Lecture 15: Genomic Imprinting
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
__________________refers to monoallelic expression that occurs in a manner specific to the parent of origin.
genomic imprinting
Usually, both alleles are capable of expression in genomic imprinting._________ of human genes (80 genes) are expressed from one allele.
<1%
Where is genomic imprinting originated from?
paternal or maternal
Imprinted genes often exist in clusters. ______ of imprinted mammalian genes exist in clusters. (not a rule)
80%
Imprinting is controlled by ____________mechanisms.
epigenetic
Imprinting genes are usually involved in ___________________.
development
Mouse chromosome translocation
maternal and paternal chromosome can be distinguished
mammals are diploid and inherit a set of chromosomes from the mom and dad
mice can be generated
inherit two copies of a chromosome from one parent and one copy from another UPD
inherit partial chromosome deletion from one parent and a wild type chromosome from other parent
inherit chromosomes carrying SNP from one parent and wild type chromosome from a
offspring with UPDs or deletions are likely to display lethal phenotypes, whereas SNPs will allow the production of viable offpsring
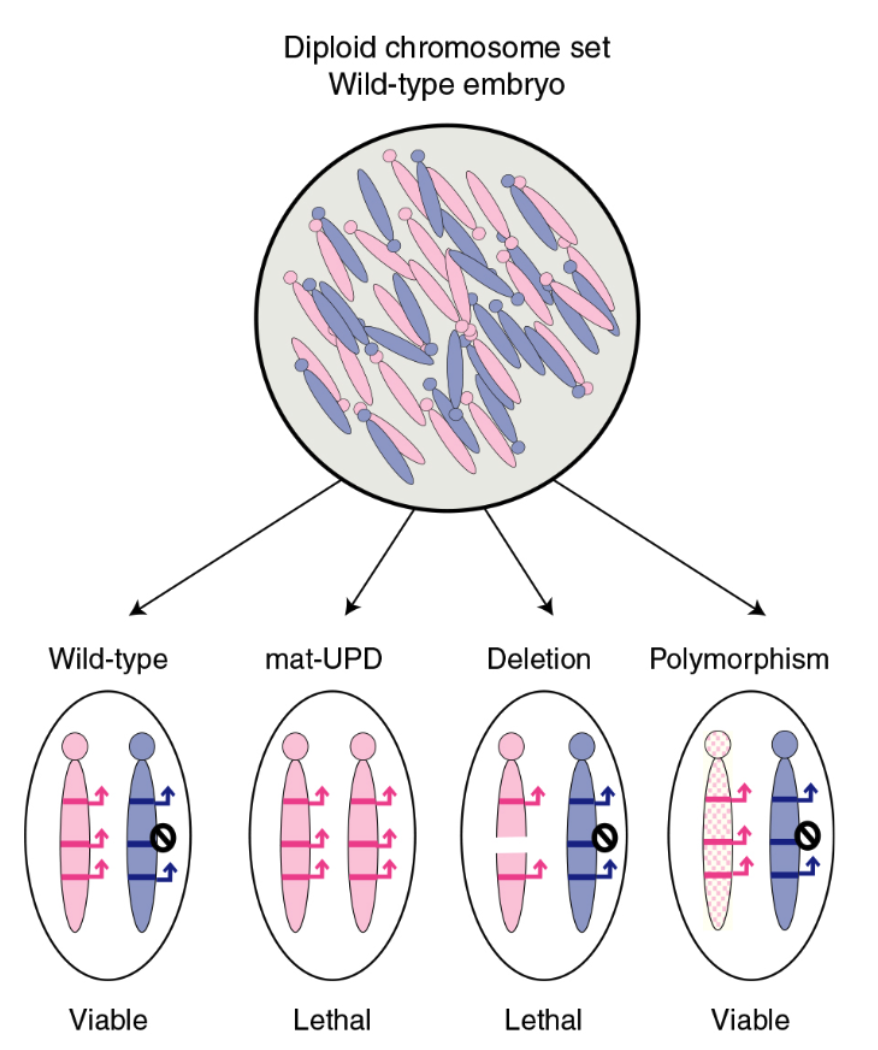
UPD
uniparental disomy
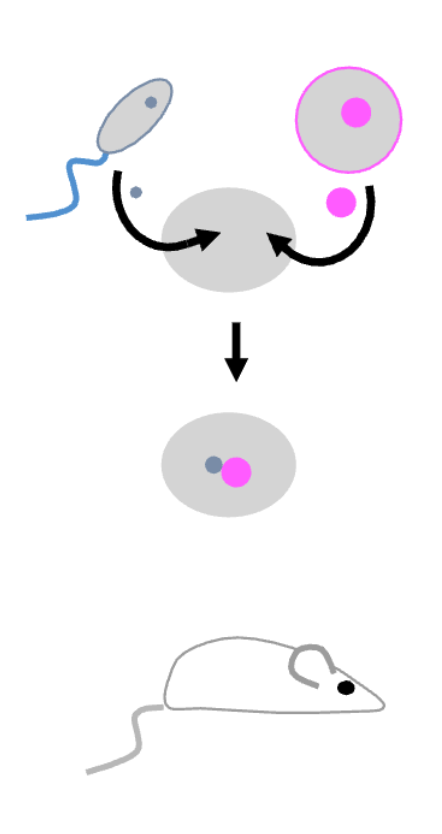
What is the imprinting nuclear transplant experiment?
Placing a sperm and an egg nucleus into an enucleated fertilized cell leads to a normal embryo
In imprinting nuclear transplant experiment, zygote that receive only maternal or paternal nuclei do not_________________.
survive
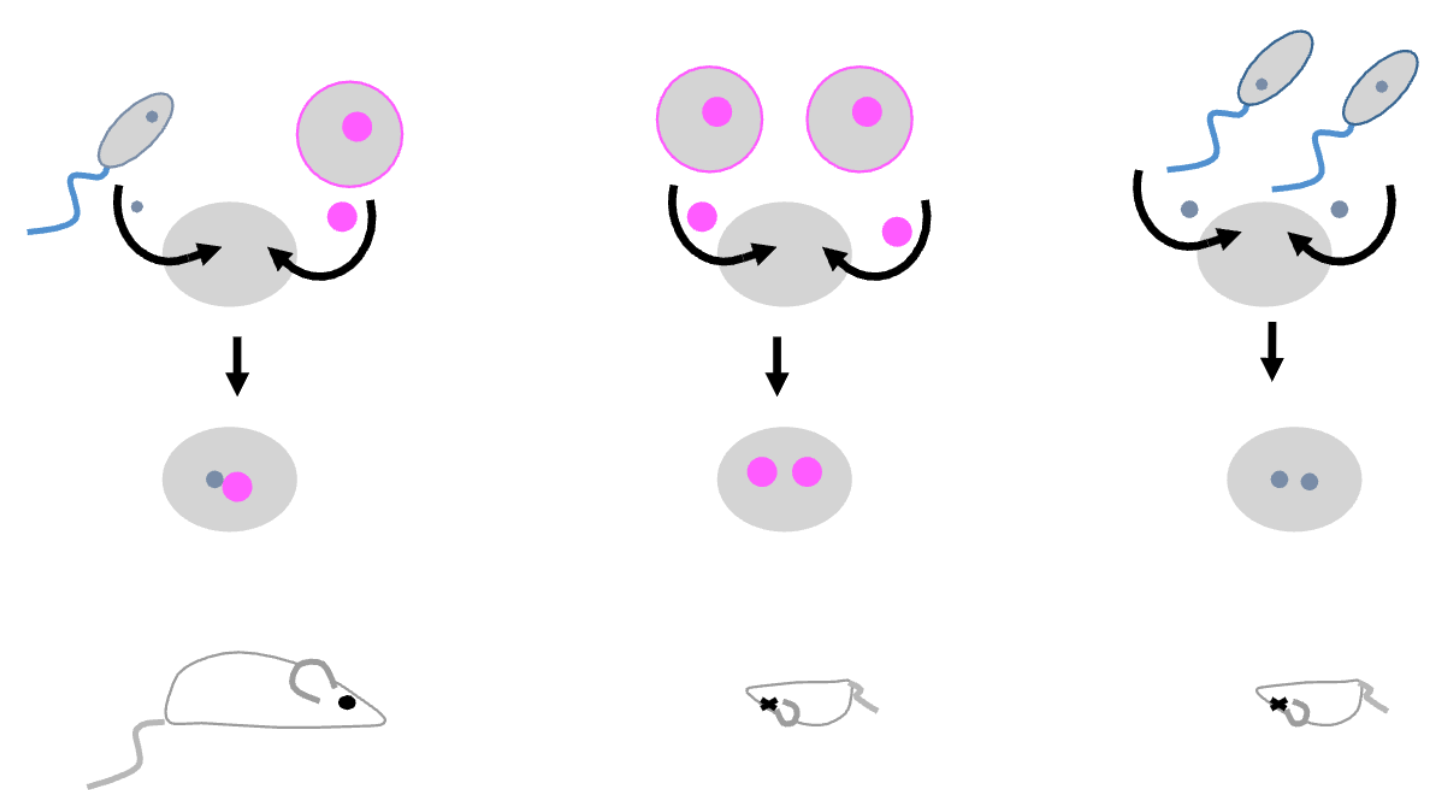
In the imprinting nuclear transplant experiment: two parental genomes are NOT equivalent, what does imprinting prevent?
