exam 1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/105
Earn XP
Last updated 8:47 PM on 2/4/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
106 Terms
1
New cards
What are the main divisions of the CNS?
the brain and spinal cord
2
New cards
What are the regions of the brain?
forebrain, hindbrain, and midbrain
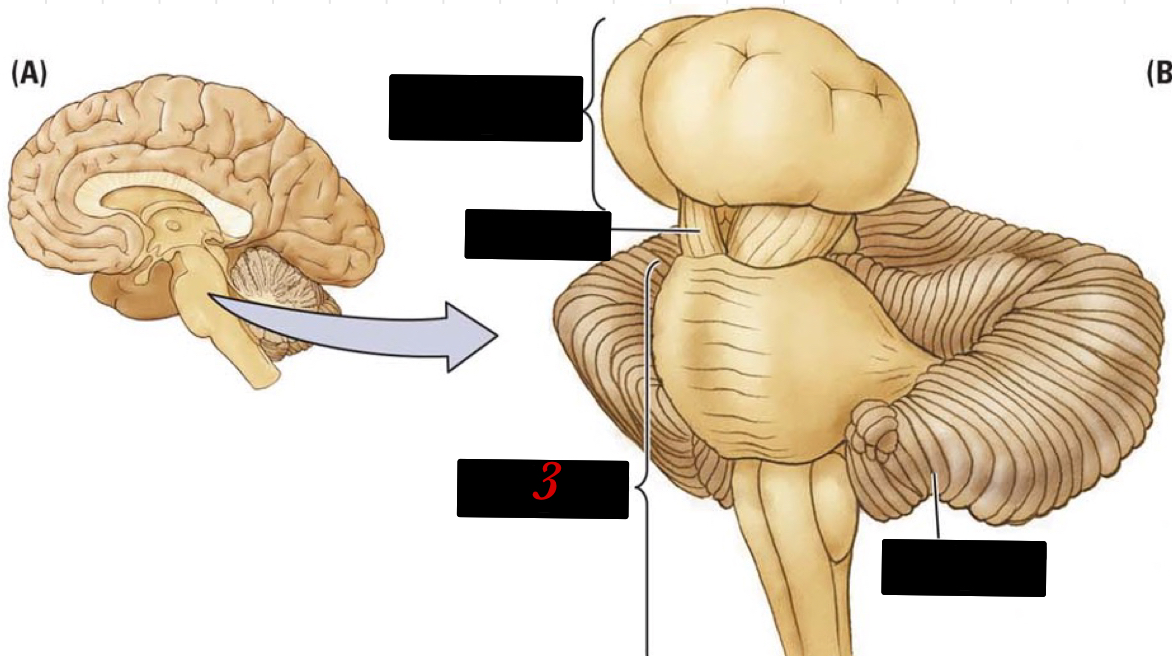
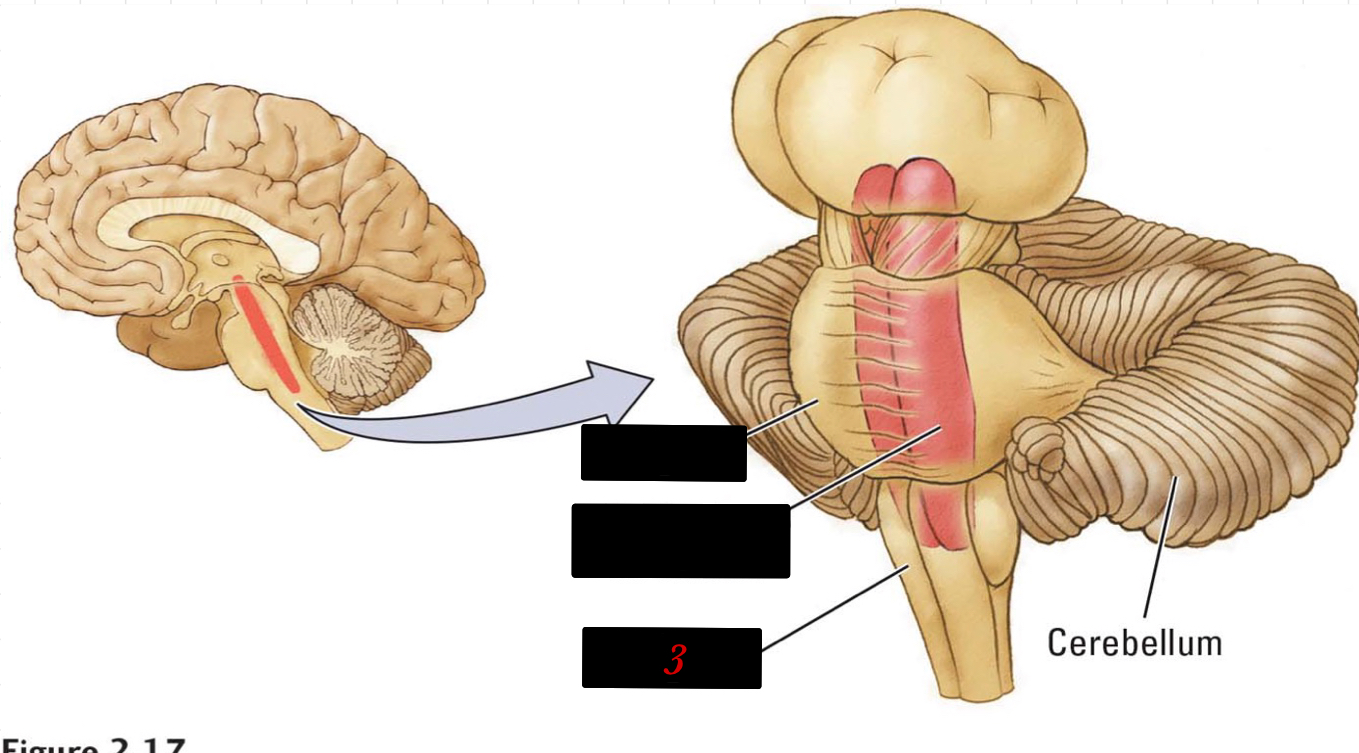
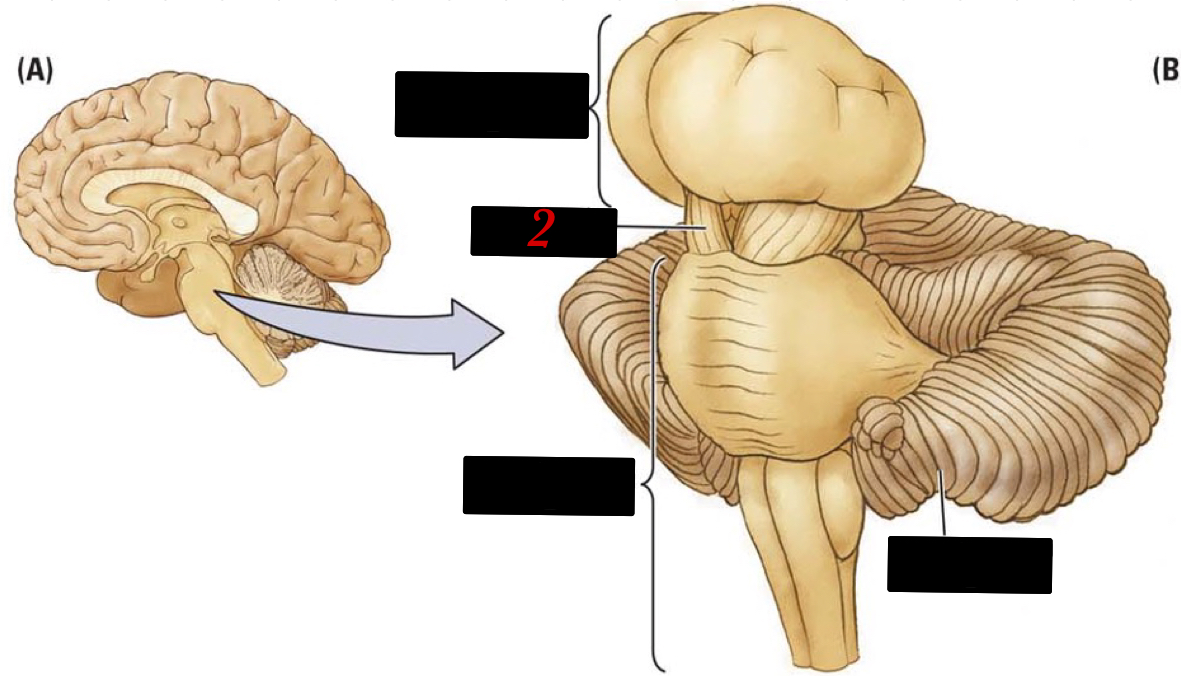
3
New cards
brainstem
controls motor functions ranging from breathing, to balance, and to fine motor skills
