Marine Bio Assessment #3 (copy)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/106
Last updated 1:25 PM on 12/6/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
107 Terms
1
New cards
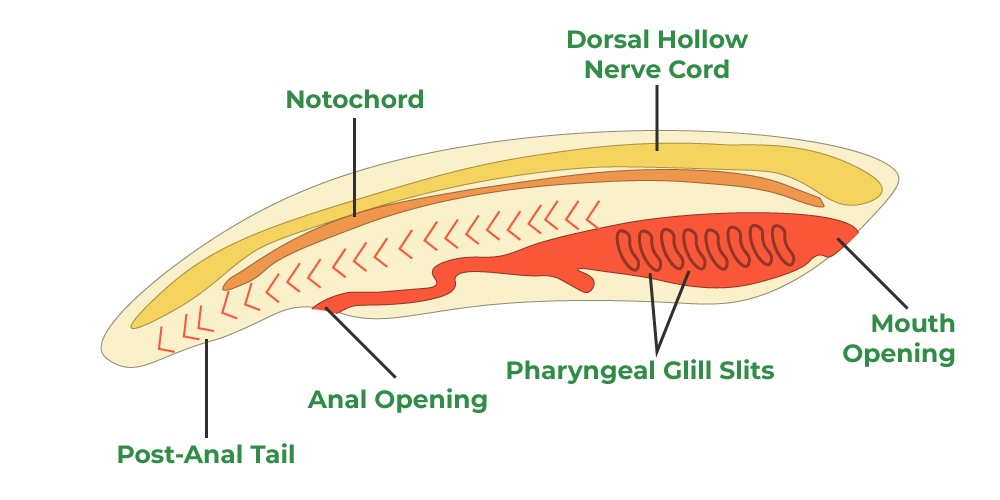
Chordata (Phylum)
Dorsal Nerve Cord
Gill Slits
Notochord
Ex: Amphioxus, Salp, Tunicate, Larvacean
Gill Slits
Notochord
Ex: Amphioxus, Salp, Tunicate, Larvacean
