Chem 124 Exam 2
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
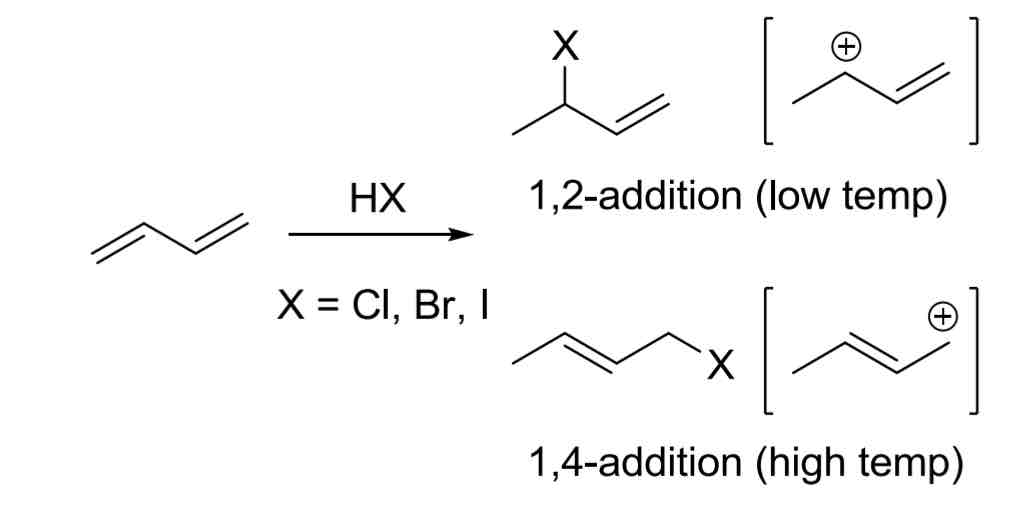
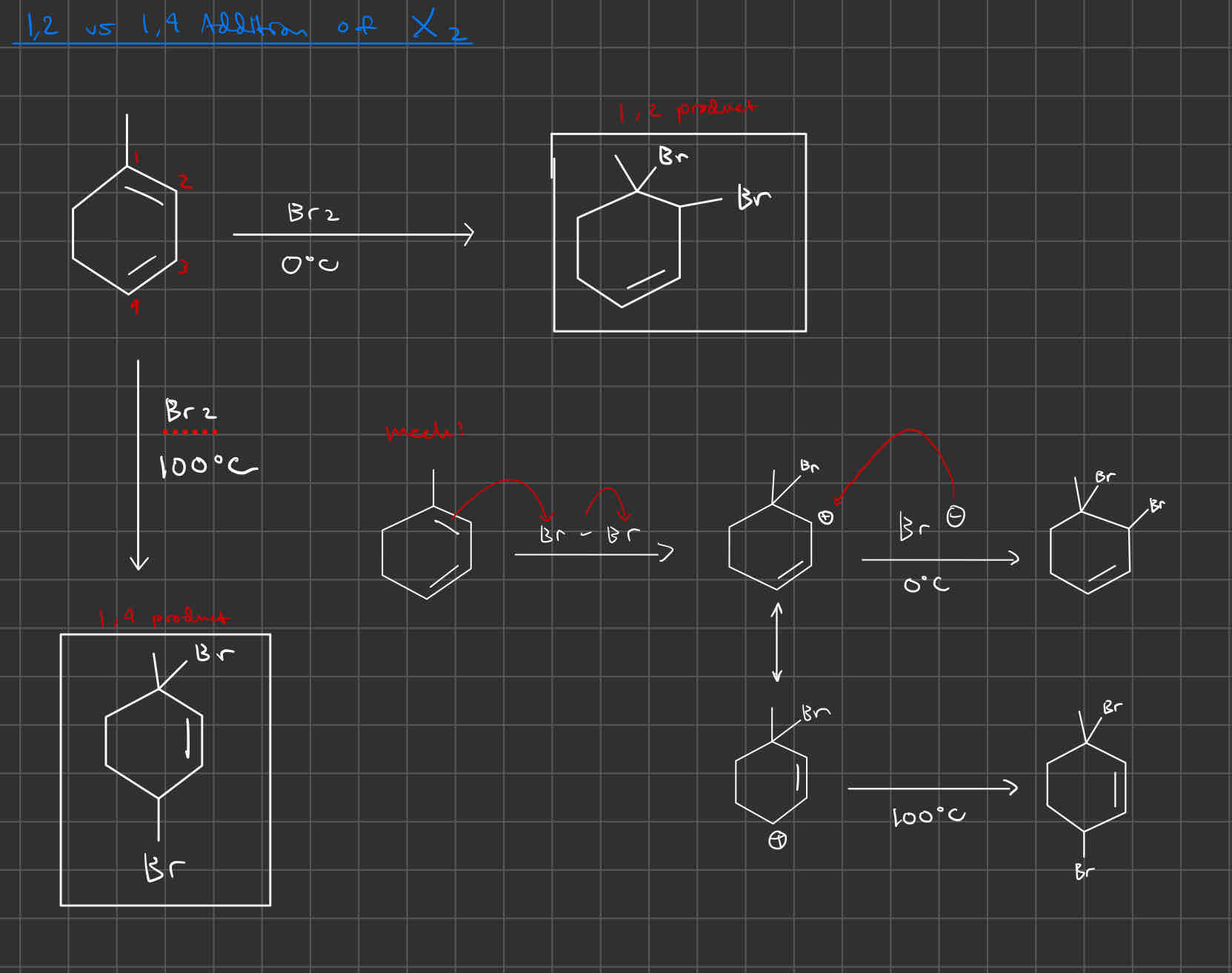
1,2- vs 1,4-Addition of HX or X2
1,2 occurs under low temp (<25 C)
1,4 occurs under high temp (>25 C)
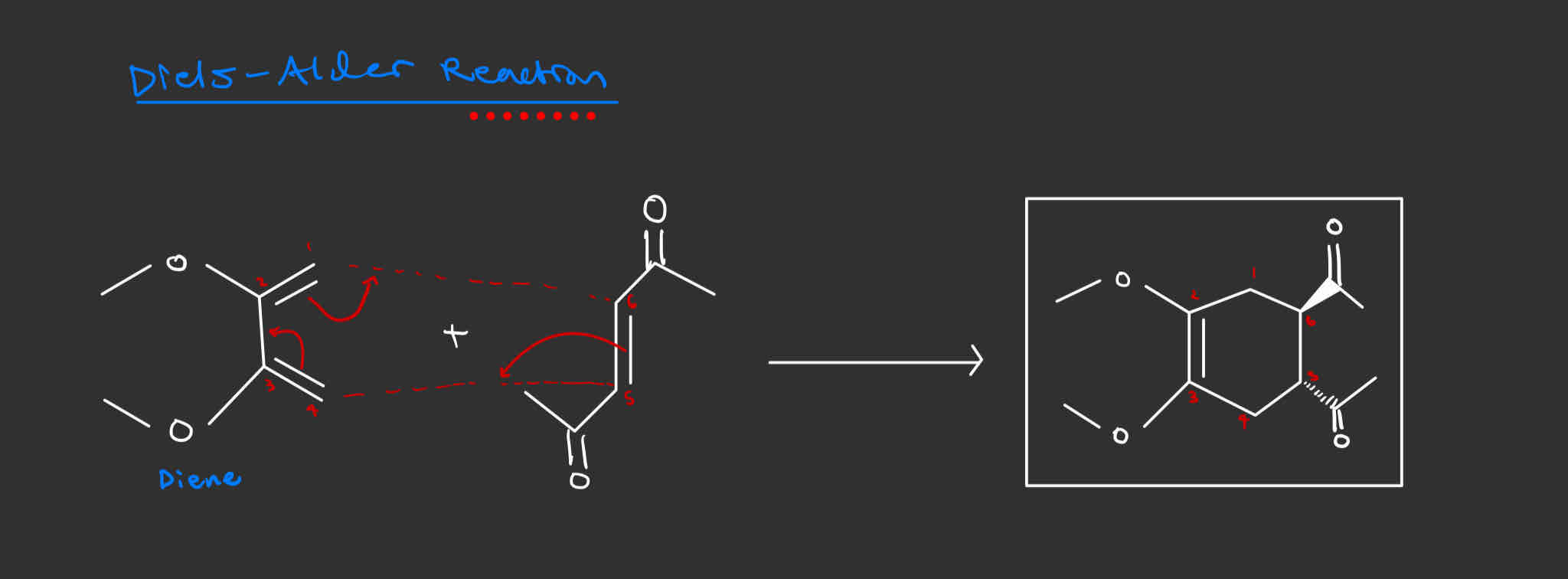
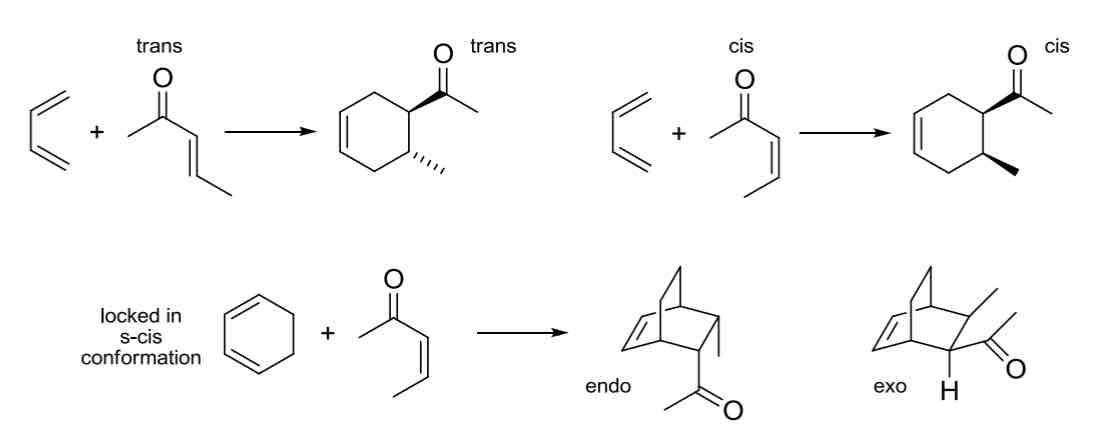
Diels Alder Reaction
Diene + Dienophile = Cyclohexene adduct
Concerted, one-step reaction mechanism
Huckel’s rule to determine aromaticity
if there is an sp3 carbon = non-aromatic

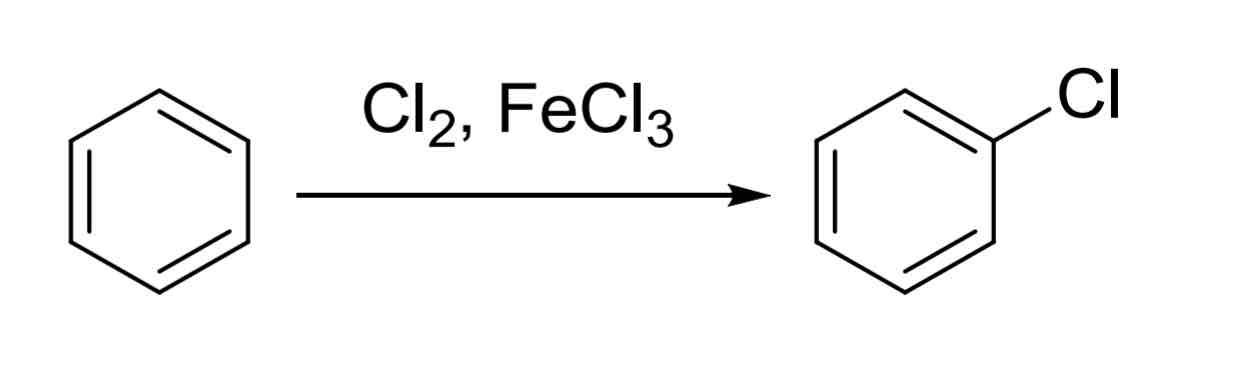
Halogenation — puttting Halide on ring, usually Br or Cl
X2, FeX3. (X = Br, Cl)
