Astronomy Exam 1
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Order of the planets
Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars,Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune
open cluster of stars
young
Globular cluster of stars
old
galaxy
large grouping of stars held together by gravity and orbiting a common center of mass
galaxy group
a grouping of a few to several 10’s of galaxiesheld together by gravity
galaxy cluster
a large groupings of galaxies including several dozen up to more than 100 galaxies all held together by gravity
galaxy supercluster
groupings of galaxy clusters
universe
the sum total of all matter and energe, encompassing all superclusters, voids, and everything within them
About how many stars are in teh milky way
100 billion (10^11)
what is the correct ordering from smallest to largest?
planet, star, galaxy, galaxy group, galaxy cluster
How many moons can fit inside of earth
approximately 4
how many times larger is the sun than the earth
110 times larger
Astronomical unit
the distance between the earth and the sun; approximately 93 million miles (150 km)
Light year
the distance that light travels in a year
Scientific method
ask a question, hypothesis, experiment, observation, analyze data, conclusion
earth’s tilt
23.5 degrees
latitude
north-south position from the equator
longitude
east-west position relative to Greenwich England
declination
stars latitude(north/south); position above or elow the celestial equator
right ascension
star’s longitude (east/west); position along the celestial equator
ecliptic
sun’s apparent path through the celestial phase
celestial equator
a projection of our equator into space
zenith
directly overhead
horizon
the half of the sky you can see at your position
circumpolar star
never set or rise below the horizon at your location
precession
the earth’s axis wobbles causing the place it points to change; takes about 26,000 years
earth’s only natural satellite
the moon
Moon’s orbit around the earth completes every
27.3 days
sidereal month
moon complete orbit around the earth
the moon returns to the same position relative to the sun every
29.5 days
lunar month
the moon returning to the same position relative to the sun
lunar cycle phases repeat every
29.5 days
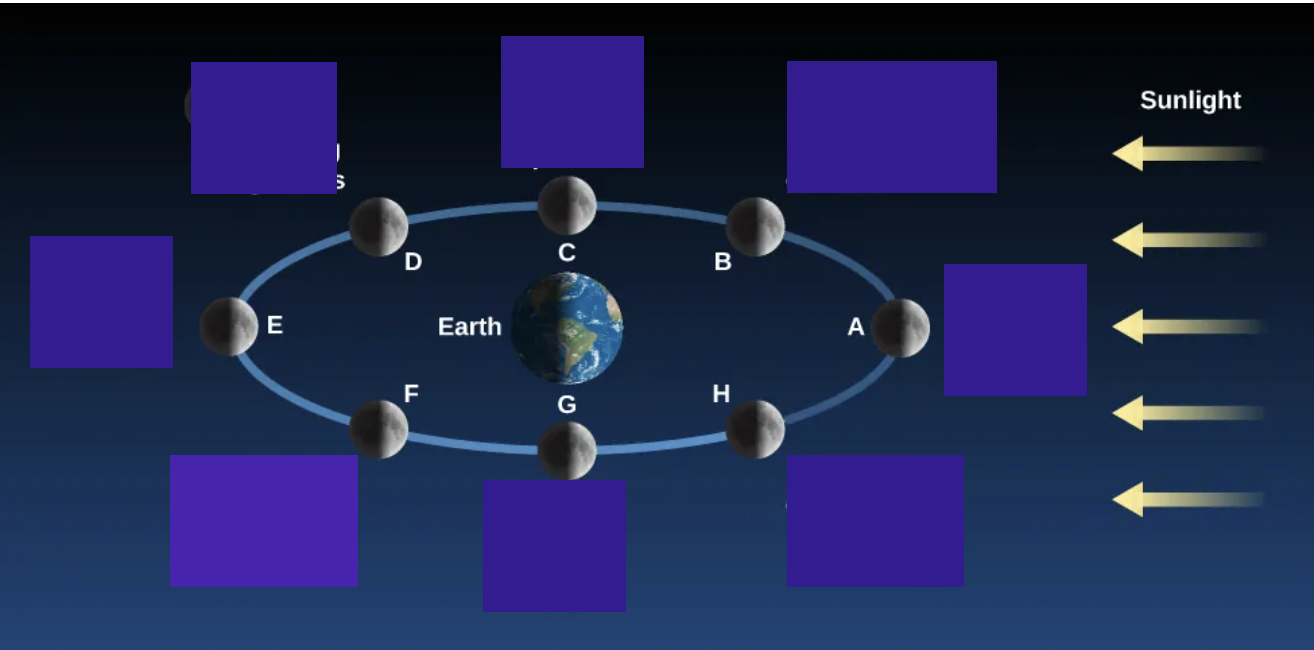
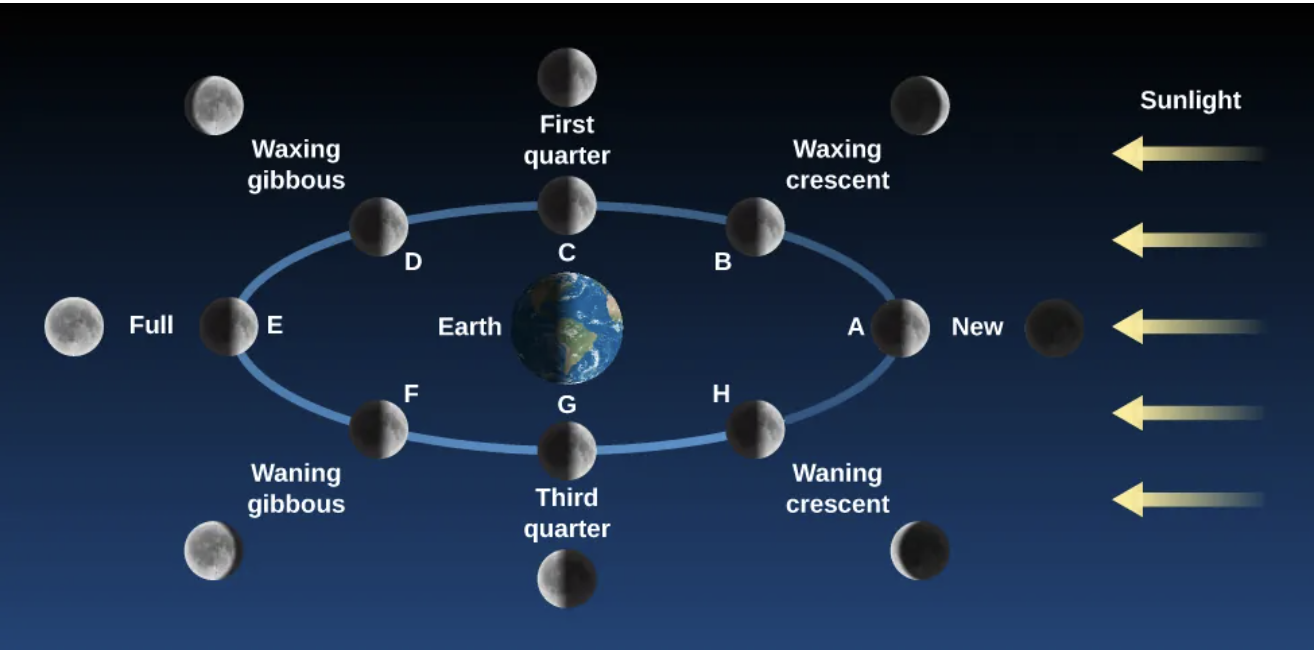
lunar phases
new, waxing crescent, first quarter, waxing gibbous, full, waning gibbous, third quarter, waning crescent
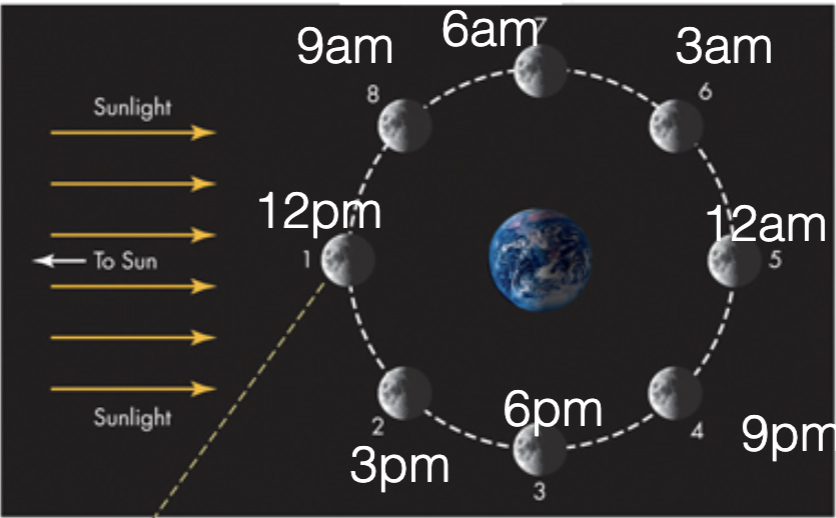

tidally locked
we see the same side of teh moon all the time
solar eclipse
moons shadow falls on earth
lunar eclipse
earth’s shadow falls on the moon
arcminute
60 per degree
arcsecond
60 per arcminute
constellation
one of the 88 section into which astronomers divide the sky
asterism
a noticeable star pattern within a constellation
Exodus model of the solar system
Earth is the center of the universe
Ptolemaic model
Builds on Exodus model; Earth at center but the outer planets needed to have special extra orbit: “epicycle”-geometric models
heliocentric model
sun is at the center and teh earth and planets rotate around it