Stress and Coping
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
What is physiologic stress?
Stress that affects the body physically, such as injury, illness, or environmental factors.
What is psychological stress?
Stress that impacts the mind or emotions, including anxiety, fear, or mental pressure.
What is sociocultural stress?
Stress arising from social or cultural factors, like relationships, work, or societal expectations.
What is a stressor?
Any event, condition, or stimulus that triggers a stress response.
What is stress appraisal?
The process of evaluating a stressor to determine whether it is a threat, challenge, or harmless.
How are stress and health linked?
Chronic stress can lead to physical and mental health problems, affecting immune, cardiovascular, and endocrine systems.
What is Sister Callista Roy’s Adaptation Model?
A nursing theory stating that individuals respond to stressors through adaptive or maladaptive coping mechanisms to maintain health and well-being.
What is homeostasis?
The body’s regulation of systems to maintain a stable, steady internal state.
What is the fight-or-flight response?
A physiologic reaction to stress involving activation of the autonomic nervous system, preparing the body to respond to threat.
What is General Adaptation Syndrome (GAS)?
The body’s physical response to stress through a predictable three-stage process.
What is distress?
Negative stress that can harm health and well-being.
What is eustress?
Positive stress that can motivate and improve performance.
What are the three stages of GAS?
Alarm, Resistance, and Exhaustion.
What happens during the alarm stage?
The body detects a stressor and activates the fight-or-flight response.
What happens during the resistance stage?
The body attempts to adapt to the stressor and maintain homeostasis.
What happens during the exhaustion stage?
Prolonged stress depletes the body’s resources, increasing risk for illness.
Scientific Foundation
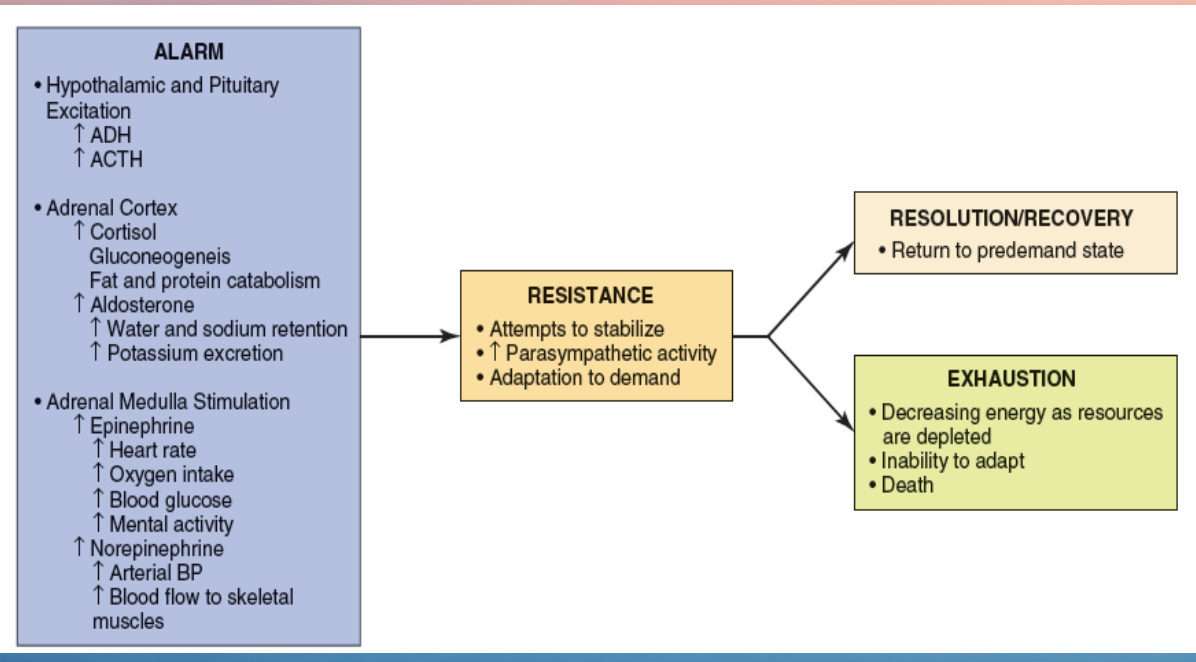
What is Local Adaptation Syndrome (LAS)?
A localized response of the body to stress, affecting a specific part rather than the whole system.
What are common responses in LAS?
Inflammation, reflexive response to pain, and hypoxia secondary to catecholamine release.
What is allostasis?
The process by which the body restores homeostasis after stress.
