AP PSYCH chapter 3 + 4
1/128
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
129 Terms
conciousness
our awareness of ourselves and our environment
cognitive neuroscience
study of the brain activity linked with cognition
(including perception, thinking, memory, and language)
selective attention
the focusing of conscious awareness on a particular stimulus
inattentional blindness
failing to see visible objects when our attention is directed elsewhere
change blindness
failing to notice changes in the environment; a form of inattentional blindness
dual processing
information is often simultaneously processed on separate conscious and unconscious tracks
blindsight
a condition in which a person can respond to a visual stimulus without conciously experiencing it
parallel processing
the processing of many aspects of a problem simultaneously;
the brain's natural mode of information processing for many functions, including vision.
sequential processing
the processing of one aspect of a problem at a time; used when we focus attention on new or complex tasks/problems
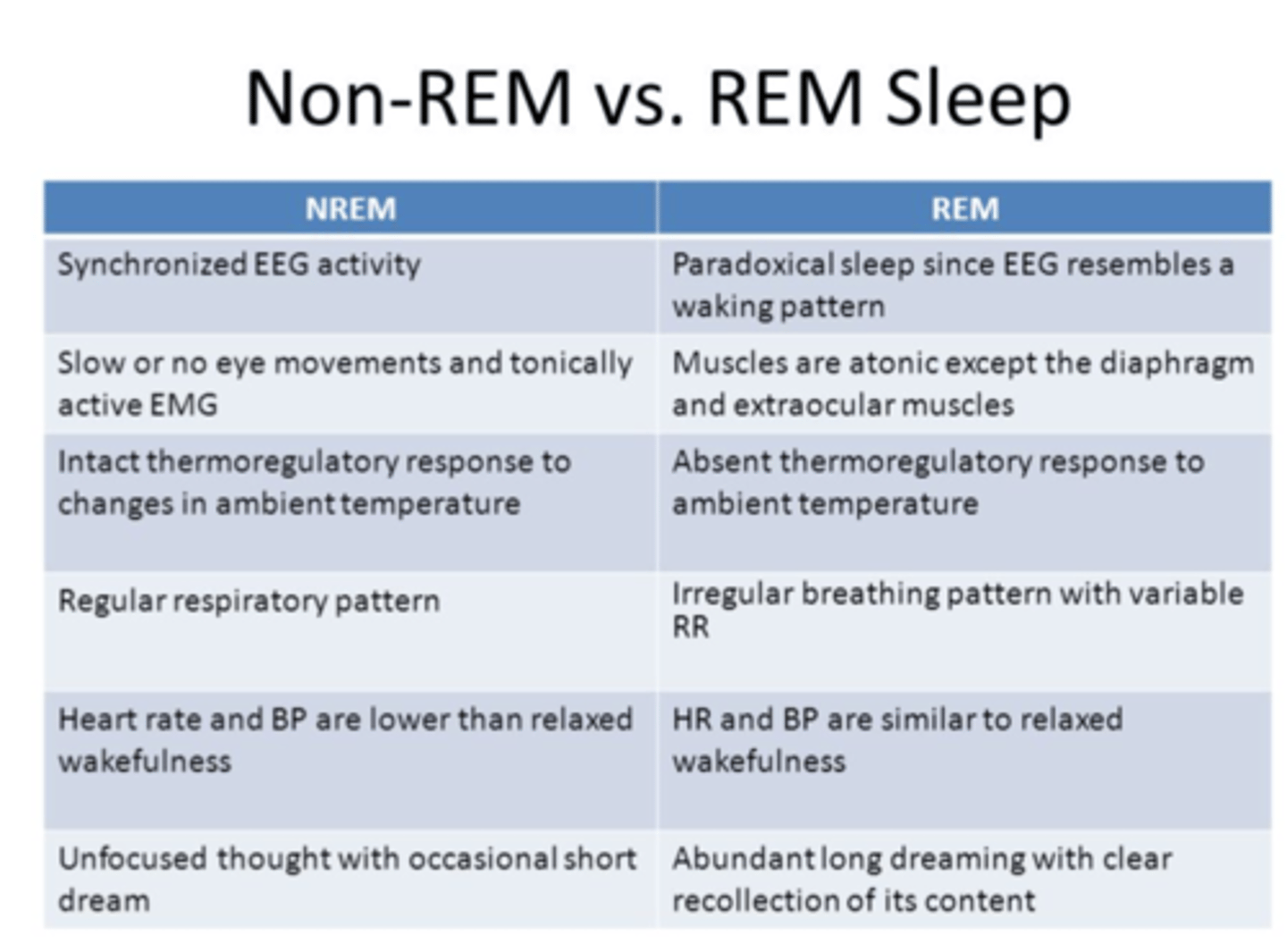
sleep
periodic, natural loss of consciousness - different from unconsciousness resulting from a coma, general anesthesia, or hibernation
circadian rhythm
the biological clock; regular bodily rhythms that occur on a 24-hour cycle
REM sleep
Rapid eye movement sleep
a recurring sleep stage during which vivid dreams commonly occur. Also known as paradoxical sleep, because the muscles are relaxed (except for minor twitches) but other body systems are active.
