MKT 300 ASU Eaton Exam 1
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
Marketing
an organizational function and collection of processes designed to plan for, create, communicate, and deliver value to customers and build effective customer relationships
Concept of Exhange
Requires two or more parties; something of value; desire; freedom to accept or reject;
4P's (Marketing Mix) tactics
Product
Price
Promotion
Place(distribution)
Demographics
group people by similar characteristics
Psychographics
differences: individual opinions, actions, skill sets, ...
Marketing Concept
philosophy that firms should analyze the needs of their customers and then make decisions to satisfy those needs, better than the competition through creation of VALUE
Value->Customer relationships->Customer Loyalty
Buyer's Market
The best time for consumers to buy; characterized by large supply, small demand, and low prices.
ex. buying a house: when available properties for sale exceeds the number of buyers seeking to purchase properties
Seller's Market
The best time for producers to sell; characterized by large demand, small supply, and high prices
ex. buying a house: there are more buyers seeking to purchase properties than there are available homes on the market
Marketing Concept Philosophies
Production
Sales
Market
Societal
production orientation
focus on efficiency of internal operations
What can we make or do best?
Sales Orientation
the belief that people will buy more goods and services if aggressive sales techniques are used and that high sales result in high profits
how can we sell more aggressively?
Market Orientation
Focus on satisfying customer needs and wants
What do they need/ want?
Societal Orientation
satisfying customer needs and wants while enhancing individual and societal well-being
What do they need/ want & how does it satisfy society?
Value-Driven Marketing
Customer Value = Customer Benefits - Customer Costs
Marketing Map
Segmenting, Targeting, Positioning--->
Branding (marking tactics, mkt strategy)--->
Customer Value
STP Marketing
segmenting, targeting, positioning
Segmenting
dividing the customers in the market who share similar needs and wants based on needs and benefits; demographics; lifestyle; behaviors
segmentation bases
Criteria used to classify and divide buyers into different groups
1. Demographics
2. Psychographics
3. Behavioral
4. Needs
Behavioral Segmentation
dividing market on the amount of product bought or consumed
80/20 rule
80/20 rule
A marketing rule of thumb that 80% of your company sales/ demand come from 20% of your customers
Targeting
evaluating the segments and choosing one or more segments to enter that the company will compete in
When selecting their target markets, companies have to make a choice of whether
they are going to be focused on one or few segments or they are going to cater to the mass market.
Four Targeting Strategies
1. undifferentiated
2. differentiated
3. concentrated
4. micro
undifferentiated targeting strategy
a marketing approach that views the market as one big market (mass market) with no individual segments and thus uses a single marketing mix
undifferentiated example
Target Market: Everyone
ex. Target
- T Ford Model. This model was available in only black color in 1930s.
Undifferentiated advantages
Potential savings on production and marketing costs
-since only one product is produced achieve mass production and Marketing costs are also lower as only one product has to be promoted and there is a single channel of distribution
Undifferentiated disadvantages
- hardly ever a well considered strategy
-unimaginative product offerings which have little appeal to consumers
-company more susceptible to competition b/c the competition will invade the market with more appropriate products for smaller different segments
Differentiated targeting strategy
-multi-segment targeting strategy
-serves two or more well- defined segments
-develops a distinct marketing mix for each one of them
-Separate brands are developed to serve each of the segments.
Differentiated example
Target Market: Groups within total market
McDonalds: they have developed unique menus suited for consumers in different countries in the world
Differentiated Advantages
most sought after target market strategy
-Greater financial success
-Economies of scale in manufacturing and marketing
Differentiated disadvantages
-High costs- product design, production, promotion, inventory, marketing research and management costs
-Cannibalization- occurs when sales of a new product cut into sales of a firm's existing products
The reason to believe is a statement providing compelling evidence and reasons why customers in your target market can have
confidence in your differentiation claims
Concentrated targeting strategy
a marketing strategy of selecting a single, primary target market and focusing all energies on providing a product to fit that market's needs
-several segments may be identified
-company may not serve all of them b/c unattractive or out of line with the company's business strengths
- A company may target just one segment with a single marketing mix b/c it understands the needs, and motives of the segment's customers and designs a specialized marketing mix.