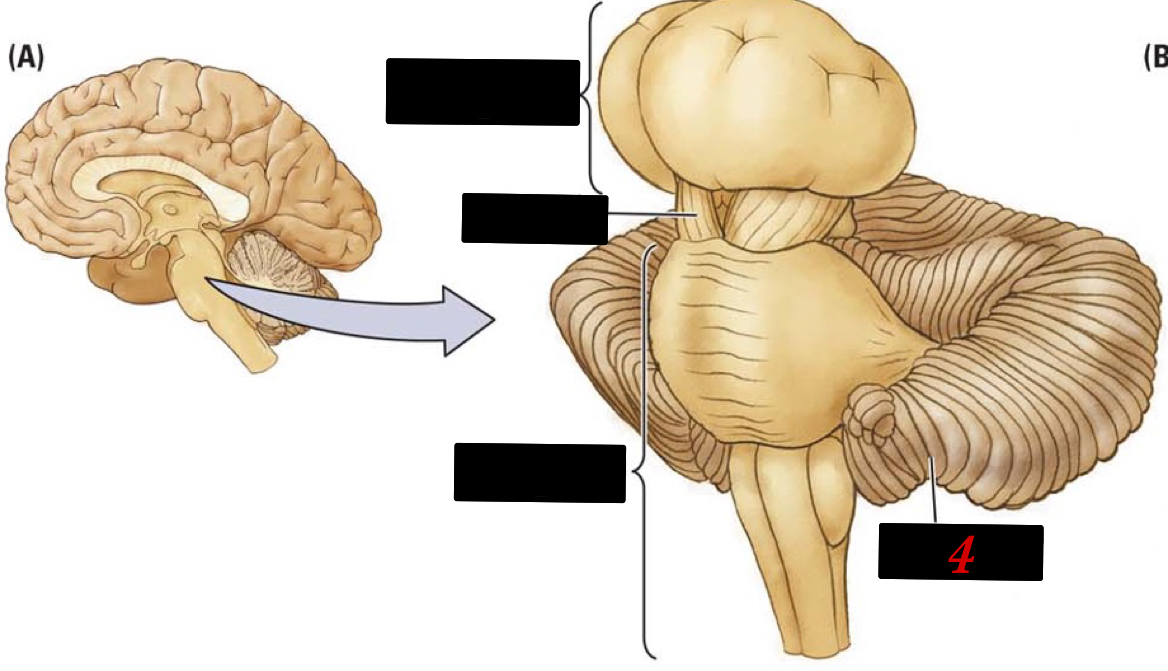
4
New cards
hindbrain
located at the lower back part of the brain and contains the cerebellum, reticular formation, pons, and the medulla
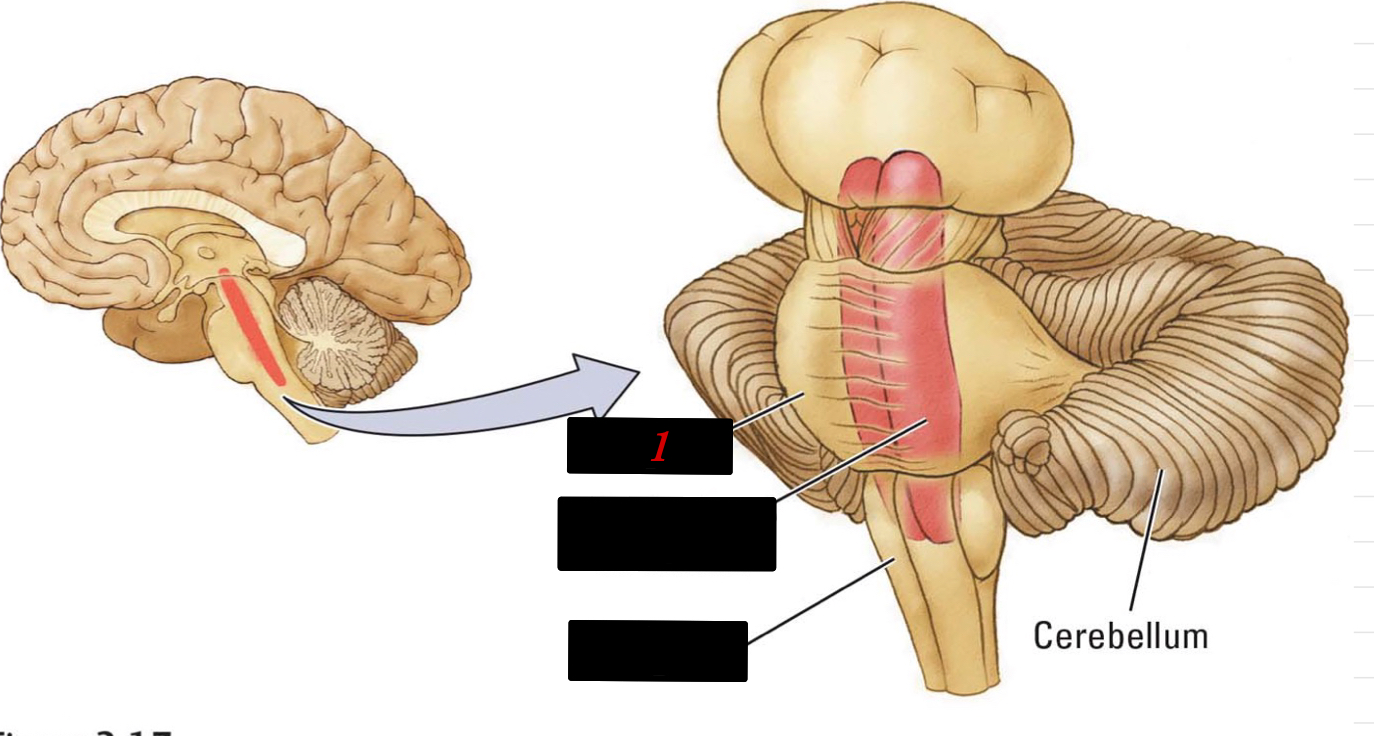
5
New cards
cerebellum
“little brain” has more neurons than the brain + spinal cord and is body control and motion memory
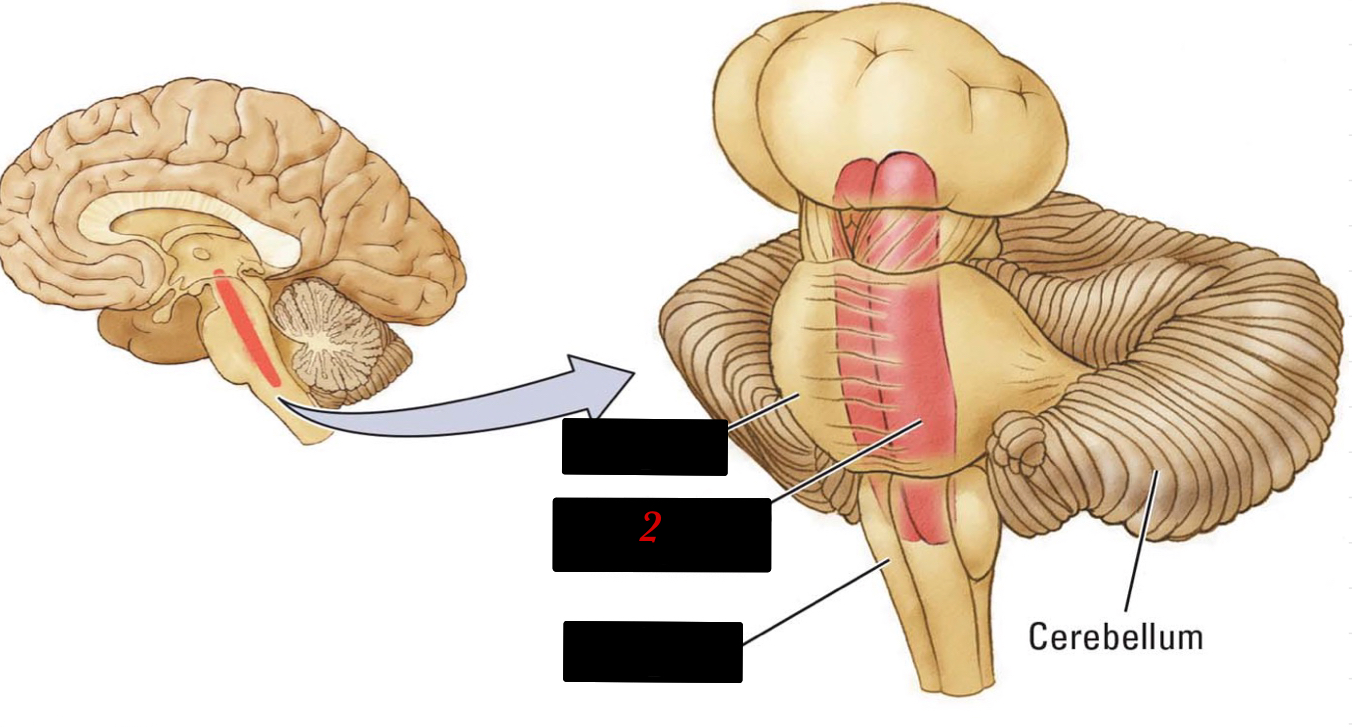
6
New cards
reticular formation
netlike mixture of neurons (gray matter) and nerve fibers (white matter)
7
New cards
pons
“bridge” to the cerebellum
8
