Psychology 102 Exam 2 Lecture 1 and 2 IUB
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What is the definition of personality?
Distinctive and enduring ways of thinking, feeling, and behaving, reflecting consistency across time and situations.
What are the three general goals in personality research?
1. Identification and description of major dimensions of personality. 2. Understanding underlying processes in trait variation. 3. Establishing how well traits predict behavior.
What are the two approaches to identifying basic personality dimensions?
1. Idiographic approach: focuses on traits that uniquely describe individuals. 2. Nomothetic approach: focuses on traits shared among individuals, measured on a continuum.
What is Gordon Allport's contribution to personality theory?
He focused on personality characteristics that make people unique, organizing traits into cardinal, central, and secondary traits.
What are cardinal traits?
Traits that have a pervasive influence on an individual's behavior; not everyone has a cardinal trait.
What are central traits?
Broad traits that influence behavior in many situations.
What are secondary traits?
Traits that influence behavior in very specific circumstances.
What is the psychometric approach in personality research?
Focuses on the measurement of traits using statistical methods, such as factor analysis, to identify trait dimensions.
What is factor analysis?
A statistical method used to investigate inter-correlations among ratings to identify clusters of variables that go together.
What are the three major trait dimensions in Eysenck's theory?
Extraversion, Neuroticism, and Psychoticism.

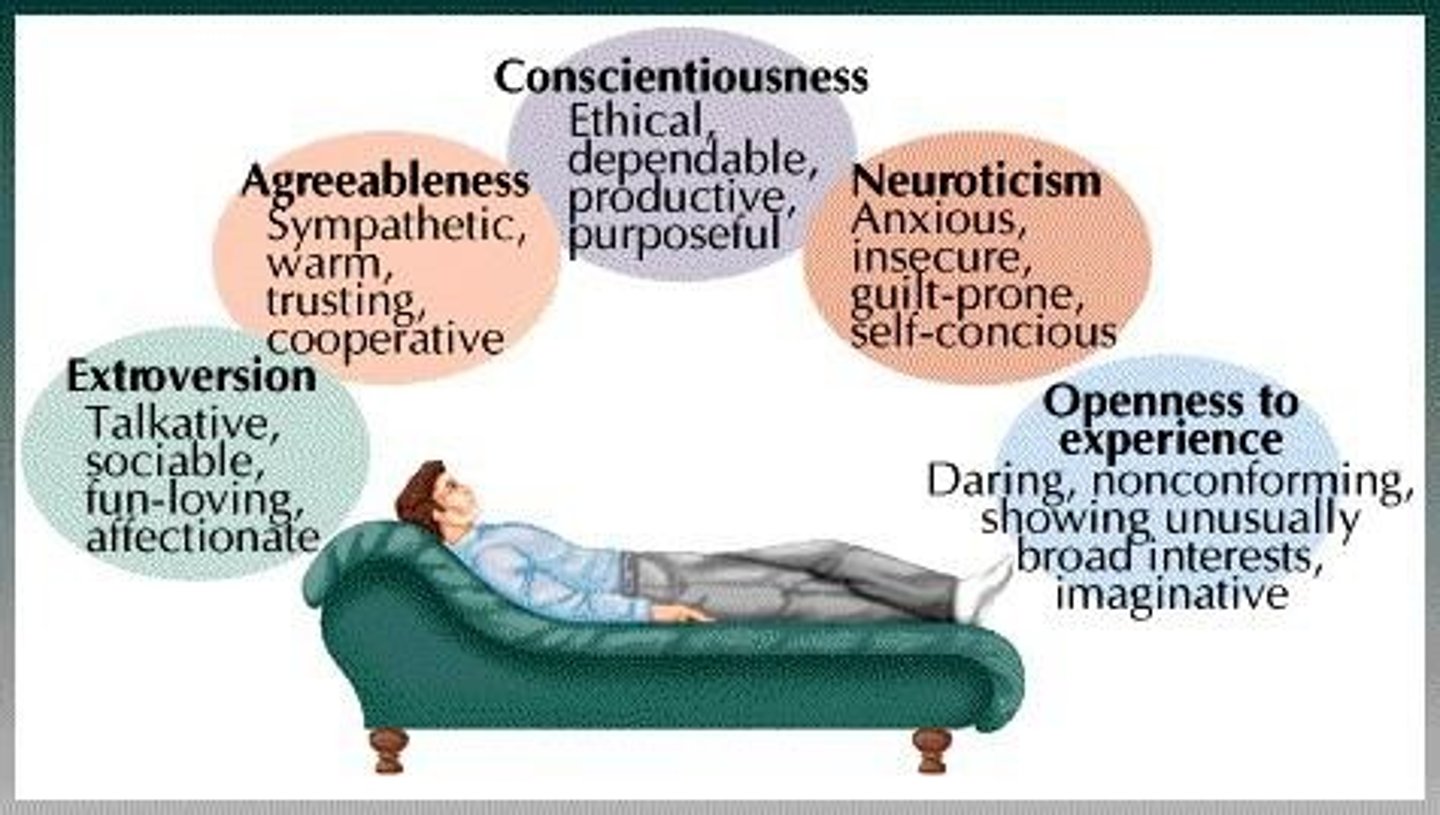
What does the Five Factor Model (Big 5) include?
