Edexcel IGCSE Physics - (Unit 7) Radioactivity
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Units for Radioactivity (Topic 7)
becquerel, centimeter, hour, minute, second (skip as necessary)
Atomic number
The number of protons an element has.
Relative atomic mass
The mass of an element's atom relative to one twelfth of carbon-12.
Isotope
An atom with the same number of protons (same element) but a different number of neutrons.
(Types of) ionizing radiation
Alpha (α), Beta (β), Gamma (γ)
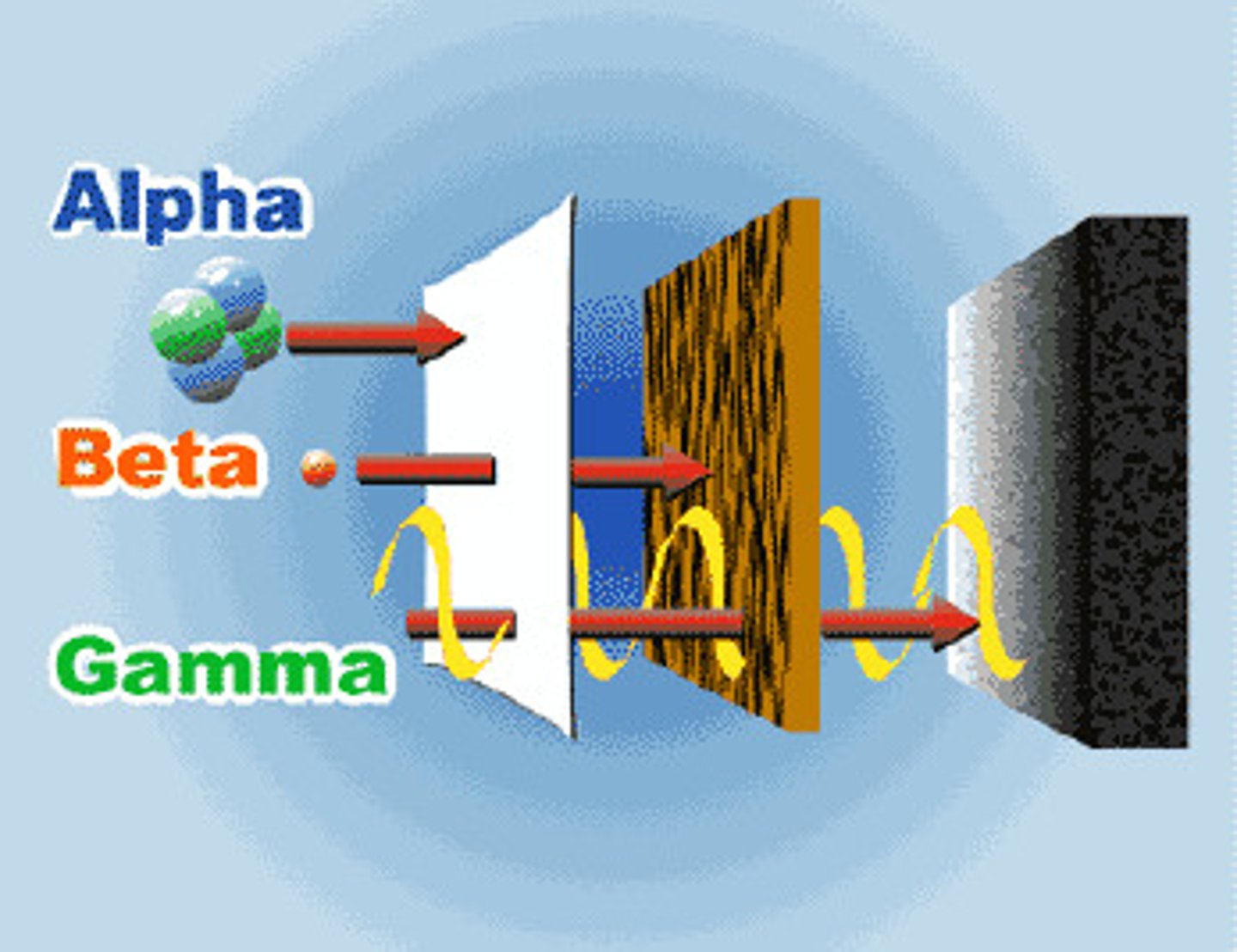
Alpha Radiation
2 emitted protons and neutrons, +2 charge, mass of 4, <5cm distance, stopped by paper, highly ionizing
Beta Radiation
Emitted when a neutron becomes a proton, -1 charge, mass of about 0, 1m distance, stopped by aluminum, low ionizing power
Gamma Radiation
A high energy electromagnetic wave, no charge, no mass, >1km distance, stopped by lead/concrete, very low ionizing power
Ion
A (positively or negatively) charged atom.
Ionization
The process where an atom becomes an ion by gaining or losing electrons.
