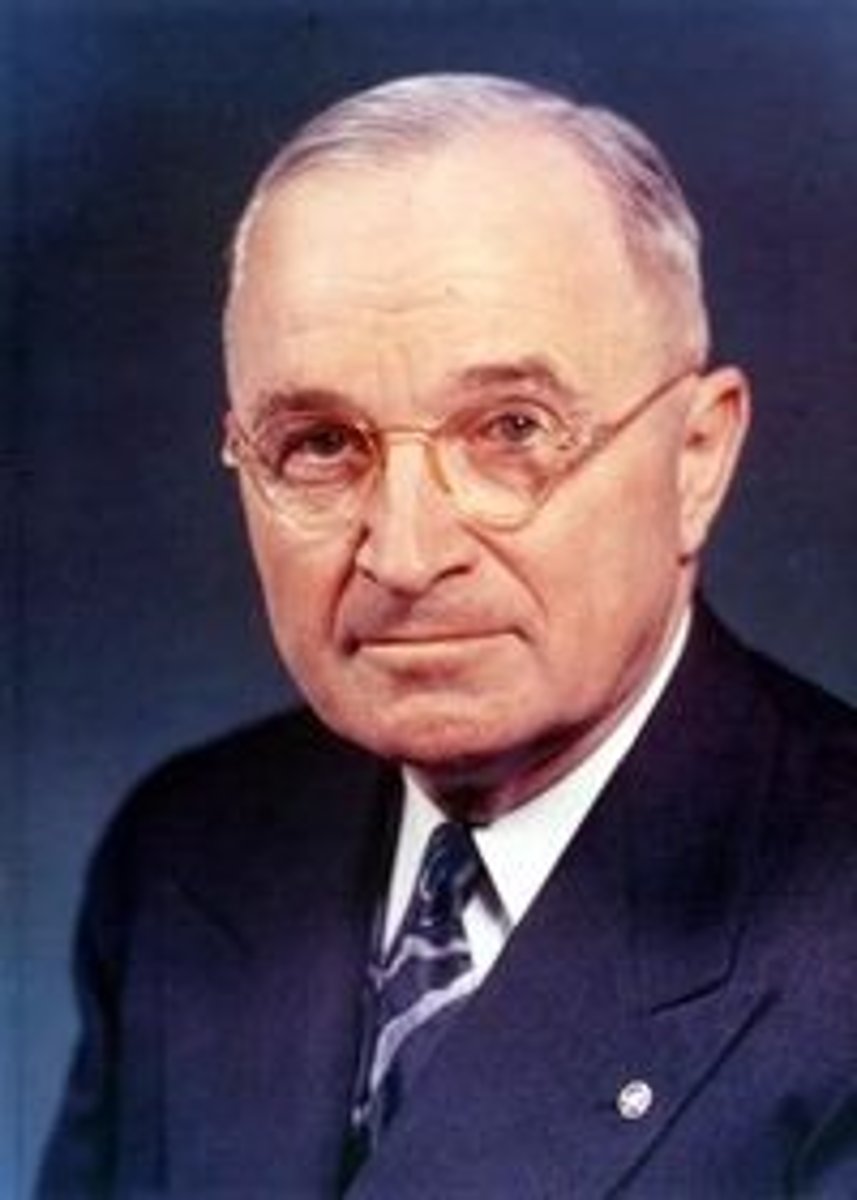
Harry Truman
33rd President of the United States. Led the U.S. to victory in WWII making the ultimate decision to use atomic weapons for the first time. Shaped U.S. foreign policy regarding the Soviet Union after the war.

Cold War
A conflict between the US and the Soviet Union (1945-1989). The nations never directly confronted each other on the battlefield but deadly threats went on for years.
Truman Doctrine (1947)
A policy set forth by U.S. President Harry S Truman stating that the U.S. would support Greece and Turkey with economic and military aid to prevent their falling into the Soviet sphere.
Containment
American policy of resisting further expansion of communism around the world
Marshall Plan
A United States program of economic aid for the reconstruction of Europe (1948-1952)

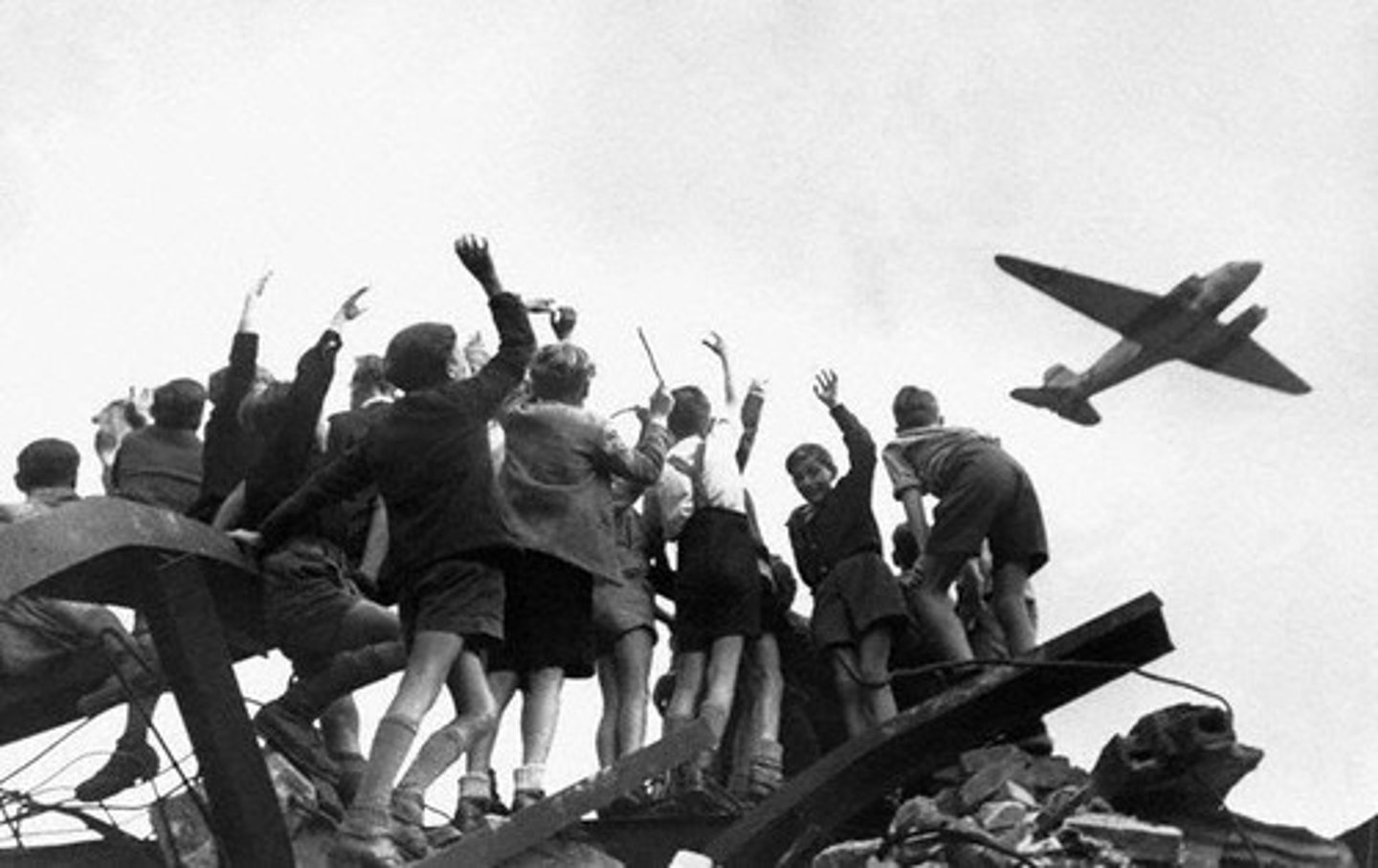
Berlin Airlift
airlift in 1948 that supplied food and fuel to citizens of west Berlin when the Russians closed off land access to Berlin

North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO)
1949 alliance of nations that agreed to band together in the event of war and to support and protect each nation involved
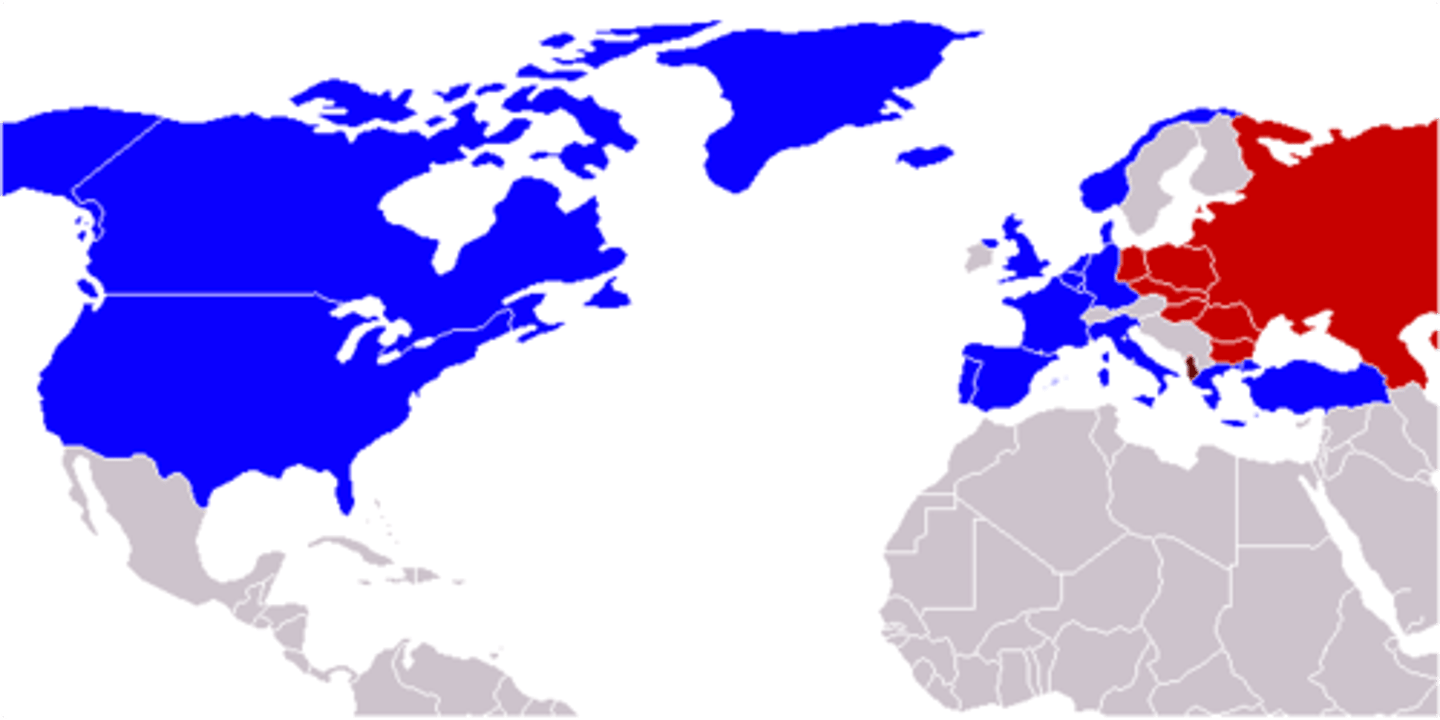
Warsaw Pact
An alliance between the Soviet Union and other Eastern European nations. This was in response to the NATO