1. Extraversion 2. Neuroticism 3. Conscientiousness 4. Agreeableness 5. Openness.
What is the significance of reliability and validity in personality measurement?
Reliability refers to the consistency of a measure, while validity assesses whether the model is scientifically tested and accurately reflects personality traits.
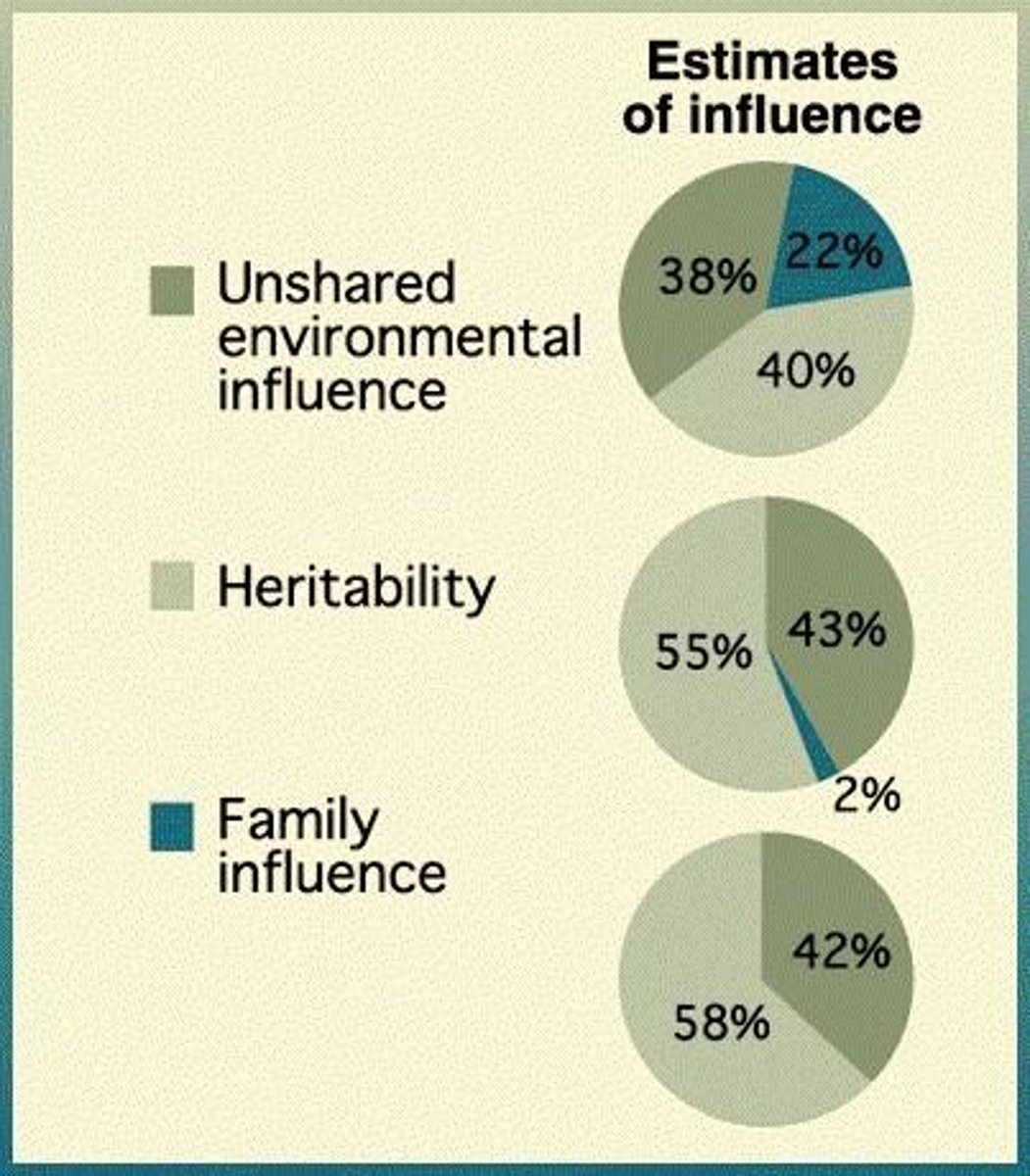
What is the heritability of most personality traits?