alpha waves
the relatively slow brain waves of a relaxed, awake state
hallucinations
false sensory experiences, such as seeing something in the absence of an external visual stimulus
delta waves
the large, slow brain waves associated with deep sleep
know the REM graphs and how to read them
suprachaismatic nucleus SCN
a pair of cell clusters in the hypothalamus that controls circadian rhythm.
In response to light, the SCN causes the pineal gland to adjust melatonin production, thus modifying our feelings of sleepiness
why do we sleep?
protection
recuperation
memory
creative thinking
growth
(P.R.M.C.G)
lack of sleep does what
increases ghrelin (makes u fat)
decreases metabolic rate (makes u fat)
increases the production of cortisol (makes u stressed)
enhances limbic brain responses to the sight of food and decreases critical responses that help us decrease temptations (cravings increase)
EEG measures
brain waves
EMG measures
muscle tension
effects of sleep deprivation on body : brain
Decreased ability to
focus
pay attention
process and store memories
increased risk of depression
effects of sleep deprivation on body : heart
increased risk of high blood pressure
effects of sleep deprivation on body : immune system
decreased production of immune cells
increased risk of viral infections like colds
effects of sleep deprivation on body : fat cells
increased production = greater risk of obesity
effects of sleep deprivation on body : joints
increased inflammation + arthritis
effects of sleep deprivation on body : stomach
increase in hunger-arousing : ghrelin
decrease in hunger-suppressing : leptin (L=LEAN)
insomnia
recurring problems in falling or staying asleep
1 in 10 adults have it
narcolepsy
uncontrollable sleep attacks. The sufferer may lapse directly into REM sleep, at random times.
1 in 2000 adults have it
sleep apnea
temporary cessations (stopping) of breathing during sleep and repeated momentary awakenings
1 in 20 adults
sleep walking/talking
walking or carrying out behaviors while asleep
1-15 in 100 in the general population
night terrors
high arousal and an appearance of being terrified; unlike nightmares, night terrors occur during Stage 4 sleep, within two or three hours of falling asleep, and are seldom remembered
1 in 100 adults + 1 in 30 children have it
effects of insomnia
chronic tiredness, reliance on sleeping pills and alcohol which reduce REM sleep and lead to tolerance
effects of narcolepsy
risk of falling asleep at dangerous moments but last less than 5 mins
effects of sleep apnea
fatigue and depression, associated with obesity (esp among males)
effects of sleepwalking/talking
not many serious concerns they return to their beds on their own or with help of family and dont remember it in the morning
effects of night terrors
doubling of a child's heart and breathing rates during the attack but they dont remember a lot of it when they wake up
dreams
a sequence of images, emotions, and thoughts passing through a sleeping person's mind
manifest content
according to Freud, the remembered story line of a dream
latent content
according to Freud, the underlying meaning of a dream
why do we have dreams
We don't know but some theories are that
help develop and preserve neural pathways
to make sense of neural static
to reflect on cognitive development
psychoactive drug
a chemical substance that alters perceptions and moods
substance use disorder
disorder characterized by continued substance craving and use despite significant life disruption and/or physical risk
tolerance
the diminishing effect with regular use of the same dose of a drug, requiring the user to take larger and larger doses before experiencing the drug's effect
withdrawal
the discomfort and distress that follow discontinuing the use of an addictive drug
What is the process that leads to drug tolerance?