2
New cards
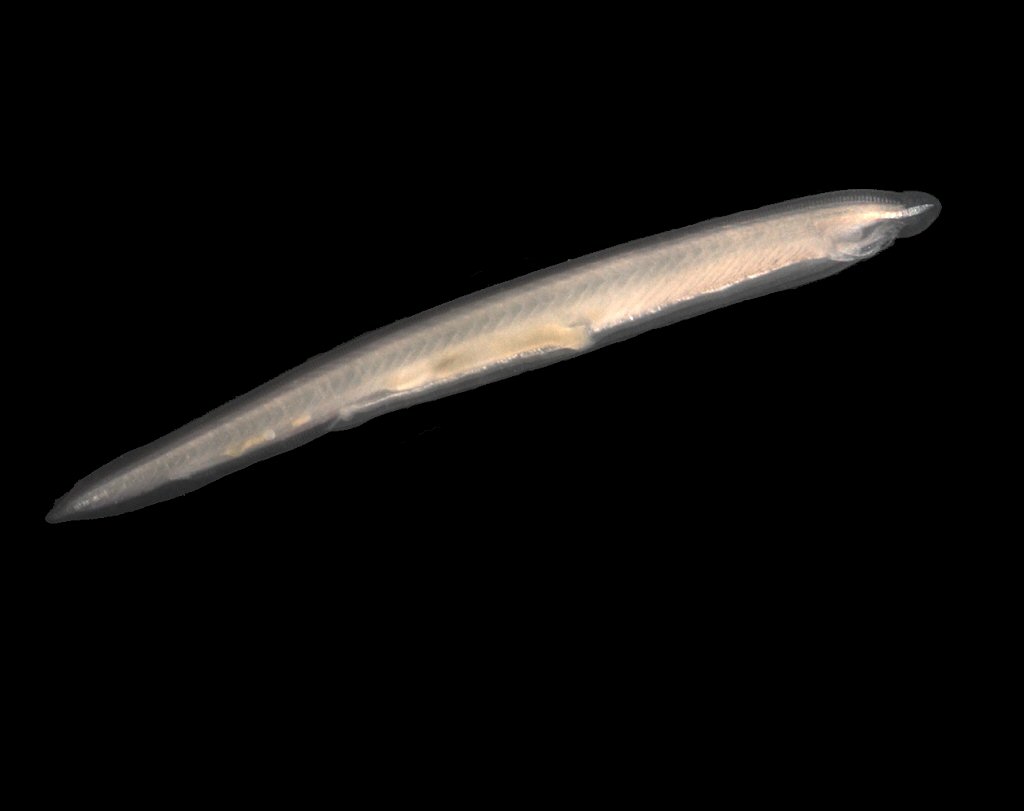
Amphioxus
P: Chordata
SubP: Cephalochordata
C: Leptocardii
SubP: Cephalochordata
C: Leptocardii

3
New cards
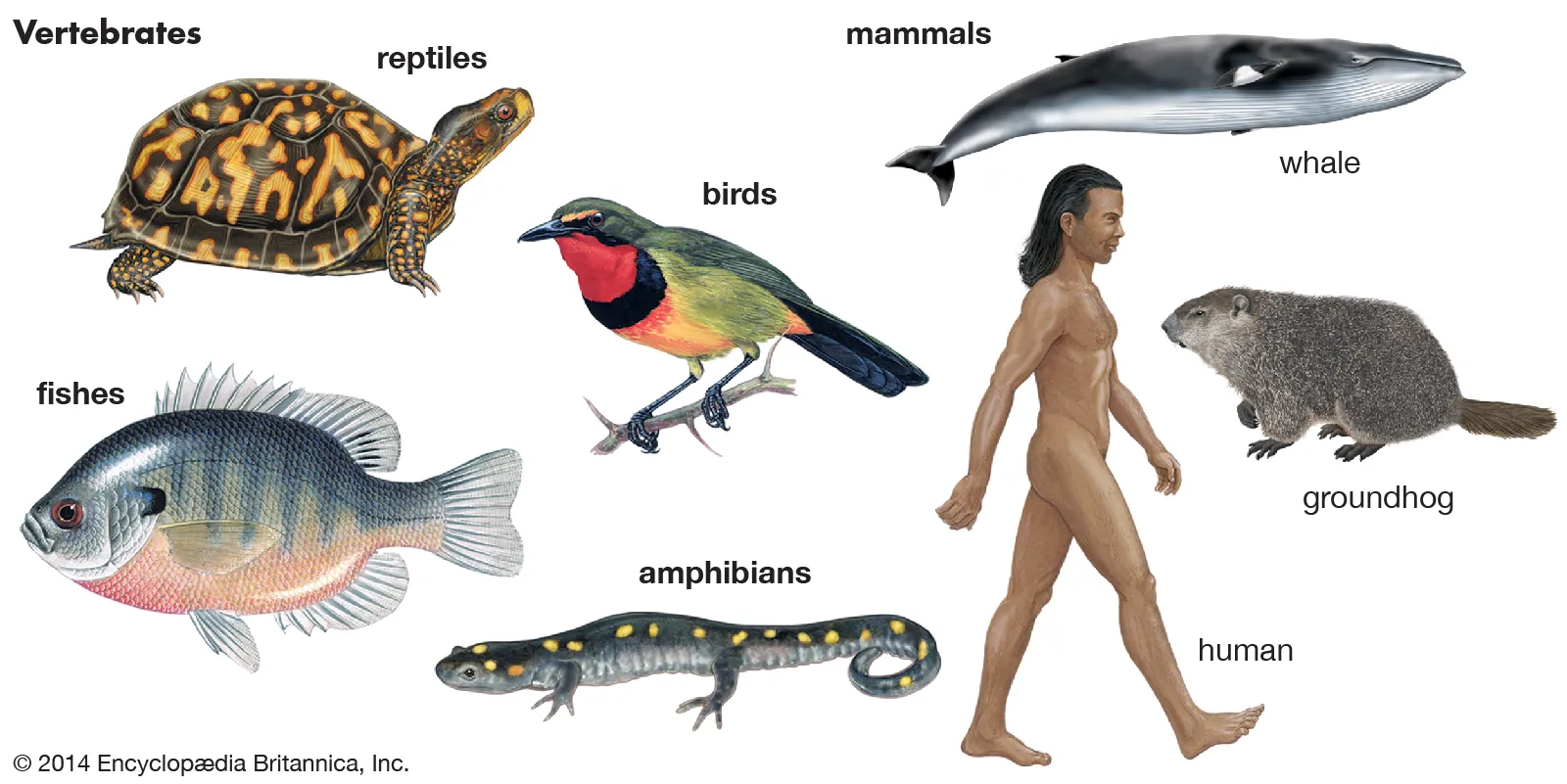
Examples Vertebrata (SubPhylum)
Mammals, reptiles, birds, amphibians, fish
4
New cards
What do lizards have
earflaps and eyelids

5
New cards
What don't snakes have?
