AP Bio Unit 3: Cellular Energetics
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Enzyme
A biological catalyst that speeds up biochemical reactions
Proteins in tertiary formation
Facilitates either synthesis or digestion reactions
Substrate
Molecule that interacts with an enzyme
Active Site
This part of the enzyme interacts with a substrate.
Unique shape, size, and sometimes charge
Denaturation
Change in pH and temperature causes a change in the conformational shape of an enzyme
Higher temperature or change in pH
Competitive Inhibitor
This molecule binds to an active site on an enzyme and prevents the substrate from binding to the enzyme, therefore slowing down or preventing reactions from occurring
Noncompetitive Inhibitor
This molecule binds to an allosteric site on an enzyme and prevents the substrate from binding to the active site of an enzyme, therefore slowing down or preventing reactions from occurring
Energy Coupling
Energy-releasing processes drive energy-storing ones
Entropy
Something all living things want to avoid: the tendency to head into chaos and disorder
Thylakoid
The light-dependent reaction of photosynthesis takes place in the _____
2 NADPH, 3 ATP
The light-dependent reaction in photosynthesis sends this to the Calvin Cycle
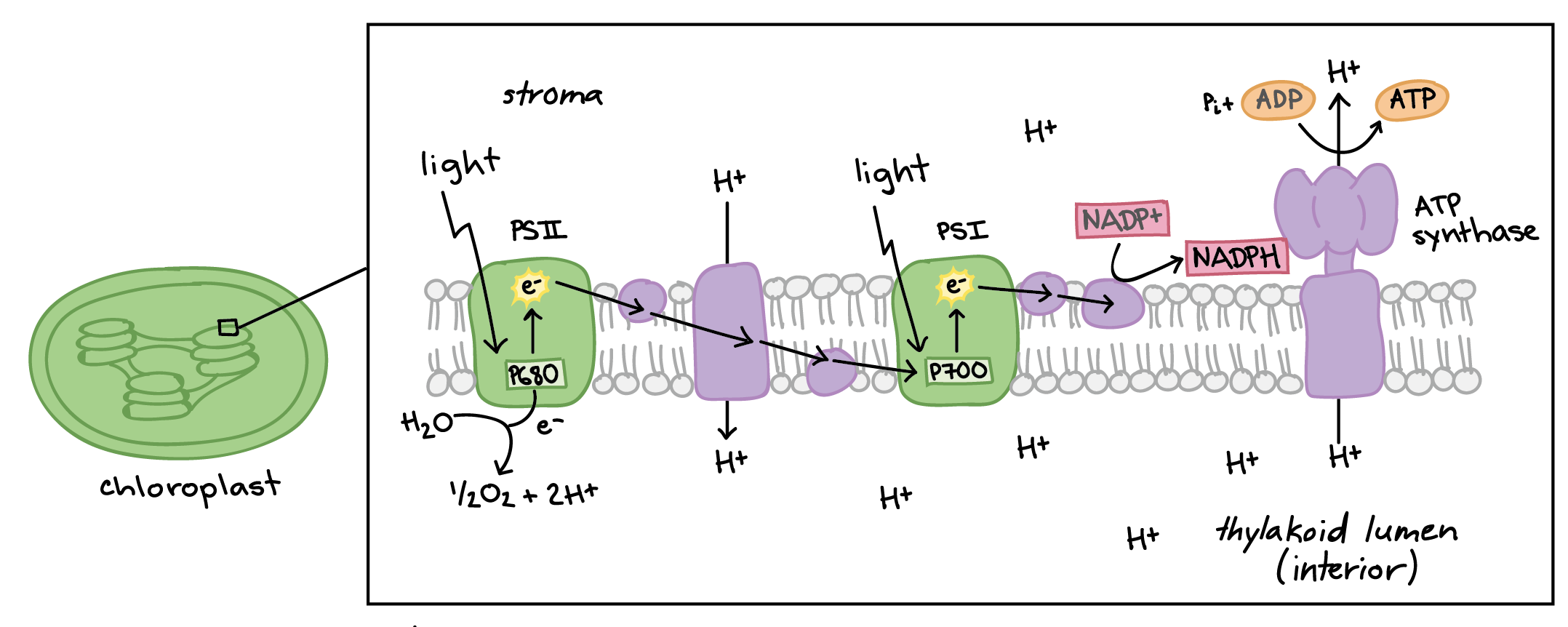
Proton Motive Force / PMF
the force that promotes movement of protons across membranes downhill the electrochemical potential
