M05 - Insurance Law
1/131
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
132 Terms
Types of Public Law?
Constitutional - main institutions of government and how they work together + treaties w/ foreign states + Government workers (the Monarch, MPs, Gov Ministers, Judiciary, Civil Services and Armed forces)
Admin law - relationship between private citizen and local / central government
Criminal law - criminal offenses
What is the function of criminal law
Punishment based:
Establish behavioural benchmarks
Forbid actions that cause harm to people / communities
Penalise offenders
Deterrence
Ways Criminal Offences can be tried
Summary - Magistrates Court - minor crimes
Either Way - Magistrates or Crown
Indictable only - Crown court with a jury - most serious offences (murder, robbery, rape etc)
Overview of Criminal Justice Process
Investigation
Arrest and Charge - formally charge or drop charges
First Court Appearance - defendant hears charge, trial date set, decide where it will be tried
Trial - Prosecution must prove defendant’s guilt -
Verdict - announced publicly in court
Sentencing - judge decides punishmen
Burden and Standard of Proof in Criminal Court
Burden - on the state / prosecution as they have resources the defendant may not.
Standard - Beyond reasonable double - due to the severe consequences from conviction
Claimant vs Prosecution vs Defendant
Claimant - brings forth an accusation in Civil law
Prosecution - brings forth an accusation in Criminal law
Defendant - the accused, have to defend their status of innocent
What is jurisdiction
the legal authority of a specific court to rule on disputes
Main Characteristics of English Law
Age - Cases / Laws go back 500+ years and remain in force
Little Codification - mostly case law
Judge-made Precedents become a binding part of law
No written constitution
Adversarial system - court listens and makes judgement (but does not investigate)
What is the North Ireland Protocol
North Ireland must remain aligned with EU customs and rules (Art 5-10)
But they have the option to discontinue this, if they wish
The UK must apply the provision of the EU law under the protoco
Who makes up the Parliament
House of Commons
House of Lords
the Monarch
What are green and white papers
Green - invites response to proposed law changes
White - advanced notice for more definite proposals
Process for the enactment of Public Bills
House of Commons
1st Reading - Formality - read the title to inform of its existence
2nd Reading - Merits of the Bill debated and voted on
Committee Stage - Standing committee discuss details and propose/vote on amendments
Report - Amended bill reported to the House, can be sent back for further work
3rd Reading - Final opportunity for debate (typically only minor changes at this point if any)
House of Lords - similar procedure, but cannot be rejected only delayed
Once passed → Royal Assent as a formality = Statute
What is a consolidating Act
Repeals all previous legislation and re-enact it in one logically arranged statute
What is a Codifying Act
Consolidation of all previous legislation and case law on a subject into a single code
Interpretation - Statutory Aids
Interpretation Act 1978 - singular = plural, man = woman, etc
Acts typically include an interpretation section
Acts have a preamble that outlines scope and purpose