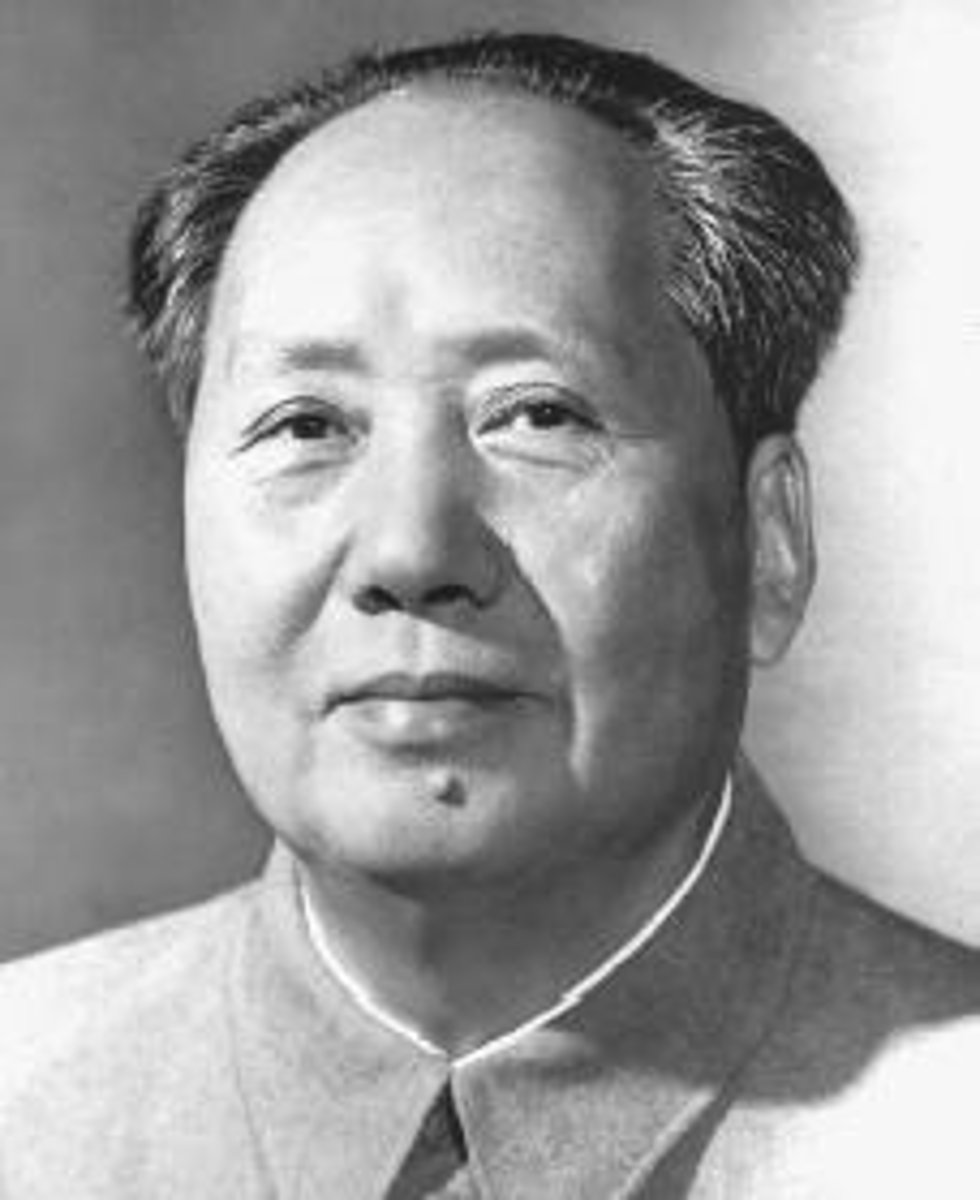
Mao Zedong (Mao Tse-tung)
Leader of the Chinese Communists whose revolutionary army seized power in China in 1949

Arms Race
Cold war competition between the U.S. and Soviet Union to build up their respective armed forces and weapons
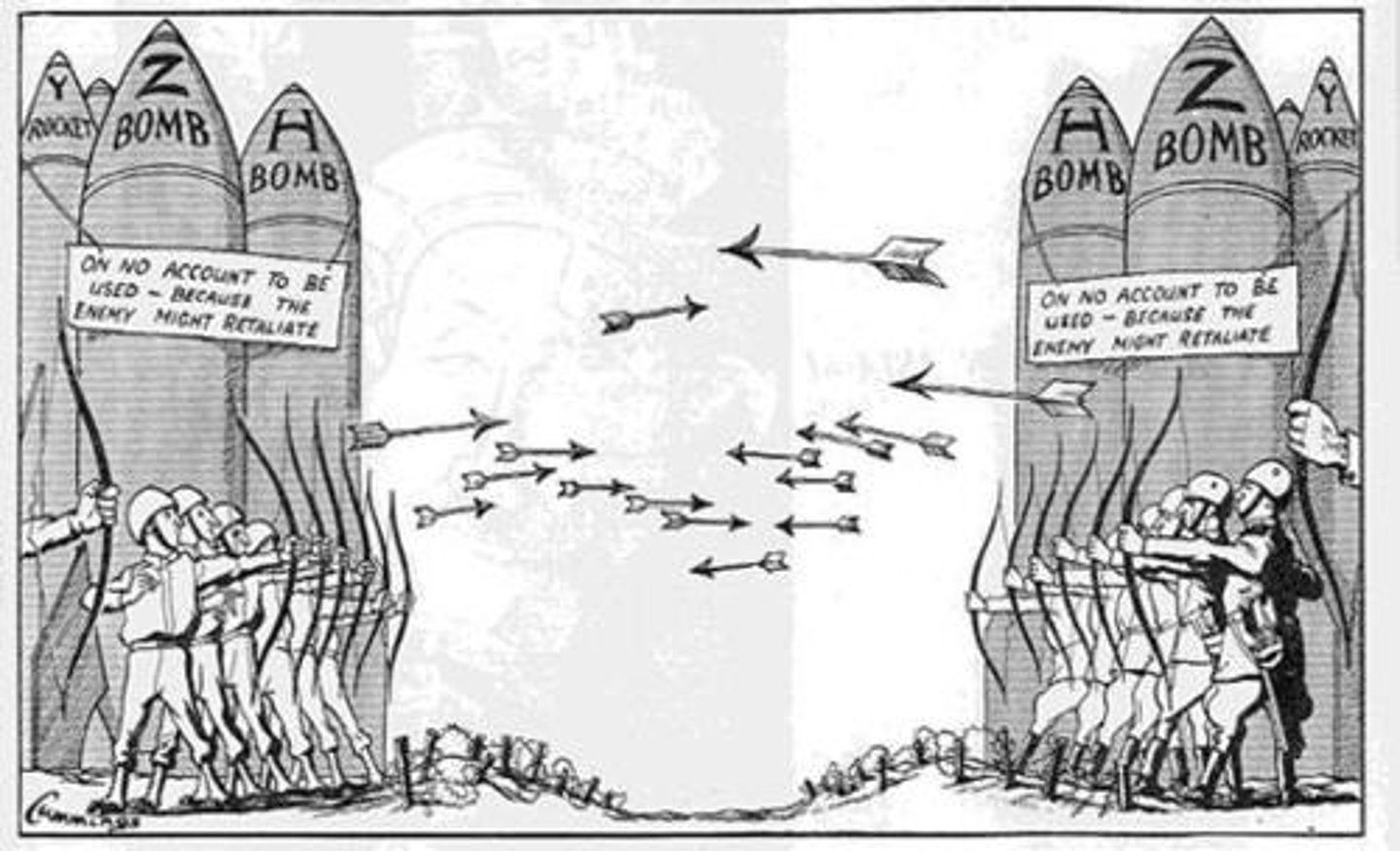
Mutually Assured Destruction (MAD)
A doctrine of military strategy in which a full-scale use of nuclear weapons by two opposing sides would effectively result in the destruction of both the attacker and the defender.
Massive Retaliation
policy of threatening to use massive force in response to aggression