With repeated exposure to a psychoactive drug, the user's brain chemistry adapts and the drug's effect lessens. Thus. it takes bigger doses to get the desired effect.
depressants
drugs (such as alcohol, barbiturates, and opiates) that reduce neural activity and slow body functions
alchohol use disorder
alcohol use marked by tolerance, withdrawal, and a drive to continue problematic use
barbiturates
drugs that depress the activity of the central nervous system, reducing anxiety but impairing memory and judgment
opiates
opium and its derivatives, such as morphine and heroin; they depress neural activity, temporarily lessening pain and anxiety
stimulants
Drugs (such as caffeine, nicotine, and the more powerful amphetamines, cocaine, and Ecstasy) that excite neural activity and speed up body functions.
nicotine
a stimulating and highly addictive psychoactive drug in tobacco
what are the physiological effects of nicotine
arouses brain to a state of alertness
increases heart rate and blood pressure
at high levels, it relaxes muscles
triggers the release of neurotransmitters that can reduce stress
reduces circulation
suppresses appetite for carbs
near-death experience
an altered state of consciousness reported after a close brush with death (such as through cardiac arrest); often similar to drug-induced hallucinations
LSD (lysergic acid diethylamide)
a powerful hallucinogenic drug; also known as acid
THC (tetrahydrocannabinol)
the major active ingredient in marijuana; triggers a variety of effects, including mild hallucinations
effects of marijuana use
alleviates chronic pain and chemotherapy-induced nausea
not associated with tobacco-related cancers like lung cancer
predictive of increased risk of traffic accidents, chronic bronchitis, psychosis social anxiety disorder, suicidal thoughts
likely contributes to impaired attention, learning, memory, and academic achievement.
alchohol
is a depressant
pleasurable effects- initial high followed by relaxation and disinhibition
negative aftereffects- depression, memory loss, organ damage, impaired reactions
heroin
is a depressant
pleasurable effects= rush of euphoria + pain relief
negative aftereffects = Depressed physiology, agonizing withdrawal
caffeine
is a stimulant
pleasurable effects = alertness
negative aftereffects = Anxiety, restlessness, and insomnia in high doses; uncomfortable withdrawal
nicotine
is a stimulant
pleasurable effects = arousal + relaxation, sense of well-being
negative aftereffects = heart disease and cancer
cocaine
is a stimulant
pleasurable effects = euphoria, confidence, energy
negative aftereffects = Cardiovascular stress, suspiciousness, depressive crash
methamphetamine
is a stimulant
pleasurable effects = euphoria, alertness, energy
negative aftereffects = Irritability, insomnia, hypertension, seizures
Ecstacy/MDMA/Molly
is a stimulant/mild hallucinogen
pleasurable effects = emotional elevation, disinhibition
negative afterffects= dehydration, overheating, depressed mood, impaired brain and immune functioning
LSD
is a hallucinogen
pleasurable effects = visual "trip"
negative aftereffects = risk of panic
marijuana THC
is a mild hallucinogen
pleasurable effects = enhanced sensation, relief of pain, distortion of time, relaxation
negative afterffects= impaired learning and memory, increased risk of psychological disorders
biological influences of disordered drug use:
genetic predispositions
variations in neurotransmitter systems
psychological influnces of disordered drug use
lacking sense of purpose
significant stress
depression
Social-cultural influences of disordered drug use
difficult environment
cultural acceptance of drug use
negative peer influences
behavior genetics
the study of how genetic and environmental factors influence individual differences in behavior.
heredity
the genetic transfer of characteristics from parents to offspring.
environment
every nongenetic influence
chromosomes
threadlike structures made of DNA molecules that contain the genes
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)
a complex molecule containing the genetic information that makes up the chromosomes.
genes
the biochemical units of heredity that make up the chromosomes
segments of DNA capable of synthesizing proteins
synthesizing = combining
genome
the complete instructions for making an organism
consisting of all the genetic material in that organism's chromosomes.
identical (monozygotic) twins
develop from a single fertilized egg that splits making them genetically identical.
if identical twins have the same genes, will they have the same number of copies of those genes repeated within their genome?
no - this helps explain why one twin can have a. greater risk of illnesses and disorders
fraternal (dizygotic) twins
develop from two fertilized eggs.
they share the same prenatal environment but are the same as normal brothers and sisters.
temperament
a person’s characteristic emotional reactivity and intensity.
heritability
the proportion of variation among individuals in a group that we can attribute to genes.