Interpretation - Common Law Rules
Literal Rule - ordinary definition - takes precedence over all others
Technical or Legal meaning
-Noscitur a sociis - word determined by its context (sentence/paragraph)
-Ejusdem generis - word determined by the words that precede it (list)
Golden rule - interpretation that doesnt result in an absurd result
Mischief rule - choose meaning that supports the intention of the Act
Presumptions - no liability without criminal intention or fault, not retrospective, doesnt reduce jurisdiction of the courts, only applies to the UK, doesnt bind the Government, doesnt infringe on rights
Organisation / Structure of Civil Courts
County Courts - 1 Circuit Judge
High Court (1 of 3) - 1 Judge
- Chancery - Business / Money matters (companies, partnerships, trusts, mortgage, revenue)
- Family - Children matters, Family law and family property disputes
- Queens Bench Division (QBD) - Commercial Court, Admiralty Court, Tech/Construction Court
Court of Appeals
Supreme Court
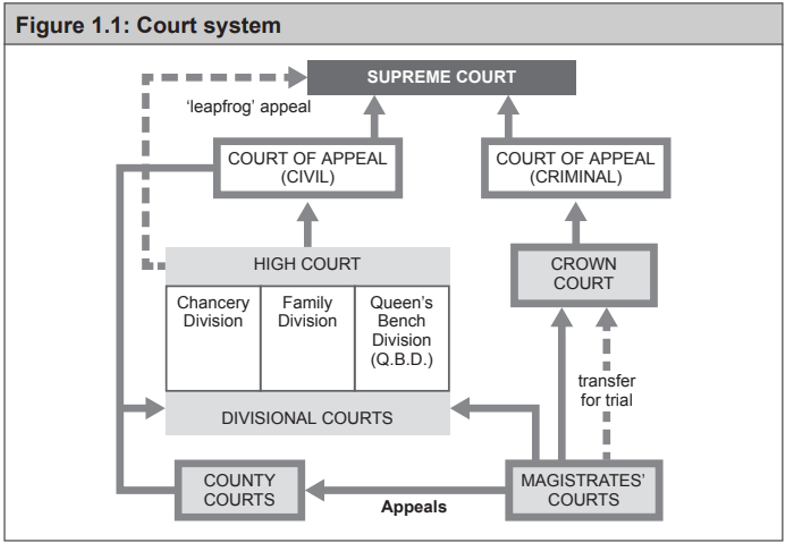
Appeals in Civil Courts
County/Mag → Divisional Court of each High Court (2+ Judges)
County/High → Court of Appeal (Civil) (3+ Judges, or Full Court of 5/7 Judges)
Court of Appeals → Supreme Court (5-12 Justices)
High → Supreme (Leapfrog Appeal)
Organisation / Structure of Criminal Courts
Magistrates Court - 3 Justices or 1 District Judge
Major - Transfer for Trial Proceedings → Crown Court - 1 Judge and Jury
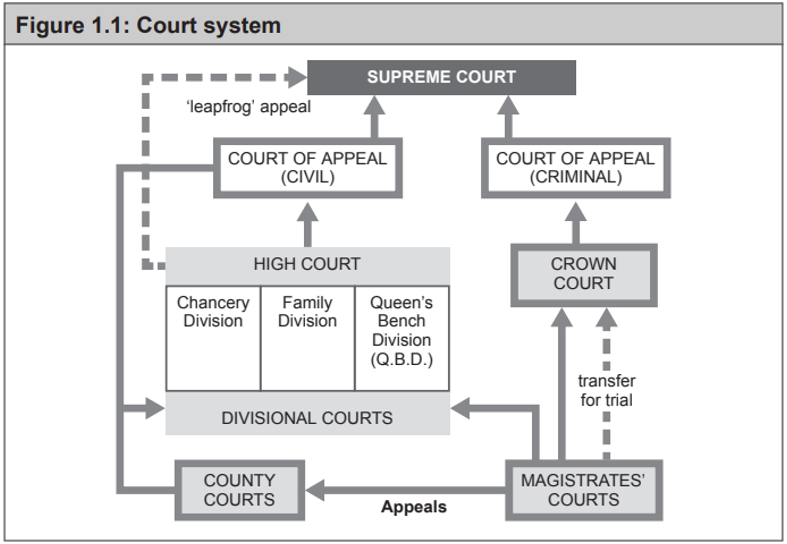
Appeals in Criminal Courts
Magistrates → High Court OR Crown Court
Crown Court → Court of Appeal (Criminal) (3+ Judges, or Full Court of 5/7 Judges)
Court of Appeals → Supreme Court (5-12 Justices)
What is the ratio decidendi
The reason for deciding - material facts of the case, decision of the judge + reason
AKA What is the basis that the precedent was set
What is obiter dicta
Things said by the way - hypotheticals said by the judge that dont form the ratio decidendi, but do provide influence to future cases
Civil Court Precedent Hierarchy
Supreme Court → Court of Appeal → High Court → County Courts
Supreme Court - can depart from its precedents, but do so sparingly
Court of Appeal - bound by its own precedents and Supreme Court
High Court - not bound by its own precedents, only strong influence, but bound by Supreme and Court of Appeal
County Courts - cannot set precedents, but bound by all higher precedents
Criminal Court Precedent Hierarchy
Supreme Court → Court of Appeal → Crown Court → Mag Court
Supreme Court - can depart from its precedents, but do so sparingly
Court of Appeal - bound by its own precedents, but Full Court (5+ Judges) can overrule, bound by Supreme Court
Crown Court - cannot set precedents, but bound by all higher precedents
Magistrates Court - cannot set precedents, but bound by all higher precedents
Reversing a Case vs Overruling a Case
Reverse - Higher court reverses a ruling from a lower court
Overrule - Lower Court rules based on an existing precedent, but Higher court changes this ruling based on a different principle, this overrules the existing precedent in this case and similar cases going forward = new ratio decidendi
Disapproving vs Distinguishing
Disapproving - Court believes that an earlier case was wrongly decided, but the ratio decidendi of the current case is not the same = opinion obiter dictum (not relevant) - disapproves case, weakening it, but not overruling it