earflaps and eyelids

6
New cards
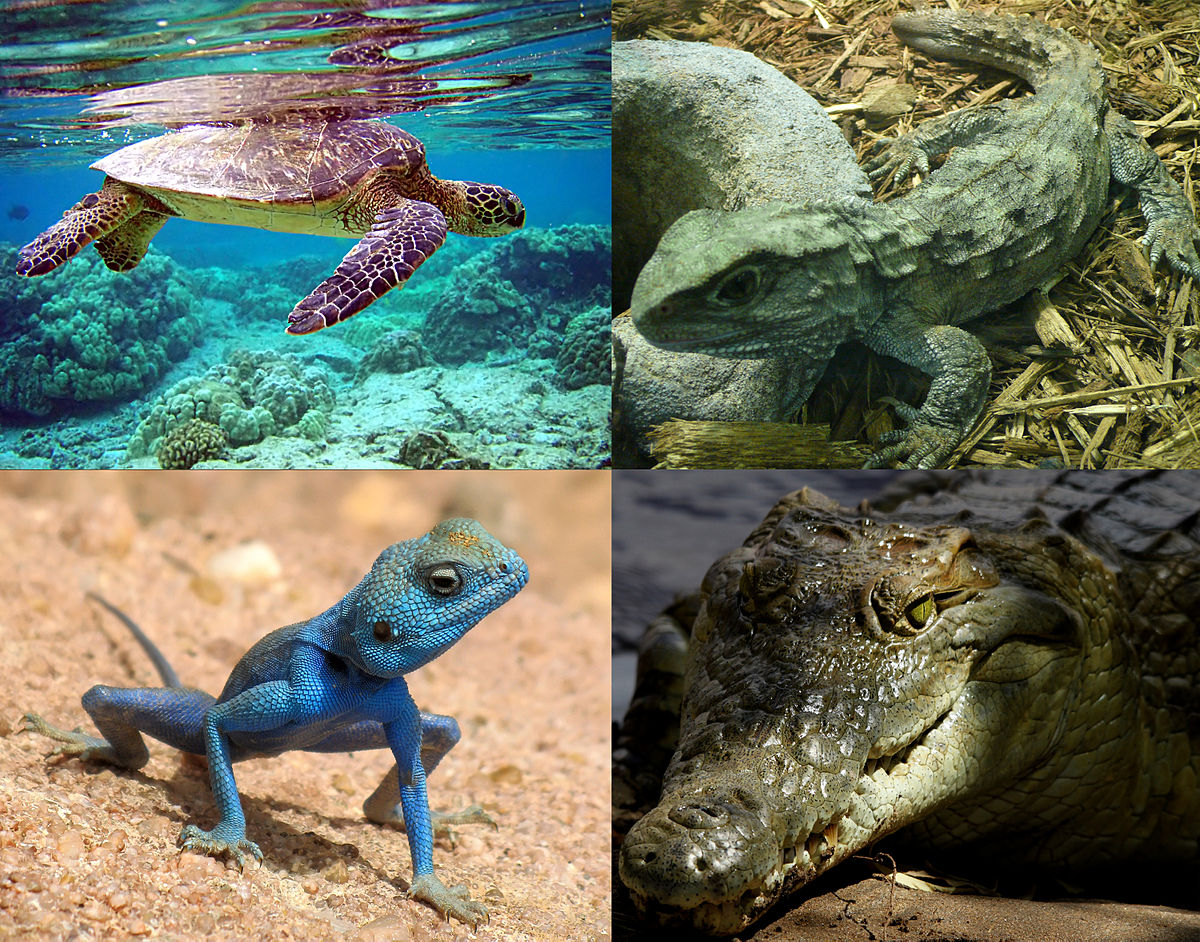
Reptilia (Class)
Cold Blooded
Internal fertilization (produces eggs)
Breath air via lungs
Order includes Squamata, Chelonia, Crocodilia
Internal fertilization (produces eggs)
Breath air via lungs
Order includes Squamata, Chelonia, Crocodilia

7
New cards
Squamata (Order)
Lizards, Snakes

8
New cards
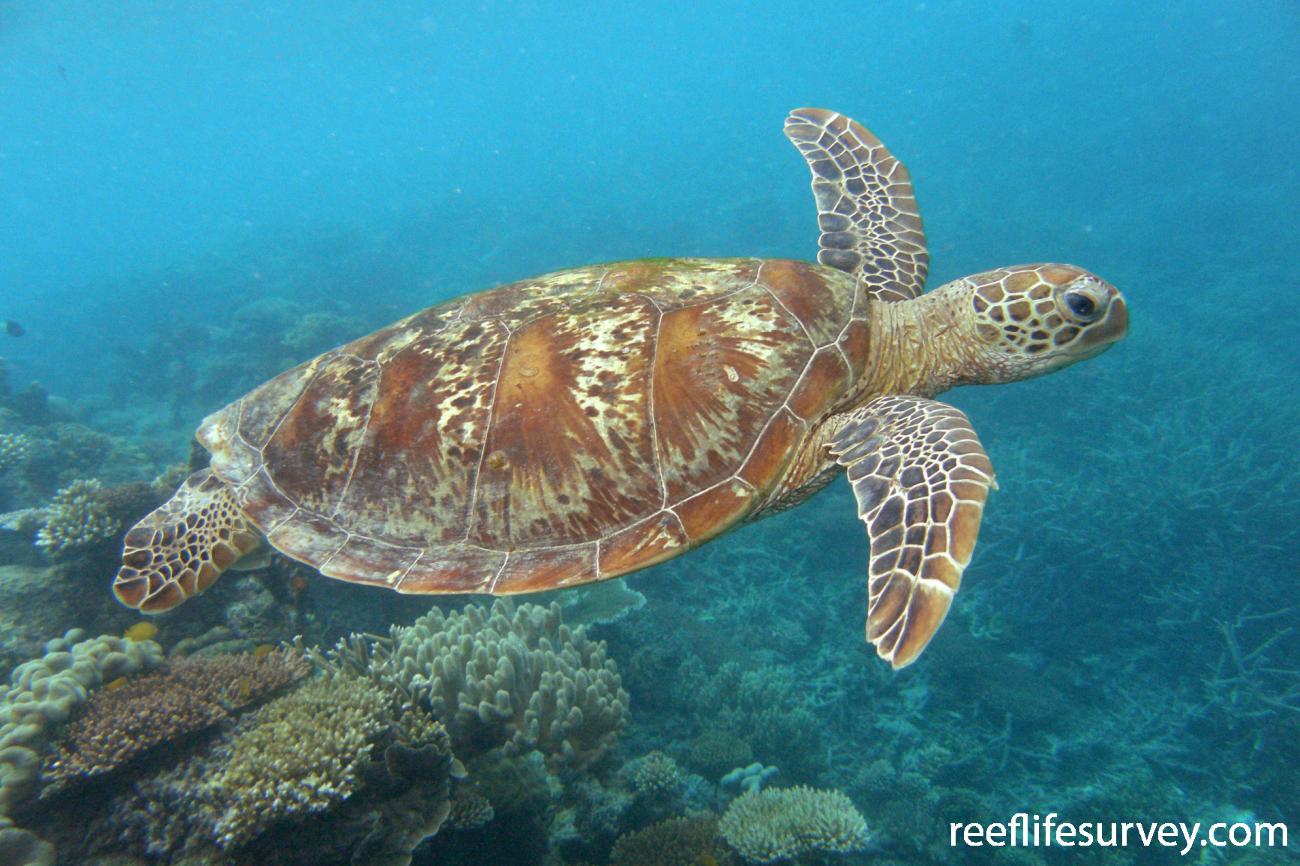
Chelonia (Order)
Turtles
Sea turtles
Tortoises
Sea turtles
Tortoises

9
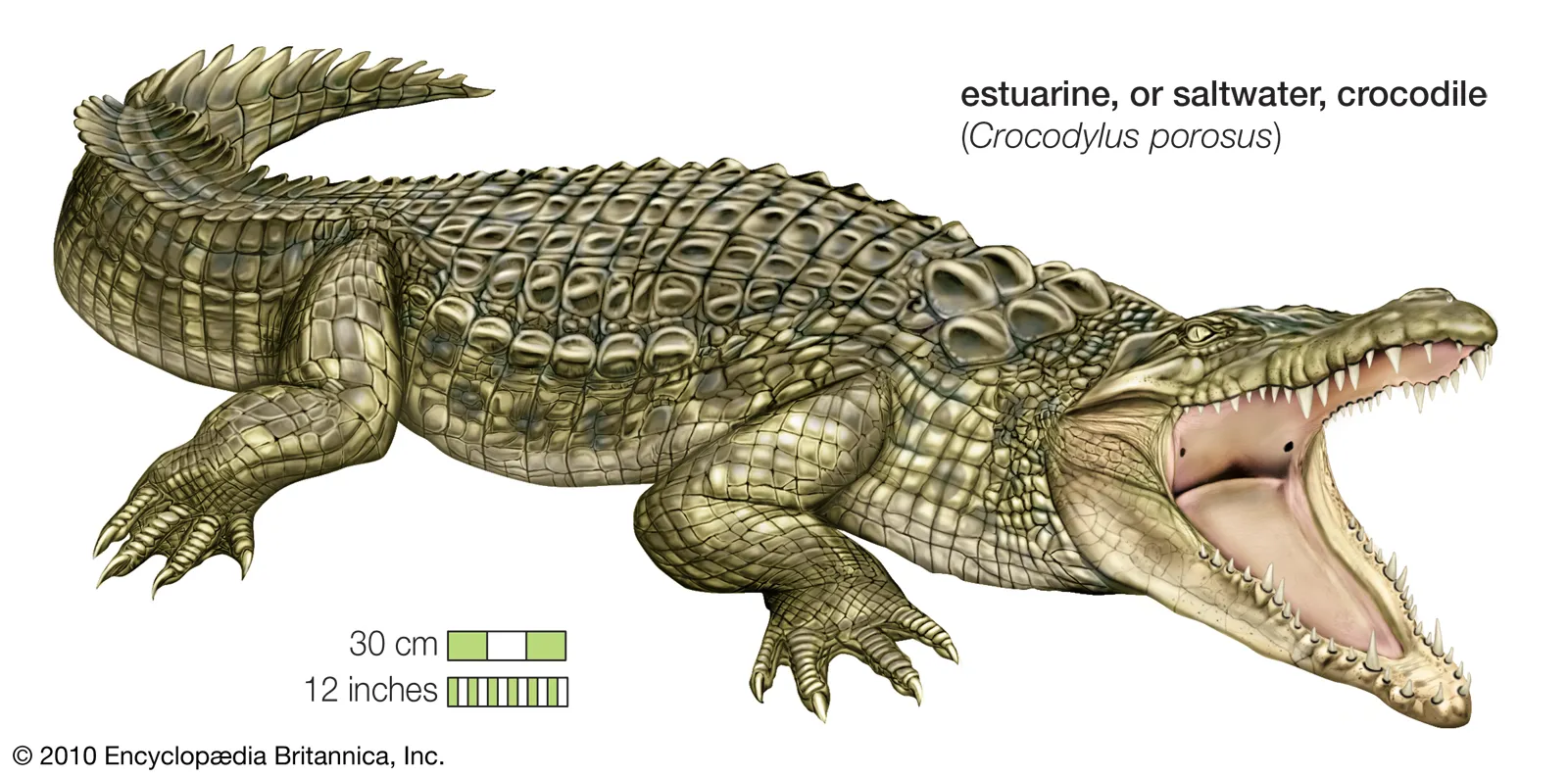
New cards
Orocodilia (Order)
Crocodiles
Alligators
Caimen
Alligators
Caimen
10
New cards
Turtles
Webbing, semi aquatic, fresh water, attached to their shell
11
New cards
Sea turtles
Flippers, have a backbone

12
New cards
Tortoises
