Logical Fallacies
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Ad-hominem
In an argument, this is an attack on the person rather than on the opponent's ideas. It comes from the Latin meaning "turn to the man."

Tu quoque
Dismissing someone's argument because he or she is being hypocritical.
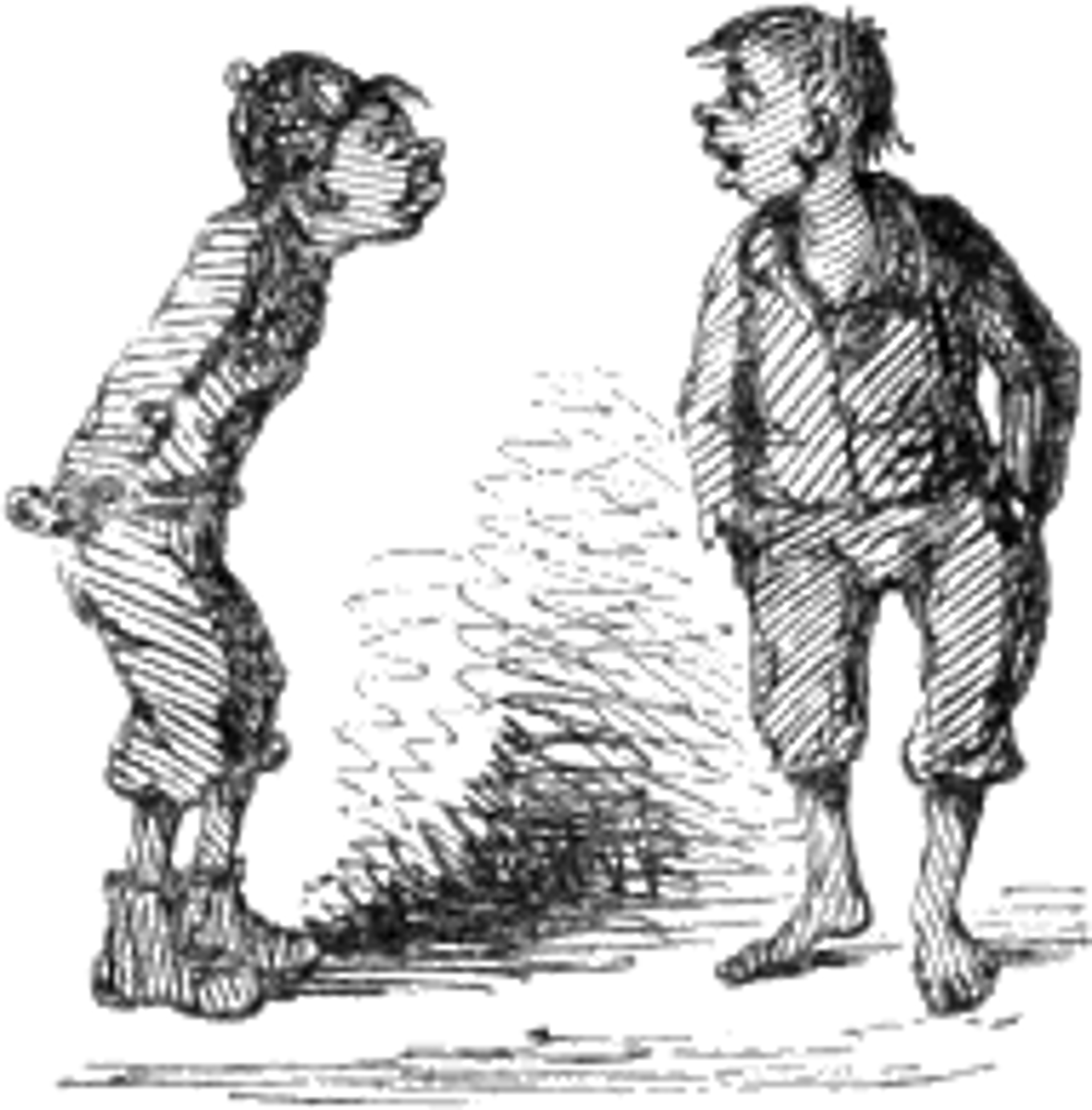

Faulty Appeal to Authority
A fallacy in which a speaker or writer seeks to persuade not by giving evidence but by appealing to the respect people have for a famous person or institution.

Strawman
Misrepresenting or exaggerating someone else's argument to make it easier to attack.