Distinguish - decline to follow an earlier precedent due to distinguishing facts between the current/previous case
Law Reporting
Incorporated Council of Law Reporting - publishes semi-official Law reports annually for cases in the High Court + their Appeals
Supreme Court Decisions are published in a separate volume of Appeal cases
Civil Procedure Rules (CPR)
Requires pre-court actions to be completed, intended to facilitate negotiation and ideally avoid court
Issuance - Claimant completes ‘Particulars of Claim’
Defence - Admit the claim and pay our / Object
Allocation - allocated to Small Claims (<10k (5k for personal injury)), Fast Track (straightforward), or Multi Track (>25k or complex
Small Claims vs Fast Track vs Multi Track
Small - Court issues standard directions, No expert evidence allowed, District judge hears case and takes an active role in asking questions etc
Fast Track - Case heard w/in 30 weeks and concluded w/in 1 day, only 1 expert witness allowed
Multi Track - Judge gives directions and oversees case from beginning to end
What is CPR Part 36
If settlement is offered to the claimant and they do not accept, and the trial outcome is less than this amount, they may have to pay extra costs to the defendant (legal fees etc)
Solicitor vs Barrister
Solicitor - qualified legal professional
- Role - negotiate, gather evidence, oversee case + represent clients / apport barristers (for higher courts)
Barrister - hired by solicitors to represent a case in court
- Role - structure argument into persuasive legal arguments + Typically specialise in 1 area and advise clients on the law / strength of their case (opinion)
What is a legal natural person
Minor - have special exemptions under law as they are inexperienced
- Criminal - <10 incapable of committing a crime ; 10-18 full criminal responsibility
Person lacking mental capacity - must have capacity to understand implications of actions for contracts, but not torts
- Criminal - must have mens rea (guilty intent) to be convicted
Bankrupts - Assets and contracts under control of the trustee, and all liabilities joined with the creditors
Company vs Corporation
Both - artificial legal person / juristic person
Company - juristic person with an independent existence from shareholders
Corporation - group of people with combined resources for a common purpose
Characteristics and Types of Corporations
Corporation sole - legal person representing an official position, but occupied by different people (ex the Monarch)
Corporation Agg - Separate legal entity formed by several individuals whose existence is separate from the persons comprising it (ex Chartered CA, Statutory CA, Registered CA)
Types of Company
Ltd - shares not available to the general public or traded on a public stock exchange
PLC - Public Ltd Company - shares freely sold/traded to the public
LLP - Ltd Liability Partnership - combination of partnership and Ltd
CIC - Community Interest Company - limited company for community benefit
Guarantee - members guarantee certain amounts towards company debts if necessary (non profits)
Unlimited - liability of members is jointly/severally liable (not limited)
Royal Chartered - established by Monarch and historically significant