terrestrial, much longer life span, more of a dome shell
13
New cards
Crocodiles
Terrestrial
V-Shaped snout
V-Shaped snout
14
New cards
Alligators
U-Shaped Snout
Webbed feet
Aquatic
Webbed feet
Aquatic
15
New cards
Invertebrate (Noodle the pug)
No bones
16
New cards
Vertebrate
Bones
Cartilaginous
Cartilaginous
17
New cards
Pharyngeal (Gill) Slits (CHORDATES)
Series of openings between the pharynx and outside of chordate animals.
18
New cards
Notochord
Flexible, rod-like structire made of cartilage shown as dark-colored line inside model of simple marine animals
19
New cards
Notochord examples
Cnidaria, mollusks, porifera, platyhelminthes, arthropoda, chordata, analid, nematoda, echnomerte
20
New cards
Kingdoms made of eukaryotic cells
fungi, animalia, protista, plantae
21
New cards
Example of medusa
jellyfish
22
New cards
Example of a polyp
sea anemone
23
New cards
What makes coral unique?
Stinging cells
24
New cards
What are stinging cells called?
nematocytes
25
New cards
2 examples of magnoliophytas
mangroves and seagrass
26
New cards
What animals are composed only of cells?
Poriferas
27
New cards
Give an example of a porifera
Sponge
28
New cards
What are some phylums of protista?
Foraminifera, Rhodophyta, pyrrophyta, euglenophyta, chrysophyta, radiozoa, bacillia, haptophyota
29
New cards
Name what plants, animals, and fungi are in the ocean
Plants - producers
Animals - consumers
Fungi - decomposers
Animals - consumers
Fungi - decomposers
30
New cards
Classify Inkfish/Cephalopod
D: eukarya
K: animalia
P: mollusca
C: cephalopod
K: animalia
P: mollusca
C: cephalopod
31
New cards
what is special about cephalopods?
they have jet propulsion and no shell
32
New cards
What is special about bivalvia?
they have muscular feet and 2 shelled
33
New cards
What is special about gastropoda
Radula - sawlike tongue and 1 shell
34
New cards
Example of Gastropoda
whelks, conch, abalone
35
New cards
Examples of cephalopods
Squid, octopods
36
New cards
Examples of bivalvia
clams, scallops, oysters
37
New cards
What is special about polyplacophora and an example?
Plated shell
38
New cards
Example is chitons
39
New cards
Name the 4 classes of mollusca
Bivalvia, Gastropoda, cephalopod, polyplacophora
40
New cards
3 examples of archaebacteria
Halophiles, methanogens, thermophiles
41
New cards
What are platyhimenthes?