Allostatis
Some stress can be energizing and toning to the system. Body systems adjust well to stressors without over taxing resources.
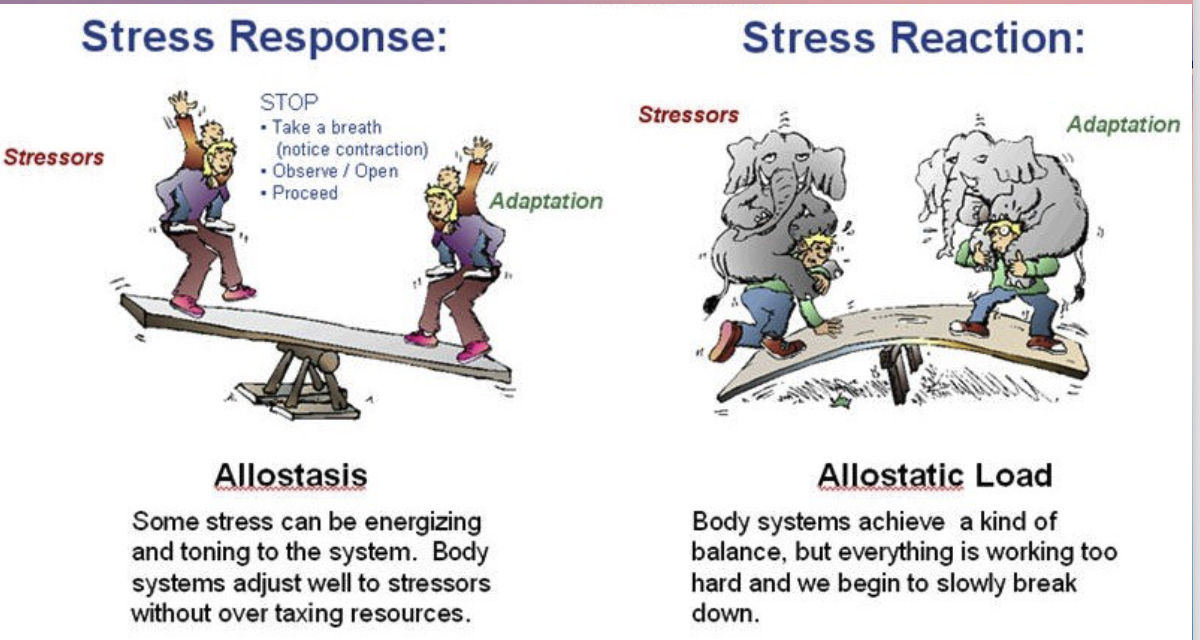
Allostatic Load
Body systems achieve a kind of balance, but everything is working too hard and we begin to slowly break down
What is the first stage of stress appraisal?
Threat assessment – evaluating whether a stressor poses a danger.
What is the second stage of stress appraisal?
Coping options – determining ways to manage or respond to the stressor.
What is sense of coherence (SOC)?
A person’s ability to perceive life as comprehensible, manageable, and meaningful, influencing stress response.
How does a strong SOC affect stress response?
Individuals with a strong SOC are likely to recognize and use available resources effectively.
How does a low SOC affect stress response?
Individuals with a low SOC are more likely to feel overwhelmed and struggle to cope.
What are defense mechanisms?
Unconscious, protective methods the mind uses to reduce anxiety or stress.
What are problem-focused coping strategies?
Techniques aimed at altering or removing the stressor to manage stress.
What are emotion-focused coping strategies?
Techniques that work to ease emotional distress rather than change the stressor.
How does the nervous system respond to stress?
Physical signs of stress are caused by sympathetic nervous system activation.
How quickly do nervous system changes occur after a stressor?
Within the first minutes of exposure.
What are common physical sensations of stress?
Palpitations, light-headedness, nausea, and anxiety.
How does the immune system respond to stress?
Through pain, vasodilation, and swelling as part of the inflammatory response.
What cellular changes occur in the immune system during stress?
Mobilization of white blood cells and lymphocytes to help defend the body.
What is the sympathoadrenal response?
Activation of the sympathetic nervous system and adrenal medulla, releasing catecholamines like adrenaline to prepare the body for stress.
What is the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) complex?
A system that releases hormones (like cortisol) in response to stress, regulating metabolism, immunity, and other functions.
What role do corticosteroids play in stress?
They help the body manage stress by reducing inflammation and mobilizing energy reserves.
How can stress affect blood sugar?
It can cause hyperglycemia (elevated blood glucose) due to hormone-mediated energy mobilization.