Eisenhower Doctrine
Policy of the US that it would defend the Middle East against attack by any Communist country
Central Intelligence Agency (CIA)
A U.S. agency created to gather secret information about foreign governments.
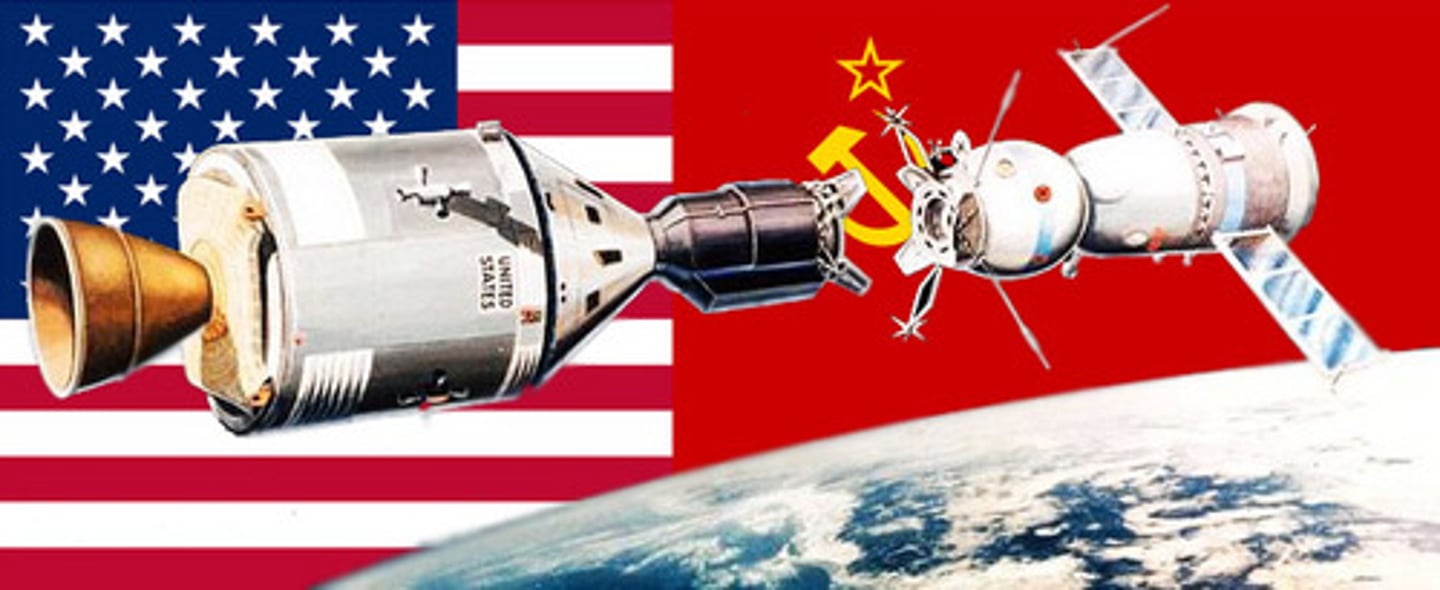
Space Race
A competition of space exploration between the United States and Soviet Union.
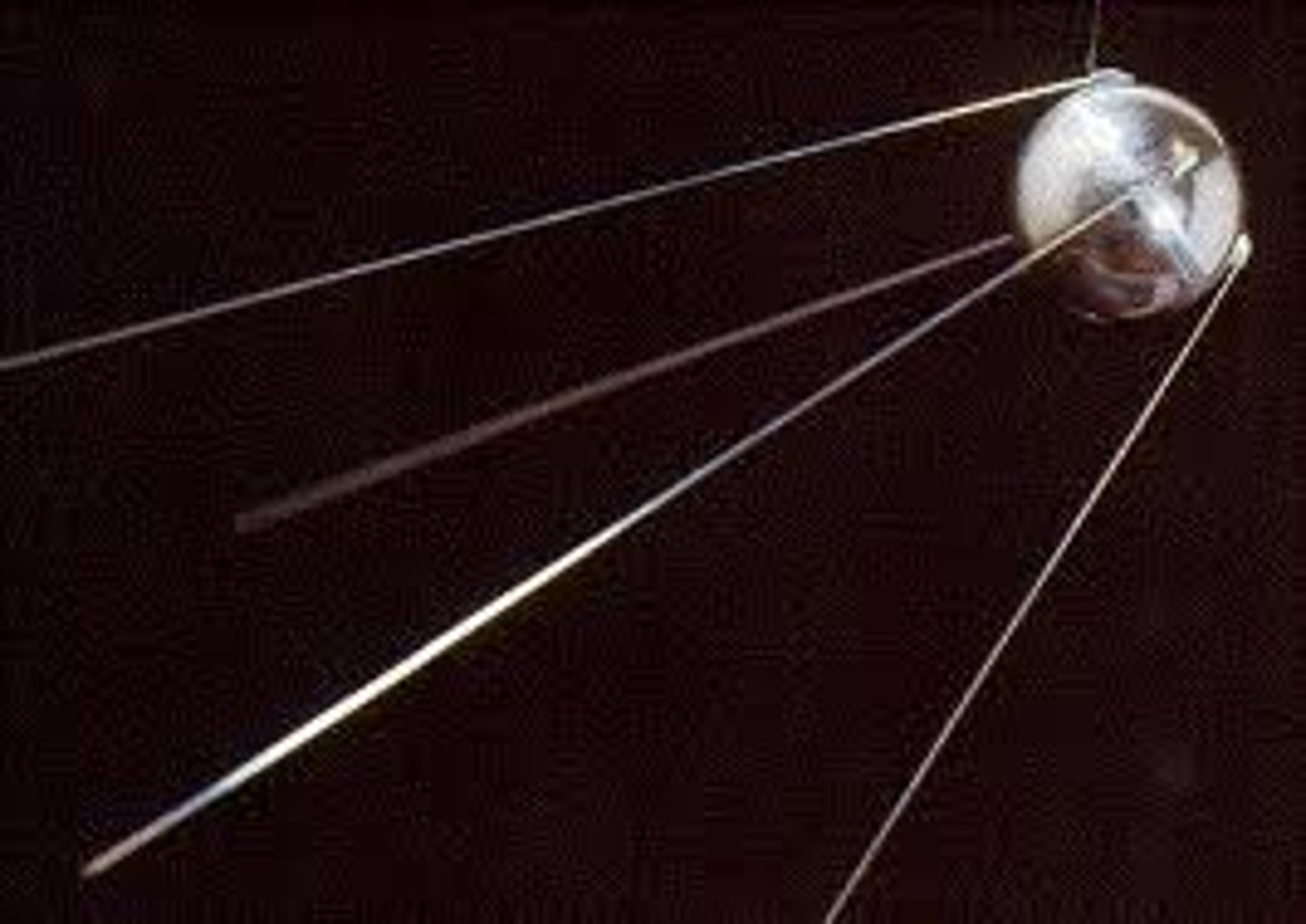
Sputnik
First artificial Earth satellite, it was launched by Moscow in 1957 and sparked U.S. fears of Soviet dominance in technology and outer space. It led to the creation of NASA and the space race.

National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA)
independent agency of the federal government, responsible for the civilian space program, and aeronautics and aerospace research. Founded in 1958.

Red Scare
A period of general fear of communists in the U.S.; took place after World War II when US locked in ideological battle with USSR; led by Sen. Joseph McCarthy

House Un-American Activities Committee (HUAC)
A congressional committee that investigated Communist influence inside and outside the U.S. government in the years following World War II.

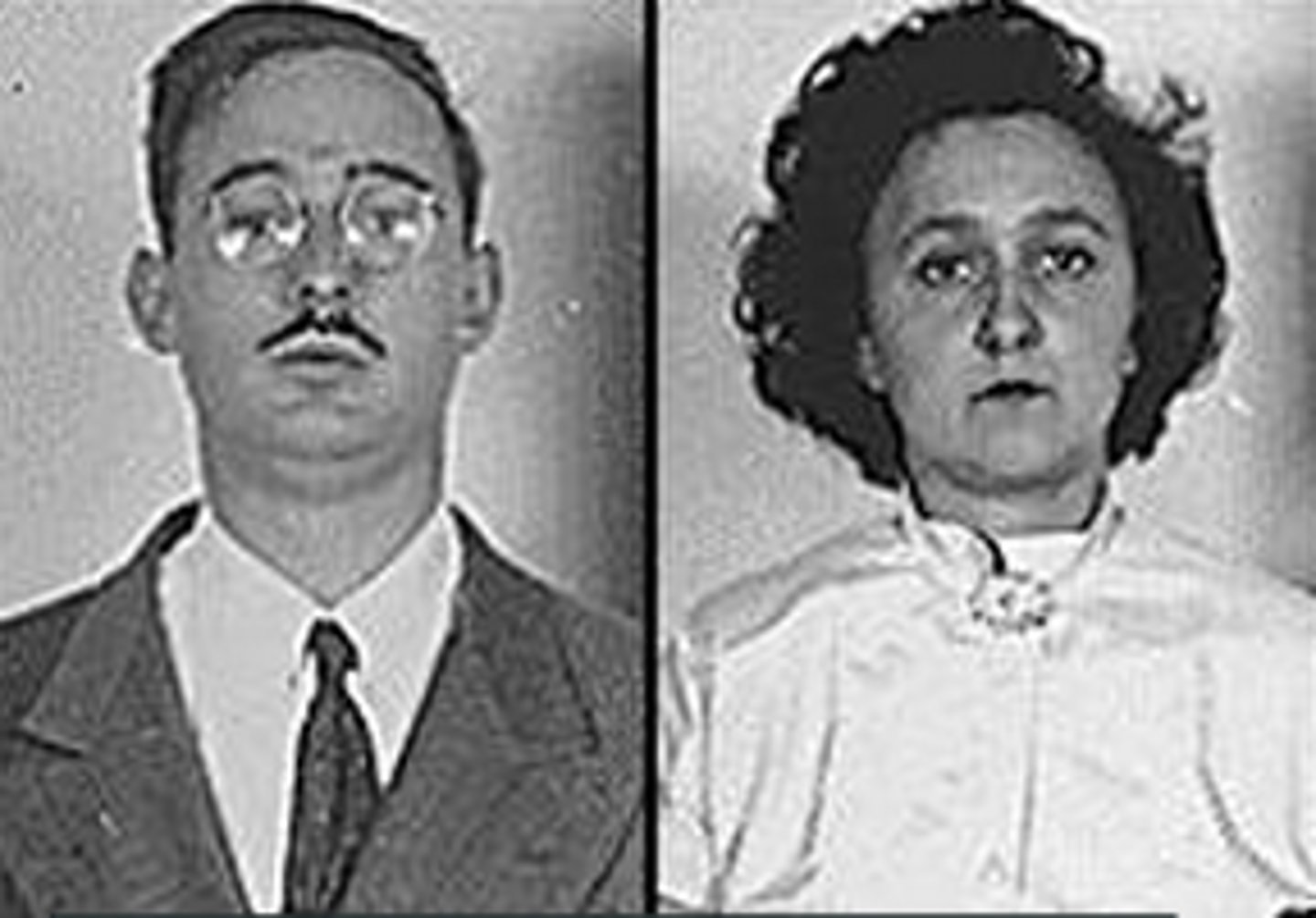
Julius and Ethel Rosenberg
American couple executed for passing atomic secrets to Soviet agents

Joseph McCarthy
U.S. Senator who led an anti-communist campaign from 1950 to 1954

McCarthyism
The term associated with Senator Joseph McCarthy who led the search for communists in America during the early 1950s through his leadership in the House Un-American Activities Committee.

John F. Kennedy
President of the US during the Bay of Pigs Invasion and the Cuban Missile Crisis

Fidel Castro
Cuban socialist leader who overthrew a dictator in 1959 and established a Marxist socialist state in Cuba

Flexible Response
A policy, developed during the Kennedy administration, that involved preparing for a variety of military responses to international crises rather than focusing on the use of nuclear weapons.
Peace Corps
Federal program established to send volunteers to help developing nations, developed under JFK
Bay of Pigs Invasion
failed invasion of Cuba in 1961 when a force of 1,200 Cuban exiles, backed by the United States, landed at the Bay of Pigs.

Cuban Missile Crisis
The 1962 confrontation between US and the Soviet Union over Soviet missiles in Cuba.