Unstable isotopes are...
radioactive isotopes (radioisotopes)
Investigating penetration of ionizing radiation (practical)
Block a source of each type of ionizing radiation with paper, lead, and concrete; detect radiation with GM tube; wait for count rate to plummet.
Alpha Radiation's Effect on a Nucleus
2 protons and 2 neutrons are lost; mass number -4, atomic number -2
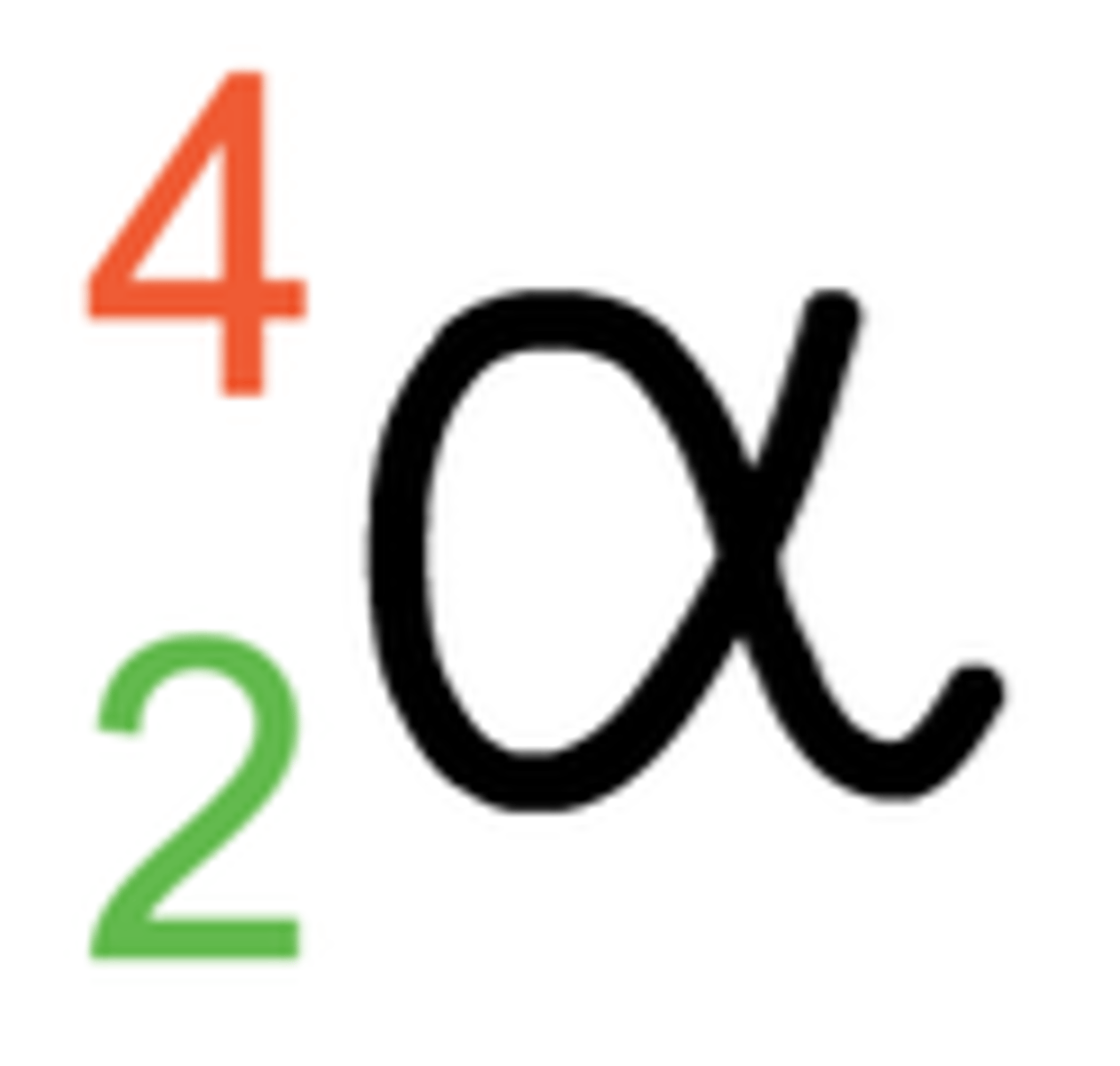