What is resilience in the context of stress?
The ability to recover and adapt effectively to stress or adversity.
How does coping relate to stress?
Coping involves strategies—problem-focused or emotion-focused—that help manage stress and its effects.
What psychological symptoms can stress cause?
Anxiety, anger, and depression.
How does prolonged stress affect the immune system?
It significantly alters immune responses, reducing the body’s ability to fight infections.
Which diseases can be worsened by high stress levels?
Autoimmune diseases, including multiple sclerosis.
What can unrelieved exposure to stress hormones cause?
It can lead to organ failure.
How is physiologic stress commonly measured in the lab?
By measuring cortisol levels.
How can nurses establish trust when assessing stress?
By developing a trusting relationship and using open-ended questions.
Why assess a patient’s ability to cope with stress?
To tailor interventions and support strategies to the individual’s needs.
How should cultural background be incorporated in stress assessment?
By integrating the patient’s cultural context and using culturally appropriate tools.
What manifestations of stress should be addressed in assessment?
Both physical and psychological manifestations.
What is an example of “Difficulty Coping”?
Supporting data: Recently separated from spouse, concerned about children, unemployed, crying, feels anxious and jittery at night, reports lack of energy to cook.
What is an example of “Anxiety”?
Supporting data: Change in health status, fatigue, difficulty concentrating.
What is an example of “Caregiver Stress”?
Supporting data: Complexity of caregiver activities, fatigue, gastrointestinal upset, weight change.
Give an example of a goal for a patient with stress.
Patient will discuss possible coping strategies during weekly office visits.
Give another example of a goal for patient stress management.
Patient will report increased ability to concentrate on care instructions before discharge.
Give an example of a goal for caregiver stress.
Caregiver will use respite care for their loved one once a week for the next month.
What is a primary intervention for managing stress?
Decrease stressors whenever possible.
How can coping strategies be addressed in stress management?
By improving existing coping strategies or helping the patient mobilize new ones.
What are internal strategies for stress management?
Strategies that address the patient’s feelings associated with stress, such as reflection, mindfulness, or emotional processing.
What are external strategies for stress management?
Strategies that provide relief through mobilization of support, like family, friends, or community resources.
What are general resistance resources in stress management?
Tools and resources (physical, social, psychological) that help the patient resist or cope with stress effectively.
What is a holistic approach to stress management?
Addressing physical, psychological, social, and spiritual needs to reduce stress and promote overall well-being.
How can time management help with stress?
By organizing tasks and prioritizing activities to reduce feelings of being overwhelmed.
How does anger management help with stress?
By teaching techniques to control anger and reduce emotional tension.
How can nutrition help manage stress?
By promoting balanced eating habits that support energy, mood, and overall health.
How can support groups help with stress?
By providing social support, shared experiences, and practical coping advice.
What are some complementary and alternative therapies for stress?
Relaxation therapy, exercise, sleep, guided imagery, yoga, meditation, biofeedback, energy therapy, and Eastern medicine.
How does relaxation therapy help with stress?
Reduces muscle tension and lowers sympathetic nervous system activity.
How does exercise help with stress?
Releases endorphins, improves mood, and reduces physical tension.
How does guided imagery help with stress?
Uses mental visualization to promote relaxation and emotional calm.
How do yoga and meditation help with stress?
Encourage mindfulness, body awareness, and relaxation responses.
How does biofeedback help with stress?
Teaches the patient to control physiological functions, such as heart rate and muscle tension.
What is crisis intervention in stress management?
Short-term assistance provided to help patients cope with an immediate stressful situation.
What characteristics define effective crisis intervention strategies?
They are simple, innovative, accessible, and practical.
What is the goal of crisis intervention?
To help patients adapt quickly and regain stability.
How do acute and chronic stress differ in resolution?
Acute stress situations resolve more quickly than chronic stress.
How can nurses assess stress in patients?
By observing patient behaviors and comparing them with the patient’s self-reported experiences.
Why should patients be reminded to continue stress reduction techniques?
Consistent use helps maintain coping skills and manage stress effectively.
How quickly are coping skills modified for stress management?
Modification is a slow process that requires time and practice.
When might referrals be needed in stress management?
When additional support, counseling, or specialized care is required to help the patient cope.
What are potential consequences of workplace stress?
Depression, compassion fatigue, burnout, and decreased job satisfaction.
Why is self-care important for nurses?
Nurses must care for themselves to provide effective care for others.
What are healthy coping strategies for nurses?
Exercise, balanced nutrition, and mindfulness therapy.