despite product being a weak EWG, it will direct next groups to ortho and para positions
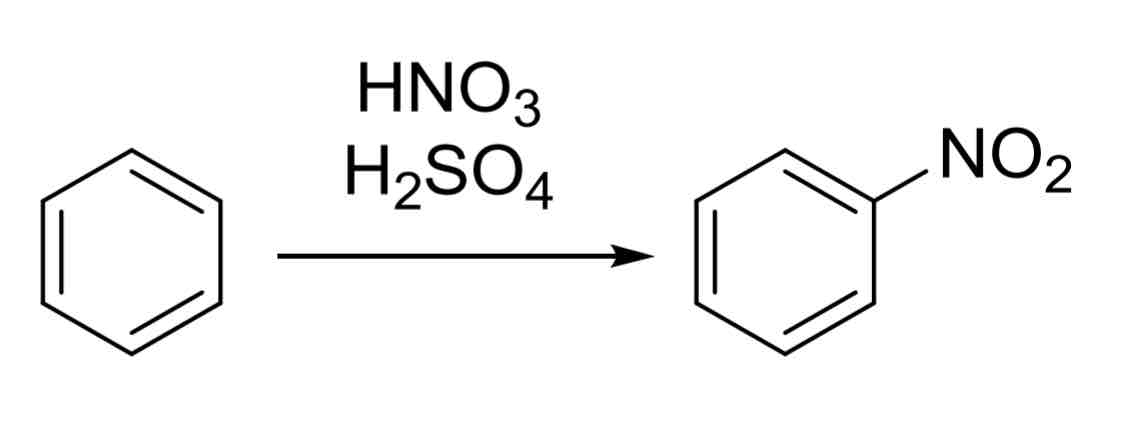
Nitration - putting NO2 group on ring
HNO3, H2SO4
forms nitro benzene
next group will add meta because of NO2 being a strong EWG
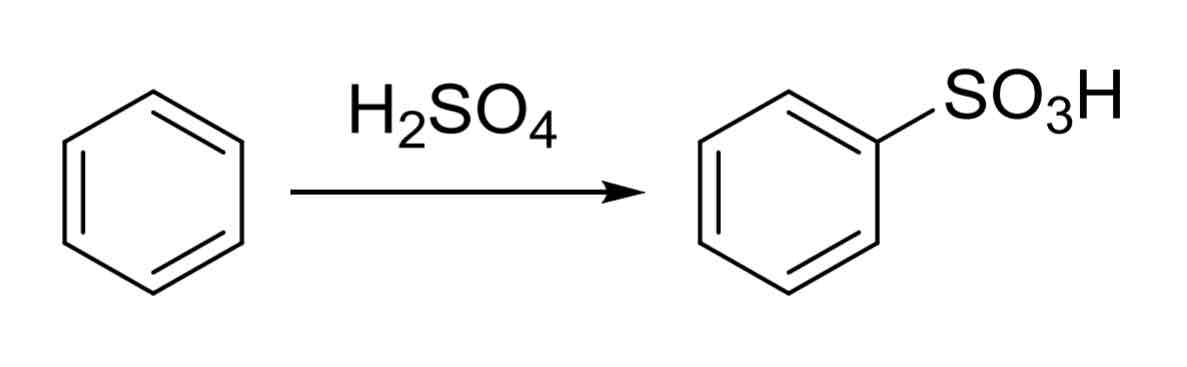
Sulfination — putting SO3H group on ring
H2SO4
forms benzene sulfonic acid
Product has a strong EWG that will direct next group to meta
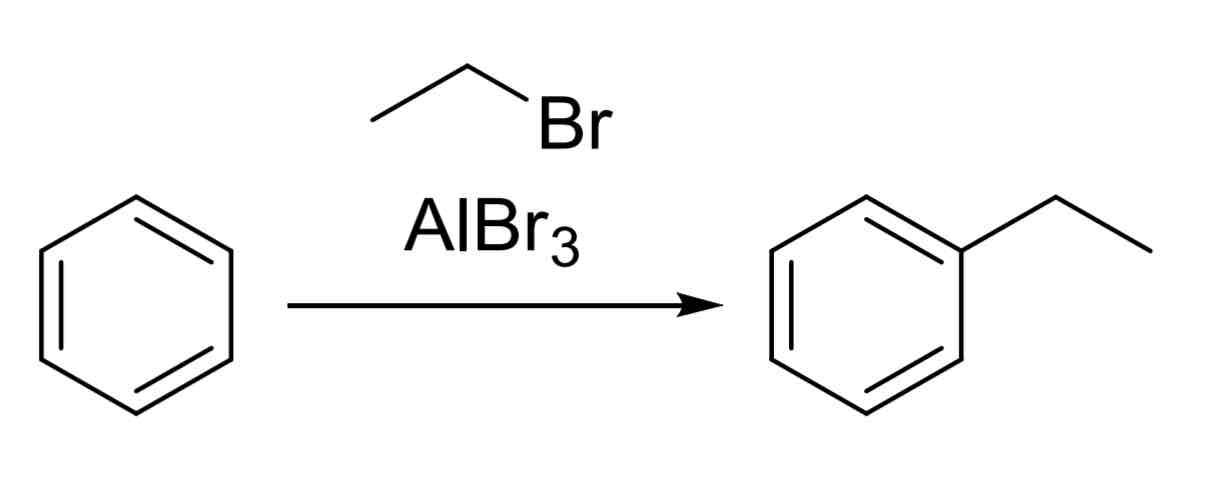
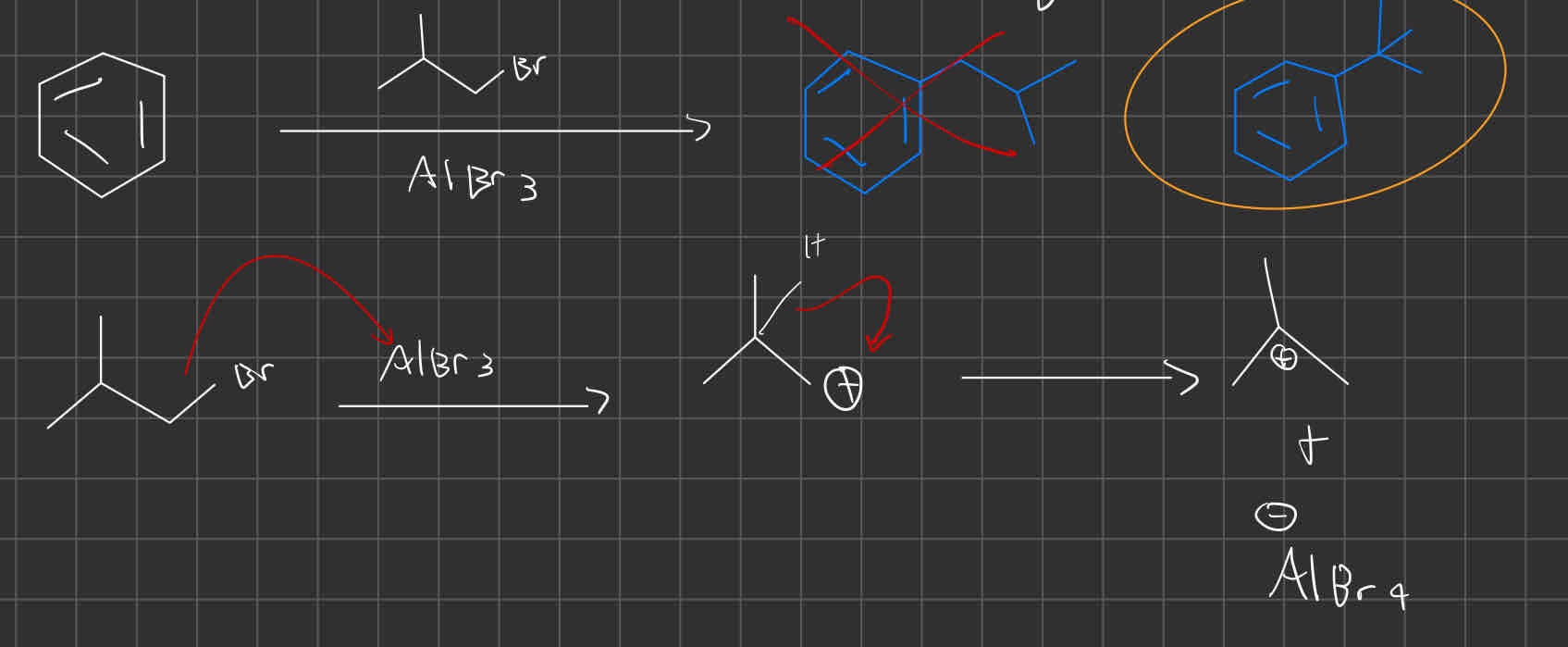
Friedel-Crafts Alkylation — adds alkyl group to ring
Alkyl halide, catalyst
Ex:
Br—CH3, AlBr3
Watch out for carbocation rearrangements; the alkyl halide may rearrange to make a more stable carbocation.