Beta Radiation's Effect on a Nucleus
1 neutron is converted to an electron and a proton; atomic number + 1 (no mass change)

Gamma Radiation's Effect on a Nucleus
Energy is lost from an atom in the form of an electromagnetic wave; mass and atomic numbers go unchanged
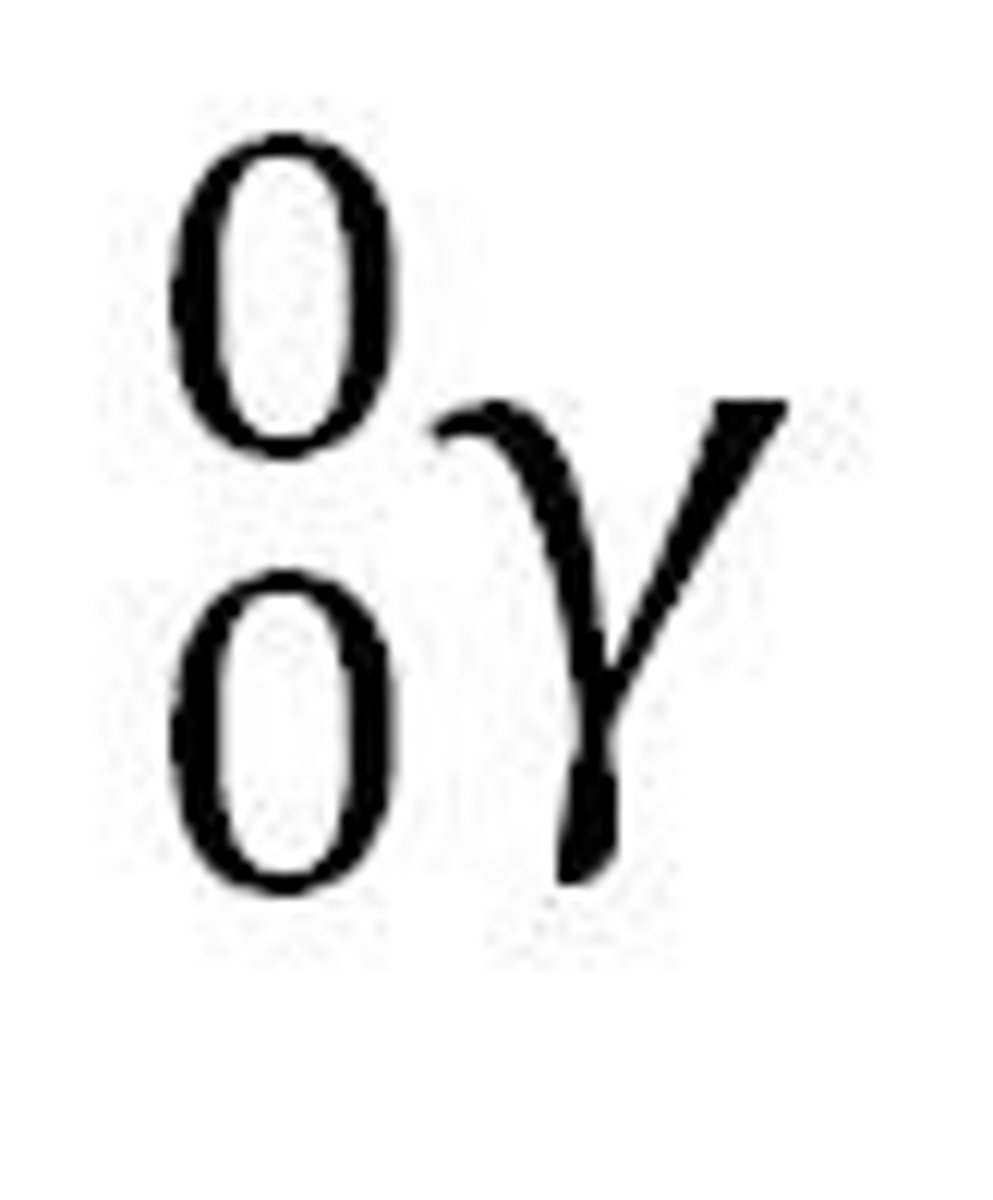
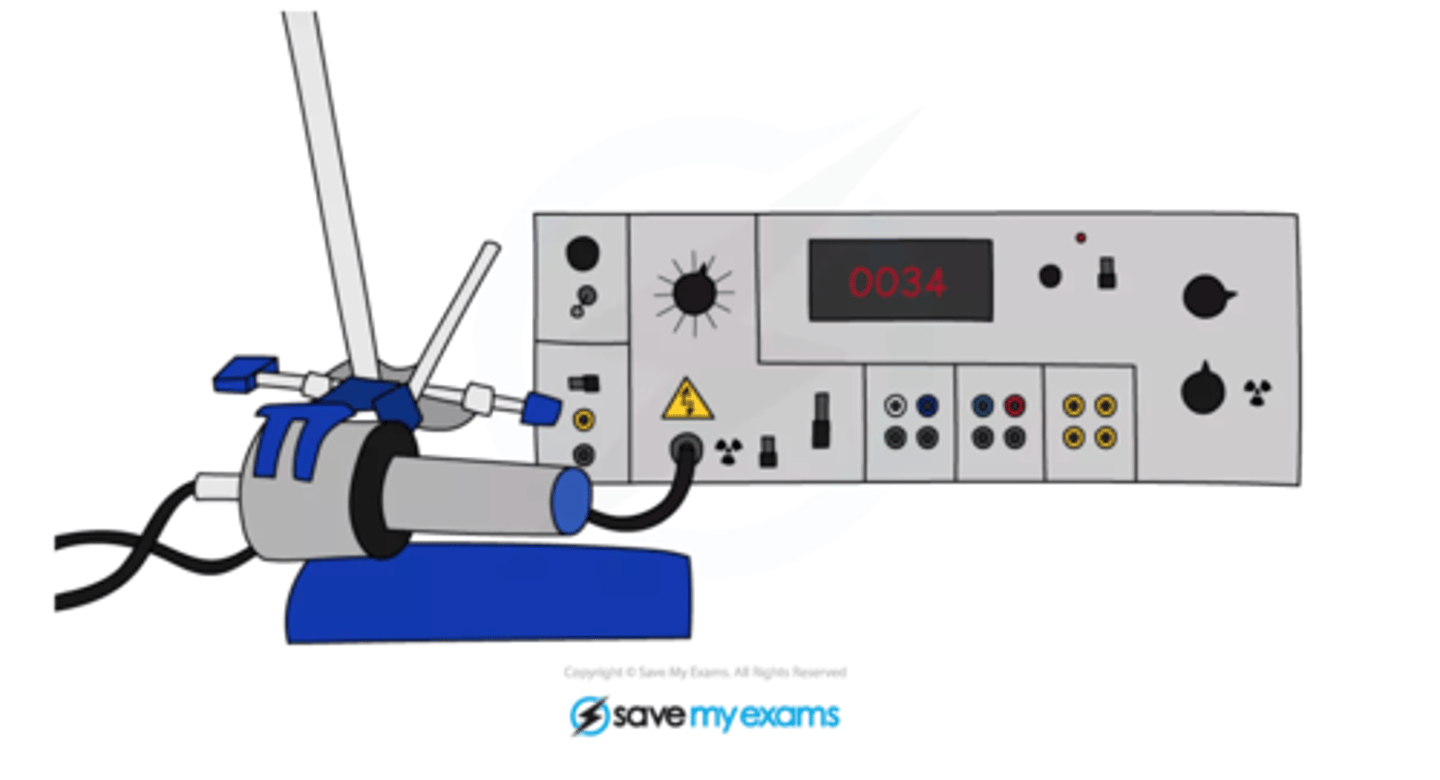
Geiger-Müller (GM) tube
A particle detector that measures radioactivity with a photographic film.