The heritability of a trait may vary, depending on the range of populations and environments studied
interaction
the interplay that occurs when the effect of one factor (such as environment) depends on another factor (such as heredity).
molecular genetics
studies molecular structure and the function of genes
molecular behavior genetics
studies how the structure and function of genes interact with the environment to influence behavior
epigenetics
environmental influences on gene expression that occur without a DNA change
evolutionary psychology
the study of the evolution of behavior and the mind, using principles of natural selection.
natural selection
inherited traits that better enable an organism to survive and reproduce in a particular environment will (in competition with other trait variations) most likely be passed on to succeeding generations.
mutation
random error in gene replication that leads to change
social script
a culturally modeled guide for how to act in various situations.
selection effect
people tend to select similar others and sort themselves out into like-minded groups.
culture
the enduring behaviors, ideas, attitudes, values, and traditions shared by a group of people and transmitted from one generation to the next
norm
what is considered normal or socially acceptable
individualism
giving priority to one’s own goals over group goals and defining one’s identity in terms of personal attributes rather than group identifications.
collectivism
giving priority to the goals of one’s group and defining their identity accordingly.
following will be contrasts between individualism and collectivism
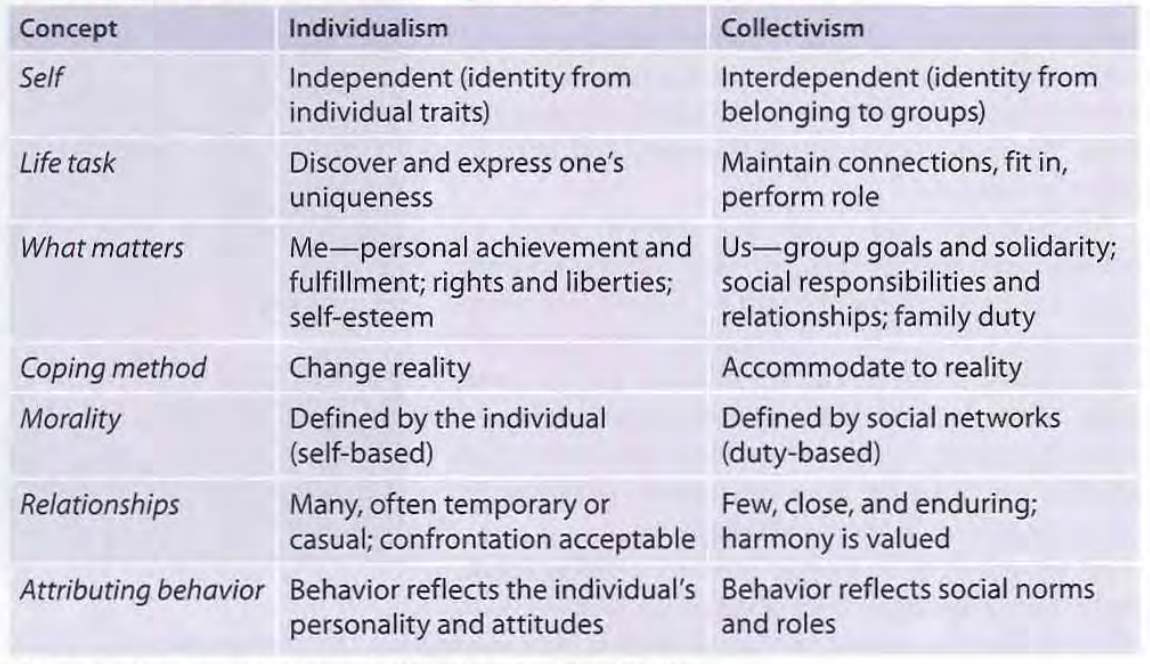
self
individualism = independent (from themsleves)
collectivism = interdependent (belonging to to other groups)
life task?
individualism = discover and express one’s uniqueness
collectivism = maintain connections, fit in, perform role.
what matters?
individualism = me
collectivism = us
coping method ?
individualism = change reality
collectivism = accommodate to reality
morality ?
individualism = self-based
collectivism = defined by social networks