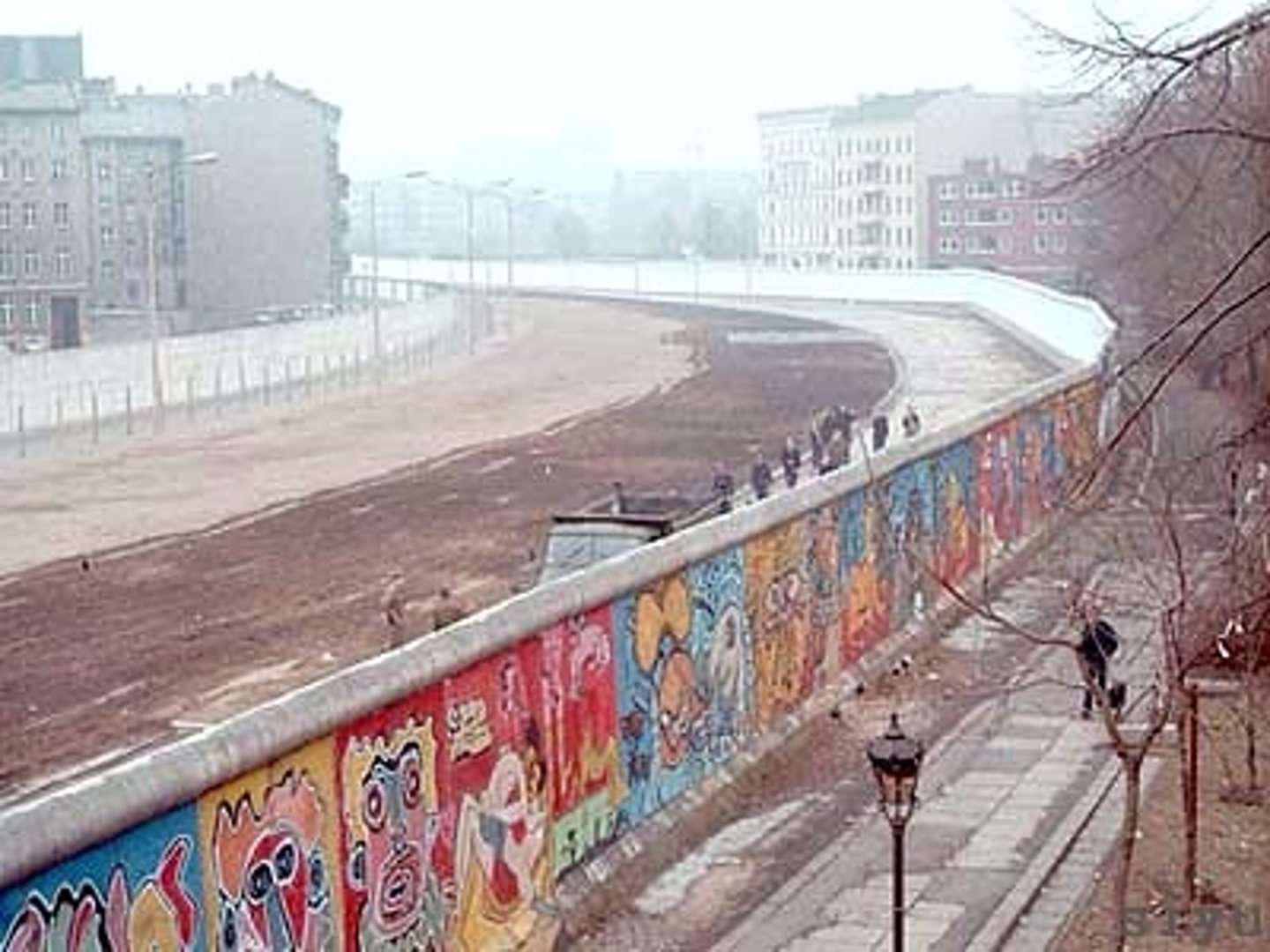
Berlin Wall
A wall separating East and West Berlin built by East Germany in 1961 to keep citizens from escaping to the West

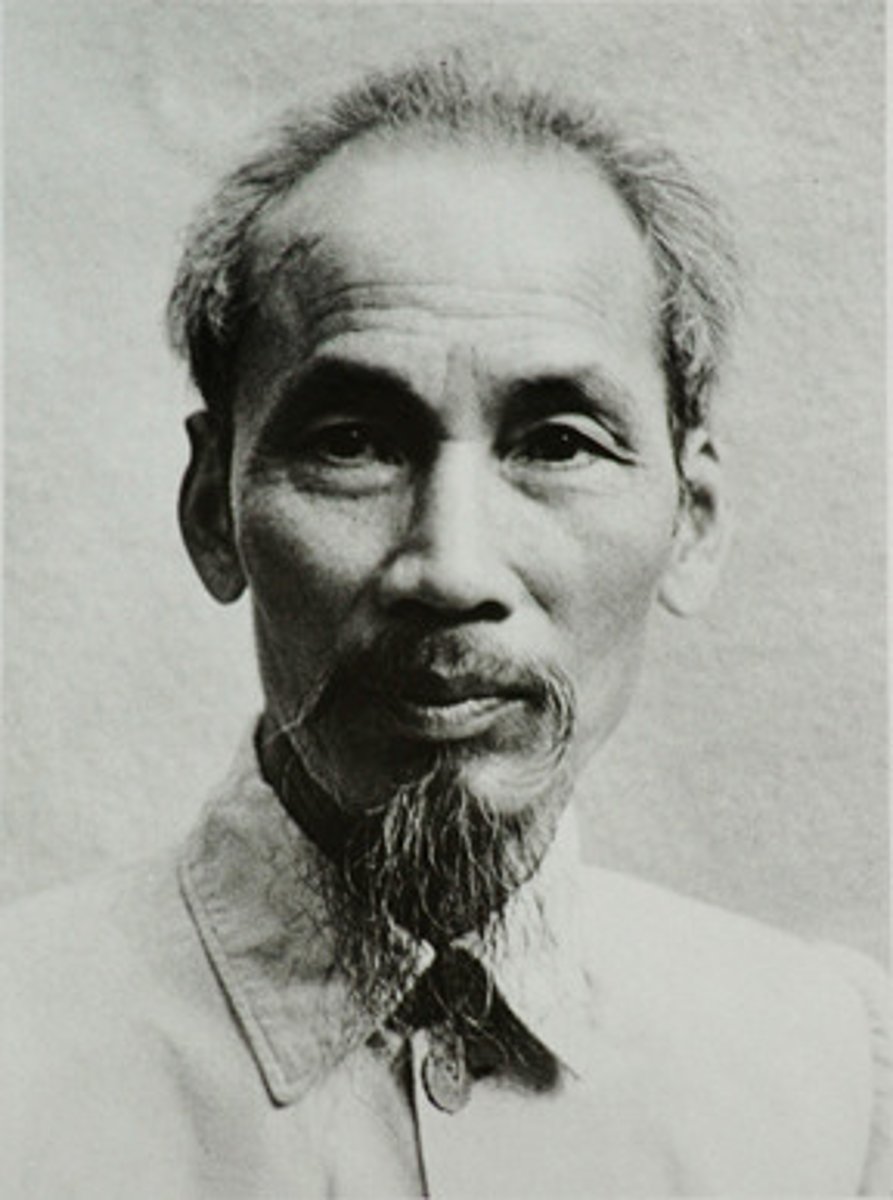
Ho Chi Minh
Communist leader of North Vietnam

Domino Theory
A theory that if one nation comes under Communist control, then neighboring nations will also come under Communist control.
Vietcong
A group of Communist guerrillas who, with the help of North Vietnam, fought against the South Vietnamese government in the Vietnam War.
Gulf of Tonkin Incident
Alleged attack of US ships by North Vietnamese torpedoes in the Tonkin Gulf on August 4, 1964. Prompted the escalation of the War in Vietnam.

Gulf of Tonkin Resolution
1964 Congressional resolution authorizing President Johnson to take military action in Vietnam

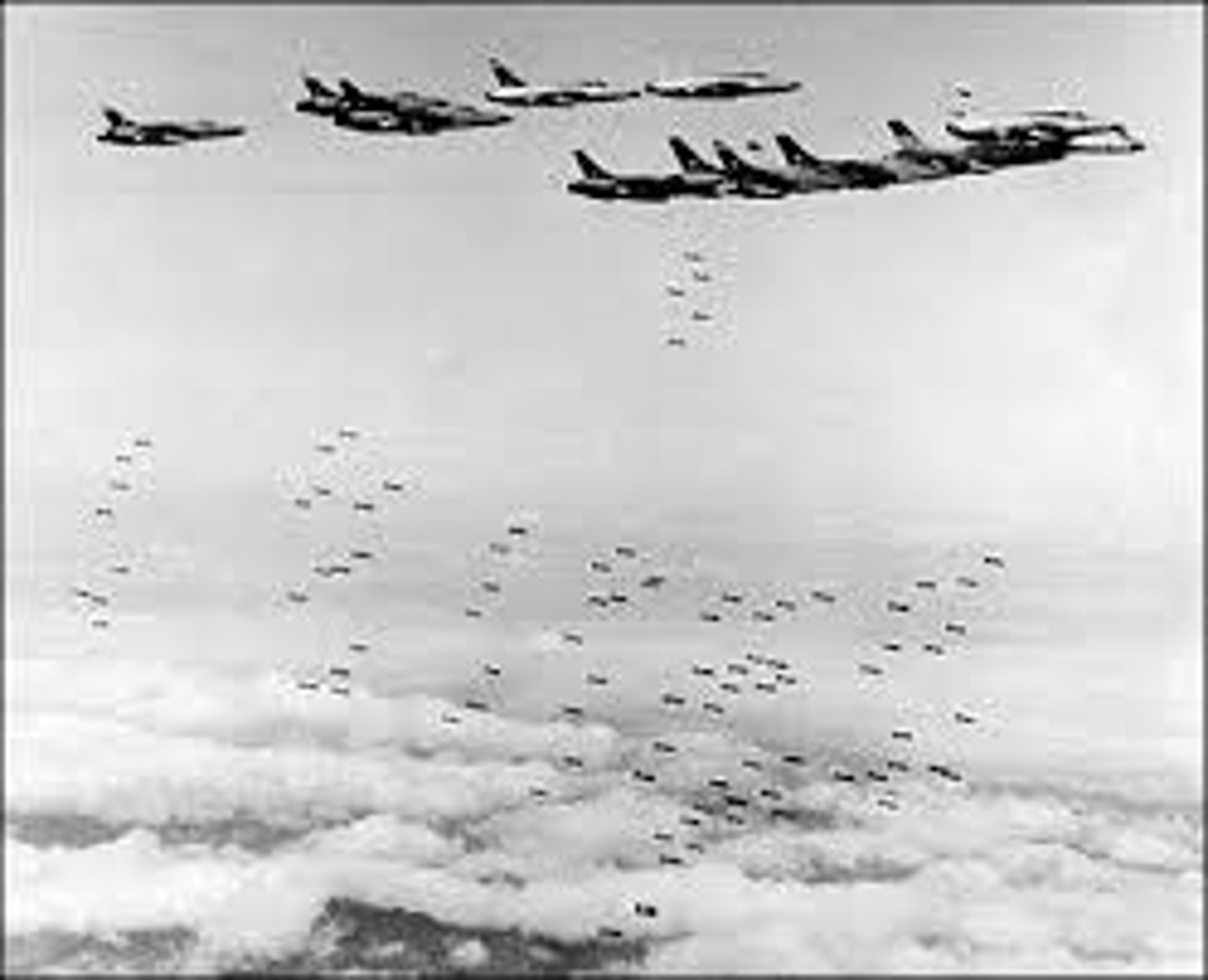
Operation Rolling Thunder
1965 bombing campaign over North Vietnam, supposed to weaken enemy's ability and will to fight