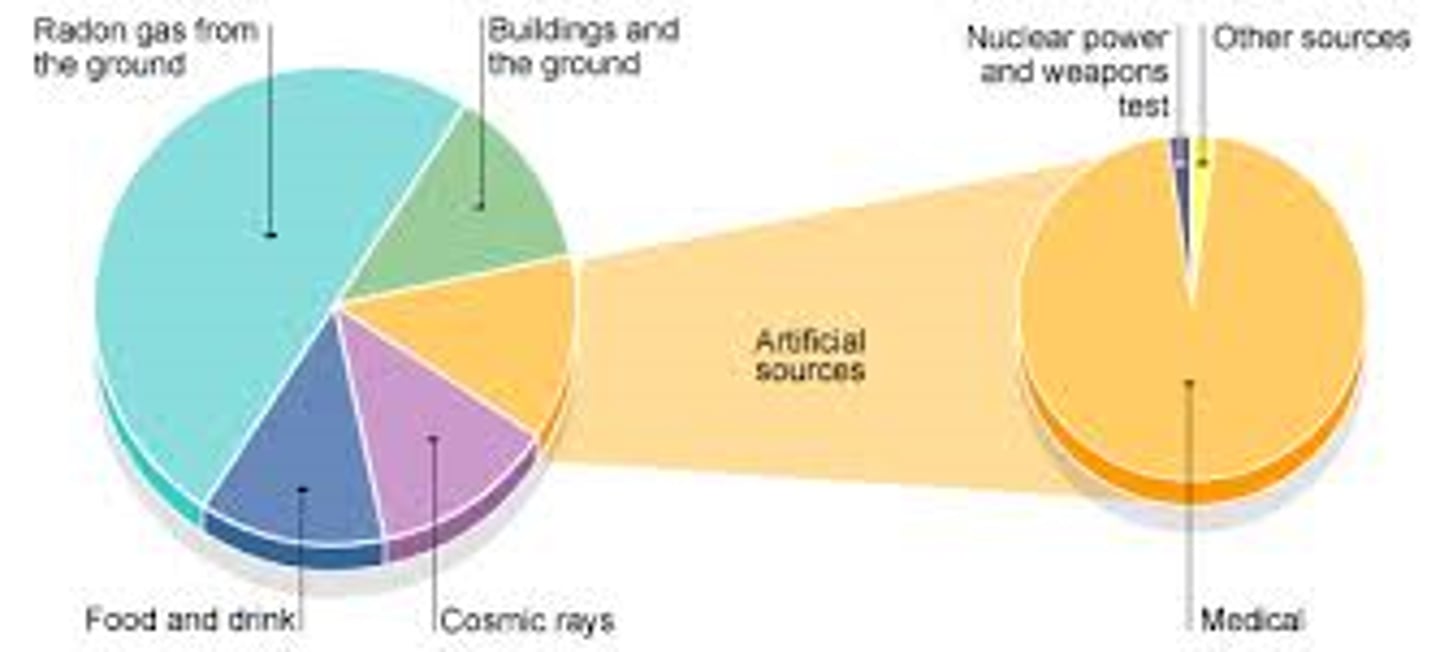
Sources of background radiation
Primarily radon gas (50%), cosmic rays, food and drink, buildings and ground, medical equipment, nuclear industry
Activity trend from a radioactive source
It decreases over time and is measured in Becquerels (Bq)
Half-life
The average time taken for an isotope's count rate (or nuclei/mass) in a sample to halve.