Overseas - outside of the UK, but established branch in the UK
Unincorporated Associations - groups defined by mutual rights/duties of members (unions)
What is a tort
legal liability for a civil wrong or breach of duty which causes a claimant to suffer loss or harm
Criteria for the tort of Trespass
Must directly cause harm/injury, must be intentional, must be actionable per se (claimant doesn’t have to prove loss/damage)
What falls under the tort of Trespass
Assault - threat of an attack / causes fear of an attack
Battery - hostile application of force, no matter how slight
False imprisonment - total bodily restraint / prevention of them going where they want to
Trespass to goods - intentional intereference with others’ goods
Conversion - taking goods with the intent to keep, modify, destroy, or sell
Trespass to land - unlawful entry, remaining, or leaving objects on others’ land
What is the tort of negligence
failure to take care, where the law requires care to be taken OR a breach of a duty of care
CASE: Donoghue v Stevenson 1932
Relates to Tort of Negligence
Reasonable Foreseeability - duty of care is owed to another person if it is reasonably foreseeable that they will be affected by ones acts/omissions
CASE: Overseas Tankship v Morts Dock and Engineering 1961 (Wagon Mound)
Relates to Tort of Negligence
Remoteness - damage is classed as too remote if it is not foreseeable
CASE: Smith v Leech Brain and Co 1961
Relates to Tort of Negligence
Eggshell Skull Rule - take your victim as you find him
Liability even if due to a pre-existing condition
What is a novus actus interveniens
New intervening cause - breaks the chain of liability
CASE: Hedley Byrne v Heller and Partners 1963
Related to Tort of Negligence - Hedley Byrne Principle
Negligent Misstatement - Liability can still arise from this if the claimant relied on advice given, even outside of an explicit contractual agreement
CASE: Spartan Steel and Alloys v Martin and Co 1973
There is no tort liability for financial loss not related to physical damage (ie BI)
Negligence - Psychiatric Illness
Primary - Caused by the direct action of the defendant - can always sue
Secondary - fear of safety of others/witness action - can sue if sufficiently related victim, saw it in person + sufficiently close in space/time to incident
What falls under the tort of Nuisance
Public nuisance - cause inconvenience / annoyance to public OR interfere with a common right
Private nuisance - interference with a person’s use of their land
Remedy - damages or an injunction
CASE: Rylands v Fletcher
Relates to Tort of Nuisance
Strict liability for those who keep something exceptionally dangerous - if that thing escapes from their land onto another’s and causes damage, its their fault even without negligence
What are the Requirements to prove Breach of a Statutory Duty in Tort
Claimant must prove:
Statute imposes a duty of defendant to claimant and was intended to allow a civil remedy
Damage must be caused by the breach of this
What are the requirements for Employers in Tort
Take reasonable care to:
Select competent staff
Provide and maintain proper plant, premises and equipment
Provide a safe system of work
How is vicarious liability determined?
Is the relationship employment / akin to employment?
Is the tort sufficiently closely connected with that ‘employment’?