New cards
medulla
basic body regulatory functions
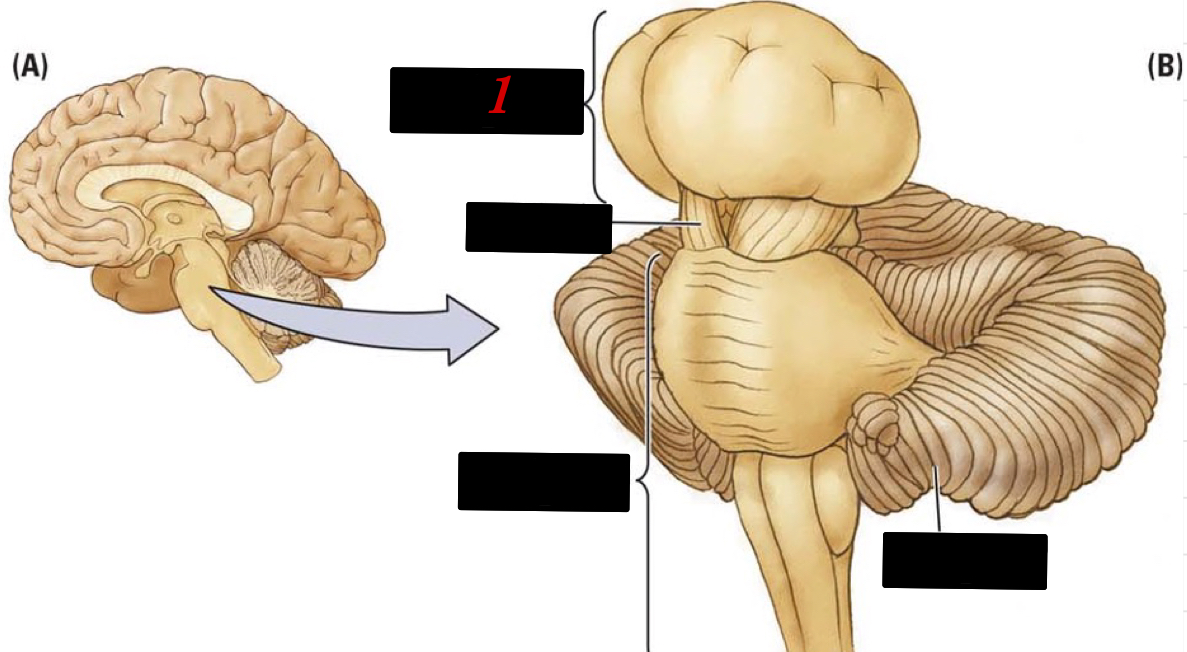
9
New cards
midbrain
the topmost part of the brainstem that contains the tectum and tegmentum
10
New cards
tectum
sensory input information
11
New cards
tegmentum
motor initiation or movement
12
New cards
diencephalon
located deep within the brain and contains the thalamus, hypothalamus, pineal gland, and the subthalamus
13
New cards
thalamus
relays sensory information to the cortex
14
New cards
hypothalamus
temperature control, sleep, eating, and stress response
