Memory Quiz: Stats
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
p̂
sample statistic
p
population proportion
po
parameter used in null hypothesis
z
standardized score
z*
upper p-critical value (right tail)
-z*
lower p-critical value (left tail)
Ho
null hypothesis
Ha
alternate hypothesis
n
sample size
N
population size
np̂
Number of successes expected in sample
nq^
Number of failures expected in sample
npo
Number of successes observed
nqo
Number of failures observed
P(A) = P(A/B)
Test for independence
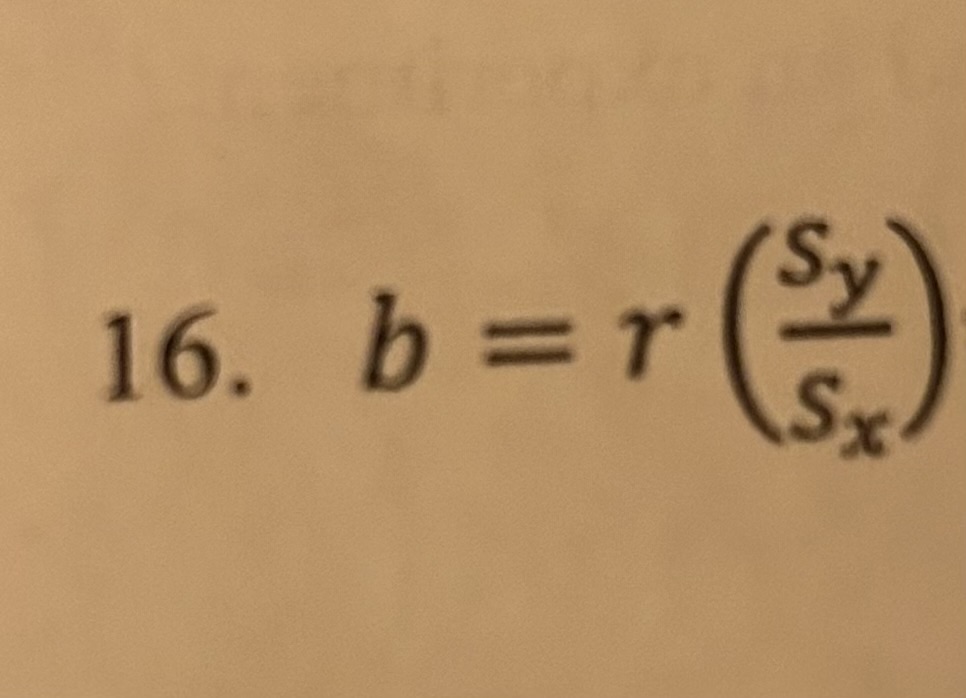
b = r(Sy/Sx)
slope in linear regression
y = a + bx
equation for Least Squares Regression Line (LSRL)
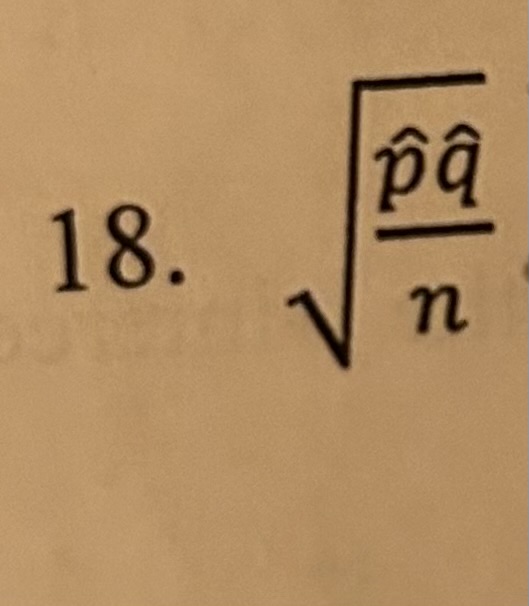
p̂q/n
standard error of sample proportion
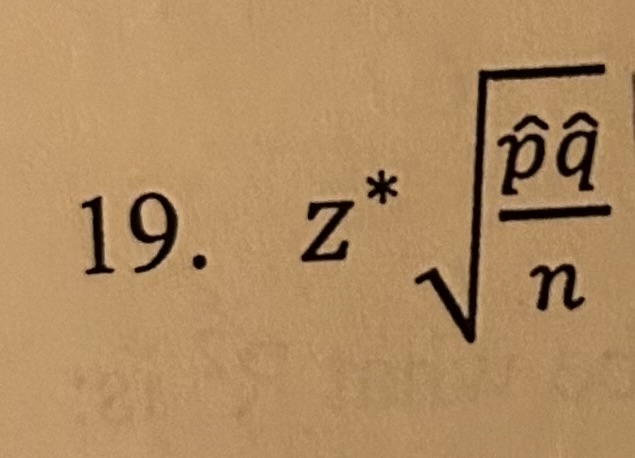
z* p̂q/n
Margin of error for 1-Prop Z-Interval
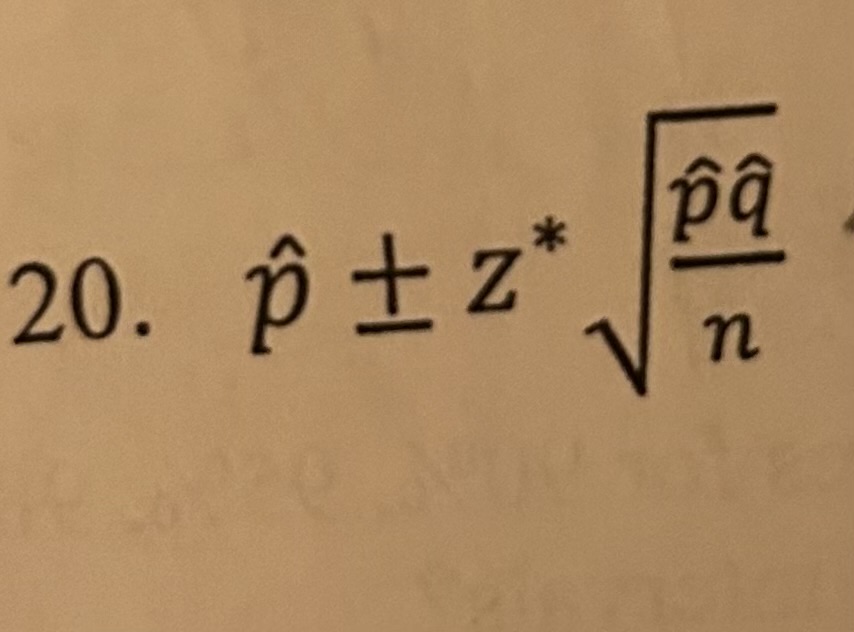
p̂ +- z* p̂q/n
1 Prop Z-Interval
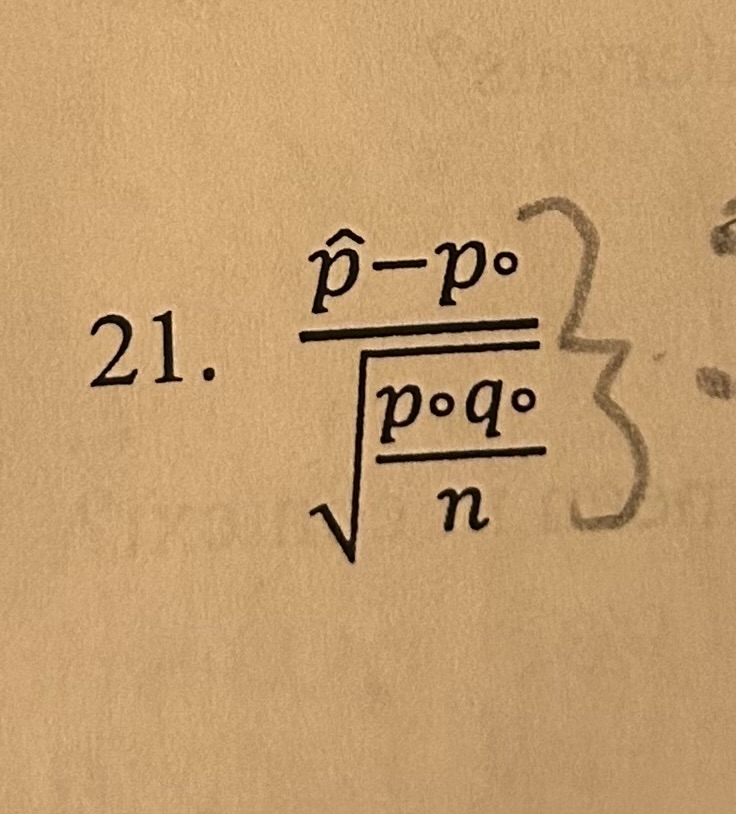
test distribution for z distribution
z-value in 1 Prop Z test
(value-mean)/SD
z-score
How do you find outliers in a set of data? What is the formula for IQR?
IQR: Q3-Q1
lower: Q1- 1.5IQR
upper: Q3 + 1.5IQR
What is the most important difference between an SRS and a stratified random sample?
SRS: Every element of population has some probability of being drawn
stratified: creates homogeneous groups then takes SRS
How do you tell the difference between an observational study and an experiment?
observational: observes only; no treatment
experiment: treatment