Concentrated example
Target Market: Smaller specialized segments
Starbucks became successful by focusing exclusively on customers who wanted gourmet coffee products
Concentrated Advantages
-Concentration of resources and meets narrowly defined segment: more profitable than spreading resources over several different segments
-Small firms can compete
-Strong positioning
Concentrated Disadvantages
-Segments too small: If their chosen segments were to become unprofitable or shrink in size, the companies will be in problem
-Changing segments: The association with one particular segment should not be allowed to become so strong that customers cannot imagine the company doing something else
-Large competitors: may try to market to ones niche segment in the industry if they are deemed very successful
Micromarketing targeting strategy
one-to-one marketing; tailors a product or service to suit an individual customer's wants or needs with hopes to increase customer loyalty
Micromarketing example
Clothes: each piece is tailored to specific person
What a company needs to select a target market & questions they should be asking
Align companies core competencies to target selection
1. Do customers needs differ? Market segmentation?
2. Which segments should company participate in?
3. Can company compete in target market?
4. Long term growth potential?
core competencies
-key abilities or strengths that a company has developed that give it a competitive advantage over its peers and contribute to its long-term success
-difficult for competing businesses to duplicate
Positioning
the placement of a product or service offering in the minds of consumer targets
value proposition
-the value a company promises to deliver to customers should they choose to buy their product.