15
New cards
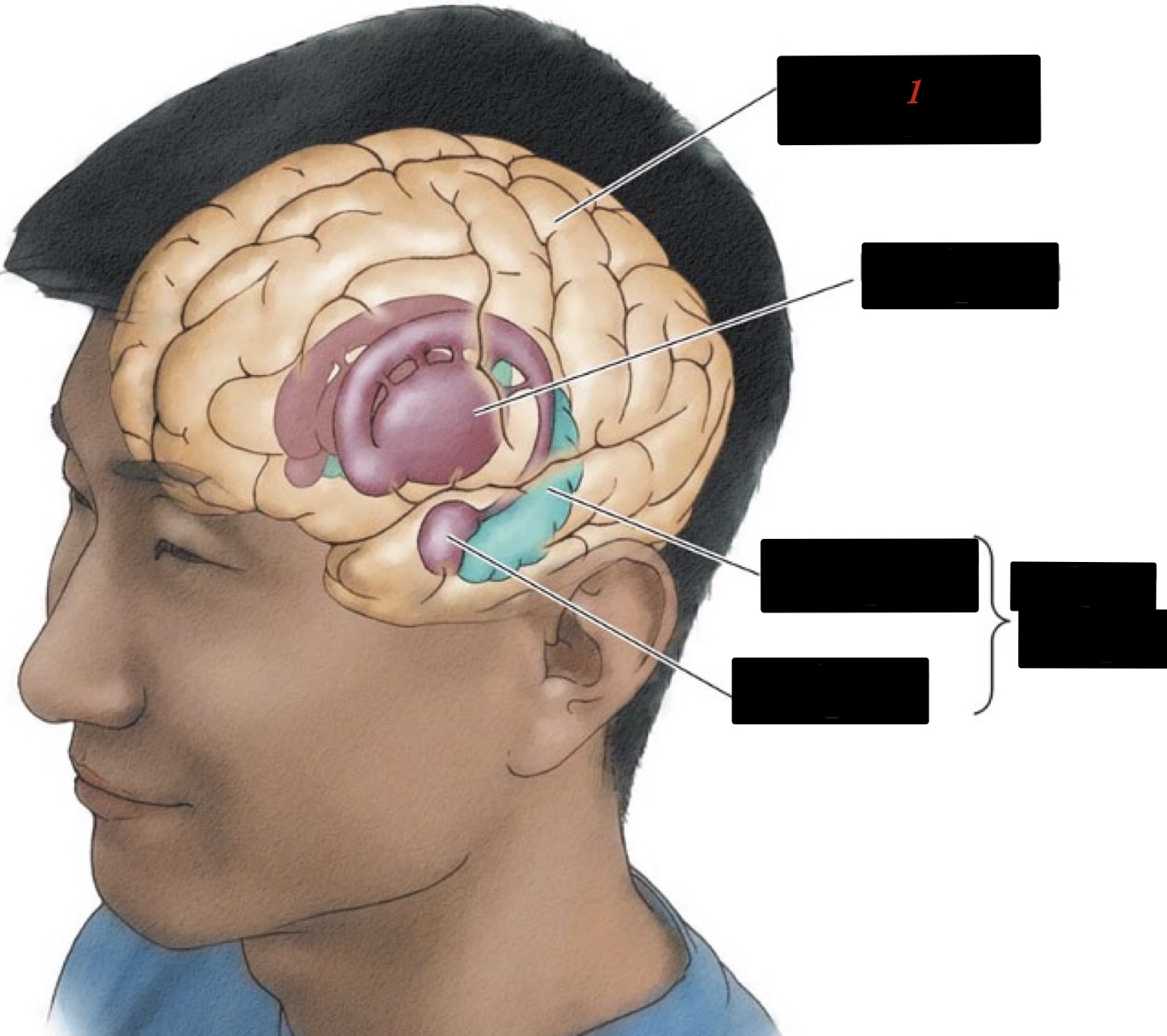
forebrain
the most forward portion of the brain that contains the basal ganglia, the limbic system, and the cortex and lobes
16
New cards
basal ganglia
controls motor and control response
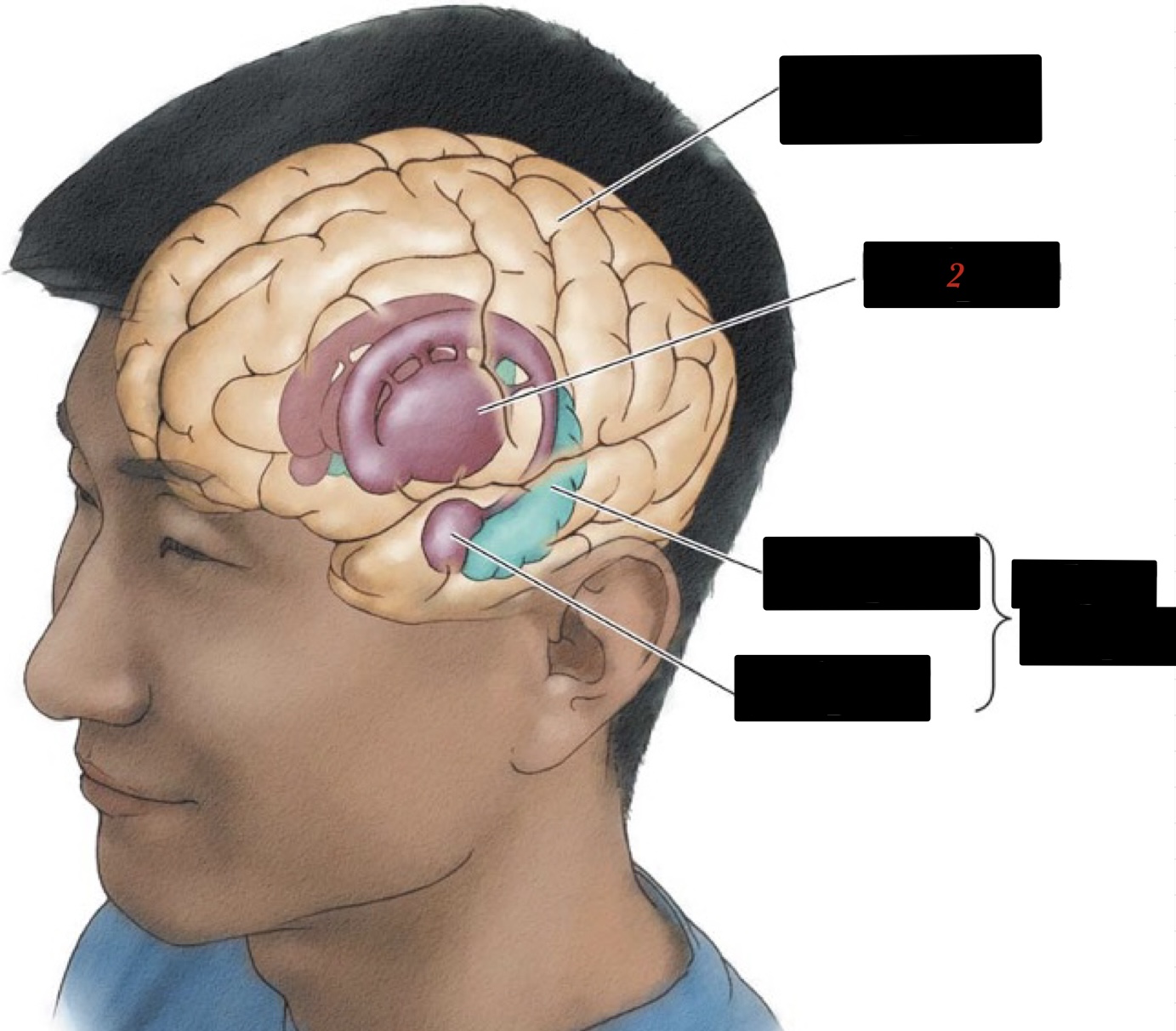
17
New cards
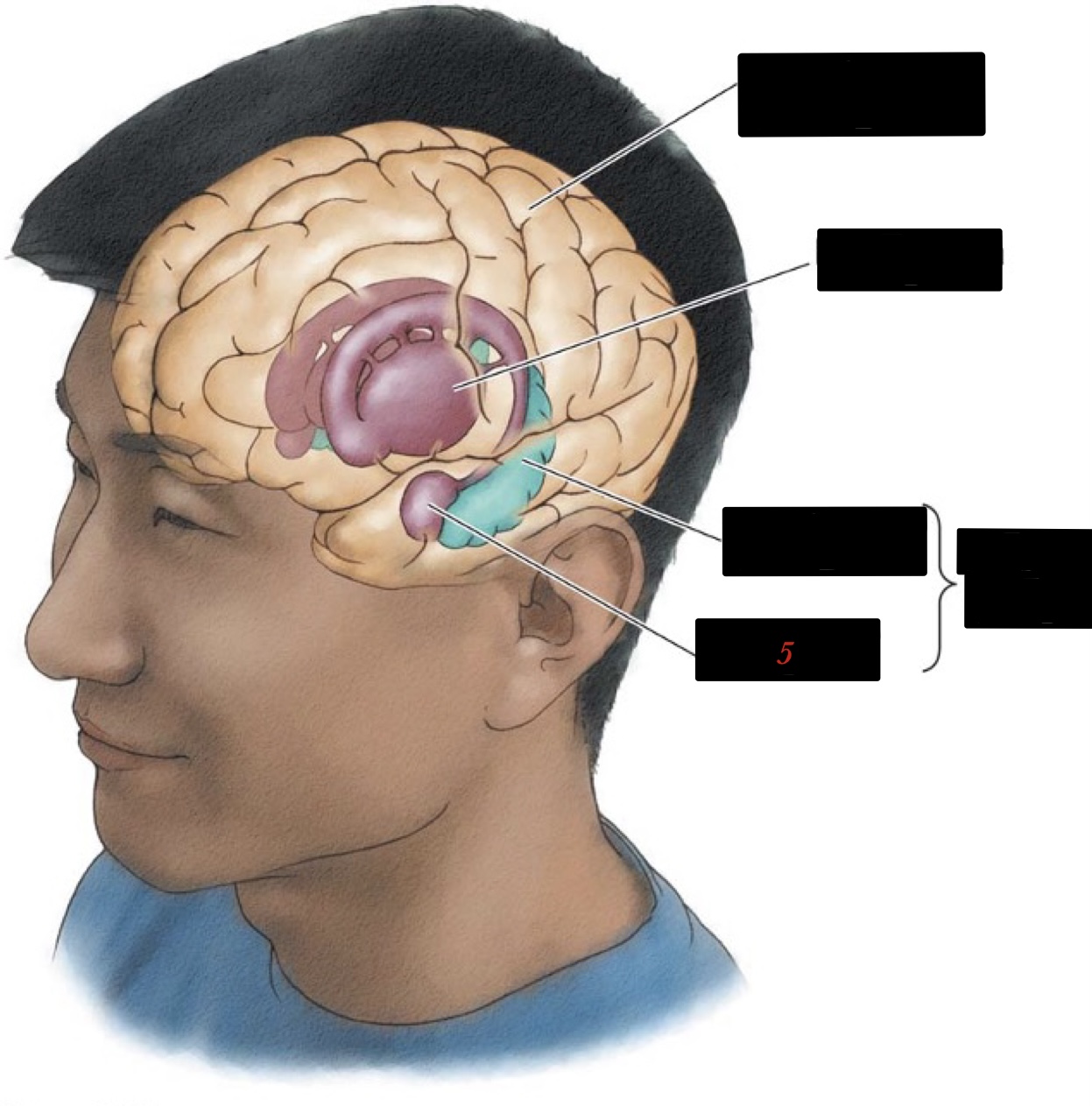
limbic system
associated with basic/primitive emotions and drives
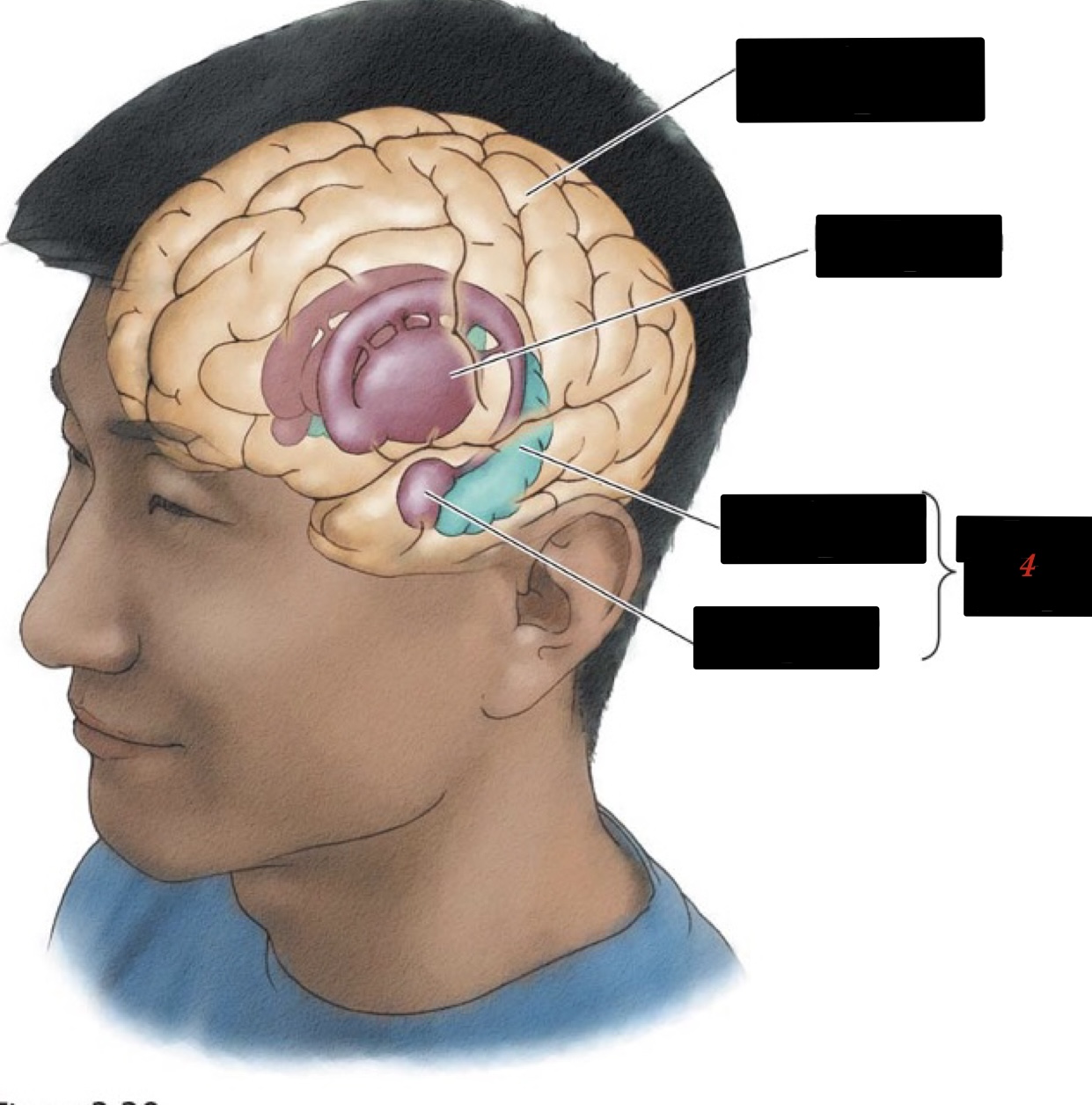
18
New cards
hippocampus
memory and learning
19
New cards
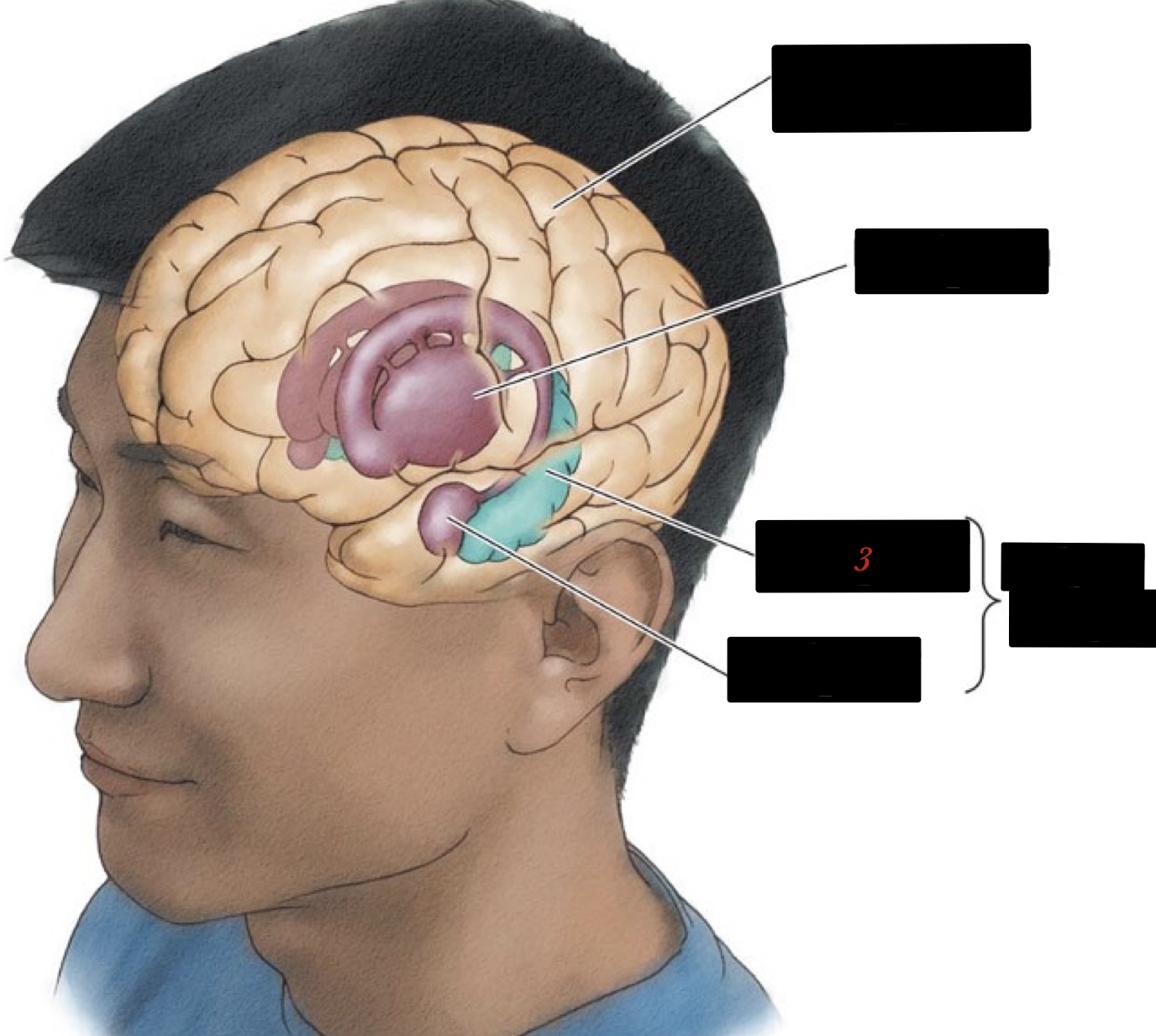