What is the liability for Producers of Goods in tort
Strict liability for any personal injury / damage to private property caused by a defect in goods
Producer = Manufacturer, Abstractor, or Processor of Goods OR those who put their branding on a product
Defective Product - safety of the product is not what a person would generally expect
What is the tort of Defamation
Defamatory statement - false and exposes claimant to hatred, ridicule, or contempt OR lowers them in the eyes of the general public
- Must harm actual reputation, not just hurt dignity
What falls under the Tort of Defamation
Slander - non permanent form (speech, gestures)
Libel - permanent form (email, text, social media, publication etc)
Damage - must be a material financial loss (loss of job, loss of opportunity / income etc)
EXCEPTION - allegations of imprisonable crimes OR that they are unfit to carry out profession
Defences for Defamation
Truth – statement was factual
Honest opinion – statement is a matter of comment/opinion – must prove it was honest, relevant and made without malice
Publication on a matter of public interest – must prove the publisher reasonably believed the publication was in the public interest, whether true or false
Innocent defamation – published unintentionally – requires a publication of a correction and an apology, along with paying damages
Privilege – applies to judicial and parliamentary proceedings for statements made to the police by members of the public
General Defences in Tort
Self Defence – law allows use of reasonable force to defend yourself, property and other people (family, employees etc) or to prevent crime (for intentional torts like battery or false imprisonment)
Necessity – act was carried out in order to avoid a greater evil (for intentional torts like trespass)
Statutory authority – act is permitted by statute law (Cannot be use in cases of negligence, because the intent would never align)
Consent – claimant agrees to a deliberate act by the defendant (boxing, haircut)
Volenti non fit injuria – claimant consented to the risk of negligence by defendant (Does not apply to rescue cases, or beach of statutory duty, and hardly in employment injury - not favoured by courts)
Contributory negligence – claimant is partly to blame or their actions exacerbated injuries suffered (ex car accident where claimant didn’t wear a seatbelt)
- Not a complete defence, merely reduces damages awarded
What is contribution
The right to recover contribution from any parties jointly or similarly liable for damages
What are the Statutes of Limitation for Torts
Defamation - 1y
Personal Injury - 3y
Most other torts - 6y
Time starts on date of the cause of action
Latent Bodily Injury / Latent Property Damage - time starts on date of knowledge
Remedies in Tort
Damages:
Special Damages - claimant sets price and prove strictly at trial (loss of earnings, med expenses etc)
General - law automatically presumes these (pain and suffering)
Aggravated - additional money to reflect motive/conduct
Exemplary / Punitive - additional money to punish the wrongdoer for their conduct (common in US)
Nominal - no real loss so a token sum marks the fact the defendant is in the wrong
Contemptuous damage - tiny sum to mark the courts disapproval of the claim / claimants conduct
Injunction:
Mandatory - command to do something
Prohibitory - command to refrain from doing something
What are the different types of Contracts?
Contracts under seal - formal contract that is signed and has the wax seal of the signer attached, and is witnessed
Unilateral Contracts - one-sided agreement to pay for a specific act (reward on a flyer)
Bilateral - agreement between 2+ parties
Void Contract - unenforceable - lack of capacity / illegality
Voidable - agreement that can be voided on certain grounds
Requirements to Form a Contract
Agreement - offer and acceptance
Intention to create legal relations
Consideration - give and take
Agreement in the form required by law (if applicable)
Capacity to Contract
What are the requirements for Agreement of a Contract?
Offer - intention for it to be immediately bound if accepted
Invitation to treat - statement made during negotiation, not an offer
Acceptance - must be a positive act and communicated to offeror/agent
- EXCEPTION: Where the terms of the offer indicate that acceptance begins with the carrying out of the offerees part of the agreement
What are the requirements for Consideration of a Contract?
Must have a real benefit / detriment, but need not be equivalent in value
Must move from the promisor - 3rd party cannot provide the consideration
EXEPTION - Promissory estoppel - A can hold B accountable for damage / loss of A relied on the promise of B (even without consideration) and B then took that promise back (only used as a defence)
What is promissory estoppel
A can hold B accountable for damage / loss of A relied on the promise of B (even without consideration) and B then took that promise back (only used as a defence)
What type of form requirements can contracts have under law?
Deeds (contracts under seal) - must be signed and witnessed
Contracts in writing
Contracts evidenced in writing
Contracts where one party must supply written particulars (ex employer, landlord etc)
Types of terms of a Contract
Express
Implied - implied in fact (obvious), Implied by custom, implied in law
What Rules did the UCTA 1977 introduce?
Unfair Contract Terms Act - Since 2015 for non consumer only
Claimant must prove unreasonableness - was it fair with the knowledge and bargaining power and options at hand?
Negligence liability for bodily injury cannot be excluded
Breach of Contract liability cannot be excluded or restricted
Quality of Goods etc cannot be excluded/restricted for Sale of Goods
What Rules did the Consumer Rights Act 2015 introduce?