Planaira
42
New cards
Prokaryotes
No nucleus
43
New cards
Eukaryotes
Yes nucleus
44
New cards
Phyla of animalia
cnidaria, porifera, Platyhelminthes
45
New cards
Classify cnidaria
D: eukarya
K: animalia
P: cnidaria
K: animalia
P: cnidaria
46
New cards
What does medusa look like
jellyfish
47
New cards
What does polyp look like
bumps growing from the inside going out
48
New cards
Examples of cnidaria
coral, sea anemone, jellyfish
49
New cards
What type of symmetry do cnidaria have?
radial symmetry
50
New cards
Classify Magnoliophyta
D: eukarya
K: plantae
P: magnoliophyta
K: plantae
P: magnoliophyta
51
New cards
Examples of magnoliophyta
Mangroves, sea grass
52
New cards
Haptophyta
coccolithophores
53
New cards
Dinoflagella or fire algae
Pyrophyta
54
New cards
Bacillariophyta
diatoms
55
New cards
Yellow/green algae
xanthophyta
56
New cards
Golden algae
chrysophyta
57
New cards
Euglena
Euglenophyta
58
New cards
Phyla for plants
magnoliophyta
59
New cards
Phyla of Sponge
porifera
60
New cards
Kingdom of sponge
Animalia
61
New cards
Phyla of coral
cnidaria
62
New cards
Phyla of shelled
mollusks
63
New cards
What mollusk has a plated shell
polyplacophora
64
New cards
Order of classification
Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genius, Species
65
New cards
3 domains of life
Eubacteria, Archaea, Eukarya
66
New cards
What makes archaea unique?
They are found in extreme environments and are very old.
67
New cards
What are the 4 kingdoms of Eukarya?
Protista, Fungi, Plantae, Animalia
68
New cards
What is a scientific name called?
binomial nomenclature
69
New cards
the study of underwater topography
bathymetry
70
New cards
3 bacteria shapes
cocci, bacilli, spirilla
71
New cards
Describes an organism that remains attached to a surface for its entire life and does not move. (coral)
Sessile
72
New cards
mobile
moving or able to move from place to place
73
New cards
2 examples of protists
amoeba, plankton
74
New cards
Euarcheota
phylum of archaea, includes methanogens
75
New cards
Monera
used to be the kingdom of bacteria, now split up
76
New cards
Crenarchaeota
One of the two major divisions of Archaea, containing sulfur thermophiles, live in hydrothermal vents
77
New cards
Halophiles
"salt-loving" archaea that live in environments that have very high salt concentrations
78
New cards
Methanogens
A group of archaebacteria that produce methane as a by product of their metabolism.
79
New cards
Korarchaeota
a phylum of Archaea
80
New cards
Thermoplasmata
Lives in extremely acidic environments.
81
New cards
nitrososphaerota
inhabits hot springs and acidic environments
82
New cards
Planktos
wanderer or drifter
83
New cards
What are drifting plankton called?
zooplankton
84
New cards
zooplankton
animal constituent of plankton; mainly small crustaceans and fish larvae
85
New cards
Some examples of zooplankton
Comb jellies, krill
86
New cards
What is Cilia?
short, numerous projections that look like hairs, they are used for movement. (only on eukaryotes)
87
New cards
What are pili?
short, hairlike protein structures on the surface of some bacteria
88
New cards
Phytoplankton
photosynthetic algae found near the surface of the ocean. Plant like.
89
New cards
How much of the biomass in the ocean is plankton
95%
90
New cards
What are the classifications of plankton
phyto- or zoo-, holo-(permanent) or mero-(temporary, ex. baby animal), microscopic or macroscopic.
91
New cards
What is seaweed?
multicellular algae- not a plant
92
New cards
Green algae
Chlorophyta; closely related to true plants.
93
New cards
Red algae
- majority are multicellular organism
- primarily live in warm tropical waters
- Rhodophyta
- primarily live in warm tropical waters
- Rhodophyta
94
New cards
Brown algae
Phaeophyta, Kelp
95
New cards
forams
porous calcium carbonate shells (tests), unicellular in sand/sediment of water bodies
96
New cards
yellow-green algae
Xanthophyta, a group of algae that includes the diatoms, not seaweed
97
New cards
Euglena
Eulenophyta, Unicellular organism; moves using its flagella; asexual reproduction; have chloroplasts to absorb sunlight
98
New cards
Fire algae
Dinoflagella, pyrophyta, Emits a light similar to that of a firefly
99
New cards
Golden Algae
chrysophyta, use flagella, swim with plankton
100
New cards
Halptophyta
coccolithophores