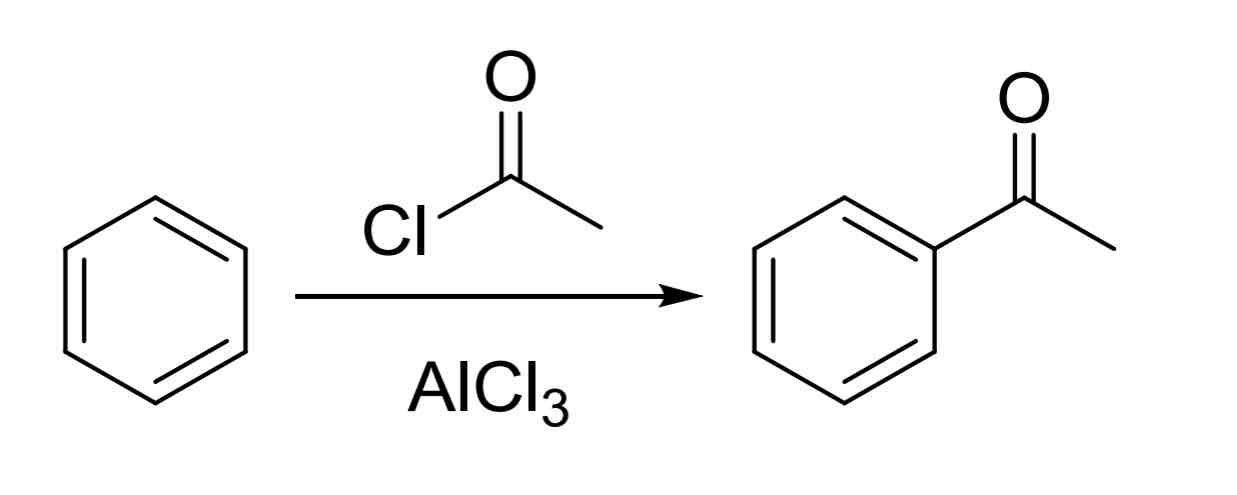
Friedel Crafts Acylation — puts acyl group on the ring
Acyl halide, catalyst
Ex:
Acyl halide, AlCl3
No carbocation rearrangement
Will always be resonance stabilized
Product has a moderate EWG so next group adds meta
Electron Donating Groups are….
Activating groups on the ring that make it more reactive.
ortho and para directors
Strong EDGs include…
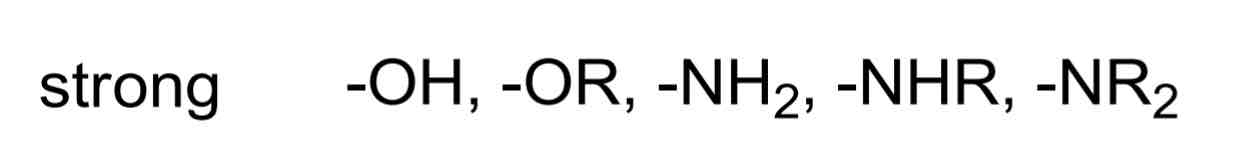
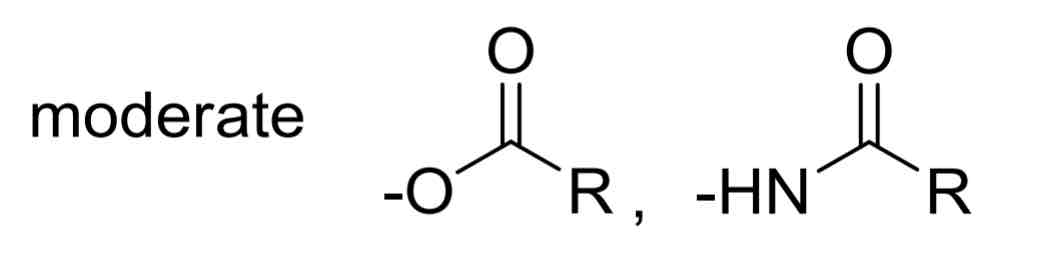
Moderate EDGs include…
Weak EDGs include…
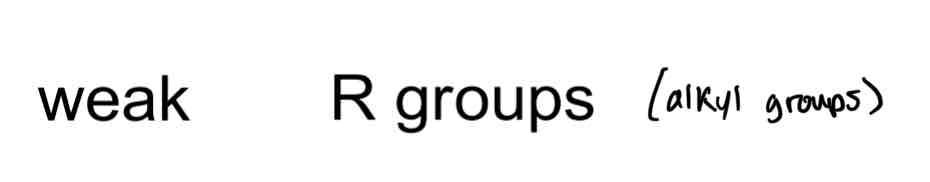
Electron Withdrawing Groups are…
Deactivating groups on the ring that make it less reactive.
Meta directors
Strong EWGs include…
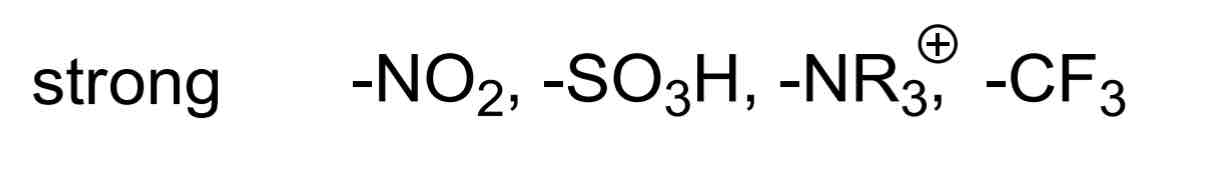
Moderate EWGs include…
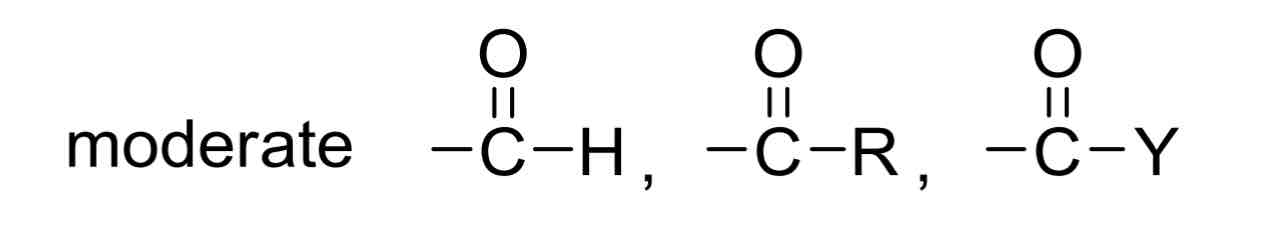
Weak EWGs include…
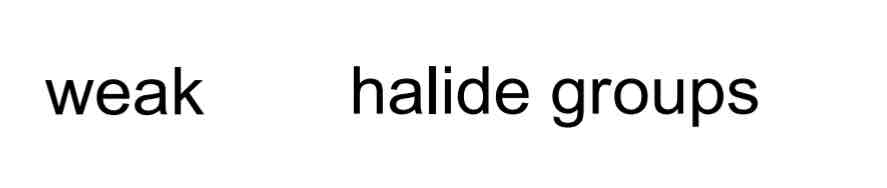
Aromatic Side Chain Reactions
Special reactions of functional groups that occur when located next to a benzene ring (some of these reactions do not normally occur if aromatic ring is not present)