- statement that introduces a company's brand to consumers by telling them what the company stands for, how it operates, and why it deserves their business.
Value is the relationship between
price and quality
- More quality for more/ same/ less price
- same quality for lower price
-less quality for much lower price
Perceptual Mapping
means of displaying or graphing the location of products, brands, or groups of products in customers' minds
-The positioning of a brand is influenced by customer perceptions rather than by those of businesses.
positioning statement
a brief description of a product or service and target market, and how the product or service fills a particular need of the target market. It's meant to be used as an internal tool to align marketing efforts with the brand and value proposition
Positioning Statement Format
For (target market), (brand) is the (point of differentiation) among all (frame of reference) because (reason to believe).
ex. For snickers, Snickers is the brand of candy bar that satisfies your hunger because it is packed with peanuts
the point of differentiation (POD) describes how your brand or product
benefits customers in ways that set you apart from your competitors
The frame of reference (FOR) is the segment or category in which
your company competes.
Repositioning
changing consumers perceptions of a brand in relation to competing brands
-includes changes to the marketing mix, such as product, place, price and promotion
-done to keep up with consumer wants and needs
ex. Campbells soup added a "whats in my food" database giving customers access to all ingredients b/c consumers love transparency
Weber's Law
the stronger the internal stimulus, the greater the added intensity needed to perceive a difference
- A consumer normally don't know differences when they are subtle. Though, they identify the differences when they are extreme.