Home smoke detectors
Emits Americium-241 (a weak source of alpha radiation) in its casing with oxygen and nitrogen which are ionized and conductive. Smoke will break the circuit between the particles and sound the alarm.
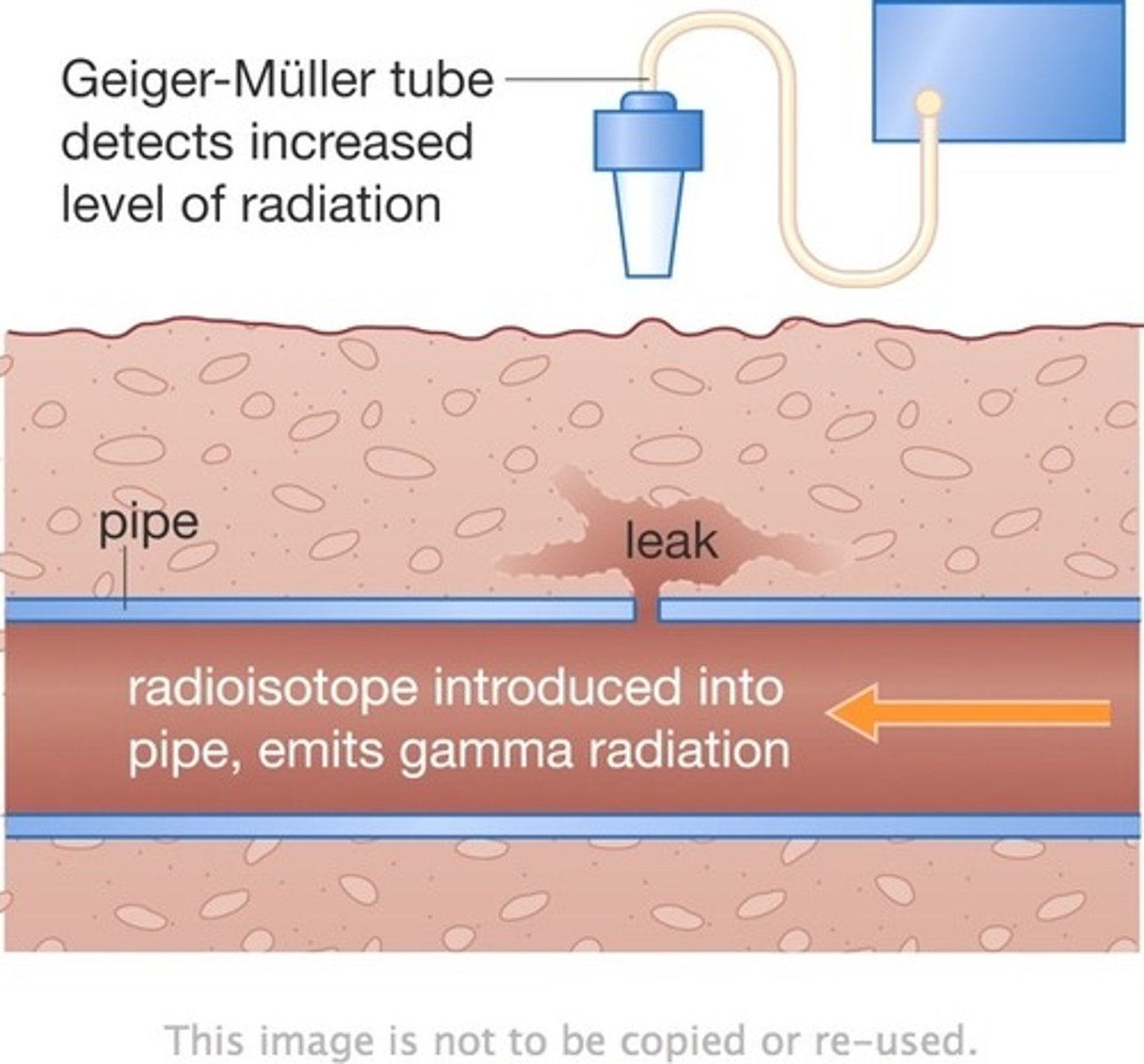
Radioactive Tracers
A radioisotope is added to the body or pipe for use as a tracer. The radiation penetrates objects and can leave the body or pipe. The escaping radiation is detected with a Geiger-Müller counter.