The heritability is estimated to be between 0.4 and 0.5, indicating 40-50% genetic influence.
What is the basic equation for personality in behavior genetics?
P = G + E, where P is phenotype, G is genetic influence, and E is environmental influence.
What is the difference between MZ and DZ twins in behavioral genetics?
MZ (monozygotic) twins are identical and share 100% of their genes, while DZ (dizygotic) twins are fraternal and share on average 50% of their genes.
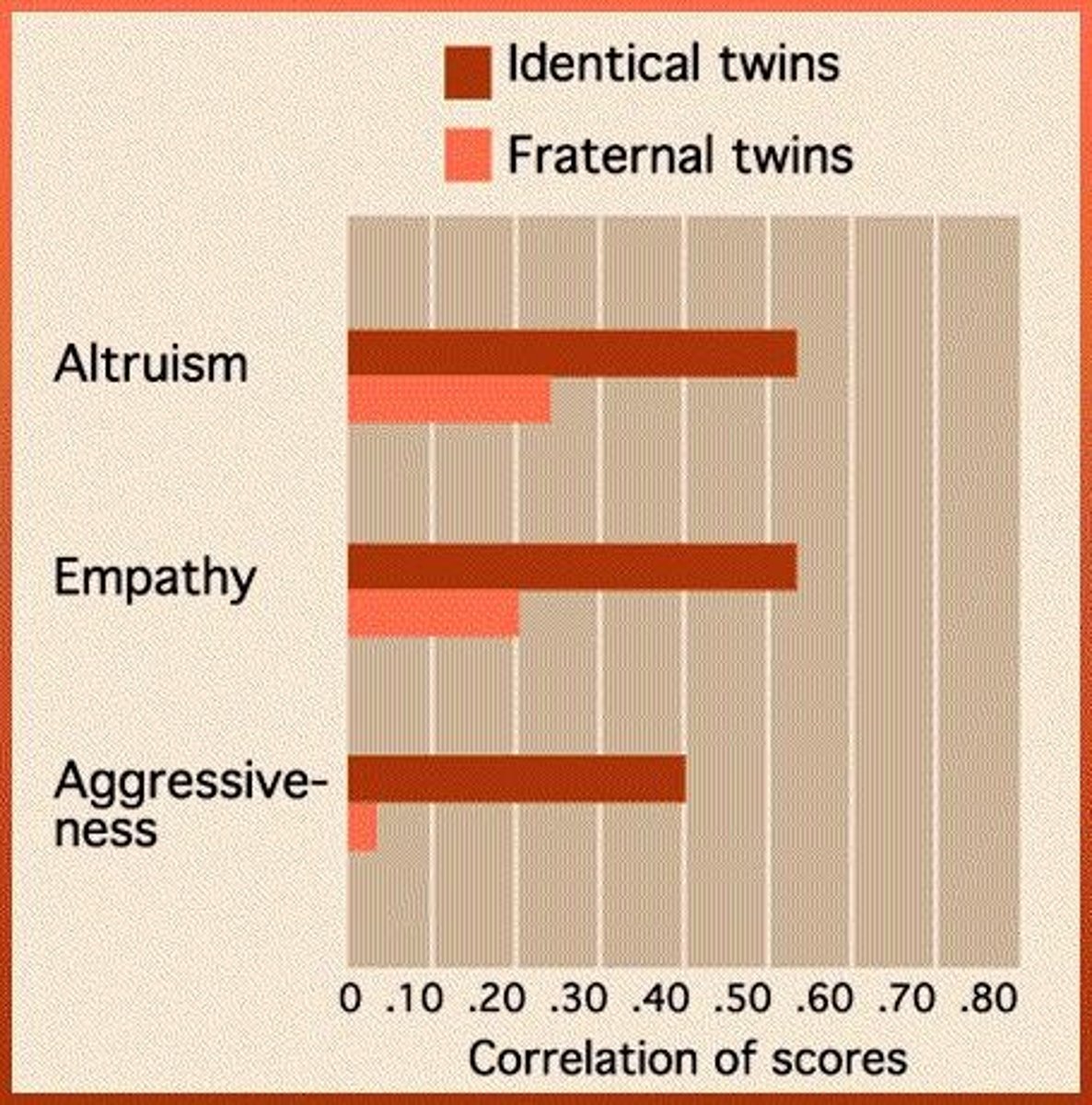
What are shared and non-shared environmental influences?
Shared environment (Es) makes siblings alike, while non-shared environment (En) makes siblings different.
