C. Hemodialysis Access
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
what is hemodialysis access?
a man made fistula or graft that allows for blood to be cleansed in patients with end stage renal disease.
what are the 3 types of access used for hemodialysis access?
AVF (arterial-venous fistula)
a graft
central venous catheter
what is the most effective/favored and durable mode of dialysis access?
surgically creating an AV fistula (AVF)
which dialysis access method does not clot as easily?
a fistula
what is a fistula (hemodialysis access) and how soon can it be used?
a man made connection of one artery and one vein in the lower arm to allow for repeated access for each dialysis session.
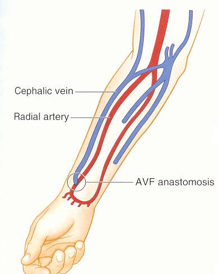
what is the preferred site to created an AVF for hemodialysis access?
in the forearm connecting the radial artery with the cephalic vein at the wrist (radiocephalic fistula AKA Brescia-Cimino)
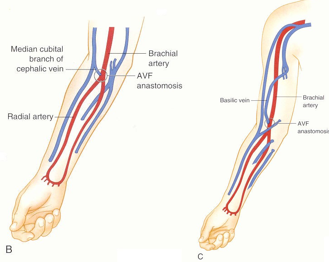
what is the second and third preferred site to created an AVF for hemodialysis access?
2nd (B)= between brachial artery and cephalic vein at antecubital fossa (elbow)
3rd (C)= brachial artery connected to basilic vein in the upper arm
how soon after creation can a fistula be used for hemodialysis access?
it may take several months for the fistula to form (and thus be usable)
what are complications of a fistula (hemodialysis access)?
infection at the site of access and clot formation (thrombosis).
what is a graft (hemodialysis access) and how soon can it be used?
a synthetic tube implanted under the skin in your arm that becomes an artificial vein used for blood access when a person has very small veins.
how soon after creation can a graft be used for hemodialysis access?
does not need to develop as a fistula does, so it can sometimes be used as soon as 1 week after placement.
complications/ problems with hemodialysis grafts?
compared with fistulas, grafts tend to have more problems with clotting or infection and need to be replaced sooner.
what is the most common type of graft used for hemodialysis?
A polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE or Gore-Tex) graft
what are the most common grafts?
forearm loop graft
upper arm straight graft
axillary loop graft
thigh graft
how is vascular mapping done prior to AVF or graft creation?
evaluate vein for vessel diameter, wall thickness, and venous compressibility
evaluate artery for vessel diameter, wall thickness, intimal thickening, and stenosis
measure depth from skin surface
what are the minimum vessel sizes in AVF/graft assessment?
artery (graft or AVF) > 20 mm
AVF vein > 25 mm
graft vein > 40 mm
what is a venous catheter (hemodialysis access)?
A tube/ catheter usually placed in a vein in the neck, chest, or groin.
if you need to start hemodialysis right away, a catheter may be used until your permanent access is ready.
why is a venous catheter not typically used for permanent hemodialysis access?
because it can clog and become infected
what are indications for hemodialysis access evaluation?
pre-op assessment
elevated pressures during dialysis
puncture problems
perigraft fluid or mass
distal limb ischemia
poor dialysis.