Food/Medical Product Sterilization
Low doses of gamma rays ionize the product - this destroys and prevents regrowth of organisms.
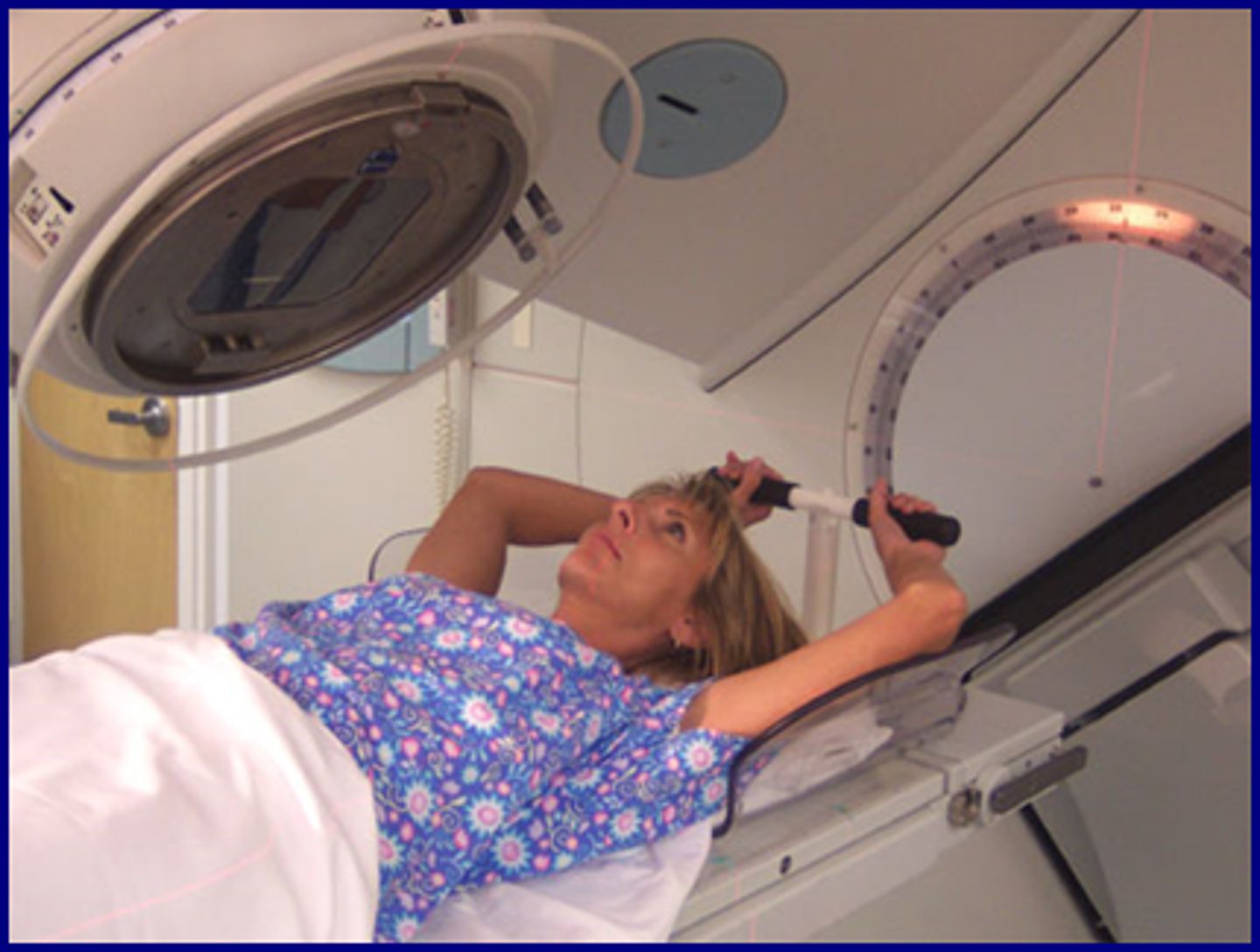
Radiotherapy
Intense beams of gamma rays destroy cells in the body. Whilst cancer cells can't repair themselves, healthy cells can. Dosages must be correct; too little won't stop the cells spreading, and too much will damage more healthy cells.
Measuring Paper Thickness
Radiation sources emit radiation to both sides of a paper roll. Machines are calibrated to produce specific amounts of radiation - thickness is signaled by the volume of radiation penetrating (which should be consistent.)
Carbon Dating
A radioisotope that every living organism has, which is used to measure one's age as it has a large half-life of 5730 years.
Irradiation
Occurs when an object is exposed to foreign source of radiation: doesn't cause the object to become radioactive, can be blocked with shielding, stops when source is removed.