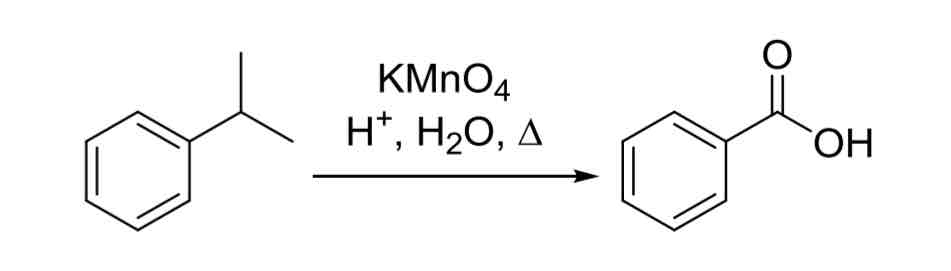
Alkyl Oxidation — any alkyl group on the ring with at least 1 benzilic hydrogen can be oxidized to form benzoic acid
KMnO4, H+, H2O, △
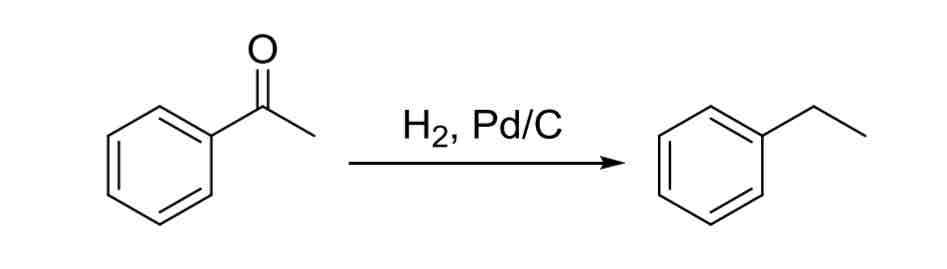
Aldehyde / Ketone Deoxygenation — Aldehyde or ketone directly next to ring can be reduced to CH2 group
H2, Pd/C
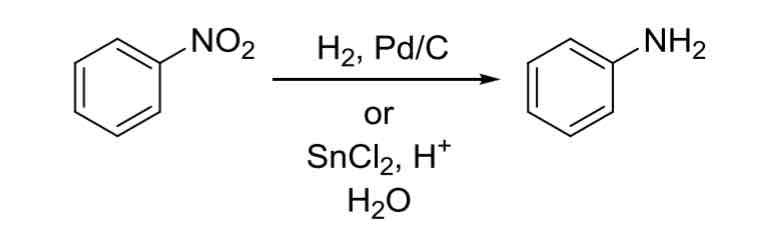
Reduction of NO2 to NH2 — Aromatic nitro groups Can NO2) can be hydrogenated to form an aromatic amine (NH2)
to reverse reaction and do NH2 —> NO2, use RCO3H
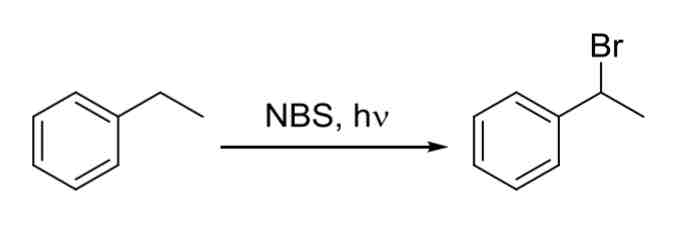
Benzilic Bromonation — replaces benzilic hydrogen with a Br
must have at least 1 benzilic hydrogen (hydrogen next to ring) for this reaction to occur
NBS, v
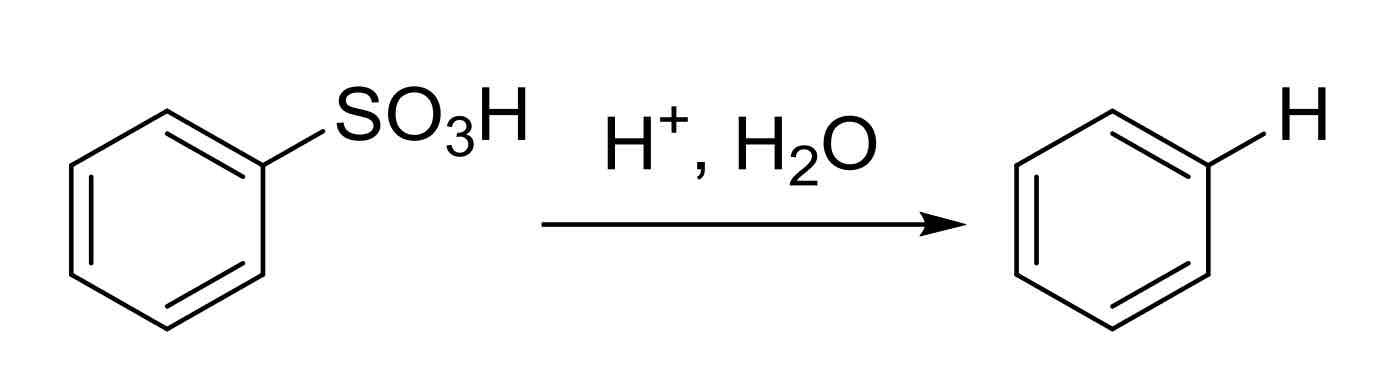
Removal of SO3H group - turns SO3H group into an H, simply removing it from ring
H+, H2O
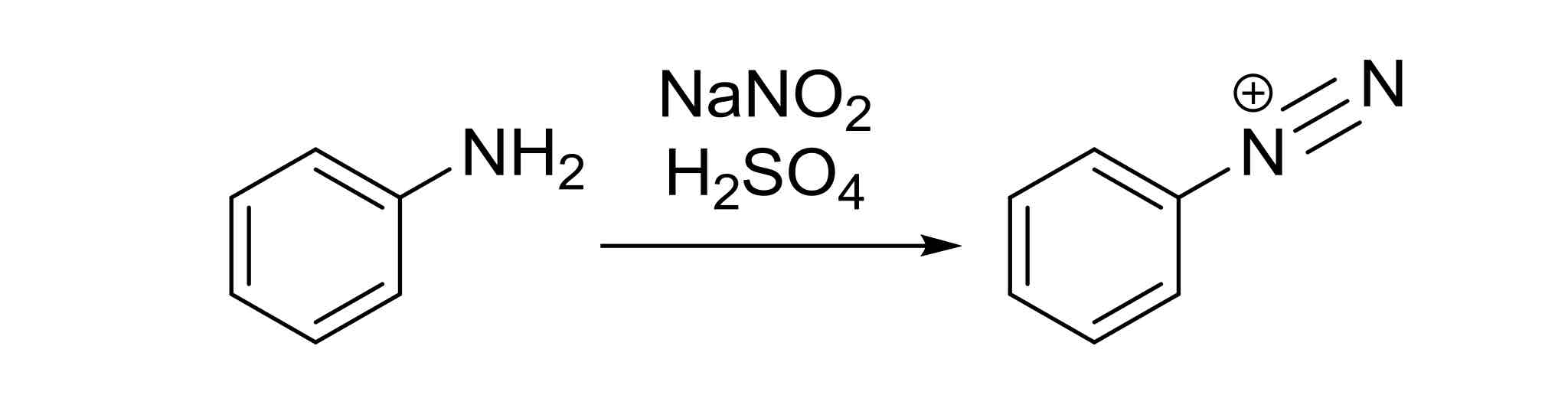
Diazotization — turns aromatic NH2 into +N≡N triple bond with plus charge