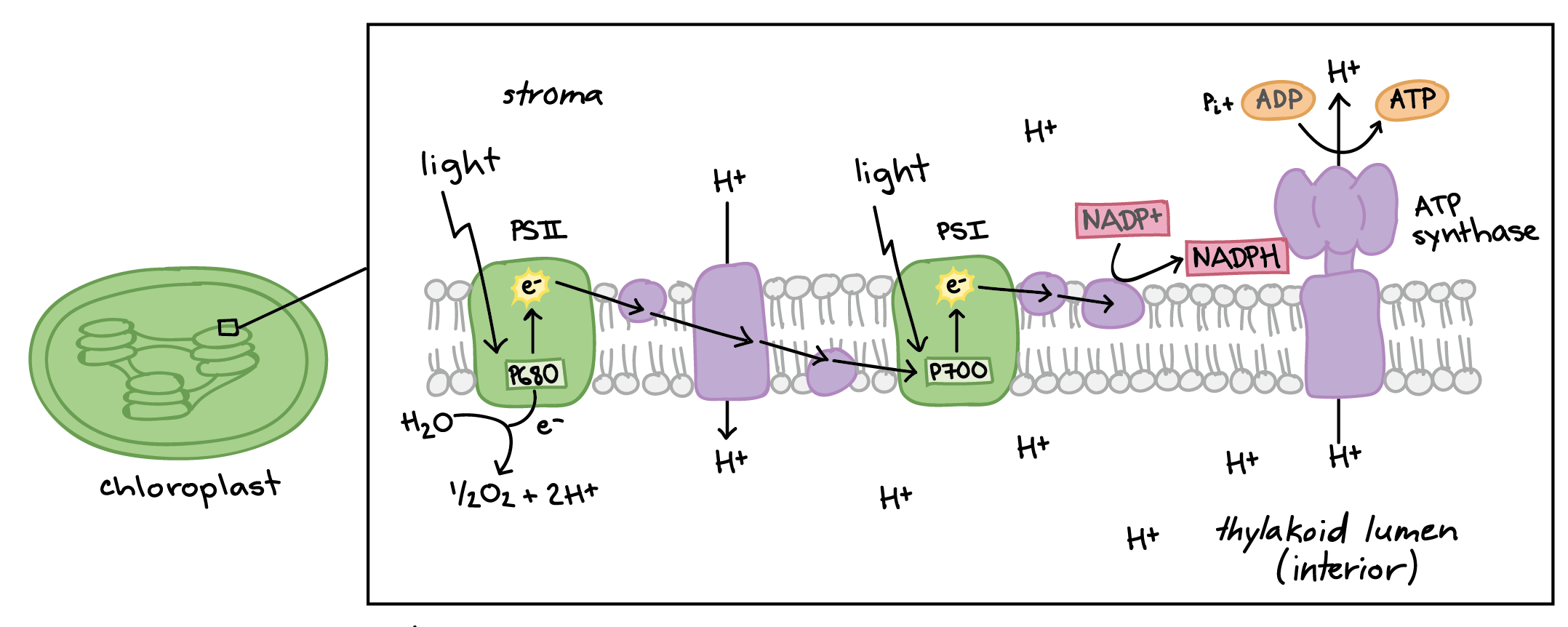
Light-Dependent Reaction
This happens in the thylakoid membrane of the chloroplasts and occurs in the presence of sunlight. The sunlight is converted to chemical energy during these reactions. The chlorophyll in the plants absorb sunlight and transfers to the photosystem which are responsible for photosynthesis
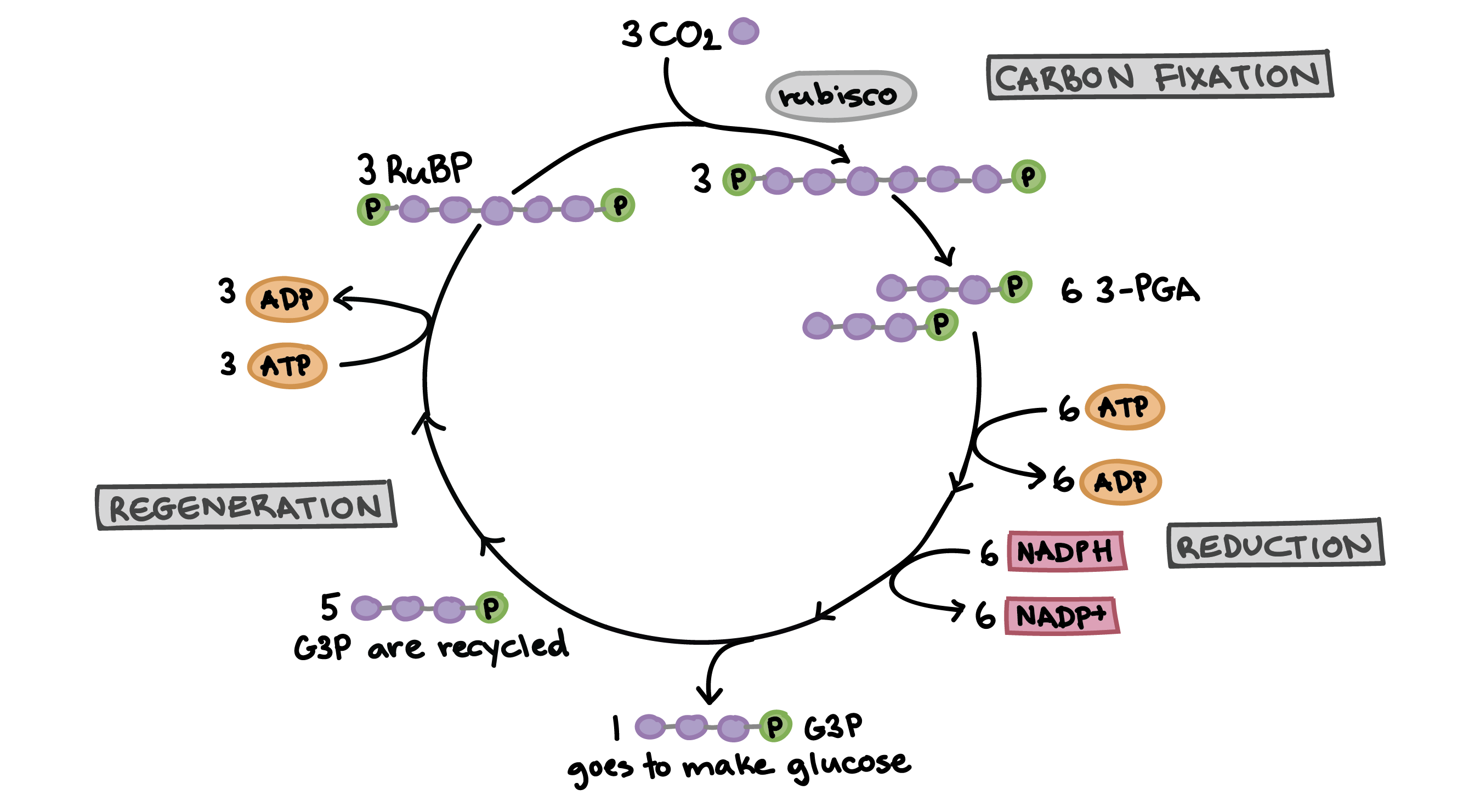
Light-Independent Reaction / Calvin Cycle