Contamination
Occurs if radioactive source is in or on the object: will be radioactive whilst the source is on or in it, radiation cannot be blocked from it, difficult to remove all the contamination.
Dangers of Ionizing Radiation
They can damage cells and tissues, cause mutations in living organisms, and contaminate our environment. Adequate shielding can stop a source from affecting the environment.
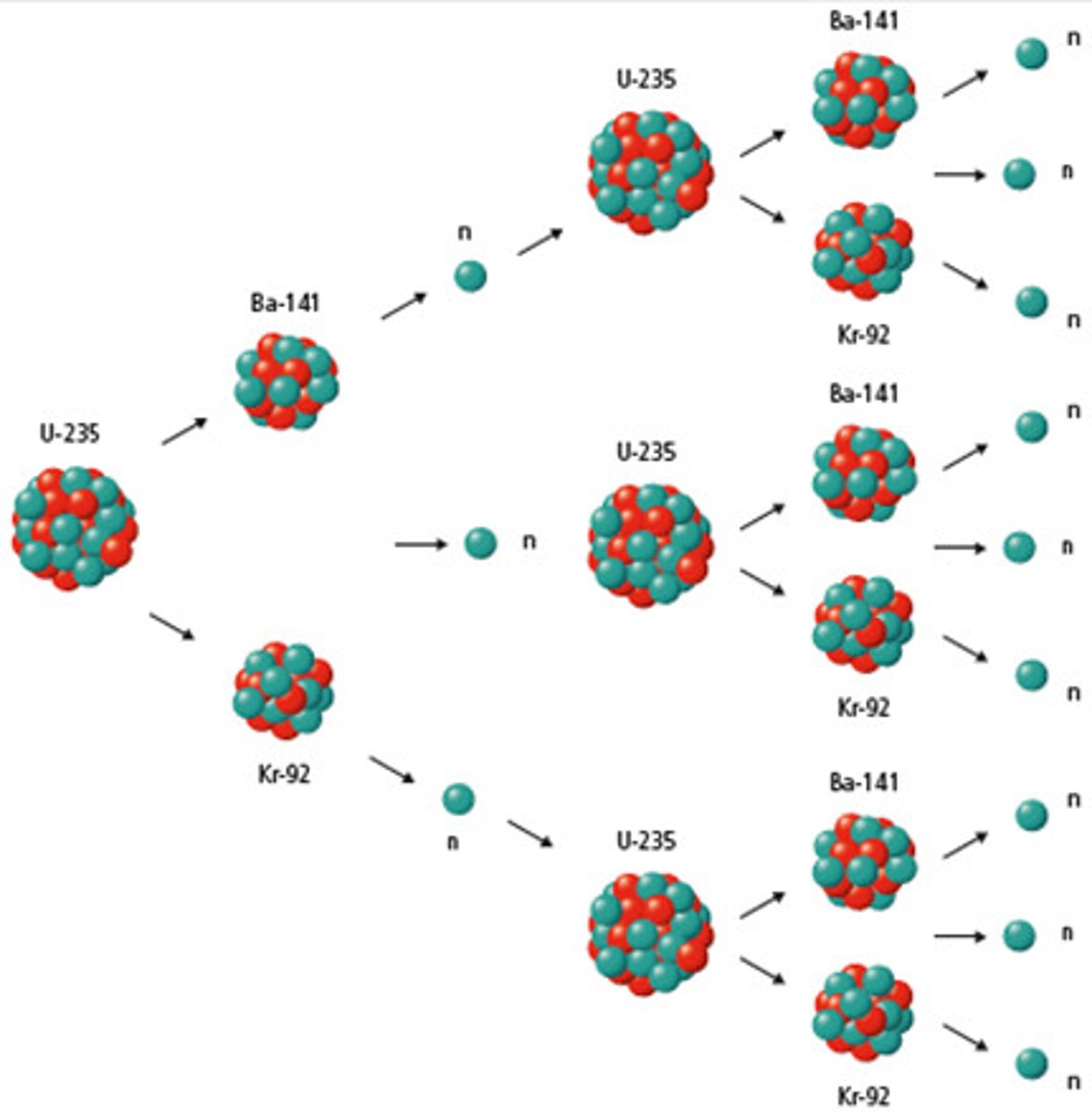
Fission
A nuclear reaction in which a large radioisotope splits into smaller nuclei and neutrons, generating large amounts of energy.
Chain Reaction
When neutrons released as a product of a fission reaction collide with other radioisotopes to create more fission reactions.
Fusion
When two small nuclei are joined (fused) to form a larger nucleus, generating large amounts of energy.
Radioactive Decay
When radioisotopes release (heat) energy in the form of radiation.
Uranium-235 Fission Reaction
A neutron is absorbed into a Uranium-235 nucleus, forming the radioisotope Uranium-236. It splits to form two smaller nuclei, three neutrons, and gamma radiation.