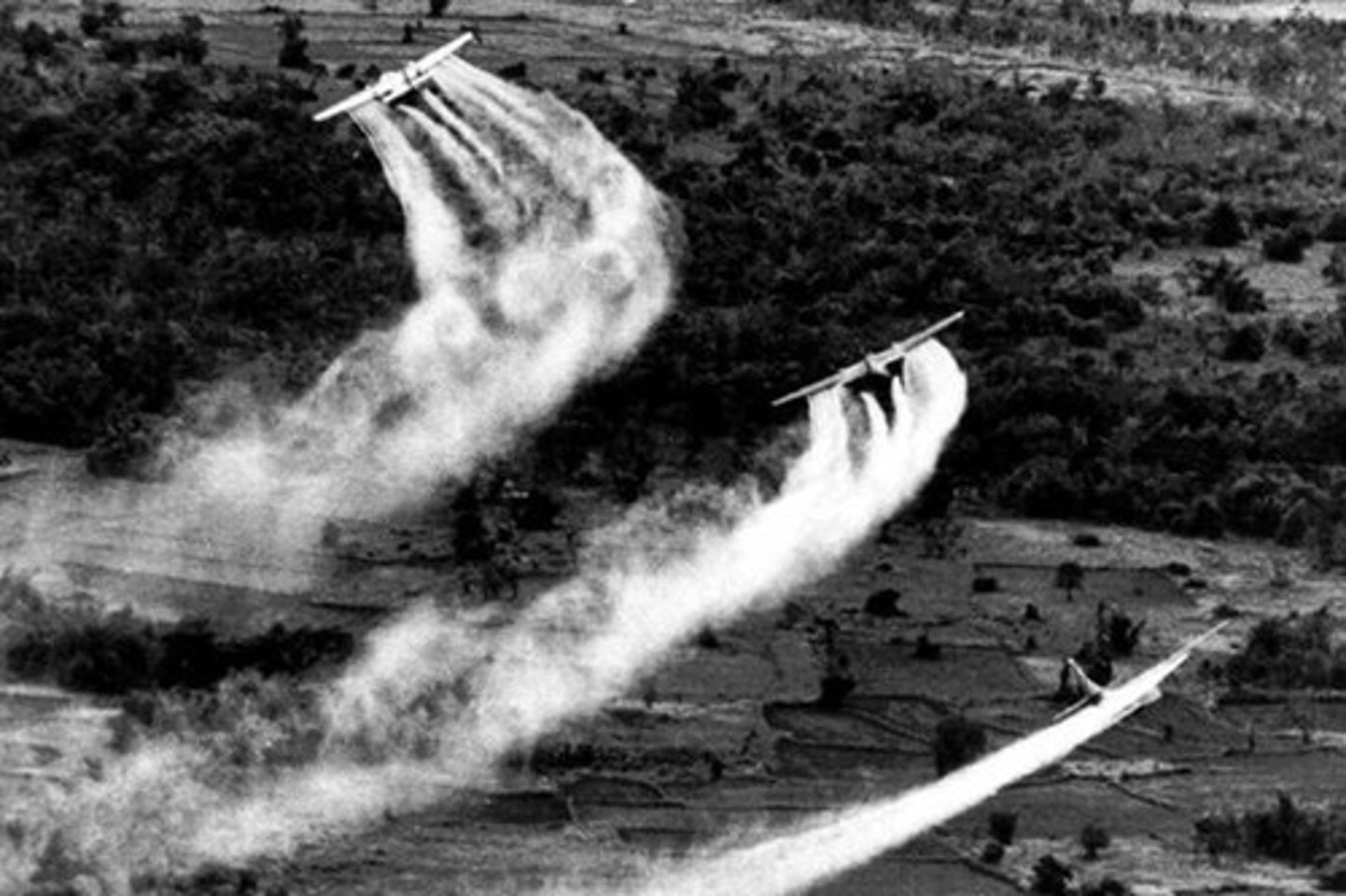
Napalm and Agent Orange
Chemical weapons used in the Vietnam war to clear forest

26th Amendment
Lowered the voting age from 21 to 18
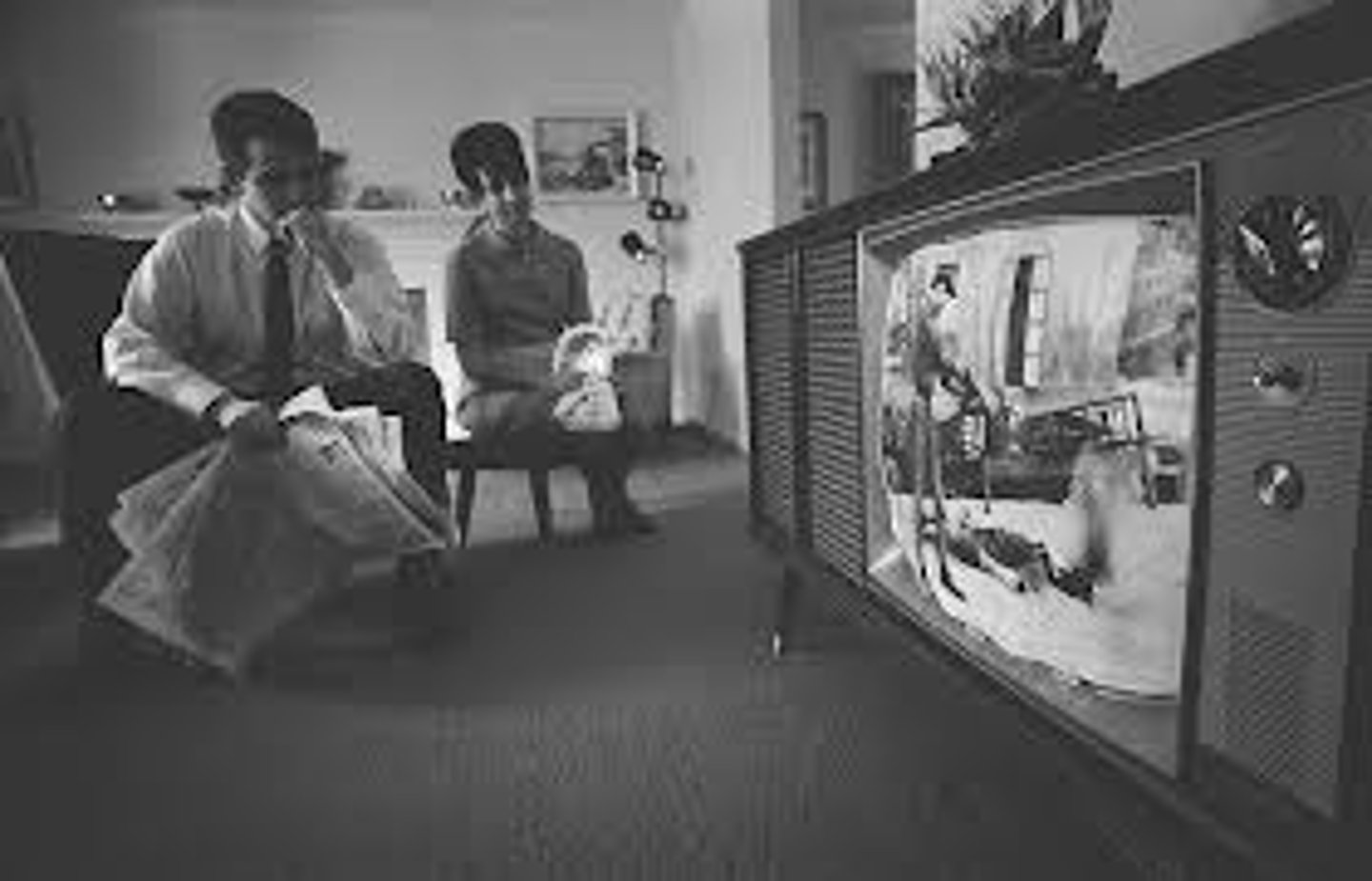
Living Room War
the Vietnam War was the first time Americans watched a war on the evening news in their living rooms

Credibility gap
American public's growing distrust of statements made by the government during the Vietnam War