This is an assembly line to create glucose in photosynthesis. It happens in the stroma
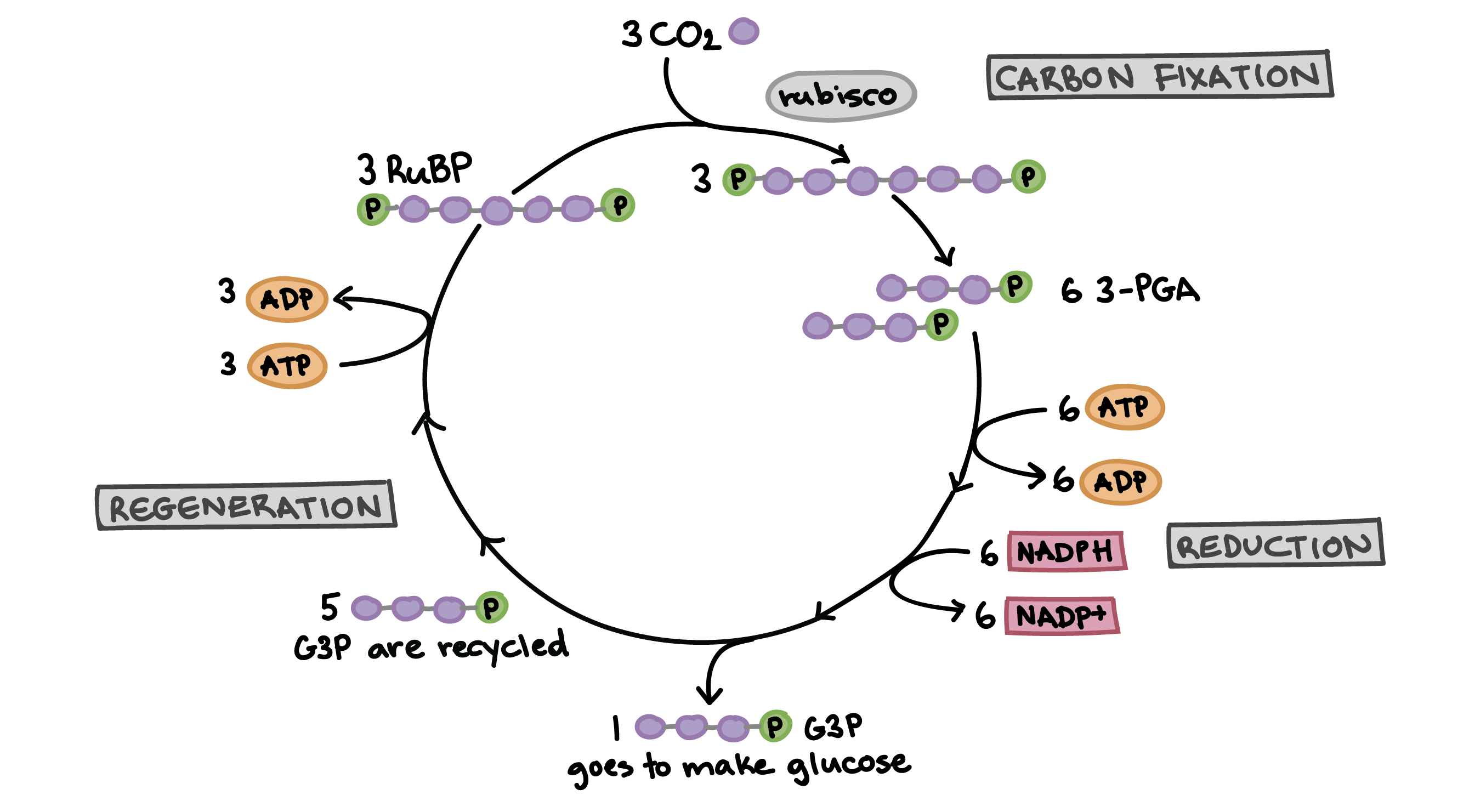
PGAL
This is half of glucose, and the output of the Calvin Cycle
Fixation
During this stage of the Calvin Cycle, byproducts of the light reaction are used for carbon fixation (facilitated by RUBISCO)
Reduction
During this stage of the Calvin Cycle, 6 ATP is converted to 6 ADP and inorganic phosphate, while 6 NADPH is converted to 6 NADP+