Claimant must prove unfairness - causes significant imbalance in parties’ rights and obligations to the detriment of the consumer
Unfair terms are not binding on the consumer, even if the term was individually negotiated by the parties
Implied terms are not binding on the consumer
Negligence liability for bodily injury cannot be excluded/restricted (does not apply to insurance)
Warranty vs Condition (general contract law)
Warranty – term which only affects a minor aspect of the agreement
- Breach – right to claim damages, but not to terminate the contract
Condition – term which related to an important aspect of the agreement
- Breach – right to claim damages and terminate the contract
NOTE: Warranty means something different in insurance
What is a defective contract?
Destroys the validity of the contract or makes it partly ineffective
May result from: illegality, improper pressure, mistake, misrepresentation, non-disclosure
- Contrary to Public Policy - brings about results harmful to the public
- Restraint of Trade - prima facie void (generally void), but may be upheld if reasonable
ex non compete clauses, sale of business, then retaining customers in new similar business
- Contrary to Law - illegal
What is a Mistake, and when will this cause a contract to be void?
Same Mistake - both believe item exists, but its destroyed
Different Mistake - each believes the transaction is about a different item
- Mistake of the subject matter - void
- Mistake of the Quality of the Subject matter - not void unless the mistake is essentially different
- Mistake of the Identity - A defrauds B by pretending to be C to sell goods - may be void
What is a Misrepresentation, and what are the Remedies available
False statement of fact which induces a party to enter an agreement
Fraudulent - knows its false, doesn’t believe its true, or doesn’t care if its true or false
Innocent - false, but the maker honestly believes its true
Negligent - false, because the person did not take sufficient care to check that it was correct (ex professionals who give bad advice and causes a loss to the victim who relied upon their statement)
Remedies - Avoidance or damages (for innocent misrep)
When are the duties under a contract dischargd?
Performance - each party has carried out their side of the agreement
Breach - right to claim damages, sometimes right to termination
Frustration - performance becomes illegal, impossible or futile
Discharge by Agreement
Discharge by Operation of Law - merger, death or bankruptcy
Remedies in Contract
Termination - for sufficiently serious breaches
Damages - main remedy for contract breaches; always have the right to claim
Equitable remedies (injunction) - awarded at the discretion of the court
Restitution - return of the property/mone
What are the Statutes of Limitation for Contracts
Simple Contract - 6y
Personal Injury Claims - 3y
Deed - 12y
Period begins on the date of the cause of action
EXCEPTION: Clauses can alter the statute by express term
What rule did Contracts (Rights of Third Parties) Act 1999 introduce?
A 3rd party can enforce a contract if:
The contract provides they may do so (expressly by name/group)
The contract is for the benefit of the 3rd party (unless it appears the parties did not intend the term to be enforceable by them)
What is Assignment in Contract Law?
transfer of rights under a contract from one person to another
Transfer of ‘Chose in Action’ (intangible contractual right)
Transfer of ‘Chose in Possession’ (tangible contractual right)
Statutory Assignment - must be absolute (whole thing and not conditional) and in writing
Equitable assignment - must inform the assignee of the transfer
What is a Novation
A debt is cancelled by agreement and replaced
All 3 parties must agree: Party A, Assignee and Party B
Assignment of Insurance Contracts
Assignment of Subject Matter – not automatic and uncommon, but possible (x. Selling a house or car with insurance)
Assignment of Contract Benefit - statutory or equitably (ex recovery of claim money, assign payment of claim to builder directly)
Assignment of Contract - must have the consent of insurer and occur at the time the property is transferred
EXCEPTIONS: Marine - assigned each change of ownership; Life - can be freely assigned
How can an agent be established?
Agreement / Through Contract
Ratification - retrospectively
Necessity - emergency
What are the duties of an agent?
Obedience
Care and skill
Personal performance - no sub-delegation of duties
Good faith - full disclosure
Accounting for money received
What is imputed knowledge
the law assumes that any information known by agent is known by principal
What are the rights of an agent?