Circular Reasoning
A logical fallacy in which the conclusion is hidden within the premises. Typically called "circular reasoning." From Plato's Euthyphro - something is pious because it is loved by the gods. That which is loved by the gods is pious.

Bandwagon
A fallacy which assumes that because something is popular, it is therefore good, correct, or desirable.

Black or White
When two alternative states are presented as the only possibilities, when in fact more possibilities exist.

Hasty Generalizations
Generalizing based on a small or poor sample population.
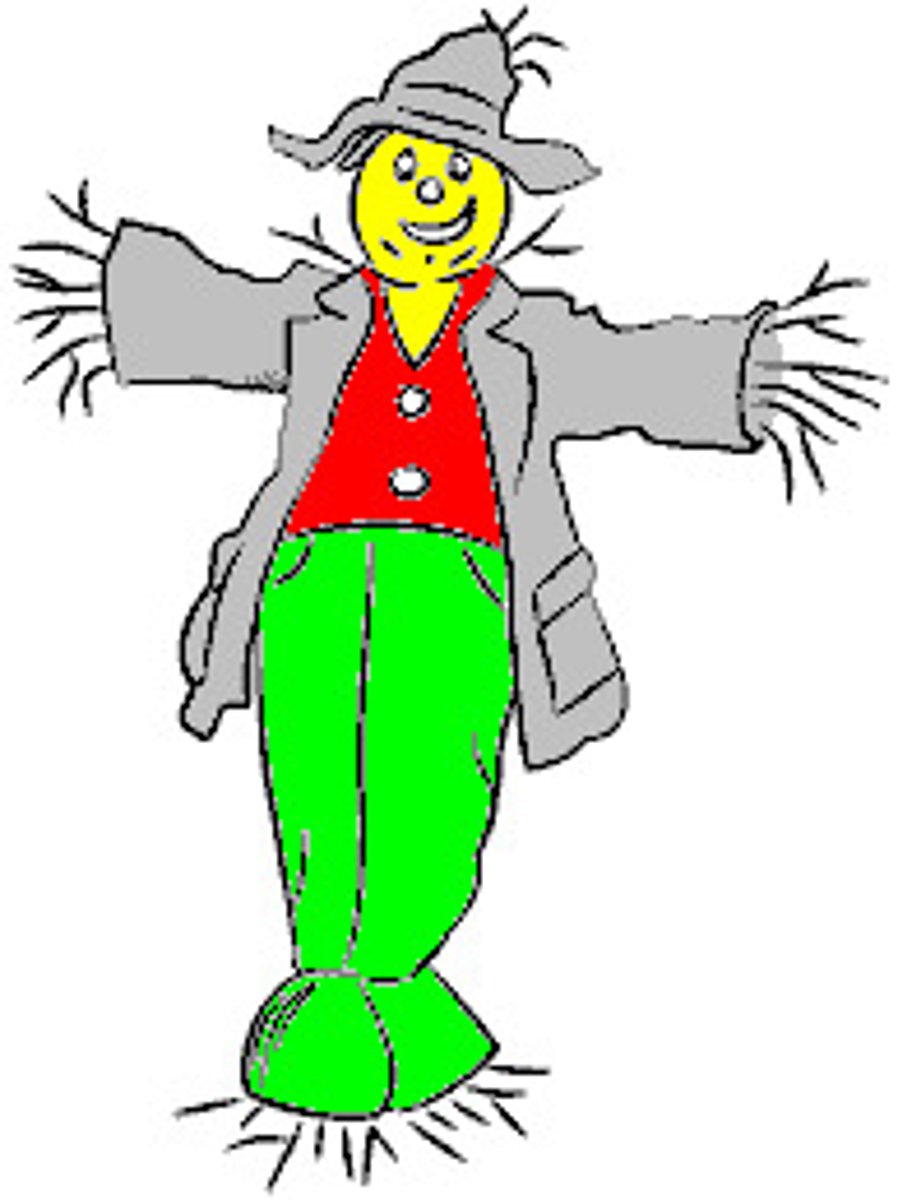
Slippery Slope
A fallacy that assumes that taking a first step will lead to subsequent steps that cannot be prevented.
False Cause
A fallacy that occurs when the alleged cause fails to be related to, or to produce the effect: "the black cat crossing the street brought me bad luck, so I had an accident."

Equivocation
A fallacy by which a key word or phrase in an argument is used with more than one meaning. "I trust you so I trust that you'll be home by 9." The word "trust" is used in two different ways.

Post Hoc Ergo Propter Hoc
Latin for "after this therefore because of this." Arguing that because something follows something else it necessarily is the cause.