-The Difference Threshold (or "Just Noticeable Difference") is the minimum amount by which stimulus intensity must be changed in order to produce a noticeable variation in sensory experience
Perceptual Organization
the processes that put sensory information together to give the perception
- Figure and Ground
- Grouping
-Closure
Figure and ground
How do you see the figure in the context of the background it is shown in
Grouping
the perceptual tendency to organize stimuli into meaningful groups
-is a thing we do to attach components to create a complete package so it stands out
Closure
- Zeigernik effect: psychological tendency to remember an uncompleted task rather than a completed one
- A person beginning a task needs to complete it
- When one is prevented from doing so, a state of tension is created that manifests itself in improved memory for the incomplete task
- someone who starts a task has the desire to finish the task
- Ex: movie cliff hangers, want to see the second one b/c need to know what happens
- Keeps people coming back
Categorizing
Experimenting= Controlling for all variables, and you are just changing on variable
Mitsubishi and Chrysler came out with an identical car and price identical, but still sold different amounts
Chryslers were known for "older people" but Mitsubishi had no image so they sold more of the "younger sport car" then Chrysler did
Social Changes
Values
Household
Component
Women
Competition
Generic - same price
Form - same purpose
Industry - same category, different price
Brand -similar product, same price, same customer
Consumers
generational and ethnic differences/changes
Porter's 5 Environmental Forces
Threat of Entry
Supplier Power
Buyer Power
Threat of Substitutes
competitive Rivalry
Segment Criteria
homogeneous
heterogeneous
substantial
identifiable
responsive
Strategic Market Plan