(Everything gets oxidized)
6 PGAL are made in a high energy state
Regeneration
During this stage of the Calvin Cycle, 1 PGAL is released
5PGAL, 3Pi make RuBP which clamps down on CO2 to continue the cycle
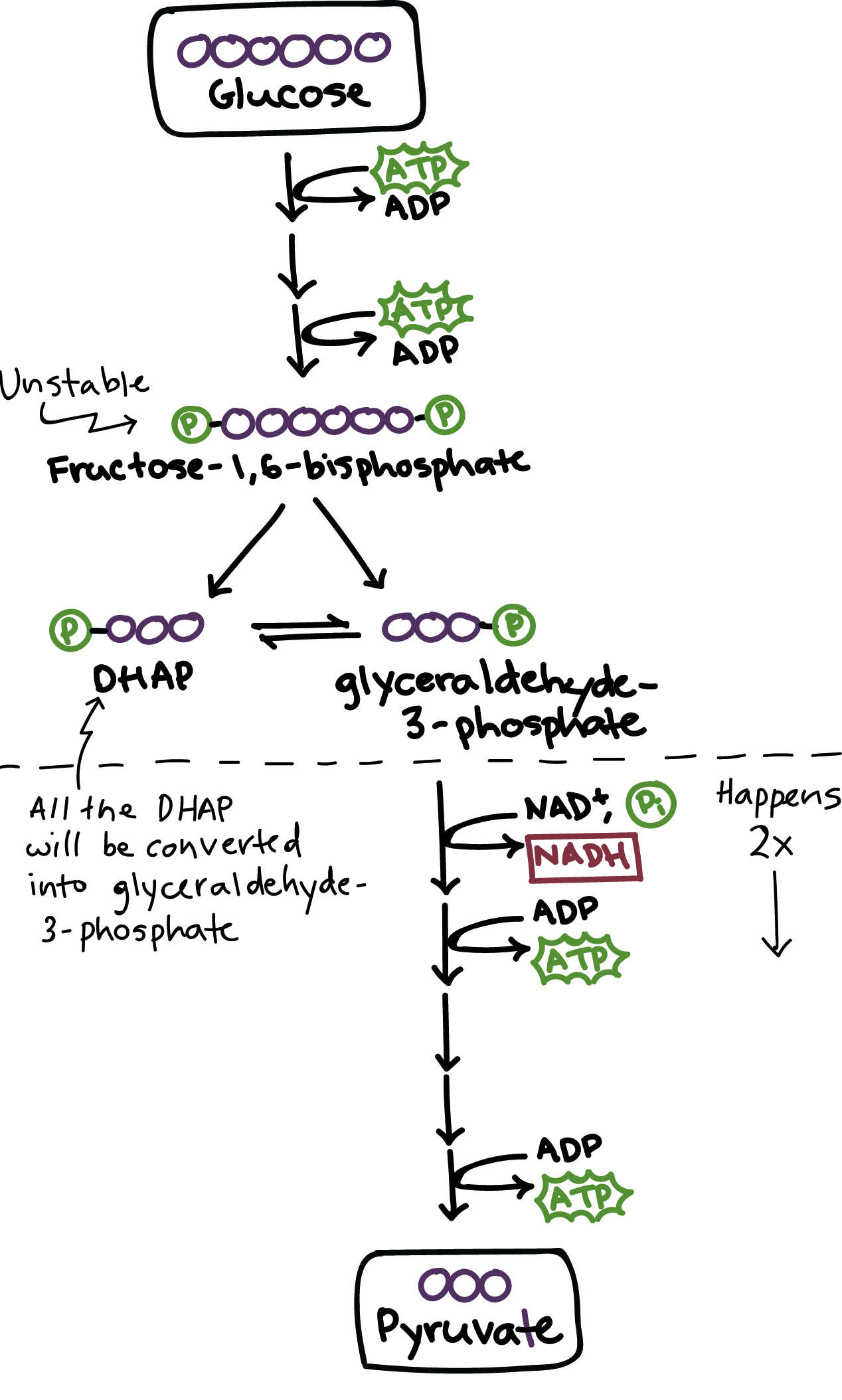
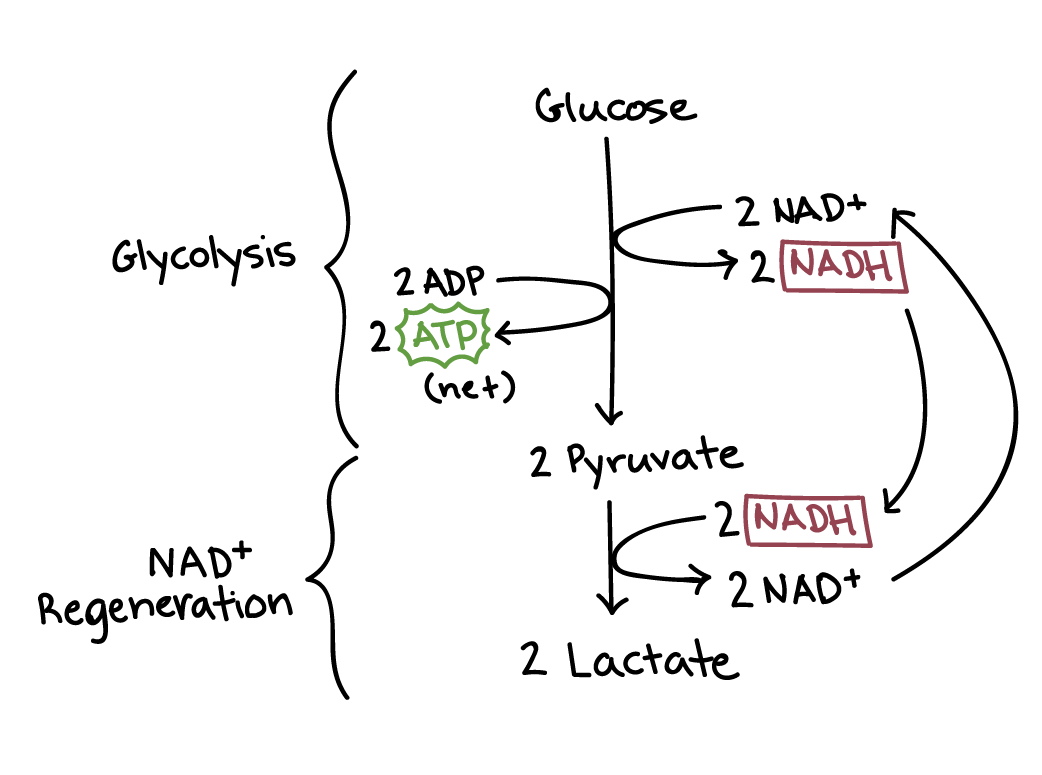
Glycolysis
a set of reactions that converts glucose to pyruvate
First step in metabolism in cellular respiration
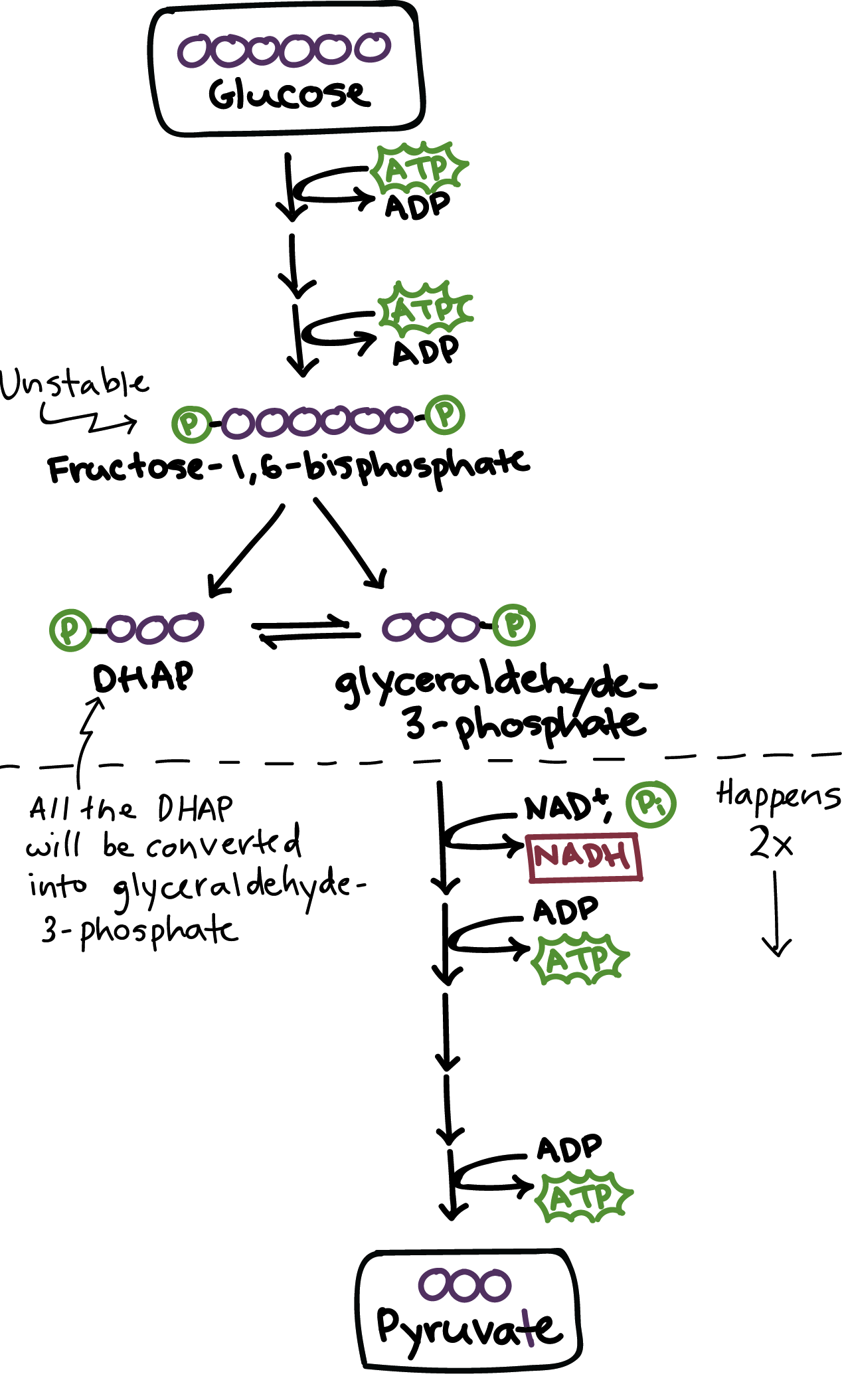
Pyruvate