parthenogenesis
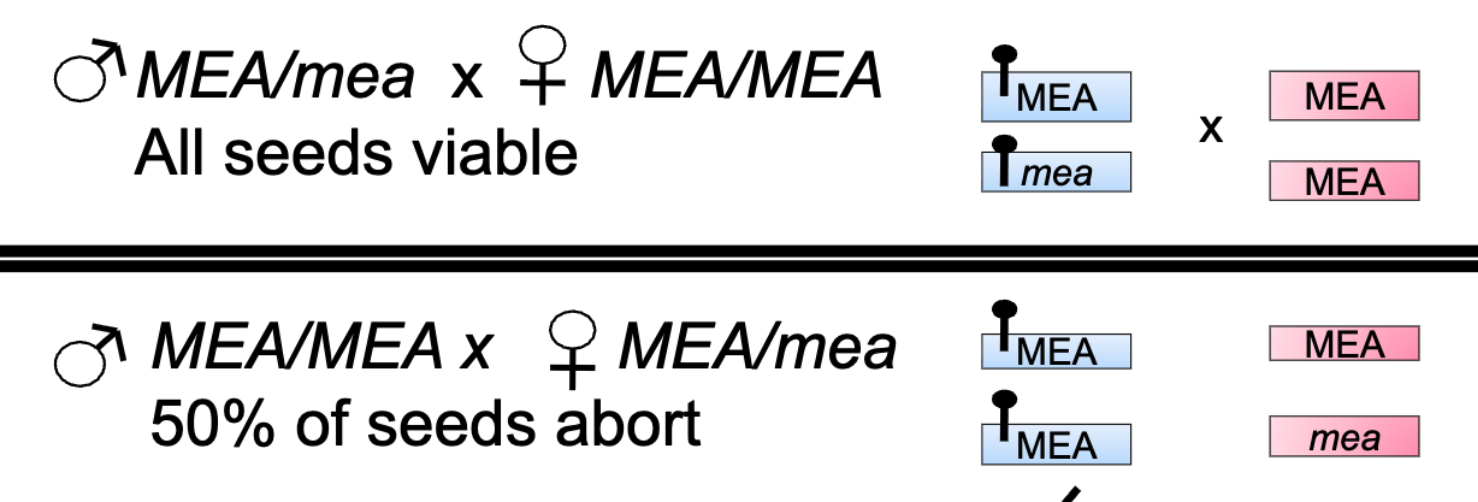
MEDEA (MEA) gene is imprinted.
What do these F MEA/mea x M MEA/MEA alleles mean?
What do these MEA/MEA x MEA/mea alleles mean?
all seeds viable
50% of seeds abort

In the second cross, 50% of the seeds receive the mutant mea allele from their mother.
These seed abort, even though they also have a ________________ MEA allele inherited from their father.
wild-type
What do the paternal allele ( first arrow) represent in this?
What do the maternal allele (second arrow) represent in this?
The paternal allele is silent.