managerial process of creating and maintaining a fit between the organization's objectives and resources and evolving market opportunities
SWOT Analysis
Strengths
Weaknesses
Opportunities
Threats
BCG Matrix
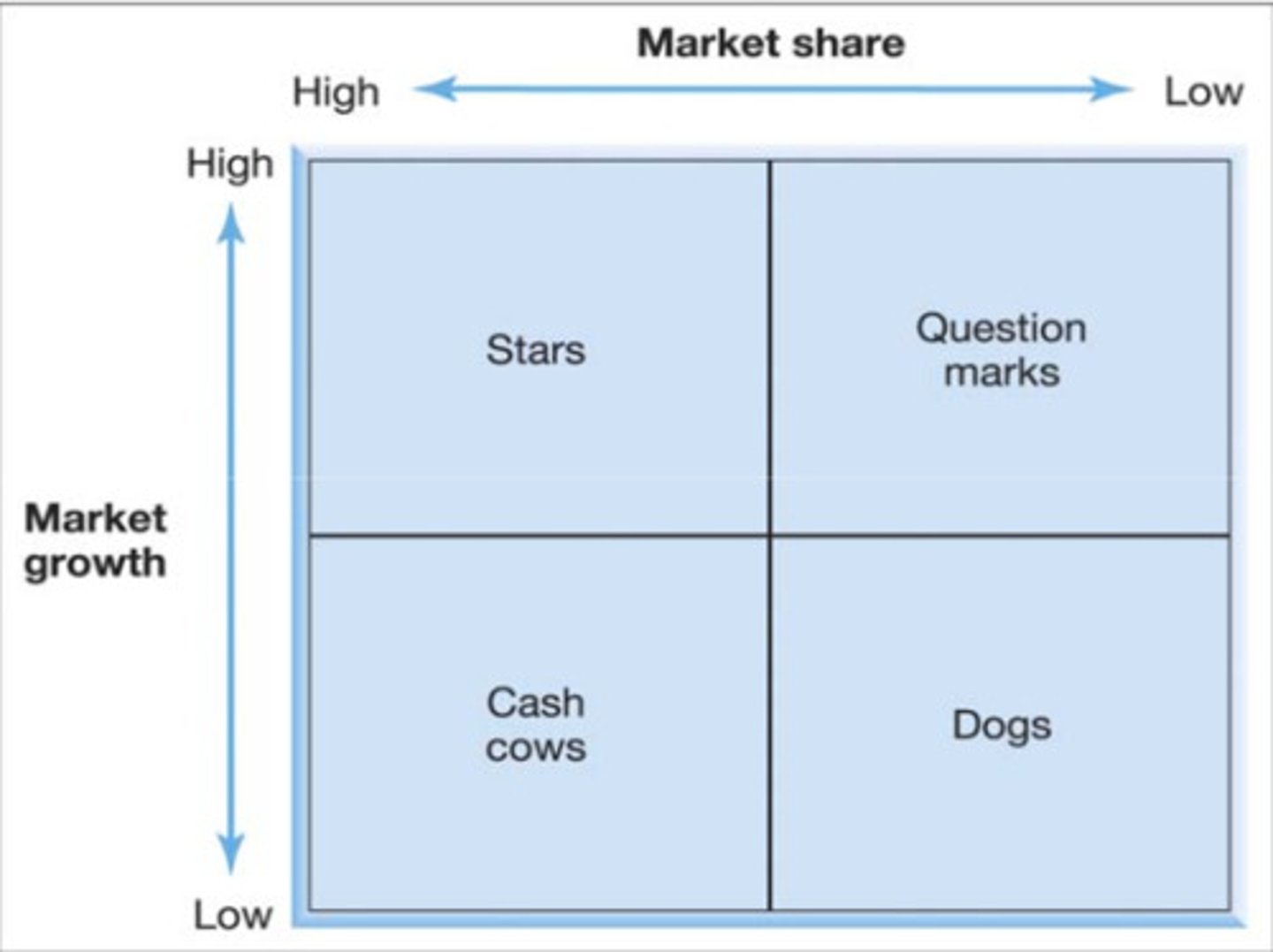
Market Strategy Focus
Aggressive: high internal strengths, high external opportunities
Diversification: high internal strengths, high external threats
Turnaround: high internal weakness, high external opportunities
Defensive: high internal weaknesses, high external threats
Competitive Advantage
unique features of a company and products that are perceived by target market as significant to competition
Competitive Advantage Types
Cost
Differentiation
Niche
Product Leadership
Strategic Opportunity Matrix
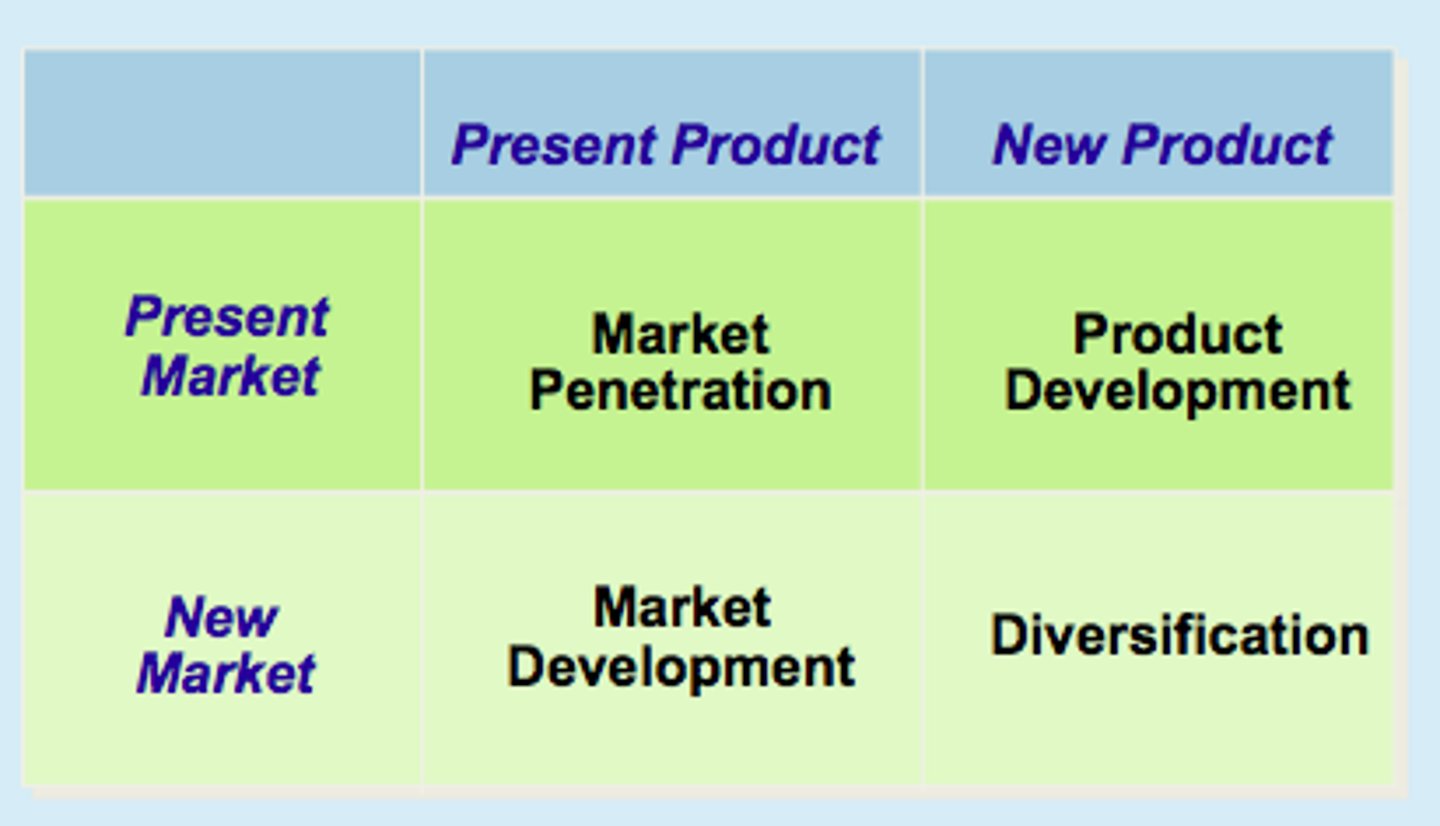
Consolidation Strategies
Retrenchment - lower advertising and distribution
Pruning - discontinue
Divesting - sell off
Marketing Plan Sections
Title page, Executive Summary, Business Overview, Market Overview, Competitive Summary, Operational Overview, Management Overview, Financial Overview
Consumer Culture
sum total of learned beliefs, values, and customs that serve to direct the consumer behavior of members of a particular society
Environmental Consumerism
Unconcerned
Drifters
Conventional
Naturalites
LOHAS
Enculturation
gradual acquisition of a culture
Acculturation
cultural modification
Regulatory Bodies
CPSC, FCC, ICC, EPA, FDA
Corporate Social Responsibility
concern for how a company's actions might affect the interest of others
Sustainability
socially responsible companies that focus on world social problems and view them as opportunities
Ethical Developmental Levels
Pre-Conventional
Conventional
Post-Conventional
Business to Business Marketing
products used to manufacture other products
Demand Types
Derived
Inelastic