Must first add in NO2 and then reduce to NH2 using: H2, Pd/C or SnCl2, H+ H2O
NaNO2, H2SO4
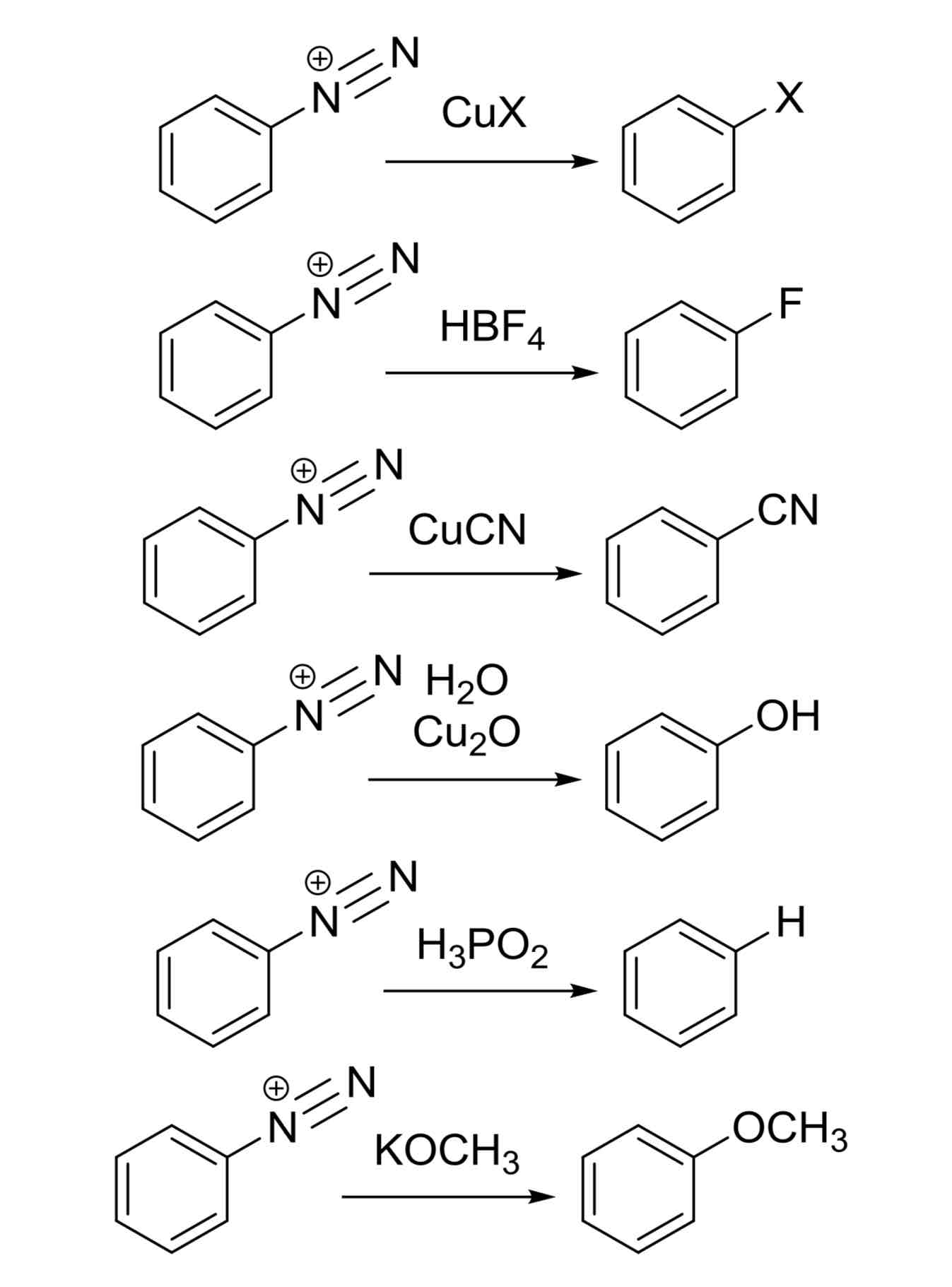
Diazotization Substitutions - Various ways to convert +N≡N into different groups
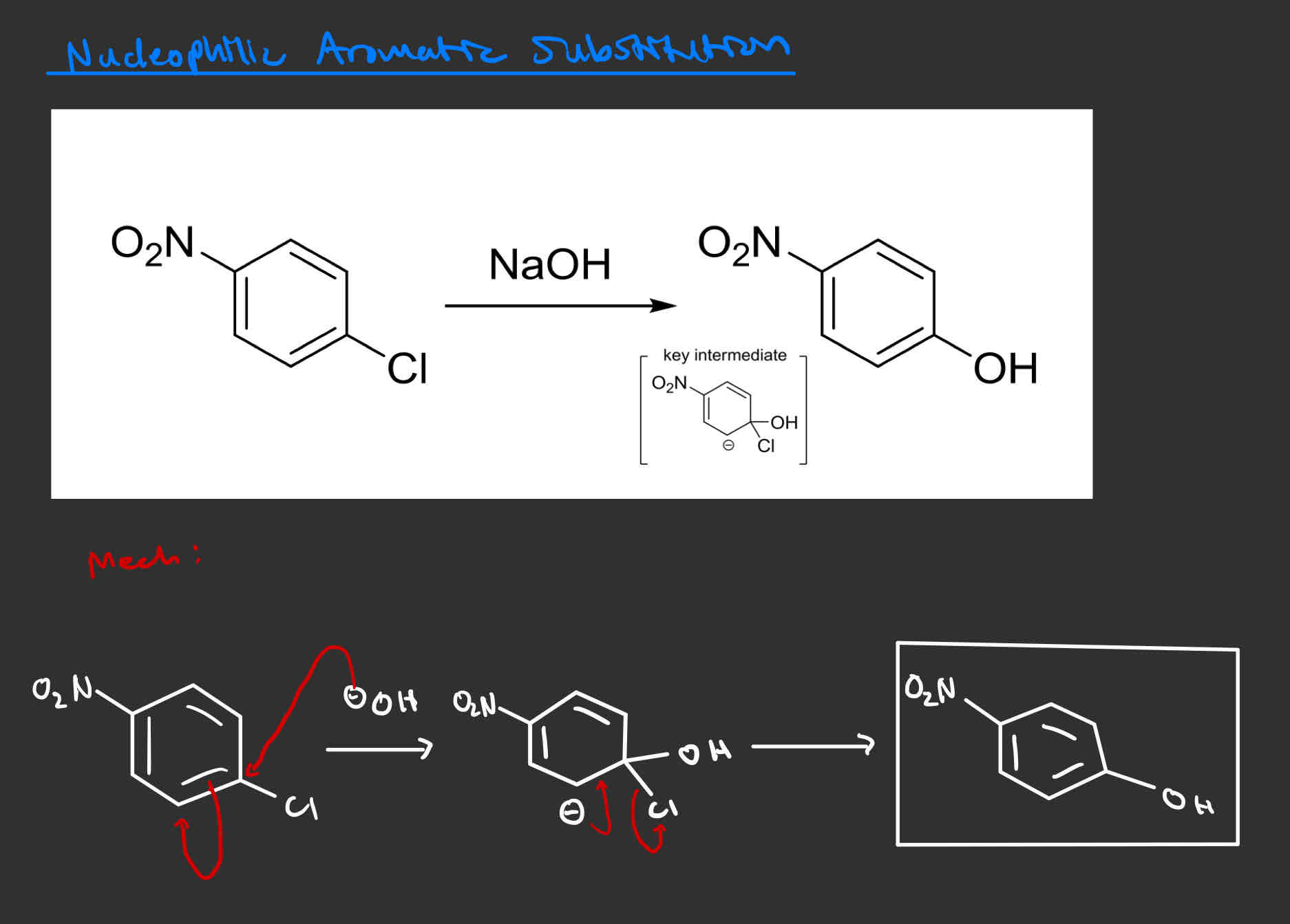
Nucleophilic Aromatic Substitution - can substitute LG with OH
Must have a halide ortho/para to a strong/moderate EWG
Na(Group adding in)
ex: NaOH
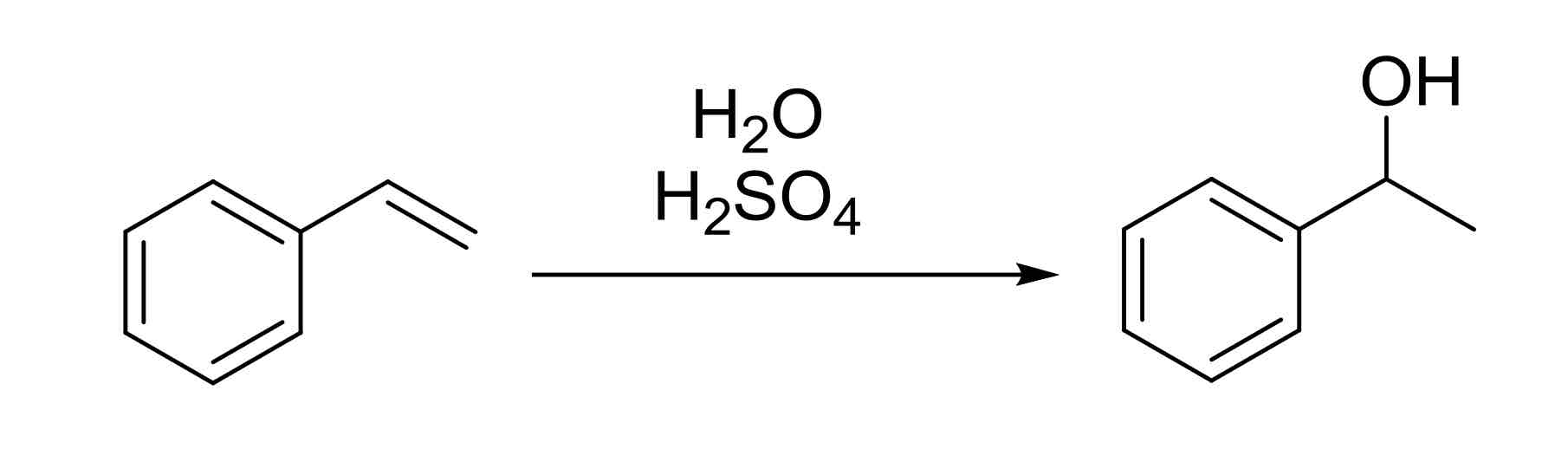
Alkene Acid Catalyzed Hydration — adds OH to more substituted carbon (Markovnikov)
carbocation rearranges
H2SO4, H2O
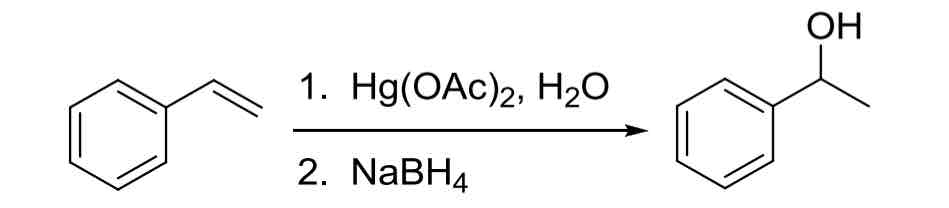
Alkene Oxymercuration Demercuration — adds OH to the more substituted Carbon (Markovnikov) but no rearrangements
no carbocation rearrangement
1. Hg(OAc), H2O 2. NaBH4
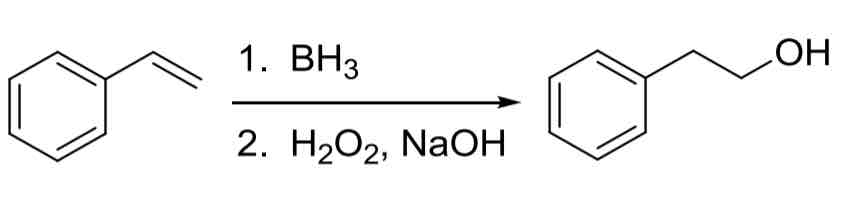
Alkene Hydroboration Oxidation — adds OH to less substituted carbon (anti-Markovnikov)
no carbocation rearrangments
Syn addition occurs
1. BH3 2. NaOH, H2O2
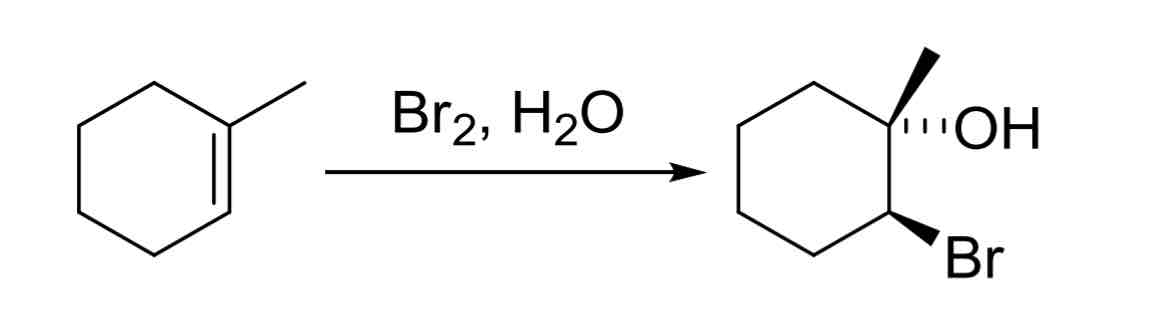