This is half of a glucose molecule, but it can also be used for other purposes
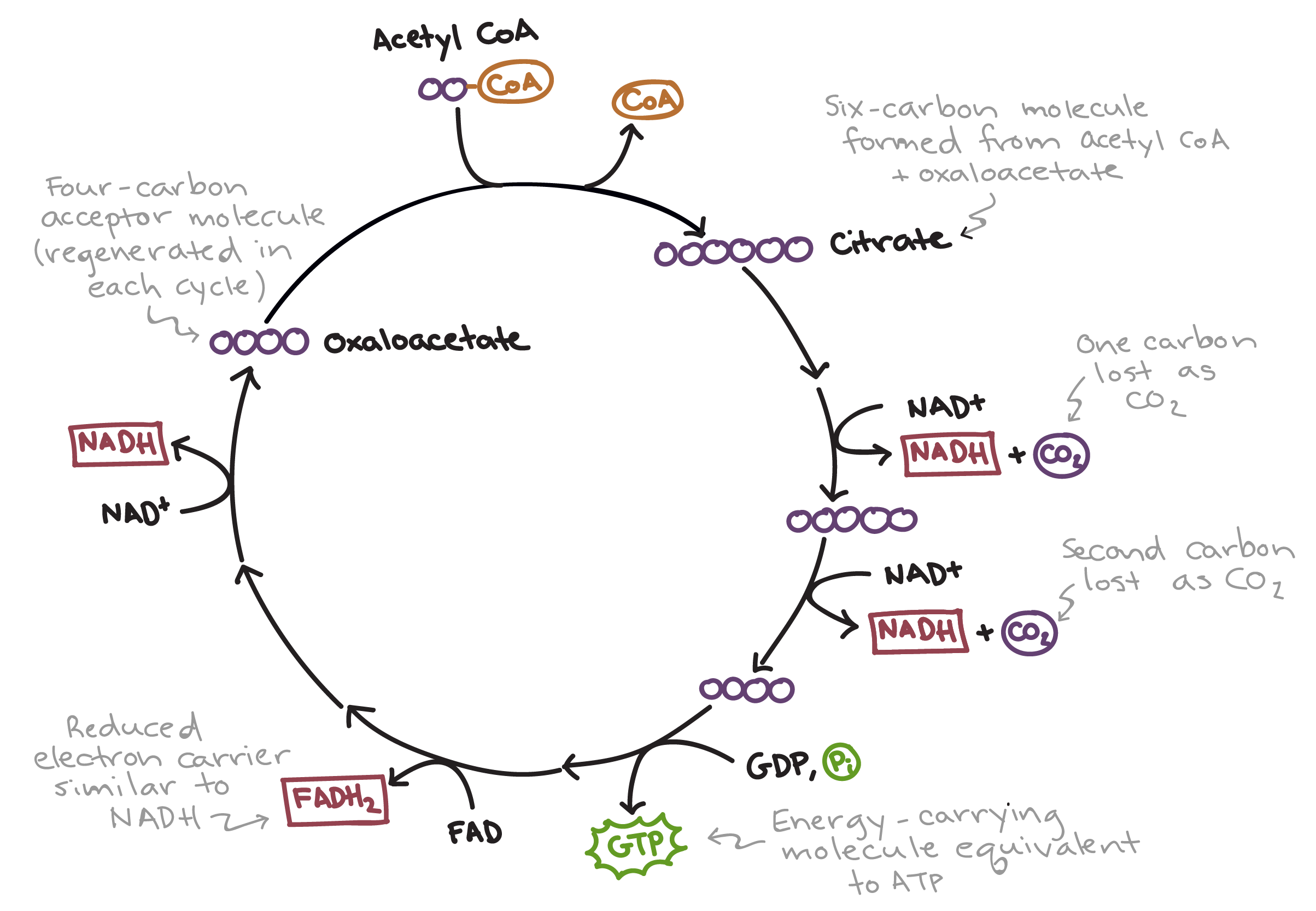
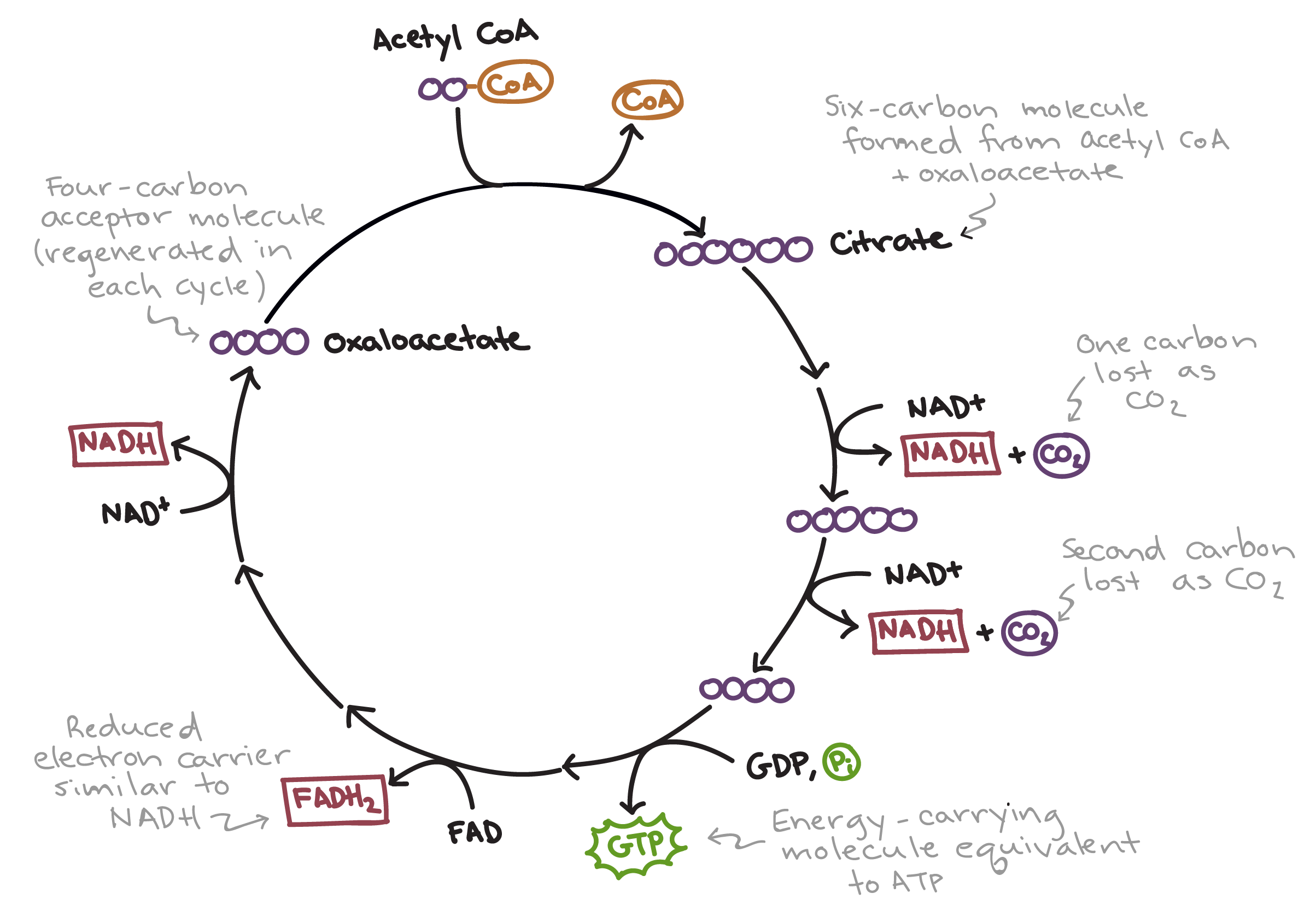
Krebs Cycle
This takes place in the mitochondria and does not need Oxygen
2 pyruvate —> 2 Acetyl CoA —> 4 CO2
Acetyl CoA from pyruvate oxidation merges with oxaloacetate
Citric Acid is formed
Citric acid is oxidized —> gives electron to NAD+ and 2 carbons are cleaved off
OUTPUT per glucose: 4CO2, 2 ATP, 6 NADH, 2 FADH2