What does the twin study design compare?
It compares the degree of similarity among MZ twins versus DZ twins to estimate genetic and environmental contributions to traits.
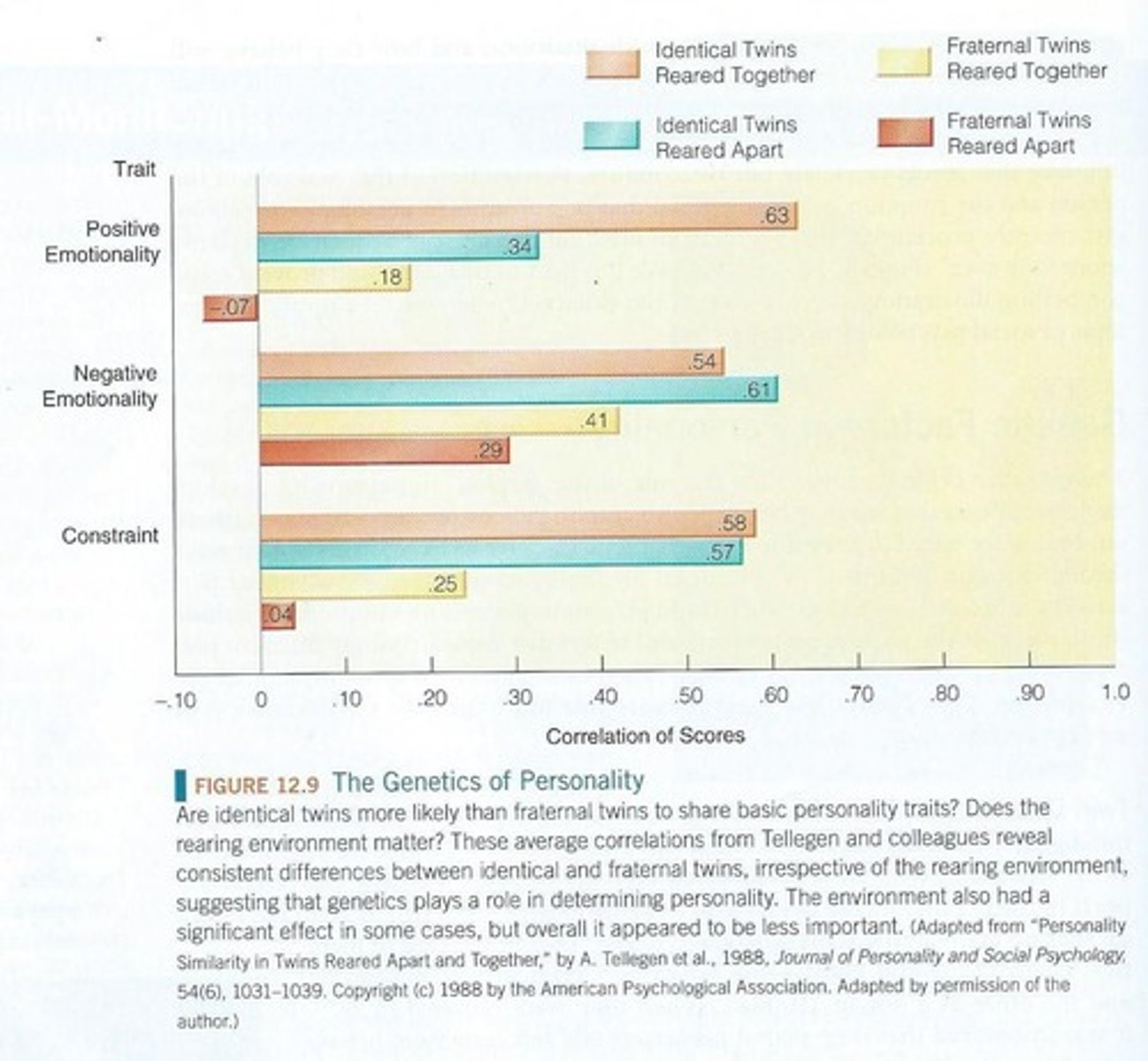
What is the correlation for MZ twins reared together for extraversion?
0.63.
What is the correlation for DZ twins reared together for neuroticism?
0.33.
What is the relationship between personality stability and age?
Personality stability increases after age 30, with declines in neuroticism and increases in conscientiousness observed from teens to 30.
What is positive emotionality in Tellegen's model?
A trait dimension reflecting a tendency towards positive feelings and experiences.
What is negative emotionality in Tellegen's model?
A trait dimension reflecting a tendency towards negative feelings and experiences.
What does constraint refer to in Tellegen's model?
A trait dimension that involves self-control and the ability to regulate impulses.