Alkene Halohydrin Formation — adds an OH and halide, OH on more substituted carbon
anti addition
X2, H2O
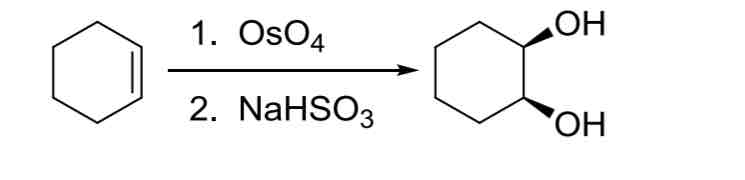
Alkene Dihydroxylation — adds two OH groups to both carbons of alkene, syn to each other
syn addition
1. OSO4 2. NaHSO3
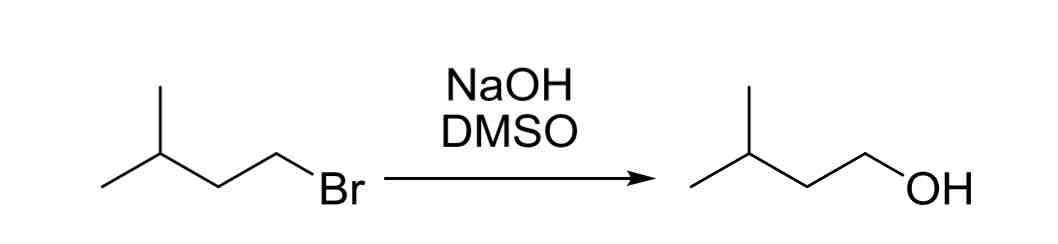
SN2 Substitution - 1° LG’s (which are not hindered) can be substituted with OH groups via reaction with:
NaOH (strong base, not hindered)
polar aprotic solvents like DMSO (leads to SN2)
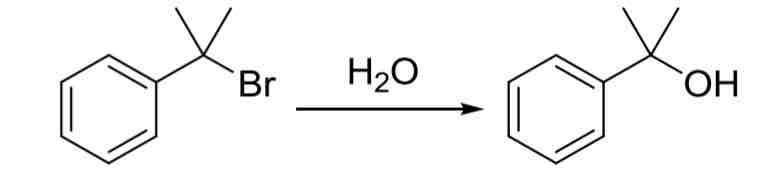
SN1 Substitution - 2° and 3° (hindered) LG’s can be substituted with OH group via reaction with
protic solvent like H2O (solvolysis) leads to SN1
carbocation rearranges
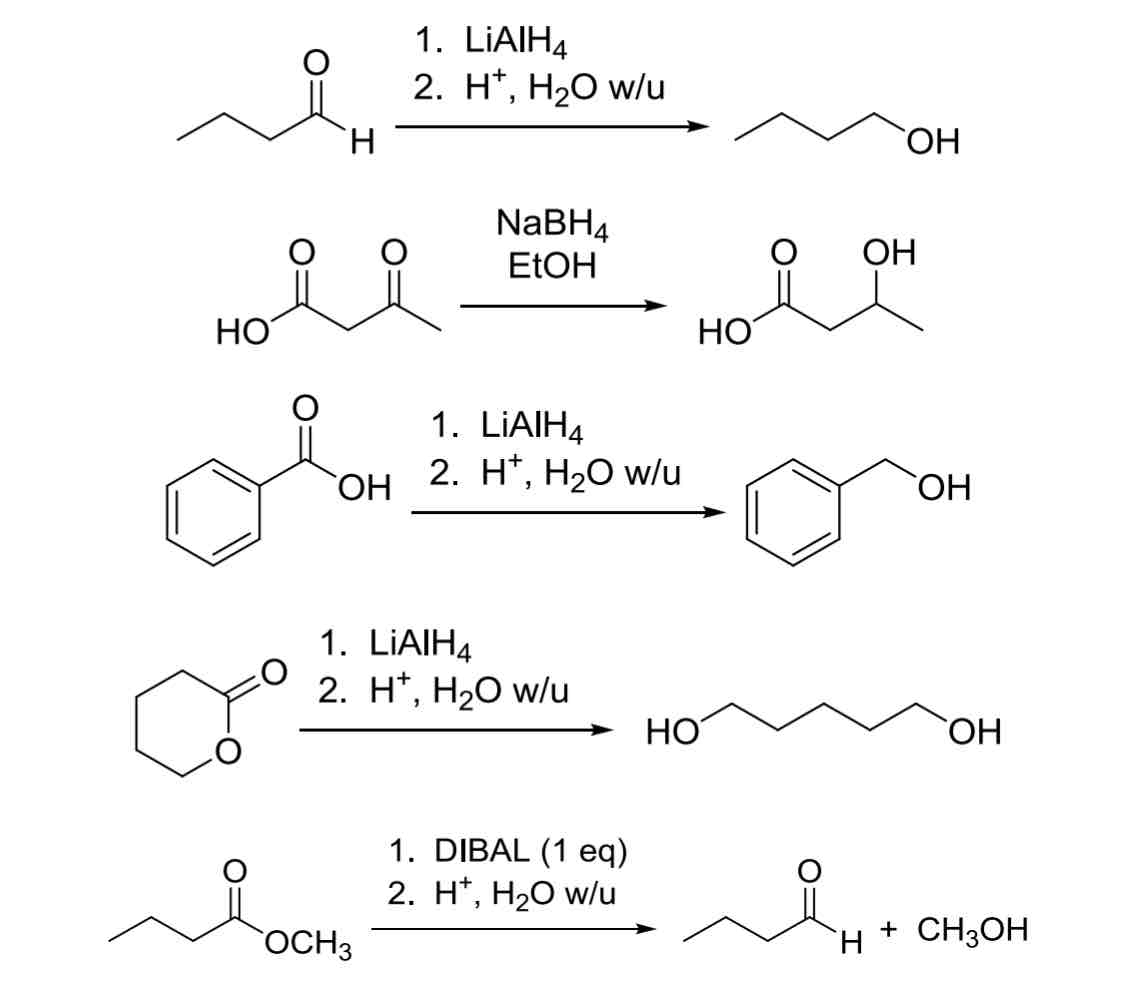
3 common Hydride Reagents H:Θ
(Reduction of Carbonyls —> OH)
NaBH4
only reacts with aldehydes and ketones
Least reactive
LiAlH4
Will react with all carbonyl groups (including carboxylic acids)
Most reactive
DIBAL
1 eq of H:Θ, good to use when reacting selectively
only reacts with aldehydes and ketones