The phenotype of the progeny is based on the maternal genotype
MEA is ______________ most cells.
silenced
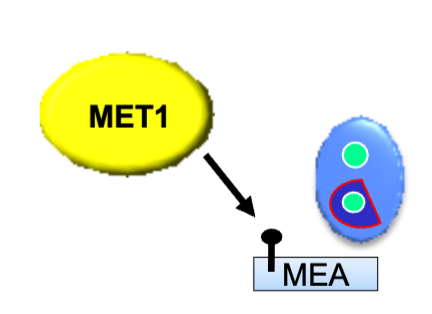
What is MEA methylated by?
MET1
in vegetative tissues and the male gametophyte
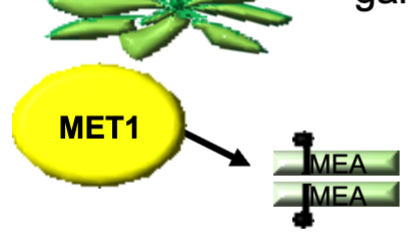
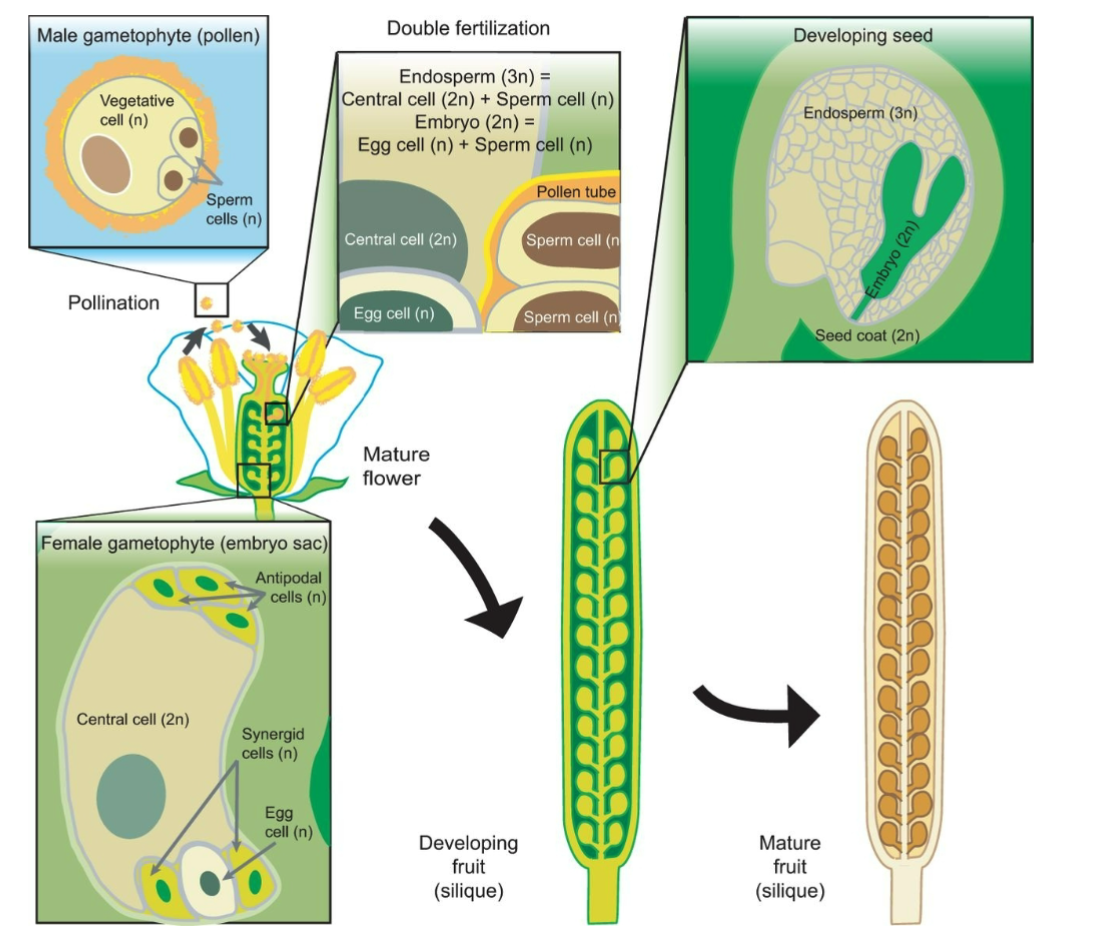
Sexual Reproduction in plants
MEA is demethylated and expressed in the ________________gameotyphyte.