Ho Chi Minh Trail
A network of paths used by North Vietnam to transport supplies to the Vietcong in South Vietnam
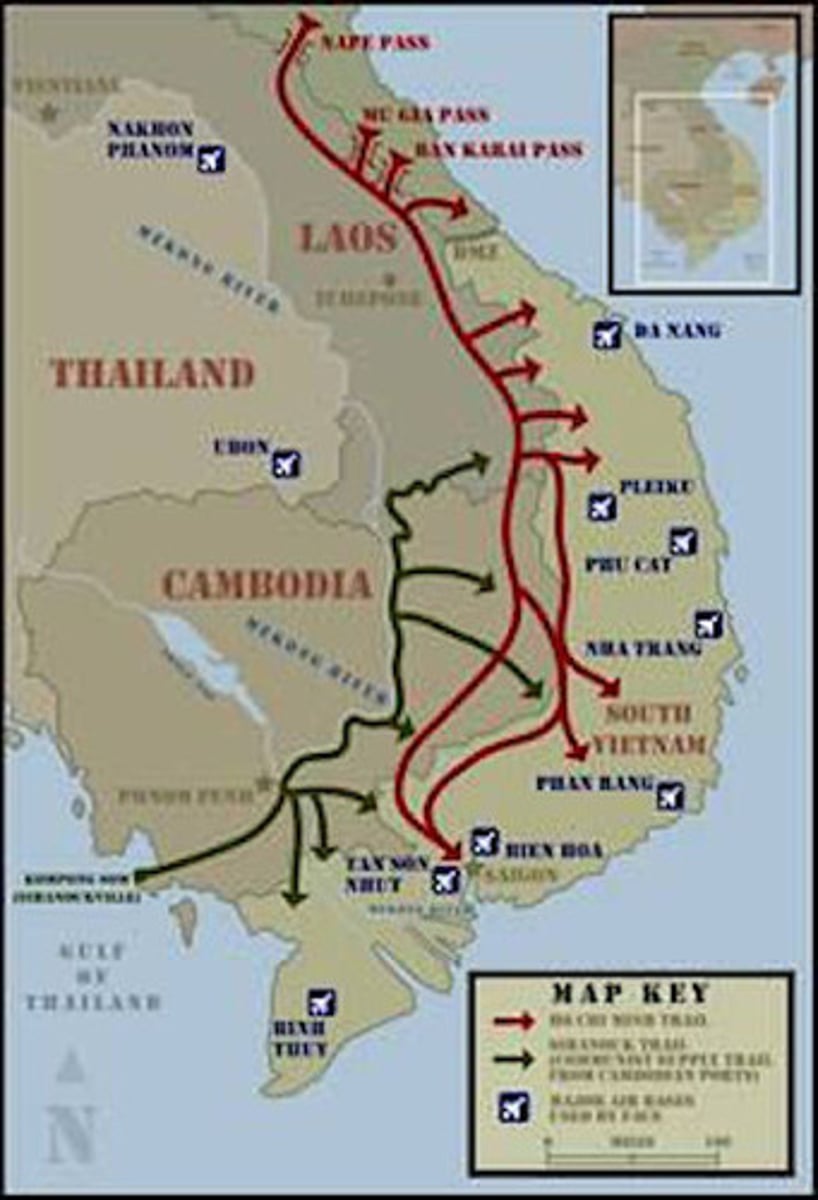
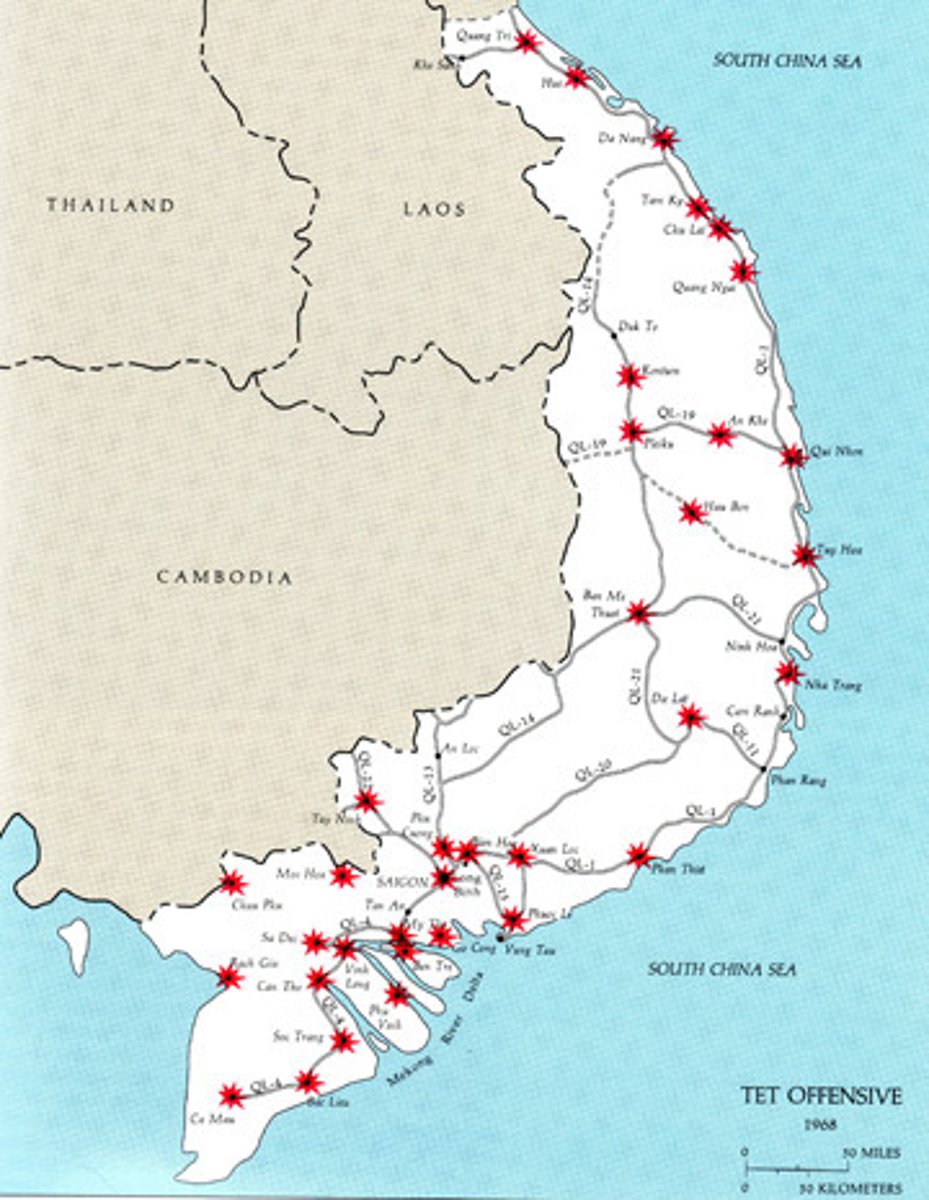
Tet Offensive
1968; National Liberation Front and North Vietnamese forces launched a huge attack on the Vietnamese New Year (Tet), which was defeated after a month of fighting and many thousands of casualties; major defeat for communism, but Americans reacted sharply, with declining approval of LBJ and more anti-war sentiment
Vietnamization
President Richard Nixons strategy for ending U.S involvement in the Vietnam war, involving a gradual withdraw of American troops and replacement of them with South Vietnamese forces

Cambodia
Nixon widened the Vietnam War by moving troops into this country to try and remove enemy camps.
Pentagon Papers
A 7,000-page top-secret United States government report on the history of the internal planning and policy-making process within the government itself concerning the Vietnam War.

Paris Peace Accords
1973 peace agreement between the United States, South Vietnam, North Vietnam, and the Vietcong that effectively ended the Vietnam War.

War Powers Act
1973. A resolution of Congress that stated the President can only send troops into action abroad by authorization of Congress or if America is already under attack or serious threat.
Richard Nixon
1968 and 1972; Republican; Vietnam: advocated "Vietnamization" (replace US troops with Vietnamese), but also bombed Cambodia/Laos, created a "credibility gap," Paris Peace Accords ended direct US involvement; economy-took US off gold standard (currency valued by strength of economy); created the Environmental Protection Agency, was president during first moon landing; SALT I and new policy of detente between US and Soviet Union; Watergate scandal: became first and only president to resign

Strategic Arms Limitation Treaty (SALT)
Treaty signed in 1972 by the United States and the Soviet Union to slow the nuclear arms race.
Detente
A policy of reducing Cold War tensions that was adopted by the United States during the presidency of Richard Nixon.
Silent Majority
A phrase used to describe people, whatever their economic status, who uphold traditional values, especially against the counterculture of the 1960s
Stagflation
a period of slow economic growth and high unemployment (stagnation) while prices rise (inflation)
Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC)
an international economic organization whose member countries all produce and export oil
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA)
The US federal agency with a mission to protect human health and the environment.
Affirmative Action
A policy designed to redress past discrimination against women and minority groups through measures to improve their economic and educational opportunities
Watergate
The events and scandal surrounding a break-in at the Democratic National Committee headquarters in 1972 and the subsequent cover-up of White House involvement, leading to the eventual resignation of President Nixon under the threat of impeachment.

executive privilege
The power to keep executive communications confidential, especially if they relate to national security.
Helsinki Accords
Political and human rights agreement signed in Helsinki, Finland in 1975 by the Soviet Union and western European countries.
Human rights
the basic rights to which all people are entitled as human beings
SALT II
Additional arms limitations signings in 1979 which places limits on long-range missiles, bombers and nuclear warheads.
Jimmy Carter
(1977-1981), Created the Department of Energy and the Department of Education. He was criticized for his return of the Panama Canal Zone, and because of the Soviet war in Afghanistan, he enacted an embargo on grain shipments to USSR and boycotted the 1980 Olympics in Moscow and his last year in office was marked by the takeover of the American embassy in Iran, fuel shortages, and the Soviet Invasion of Afghanistan, which caused him to lose to Ronald Regan in the next election.

Christian Fundamentalism
individual who believes in a strict, literal interpretation of the Bible as the foundation of the Christian faith
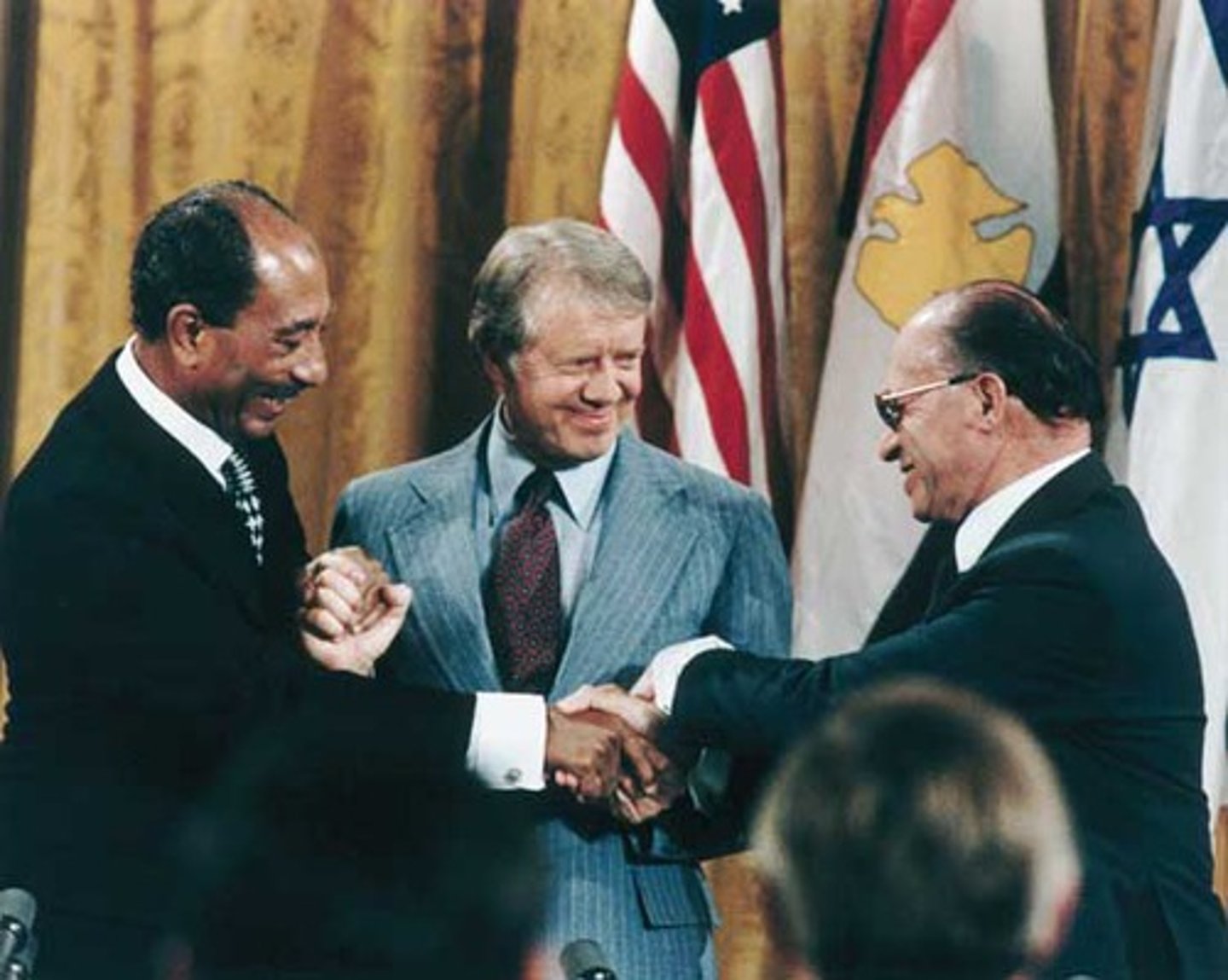
Camp David Accords (1978)
Peace treaty between Egypt and Israel; hosted by US President Jimmy Carter; caused Egypt to be expelled from the Arab league; created a power vacuum that Saddam hoped to fill; first treaty of its kind between Israel and an Arab state