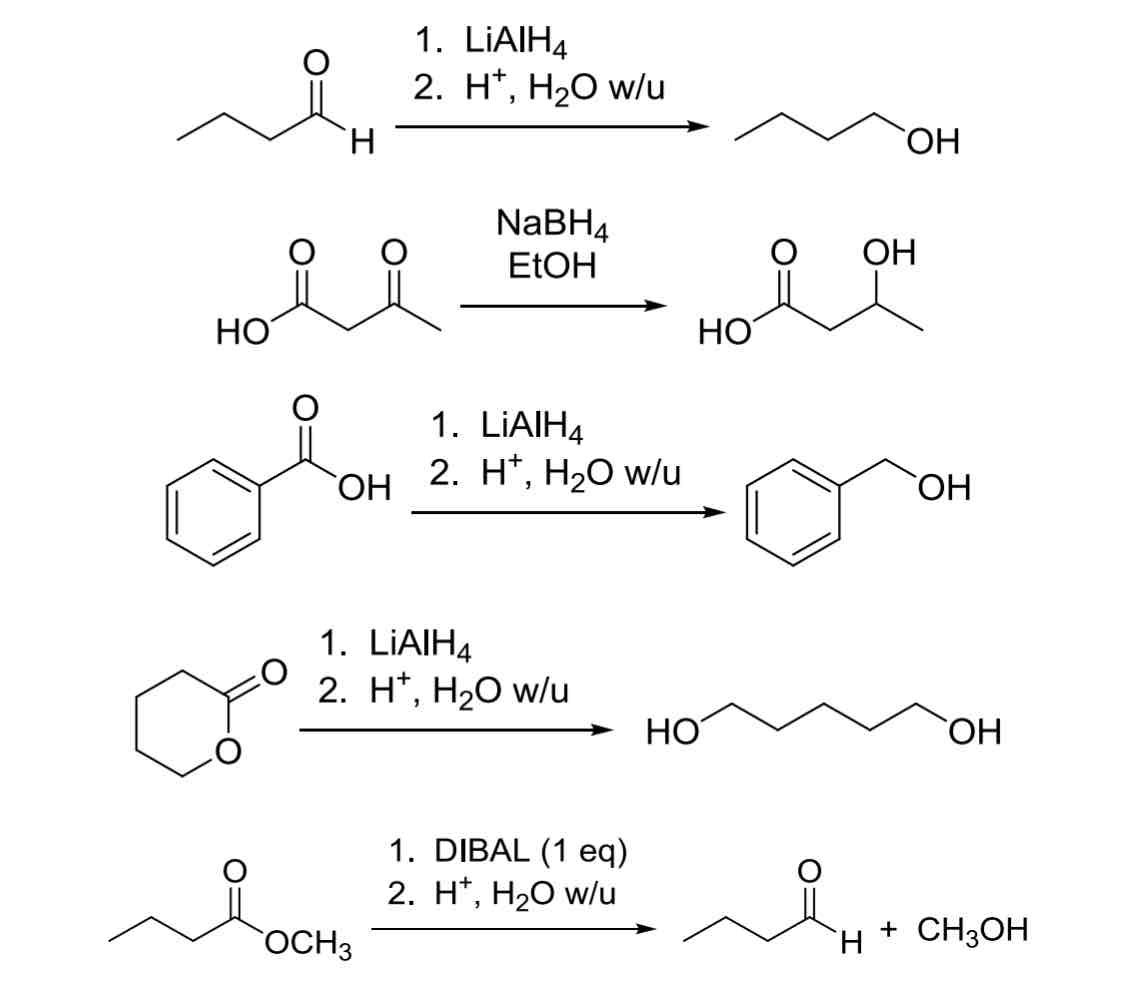
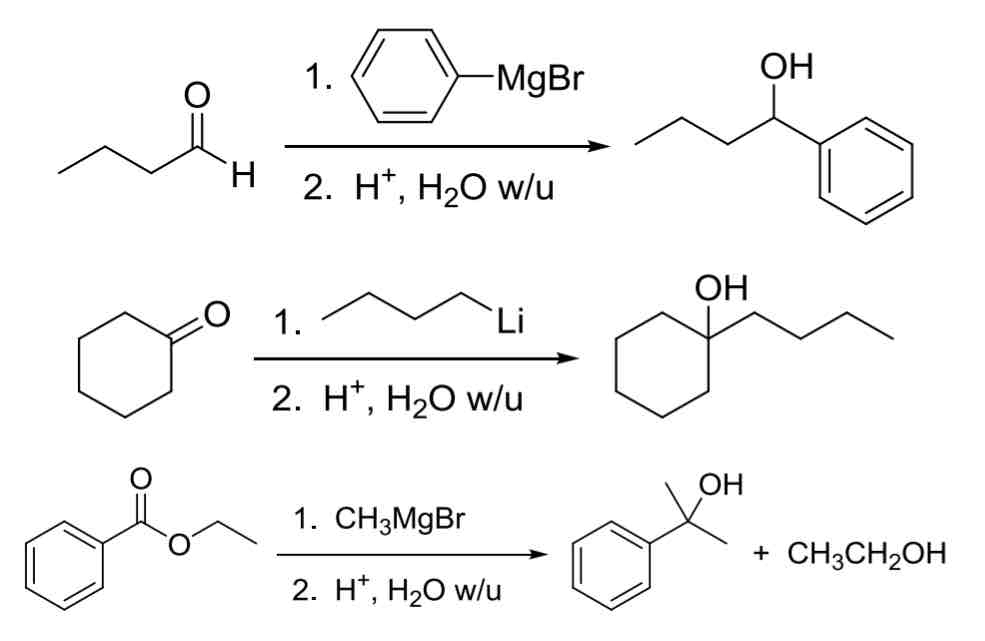
3 common Carbanion Nucleophiles R:Θ
(Used to make C—C bond)
R-MgBr (Gringard Reagent)
most common
R-Li (organolithium reagent)
super reactive
R2CuLi (organocuprates)
All three add similarly to aldehydes and ketones while esters will add two equivalents
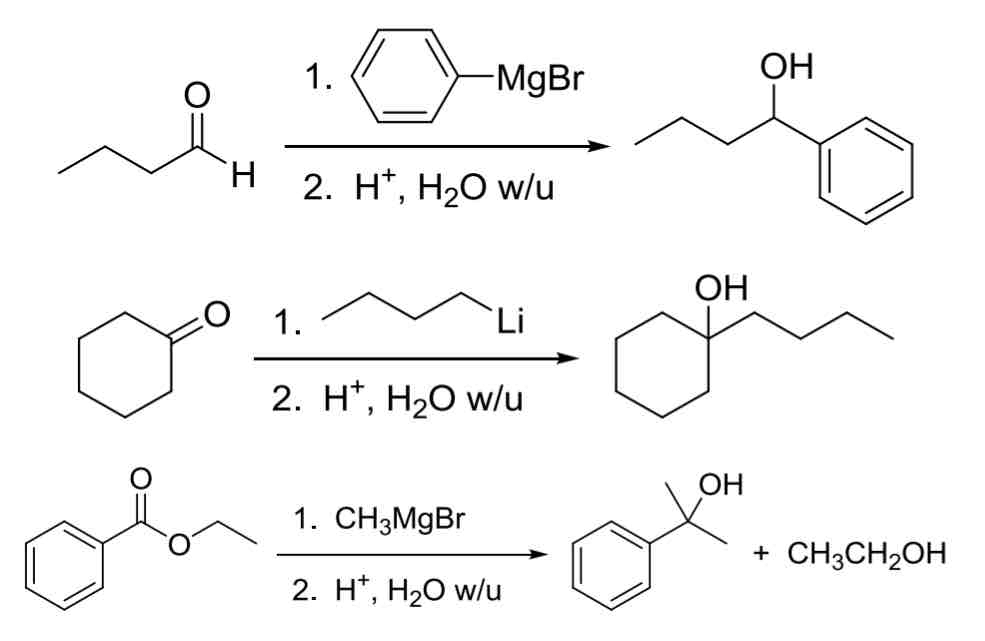
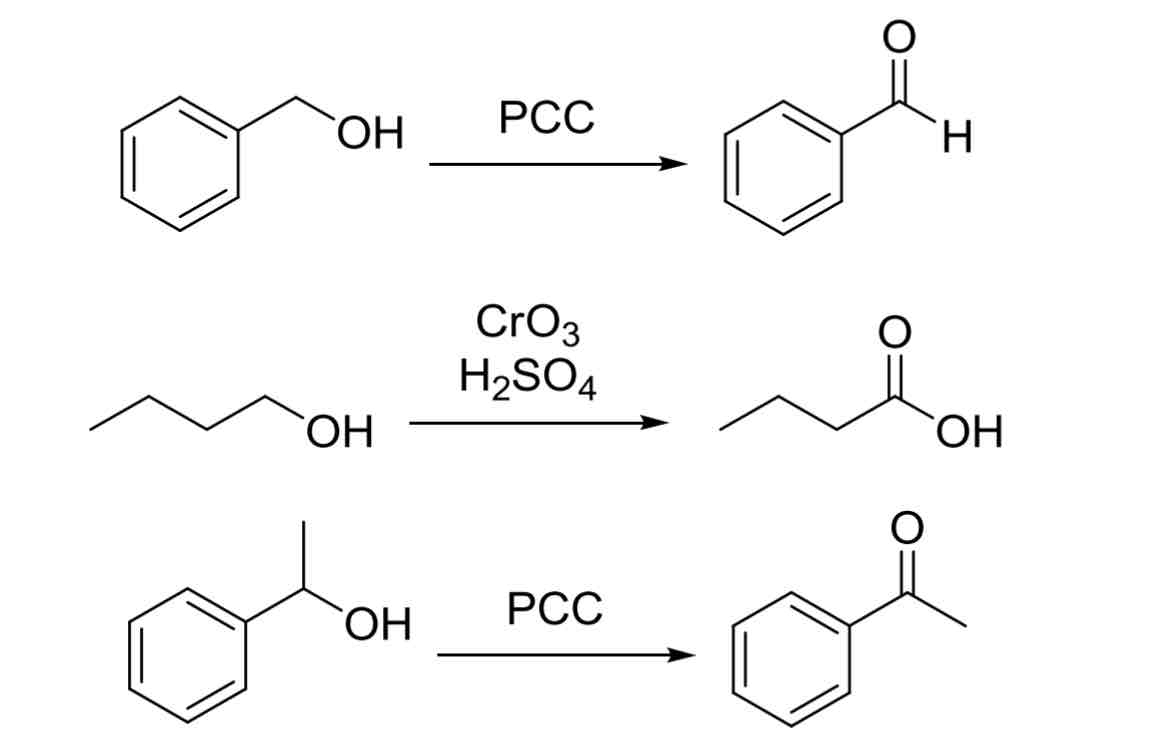
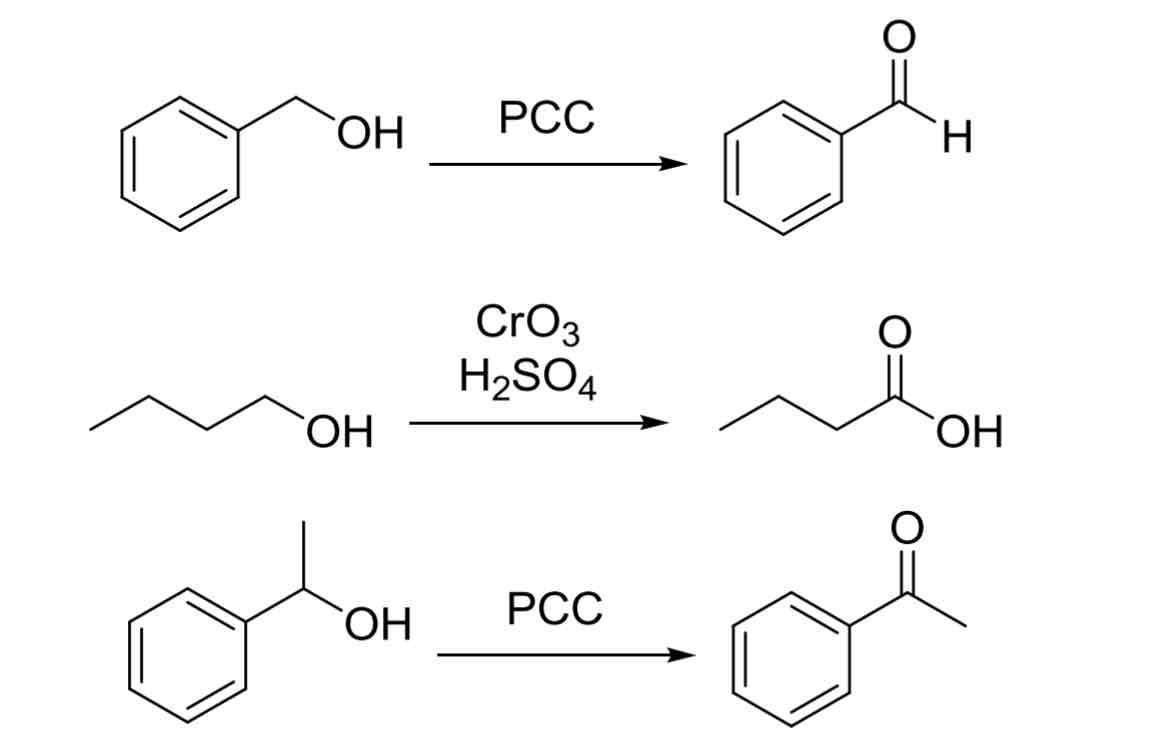
Alcohol Oxidation Oxidants
(OH —> Carbonyl group)
PCC
1° OH —> Aldehyde
2° OH —> Ketone
3° OH —> No reaction
CrO3, H2SO4
1° OH —> Carboxylic Acid
2° OH —> Ketone
3° OH —> No reaction
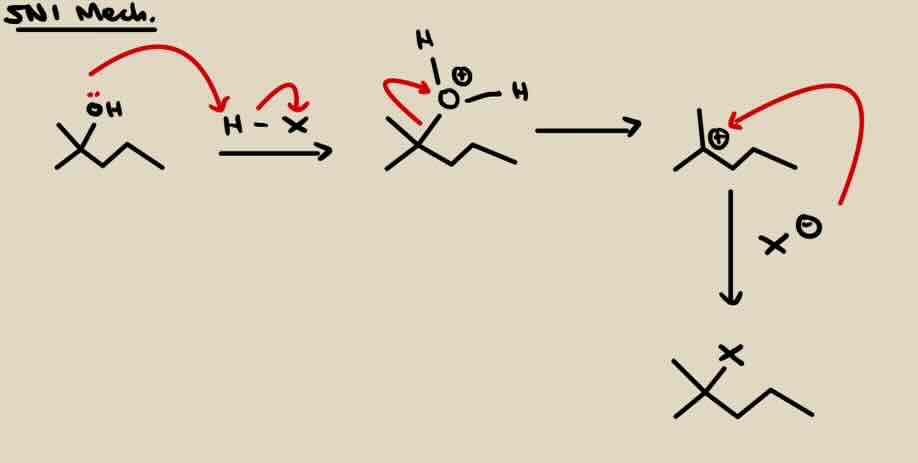
SN1 Conversion of OH to Alkyl Halide (Br, Cl)
3° > 2° substrate
H - X
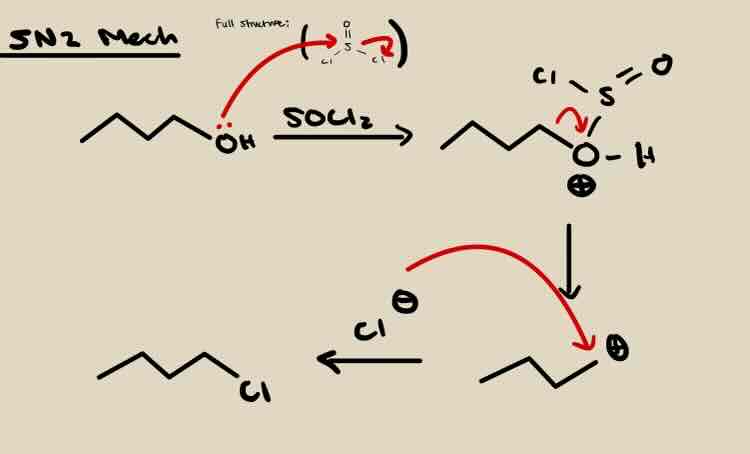
SN2 Conversion of OH to Alkyl Halide (Br, Cl)
CH3 > 1° > 2° > substrate
PBr3, SOCl2
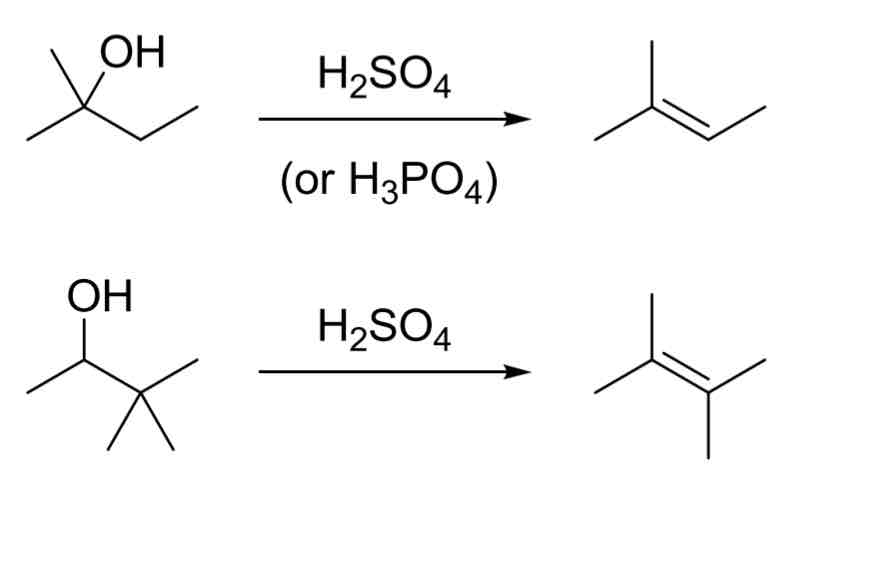
E1 Acid Catalyzed Dehydration
3° > 2° substrate
Carbocation rearranges