female
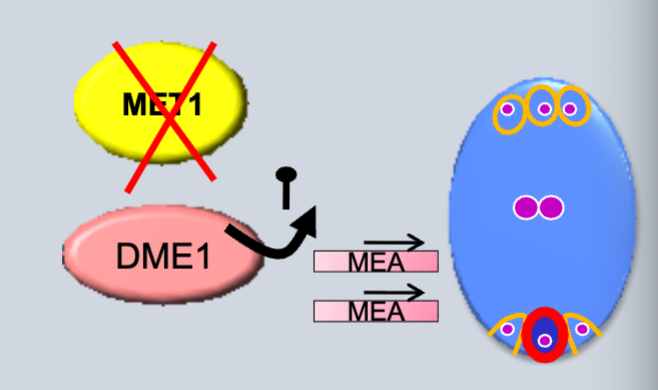
In females, the central cell DME removes DNA methylation from maternally expressed genes__________ and __________; and from the paternally expressed gene__________.
MEA and FIS2
PHE1
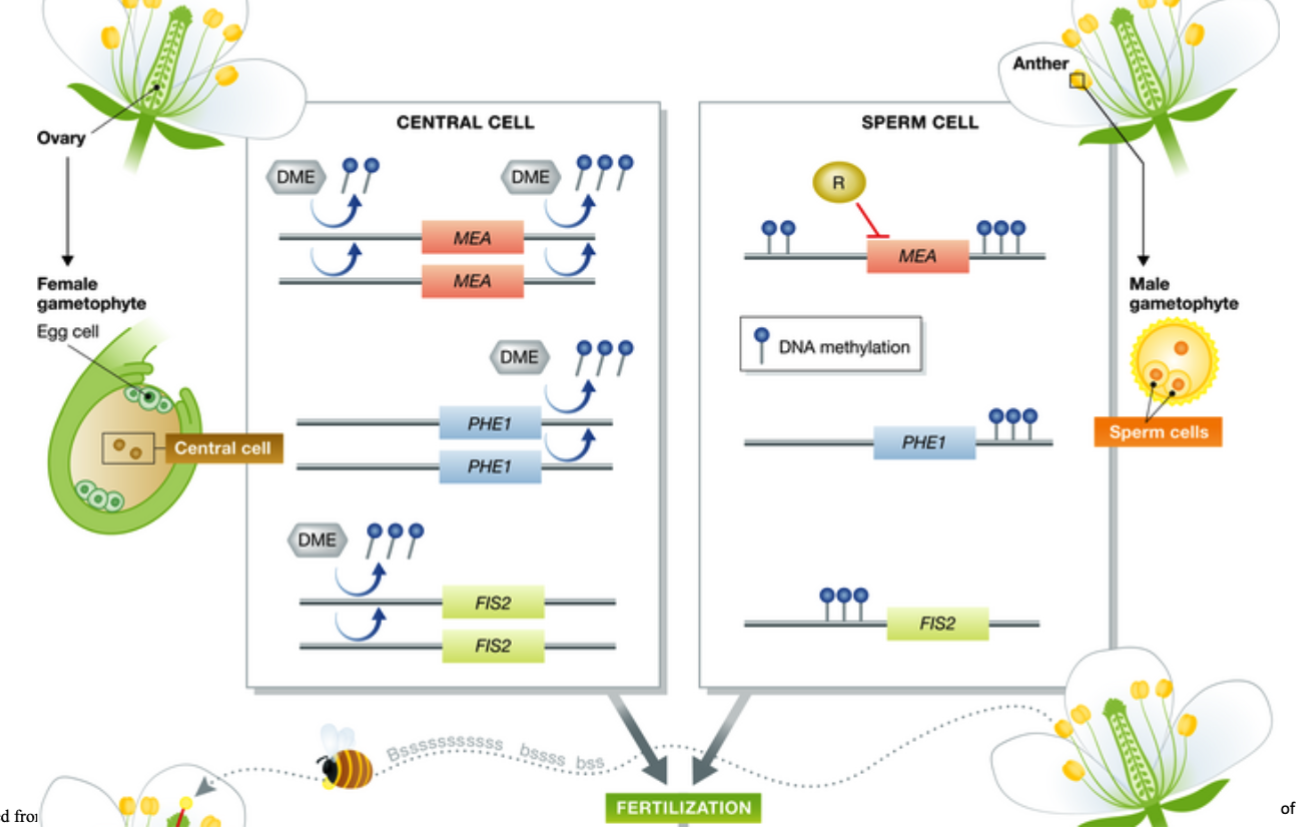
DNA methylation at these loci are maintained in the ________gametophyte. Another unknown repressor (R) may be required for repression of the paternal allele in of MEA.