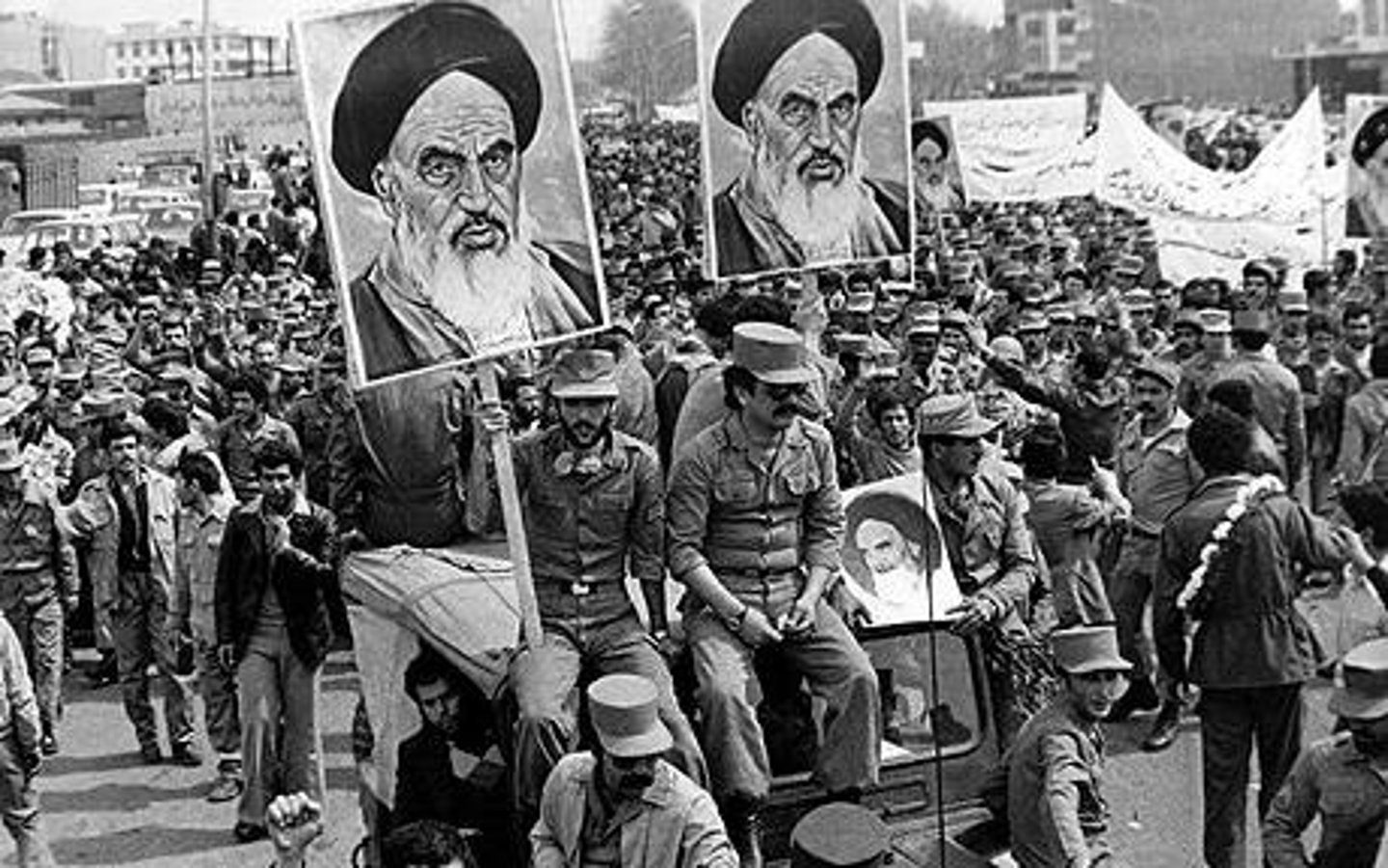
Iranian Revolution
(1978-1979) a revolution against the shah of Iran led by the Ayatollah Ruhollah Khomeini, which resulted in Iran becoming an Islamic republic with Khomeini as its leader

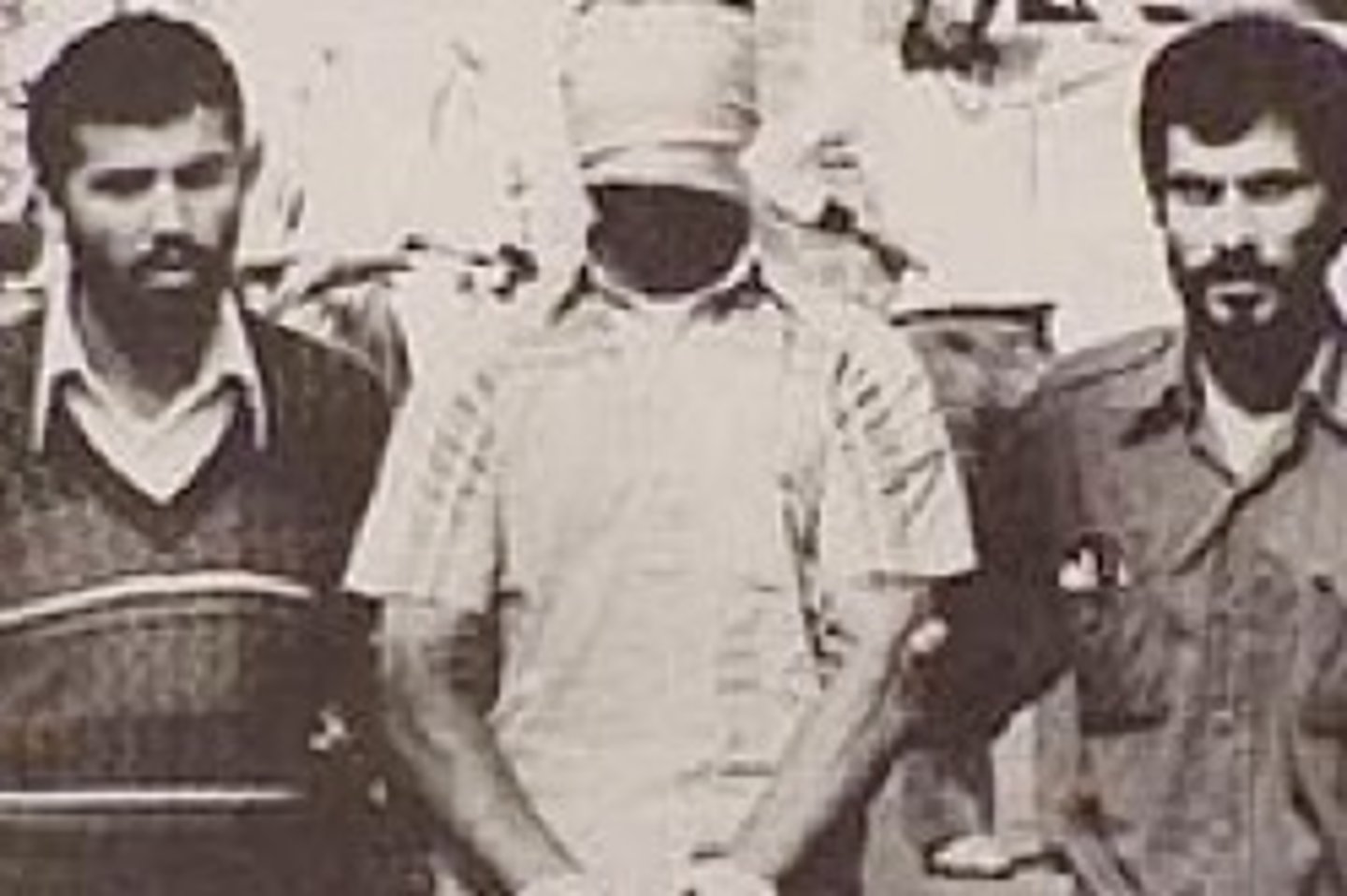
Iranian Hostage Crisis
In 1979, Iranian fundamentalists seized the American embassy in Tehran and held fifty-three American diplomats hostage for over a year. The Iranian hostage crisis weakened the Carter presidency; the hostages were finally released on January 20, 1981, the day Ronald Reagan became president.