Joint
Fluctuating
Buying Situations
Straight Rebuy
Modified Rebuy
New Task
Entering the Global Marketplace
Export
Licensing
Contract Manufacturing
Joint Venture
Direct Investment
5 Step Consumer Decision-Making Process
1. Need Recognition
2. Information Search
3. Evaluate Alternatives (multiattribute, conjunctive, lexicographic)
4. Purchase
5. Post-Purchase Behavior
Cognitive Dissonance
the state of having inconsistent thoughts, beliefs, or attitudes, especially as relating to behavioral decisions and attitude change.
Social Factor
Group - direct (primary and secondary) and indirect (aspirational and non)
Social Class - upper, middle, lower
Personal Factor
Personality - internal
image congruence hypothesis
Lifestyle - external
Psychological Factor
Behavior
Perception
-selective exposure
-selective distortion
-selective retention
Situational Factor
time, environment, context
Theory of Reasoned Action
Consumer beliefs and attitudes
A(act)
Bi x Ei
SN
NBj x MCj
Marketing Research Process
1. Define Problem
2. Develop Research
3. Conduct Research
4. Analyze Research
5. Address the Problem
BDI
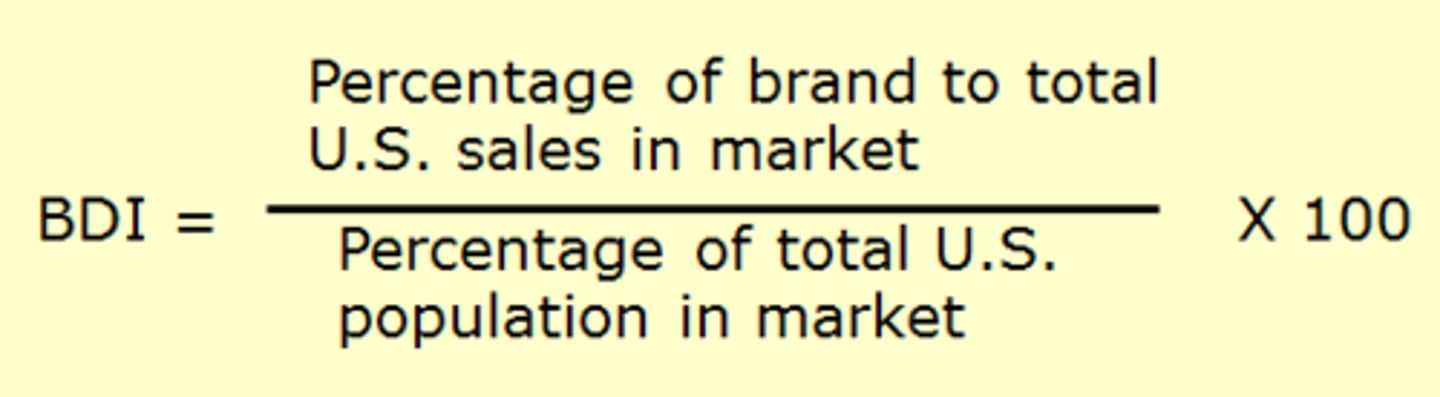
CDI

Brand
identifying name, term, design, symbol, feature, that identifies one marketers product as distinct
Brand Equity
the marketing and financial value associated with a brand's strength
Intangible Value
method of valuing a company's intangible assets. This calculation attempts to allocate a fixed value to intangible assets that does not change according to the company's market value. Examples of intangible assets include brand equity and proprietary technology
Brand Asset Valuator
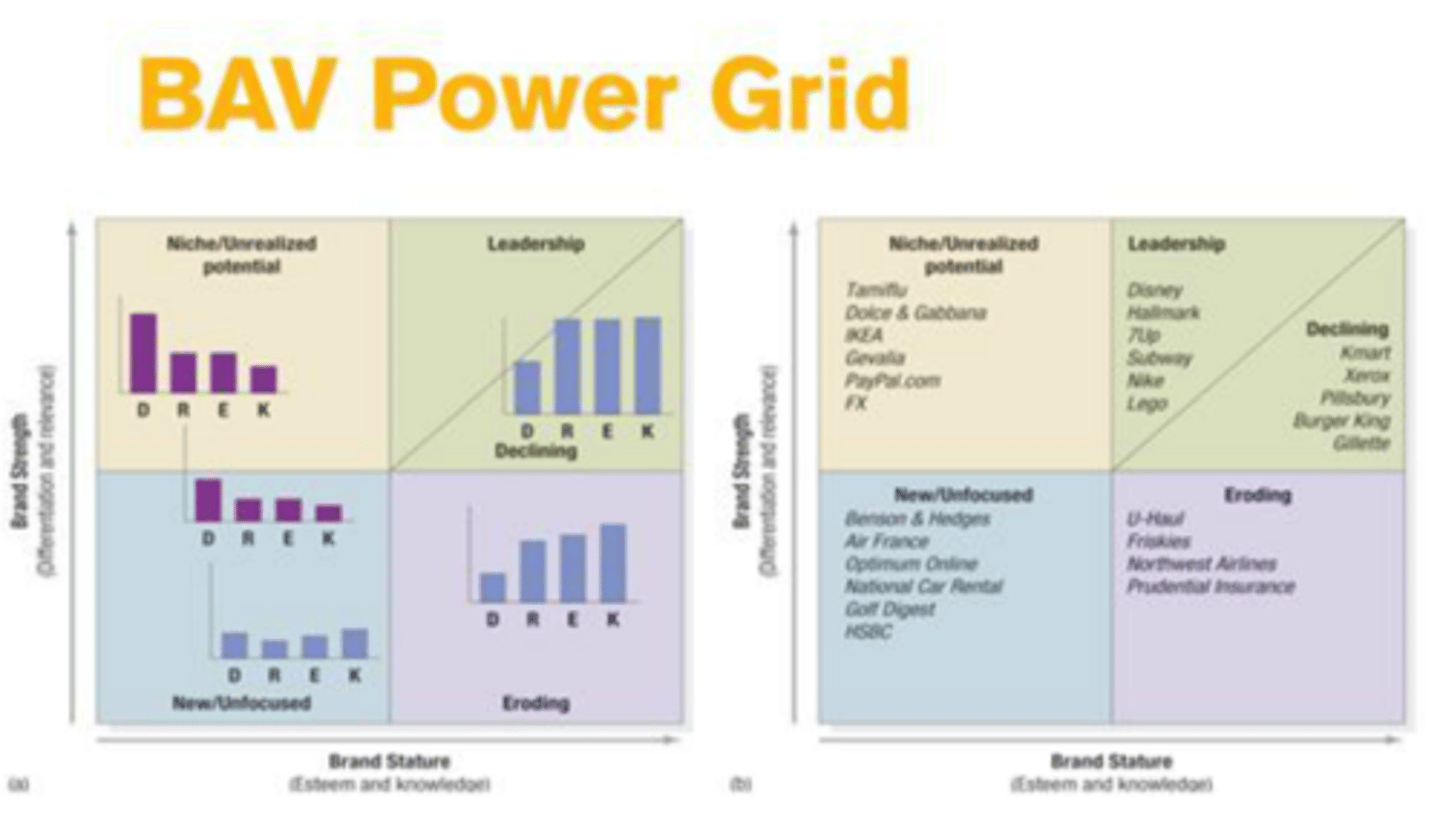
Branding Strategies
Individual: name stands alone
Family: use company name
Combination: both names are displayed
Packaging
protection, economy, safety, convenience