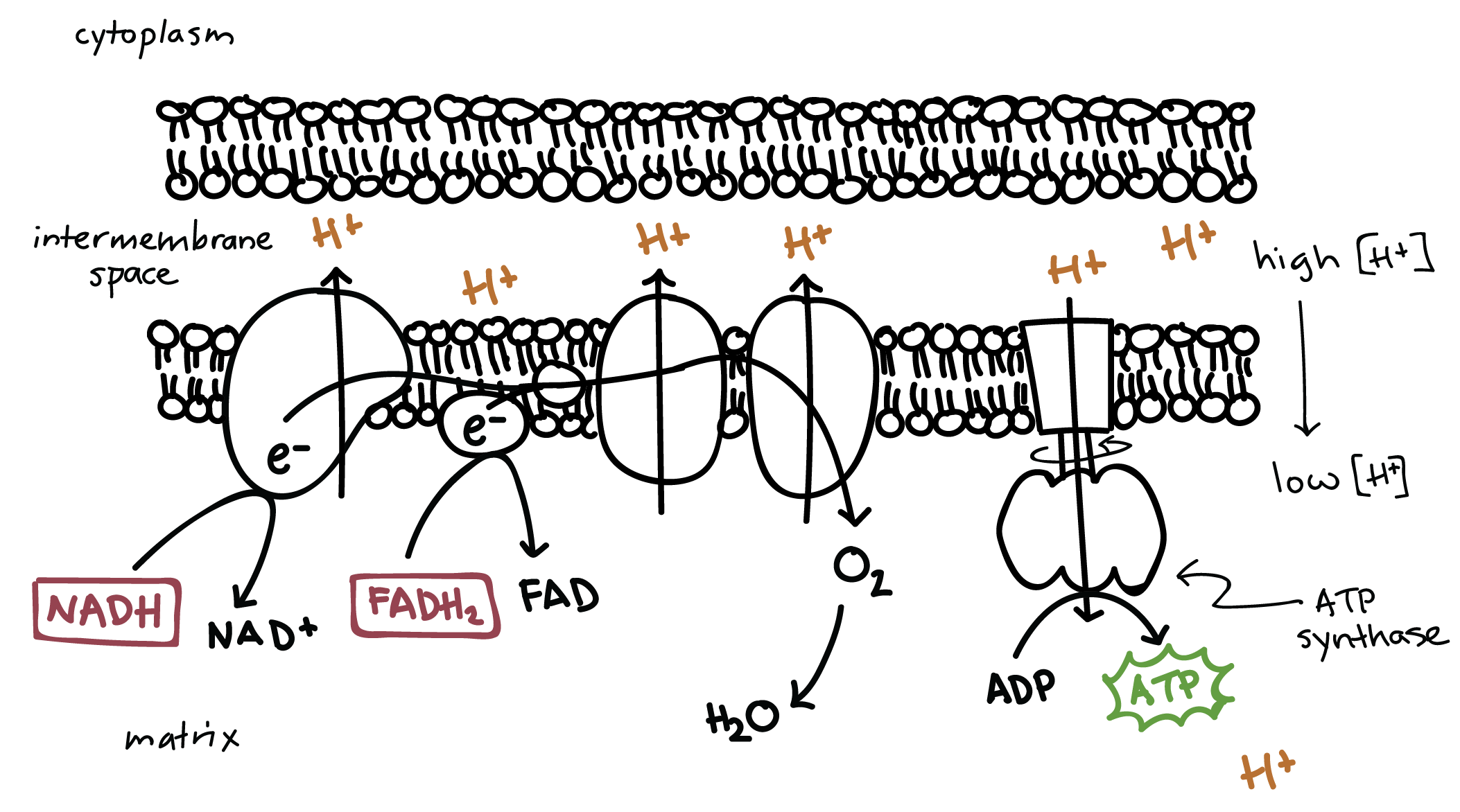
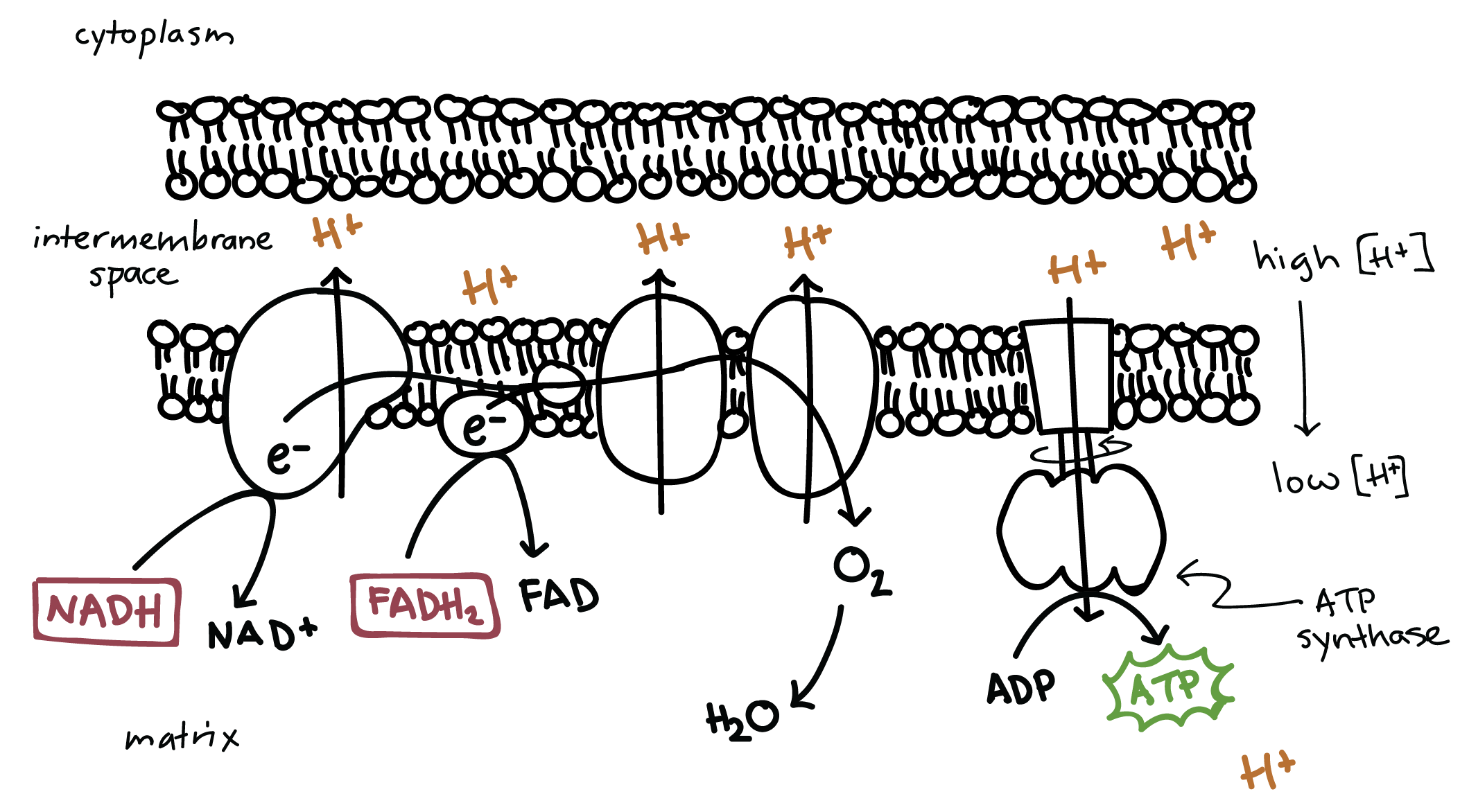
Electron Transport Chain
a series of four protein complexes that couple redox reactions, creating an electrochemical gradient that leads to the creation of ATP in a complete system named oxidative phosphorylation
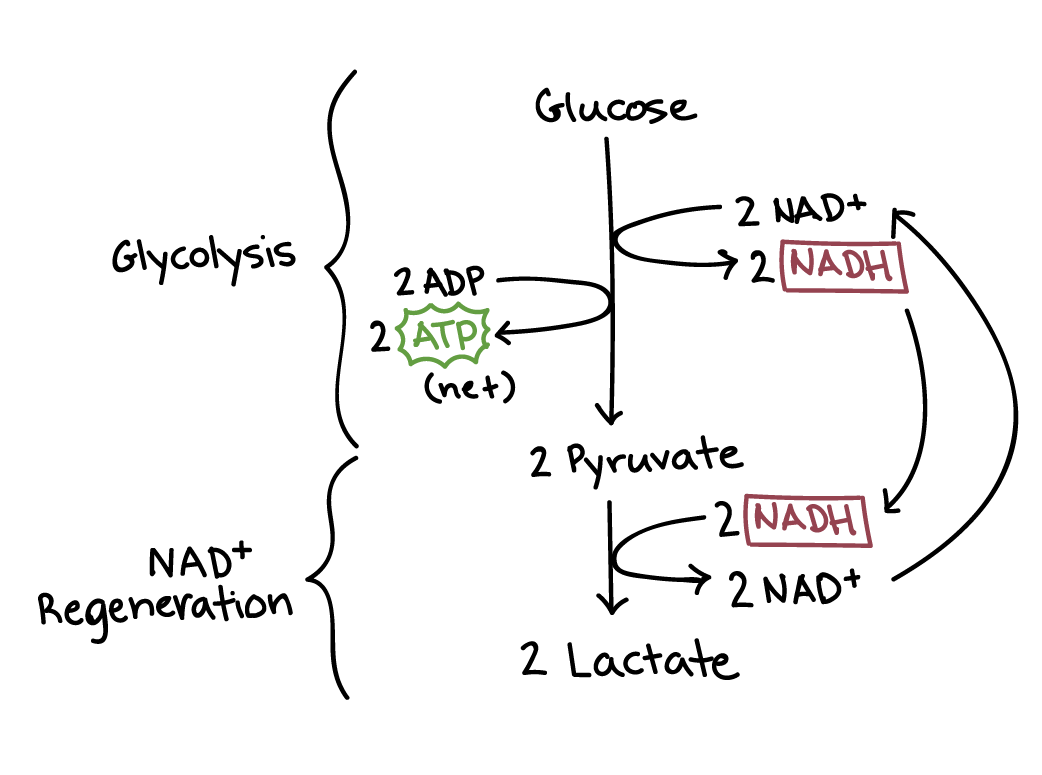
Fermentation
An anaerobic pathway for breaking down glucose, returning either lactate (animals) or ethanol (fungi/yeast)