male
In endosperm, maternal alleles of MEA and FIS2. The ________complex mediates silencing of maternal allele of PHE.
PRC2
The maternal removal of DNA methylation downstream of the _________gene is required for silencing of it’s maternal allele.
PHE
Comparison of Imprinting in Plants and Mammals
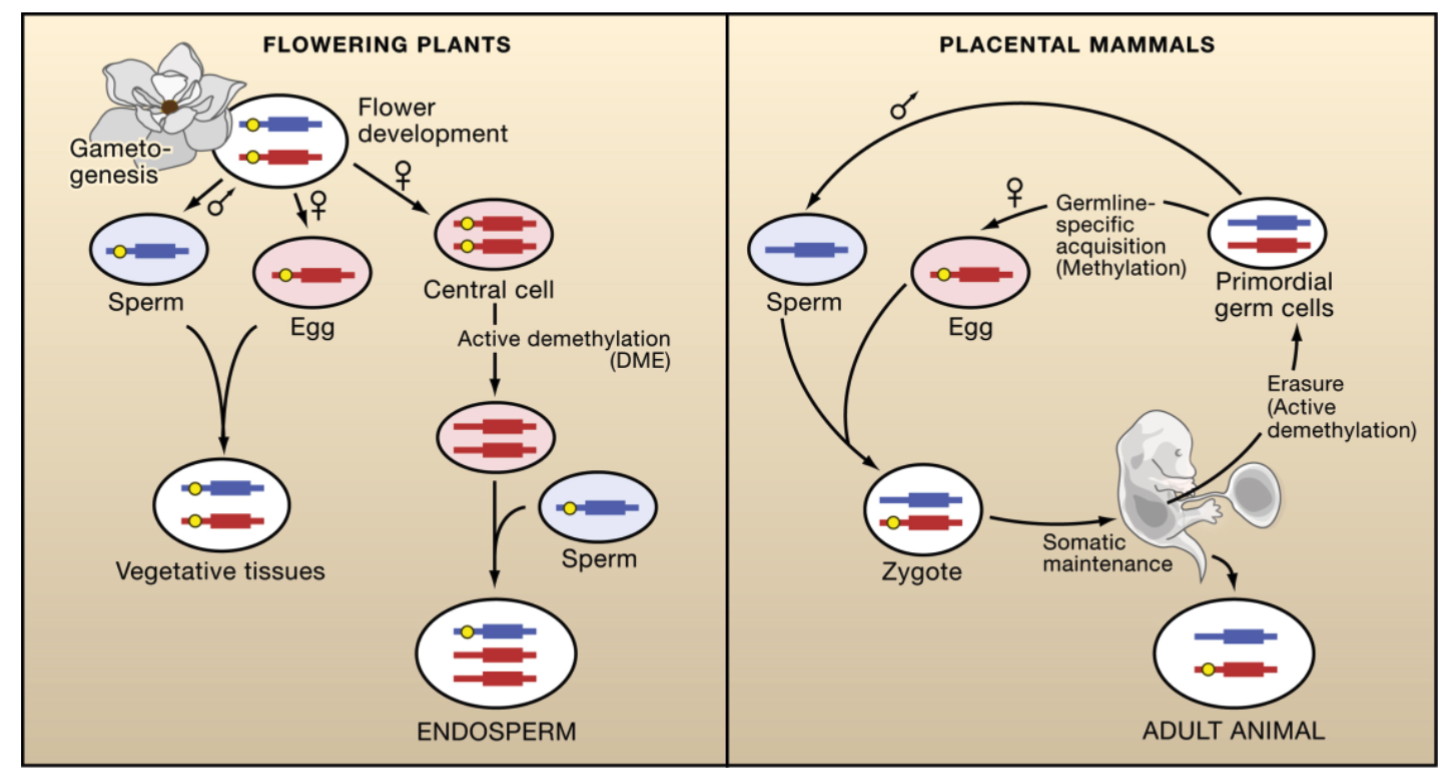
Imprints acquisition and erasure in mammalian development
1st generation imprints
2nd generation maternal imprints: acquired in oocytes
2nd generation: paternal imprints acquired in sperm