Role of control rods
They are inserted and retracted into the core to absorb neutrons, slowing down the rate of reaction.
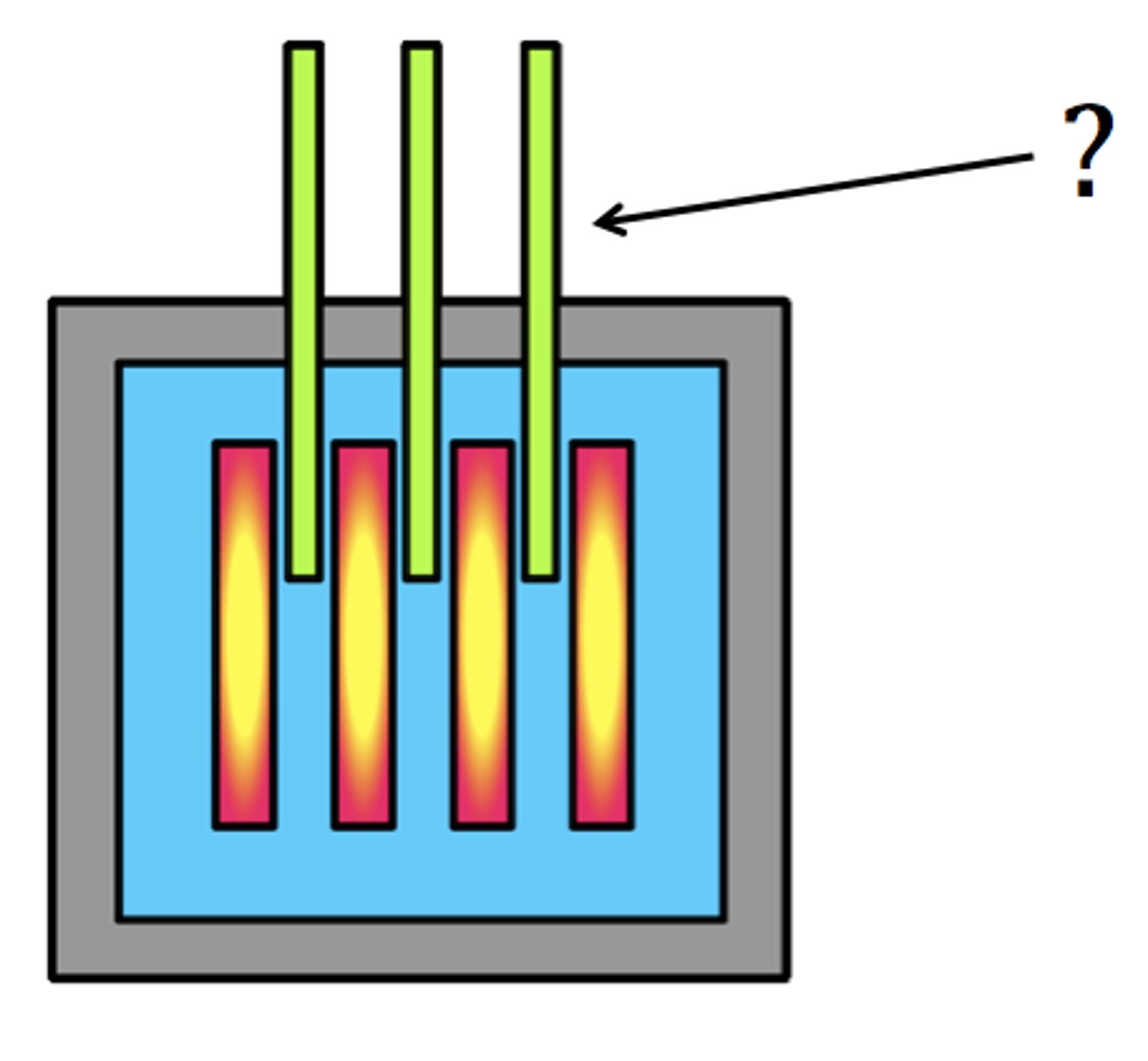
Role of the moderator
A material like graphite absorbs some of the kinetic energy in neutrons which slows them down. Slower neutrons are more easily absorbed by Uranium-235.
Role of shielding around a nuclear reactor
Made of steel and 5-meter-thick concrete to prevent radiation and neutrons escaping.
Fission vs. Fusion
Fission splits larger nuclei into smaller nuclei, and Fusion collides smaller nuclei to form a larger nucleus
Mass decrease in Fusion
Hydrogen isotopes collide at a high speed, which reduces the mass from the smaller nuclei in the reaction.
Energy source for stars and the sun
Fusion is their main energy source; hydrogen undergoes fusion to make helium in our sun.
Temperature requirement for fusion
Must be high to overcome repulsive forces between positively charged nuclei from each isotope.
Pressure requirement for fusion
High levels increase the chance for fusion between nuclei.