Remuneration - typically via commission
Indemnity
Lien - retain goods as a means of security for a debt
What are the types of authority of an agent?
Actual - express or implied authority
Apparent - no real authority, but it appears so to a 3rd party
Disclosed vs Undisclosed Principal during contract formation
Disclosed - aware of the fact that there is a principal (though not necessarily their identity)
Undisclosed - unaware they are dealing with an agent - this can still be enforced by the principal
- Unless they didn’t have capacity or 3rd party only entered bc they thought it was the agent
- in this case 3rd party can enforce against agent or principal, but not both
Payments made through an agent
Payment by Principal - debt only considered paid once it reaches the 3rd party
Payment by 3rd Party - debt considered paid once it reaches the agent (if they have authority to receive payments on principals behalf)
Ways Agency Agreements can be Terminated
Agreement
Performance of duties to completion
Lapse of time
Withdrawal - principal revokes agents authority
Death of either party
Bankruptcy
Insanity
Frustration
What are the formal requirements of a Marine Contract of Insurance
Must be in writing, specifying the subject matter and name of insured (or agent) signed by the insurer (or agent) - in order to make a claim
What classifies as insurable interest?
the insured would suffer a loss if this subject matter is damaged or lost
- Cannot be based on expectancy of receiving goods, must currently have them
What did the MIA 1906 change about insurable interest?
Policies void without an insurable interest at the time of loss (for Marine policies)
What are the requirements for insurable interest in Life Insurance?
Family - own life and spouse = unlimited
Business relationship - Partners, key employees, debtor = limited interest
Property
Owners, both Mortgagees and Mortgagors, Executors and trustees, Bailee, Landlord and Tenant, People living together - limited interest typically
What does liability insurance protect against and what can you claim for?
Peril - risk of liability due to negligence/error/omission to pay compensation to a 3rd party who suffered a loss or damage
Claim - cost of compensation for justified claims OR cost of defending against unjustified claims, the handling of the claim, and the court costs
Pre-contractual information duty under the Insurance Act 2015
Non Consumers
Duty to make a fair representation - duty to NOT misrepresent AND disclose all material facts
- Must give insurer sufficient information such that a prudent insurer would ask additional questions if necessary
What is the Actual Inducement Test
Test of Materiality - for both Consumer and Non Consume
Statutory for remedy for Breach of Fair Presentation - must prove that the UW was induced based on the material non-disclosure / misrepresentation
- Does not have to relate to the loss to stand
Remedy available if: Insurer would not have entered, or would have entered on different terms
Remedies for Breach of Duty of Fair Presentation
Inducement Test first
IF Deliberate or Reckless - avoid contract from incept + retain premiums
IF NOT deliberate or Reckless:
- If would not have entered: avoid contract, return premium
- If would have entered on different terms: act as if it had entered on those terms
- If would have entered for more premium: proportionally reduce that amount of premium from the claim
Calculation for Proportional Reduction of Payment of a Claim based on Premium Charged / Sums Insured

Remedies for Breach of Reasonable Care to not make a Misrepresentation
Inducement Test first
IF Deliberate or Reckless - avoid contract from incept + retain premiums
IF Careless (honest mistake):
- If would not have entered: avoid contract, return premium
- If would have entered on different terms: act as if it had entered on those terms
- If would have entered for more premium: proportionally reduce that amount of premium from the claim
What are the requirements of PRIN 12
Act to deliver good outcomes for retail customers
- Act in good faith
- Avoid causing foreseeable harm
- Enable and support customers to pursue their financial objectives
What are the Remedies for Fraud in the claims process
Burden of proof lies with the insurer
Type: Falsification, Deliberate, Exaggeration
Remedy (Consumer and Non Consumer) - forfeiture of the claim + recovery of any funds paid + termination of the contract from time of fraud + insurer may be able to claim damages
Type: Collateral - lie about circumstances of a genuine loss - Insurer NOT entitled to reject the claim under Versloot 2016