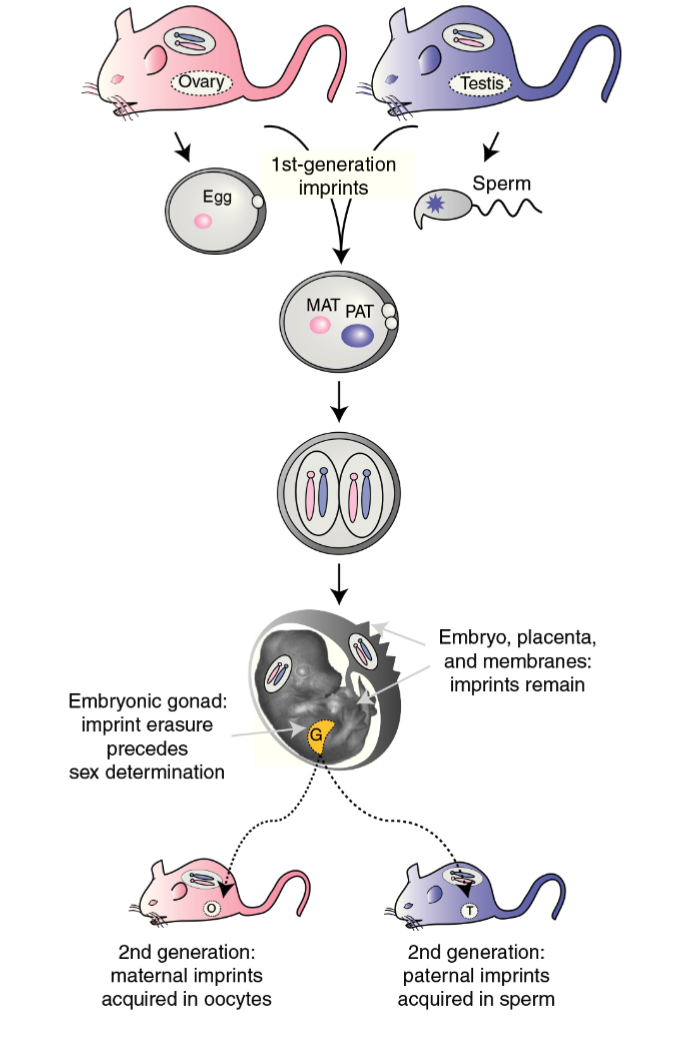
Embryonic gonad during imprint acquisition and erasure in mammalian development
imprint erasure precedes sex determination
Embryo, placenta and membrane during imprint acquisition and erasure in mammalian development
imprints remain
Establishment, Maintenance and Erasure of Imprints during Mouse development

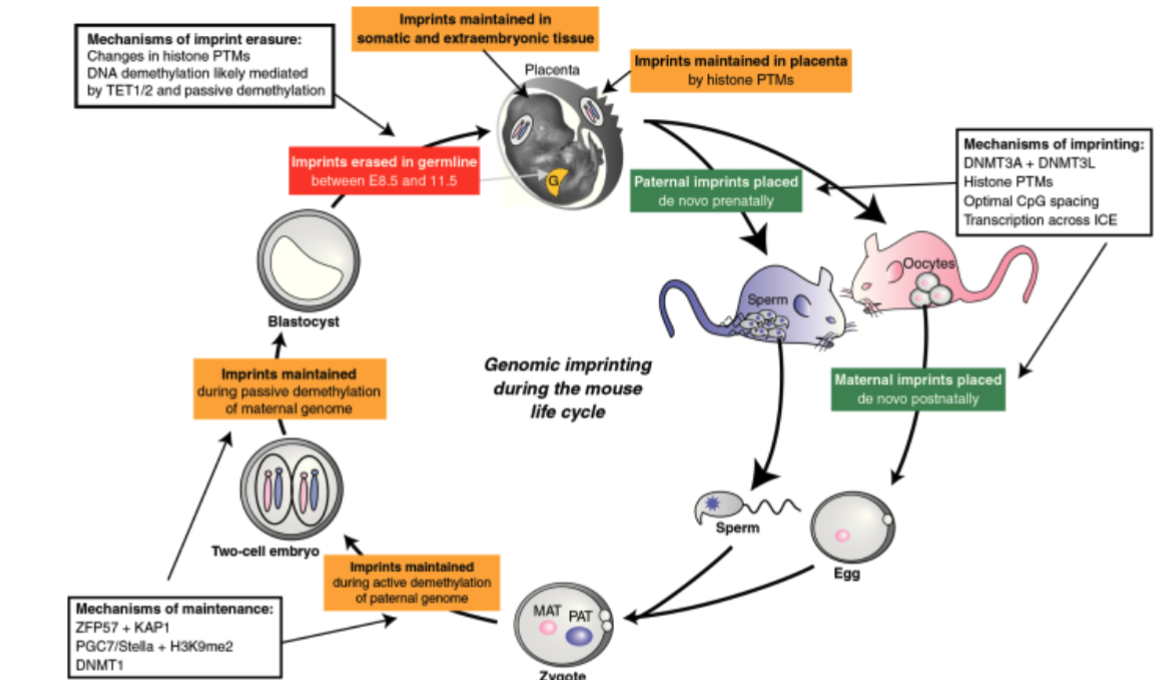
Mammalian Imprinted Genes Controlled by _______________ control elements.
imprint
Imprinted genes exist in __________.
clusters