Forms most stable alkene product (Zaitsev product)
H2SO4 (or H3PO4)
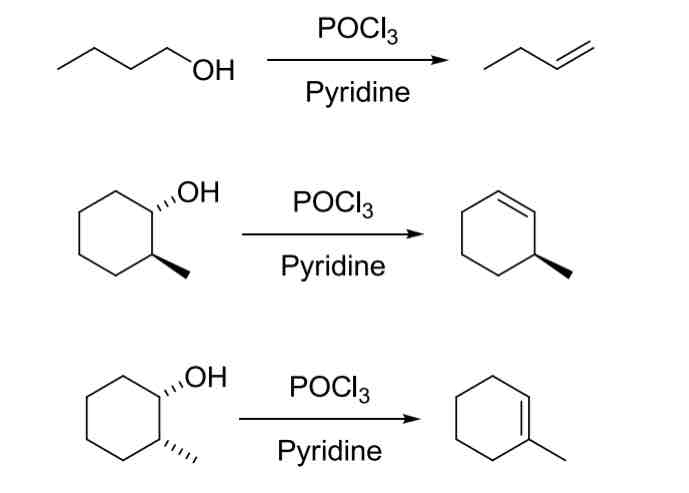
E2 Promoted Dehydration
1° = 2° = 3°
Forms most stable alkene product (Zaitsev product)
POCl3, Pyridine
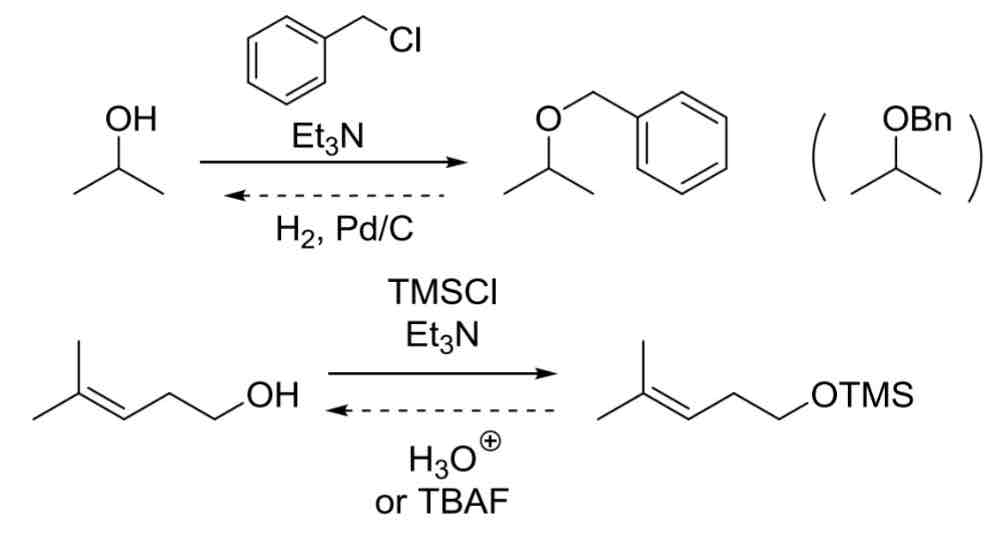
Alcohol Protecting Groups
Blocks OH group from doing typical OH reactions by adding group
Reactivity order: CH3 > 1° > 2° > 3° (all work)
Benzyl Protecting group
BnX, Et3N
Unprotect using H2, Pd/C
Trimethylsilyl Protectint Group
TmsX, Et3N
Unprotect using H3O+ or TBAF
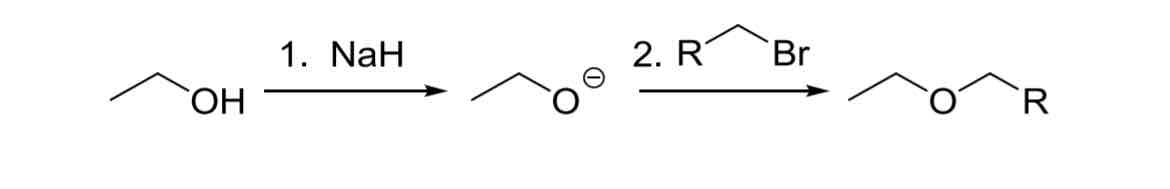
Williamson Ether Synthesis
Ideal for CH3 and 1° alcohols (and some 2°), not 3, leads to Elim
Alkyl halides must be CH3 or 1° only (or competing elimination will occur)
NaH, non-hindered Alkyl Halide
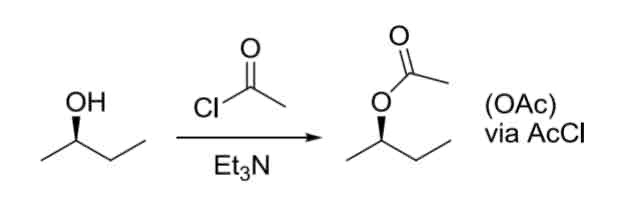
Conversion of OH —> OAc, Oms, OTos LG
Reactivity order: CH3 > 1° > 2° > 3° (all work)
(AcX) or (msX) or (TosX), and Et3N
For Acidity, if there are EWG present, it is a stronger acid. If there are EDG present, it is a weaker acid.
TRUE