Template answer to describe the slope of the LSRL in context:
For every 1 unit increase in x-variable, the y is predicted to increase/decrease according to slope
Template answer to describe the y-intercept of LSRL in context:
The predicted value of y when x-variable = 0
Template answer to describe what R² is:
The % of variability of y that can be explained by the LSRL relating x and y
What are the Z-scores for 90%, 95%, 98%, and 99% confidence intervals
90%: 1.645 98%: 2.326
95%: 1.96 99%: 2.576
What does the p-value mean in context?
Probability the observed statistic or one more extreme will happen by natural variation is true
Conditions for T-Tests:
random
10%
Large Enough (n>30 or graph)
Conditions for z-tests:
random
10%
Large Enough (S/F)
Conditions for x² tests:
What is a Type I error and a Type II error?
Type I: reject null when true
Type II: fail to reject null when false
What is meant by the Power of the Test?
Probability of correctly rejecting null when false
What are the 2 most effective ways to increase the power of a test?
-Increase sample size
- Increase significance level (alpha)
Formulas for ALL confidence intervals
statistic +- critical value x (SX of statistic)
Formulas to find the test statistic for ALL tests:
(statistic-parameter)/(SX of statistic)
What is ALWAYS the null hypothesis for a matched pairs t-test?
Mdiff= 0
What are the null hypotheses for the 3 different x² tests?
GOF: Ho= sample data match population
Independence: Ho= 2 variables are independent
Homogeneity: Ho= There is NO difference in group proportions