Imprint control elements are required for imprinting:
deletion of ICE leads to loss of imprinting
ICEs carry parent of origin specific epigenetic modifications
these include differentially methylation regions (DMR)
There is at least one _______________(IncRNA) presente, often expressed from chromosome carrying silenced genes.
long non-coding RNA
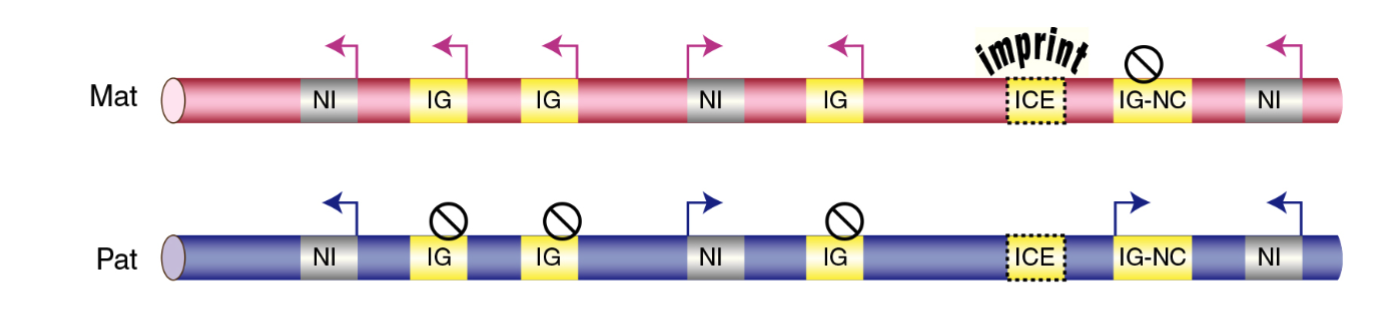
Imprinting is controlled by _______.
DMRs
Deletion of __________only causes loss of imprinting when deleted from parental chromosome expressing IncRNA.
ICE