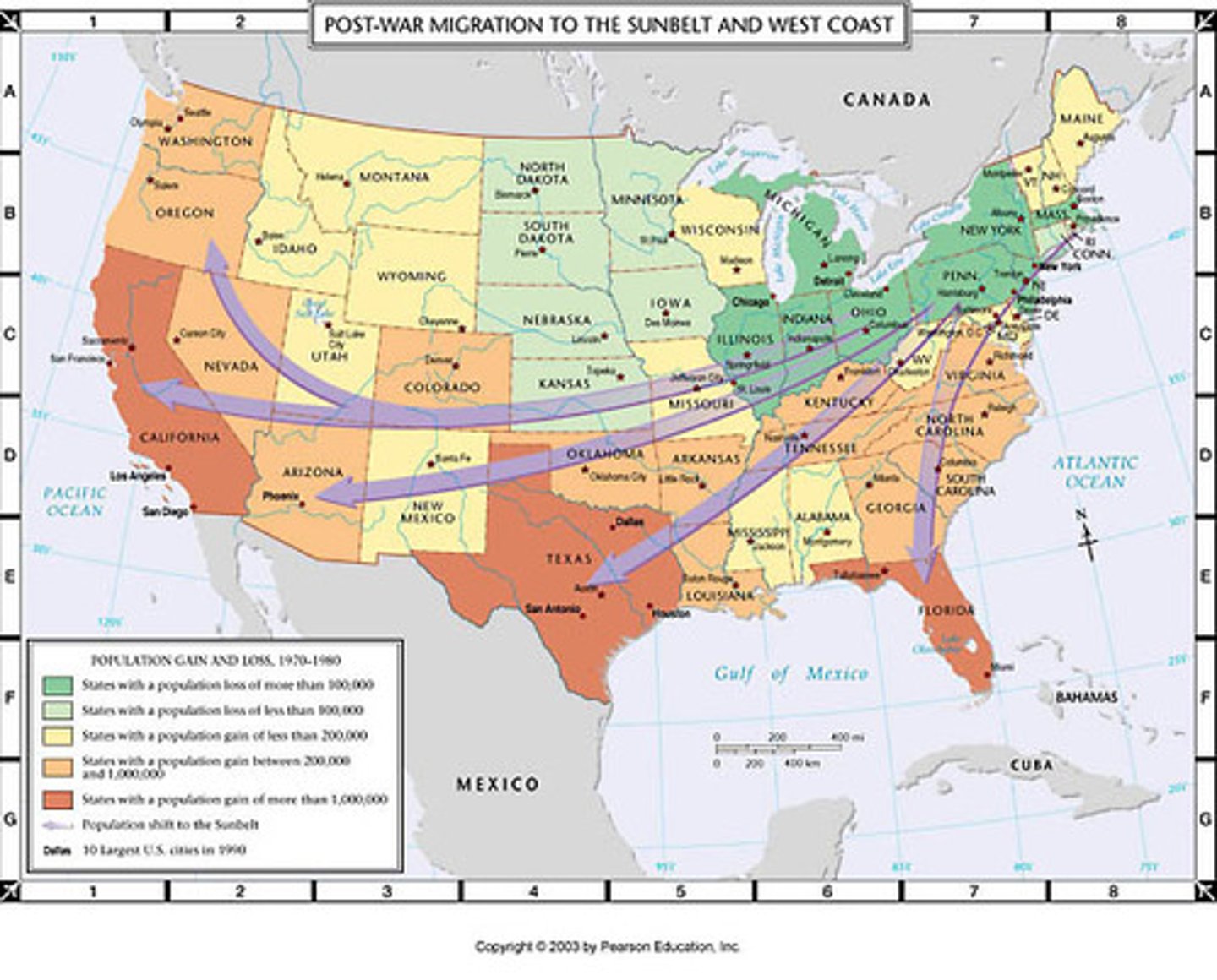
Sunbelt Migration
the movement of large number of American population to areas of the country with warmer climates
Jerry Falwell
Leader of the Religious Right Fundamentalist Christians, a group that supported Reagan; rallying cry was "family values", anti-abortion, favored prayer in schools

Televangelists
term used to describe ministers who would spread their messages via television networks
Moral Majority
"Born-Again" Christians become politically active in the 1980s. The majority of Americans are moral people, and therefore are a political force.
Liberal
open to new behavior or opinions and willing to discard traditional values.
Conservative
A person who believes government power, particularly in the economy, should be limited in order to maximize individual freedom.
GI Bill of Rights
Law Passed in 1944 to help returning veterans buy homes and pay for higher education

Baby Boom
the larger than expected generation in United States born shortly after World War II

Productivity
The value of a particular product compared to the amount of labor needed to make it. Increased post-WWII
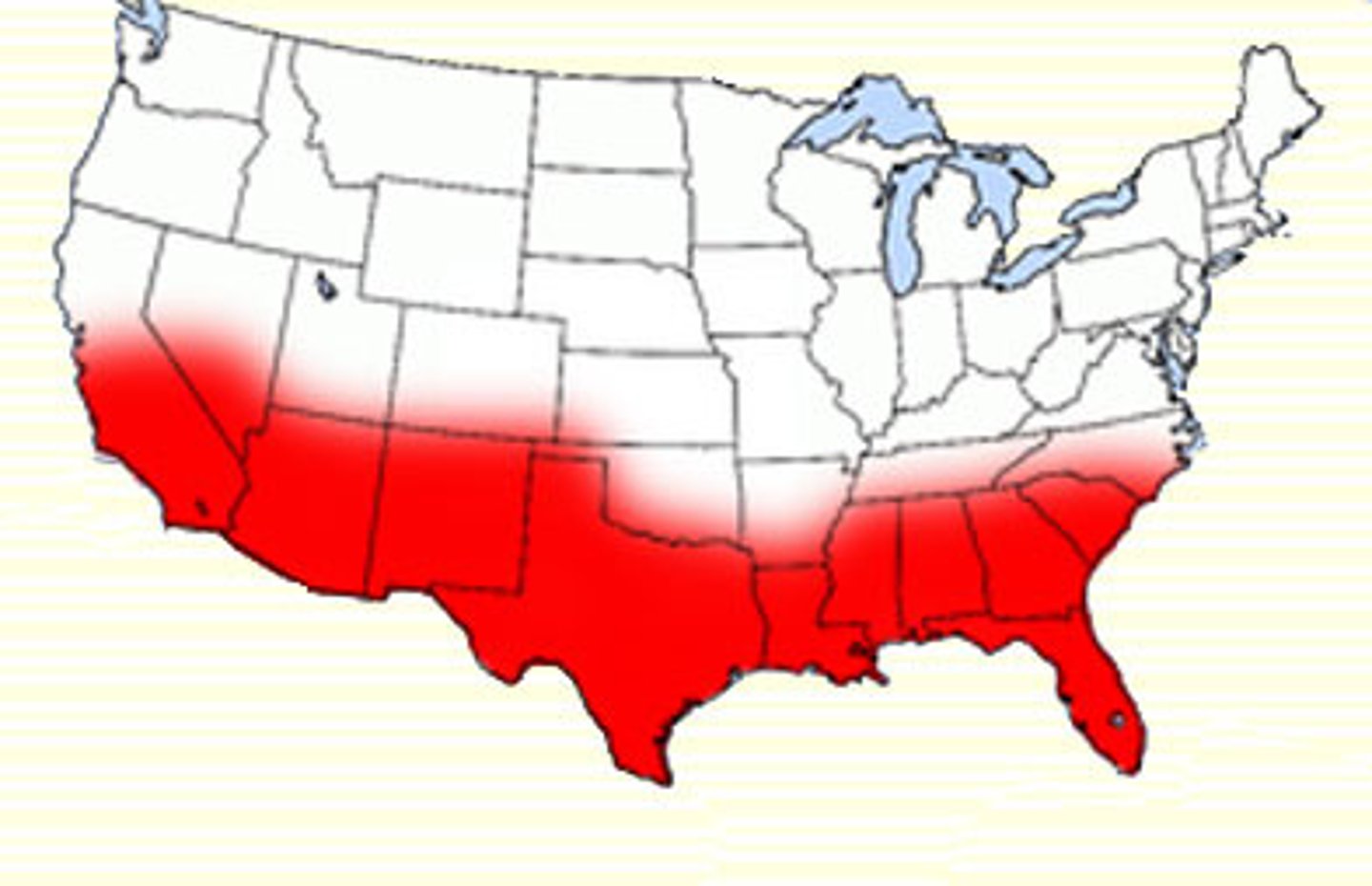
Sunbelt
A region of the United States generally considered to stretch across the South and Southwest that saw substantial population growth in the 1950s due to job growth
Service Sector
The sector of the economy that provides services--such as health care, banking, and education--contrast to the sector that produces goods.
Franchise business
An independently owned retail outlet of a larger company

Interstate Highway Act
1956 law that authorized the spending of $32 billion to build 41,000 miles of highway

Consumerism
A preoccupation with the purchasing of material goods. Expanded in the 1950s
nuclear family
Mother, father and children living as a unit - accepted family of the 1950s

Beatniks
A United States youth subculture of the 1950s that rebelled against the mundane horrors of middle class life. Led to 1960s hippies

Rock and Roll
music that grew out of rhythm and blues and that became popular in the 1950s
Elvis Presley
United States rock singer whose many hit records and flamboyant style greatly influenced American popular music (1935-1977)

urban renewal
Program in which cities identify blighted inner-city neighborhoods, acquire the properties from private members, relocate the residents and businesses, clear the site, build new roads and utilities, and turn the land over to private developers.
Jonas Salk
Developed the polio vaccine in 1952
Polio Vaccine
created by Dr. Jonas Salk. worked by introducing killed or weak pieces of the virus to allow body to develop antibodies thus preventing polio
Television
1950s-1960s
*Invented in the 1930s
*Seminal shows during the 1950s and 1960s included The Honeymooners, I Love Lucy, and The Ed Sullivan Show
*By 1960, over forty million homes had televisions, spread a national culture

Great Society
a domestic program in the administration of President Lyndon B. Johnson that instituted federally sponsored social welfare programs; advocated for civil rights; war on poverty
War on Poverty
set of programs introduced by President Johnson to fight poverty
Medicare and Medicaid (1965)
Programs that established health insurance for the poor, elderly, and disabled. Part of LBJ's Great Society
Cuyahoga River Fire (1969)
The Cuyahoga River is a river in the United States, located in Northeast Ohio, that feeds into Lake Erie. The river is famous for having been so polluted that it "caught fire" in 1969.
Clean Water Act of 1972
Establishes and maintains goals and standards for U.S. water quality and purity. It has been amended several times, most prominently in 1987 to increase controls on toxic pollutants, and in 1990, to more effectively address the hazard of oil spills.
Clean Air Act of 1970
The law aimed at combating air pollution, by charging the EPA with protecting and improving the quality of the nation's air.
Three Mile Island Nuclear Accident
This is the worst nuclear disaster in U.S. history; it occurred on March 28, 1979. One of the two reactors on Three Mile Island in central Pennsylvania experienced a partial meltdown. It was caused by a failure of a valve that controlled cool water entering the reactor core. There were no direct injuries; minor amounts of radiation were release around the site.
Love Canal Disaster 1978
A neighborhood in Niagara Falls, New York, which became the subject of national and international attention, controversy, and eventual environmental notoriety following the discovery of 21,000 tons of toxic waste buried beneath the neighborhood.
Voting Rights Act of 1965
a law designed to help end formal and informal barriers to African-American suffrage
Civil Rights Act of 1964
This act made racial, religious, and sex discrimination by employers illegal and gave the government the power to enforce all laws governing civil rights, including desegregation of schools and public places.
Martin Luther King Jr.
U.S. Baptist minister and civil rights leader. A noted orator, he opposed discrimination against blacks by organizing nonviolent resistance and peaceful mass demonstrations. He was assassinated in Memphis, Tennessee. Nobel Peace Prize (1964)
Malcolm X
1952; renamed himself X to signify the loss of his African heritage; converted to Nation of Islam in jail in the 50s, became Black Muslims' most dynamic orator and recruiter; his beliefs were the basis of a lot of the Black Power movement built on separationist and nationalist impulses to achieve true independence and equality
Montgomery Bus Boycott (1955)
In 1955, after Rosa Parks was arrested for refusing to give up her seat on a city bus, Dr. Martin L. King led a boycott of city busses. After 11 months the Supreme Court ruled that segregation of public transportation was illegal.
Greensboro Sit-ins 1960
nonviolent protest against a segregated lunch counter in Greensboro, N.C., that began on Feb. 1, 1960. Its success led to a wider sit-in movement, organized primarily by the Student Nonviolent Coordinating Committee (SNCC), that spread throughout the South.