amygdala
regulates emotions such as fear and agression
20
New cards
cerebral cortex
the part of the brain that is the most human
21
New cards
neocortex
contains axons, dendrites, and various cerebellar neurons
22
New cards
frontal lobe
executive functioning, planning, conscious thought, and decision making
23
New cards
temporal lobe
facial and emotional processing, language, ductory, and gustory
24
New cards
occipital lobe
visual processing
25
New cards
parietal lobe
directing movements to perform a task
26
New cards
What protects the brain?
the corpus callosum, blood-brain barrier, and the cerebrospinal fluid
27
New cards
corpus callosum
ensures that both sides of the brain can communicate and send signals to each other
28
New cards
blood-brain barrier
tightly packed cells of blood vessel walls prevent entry of many molecules
29
New cards
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
cushioning, waste removal, and communication
30
New cards
What are the four parts of the nervous system?
central nervous system, somatic nervous system, autonomic nervous system, and enteric nervous system
31
New cards
central nervous system (CNS)
meditated behavior
32
New cards
afferent
incoming information into the CNS
33
New cards
efferent
incoming information from the CNS
34
New cards
autonomic nervous system (ANS)
involuntary movements and preps the internal organs
35
New cards
What are the two parts of the ANS?
sympathetic division and parasympathetic division
36
New cards
sympathetic division
arousing (fight or flight) which uses energy
37
New cards
parasympathetic divison
calming and relaxation which reserves energy
38
New cards
somatic nervous system (SNS)
voluntary movements and provides information for the CNS
39
New cards
What are two parts of the SNS?
cranial nerves and spinal nerves
40
New cards
cranial nerves
nerves that make up the muscles, joints, and skin
41
New cards
enteric nervous system (ENS)
controls digestion and stomach contractions
42
New cards
What is the function of a neuron?
acquire information → store it as memory → interpret it → pass the information along to other neurons to produce behavior
43
New cards
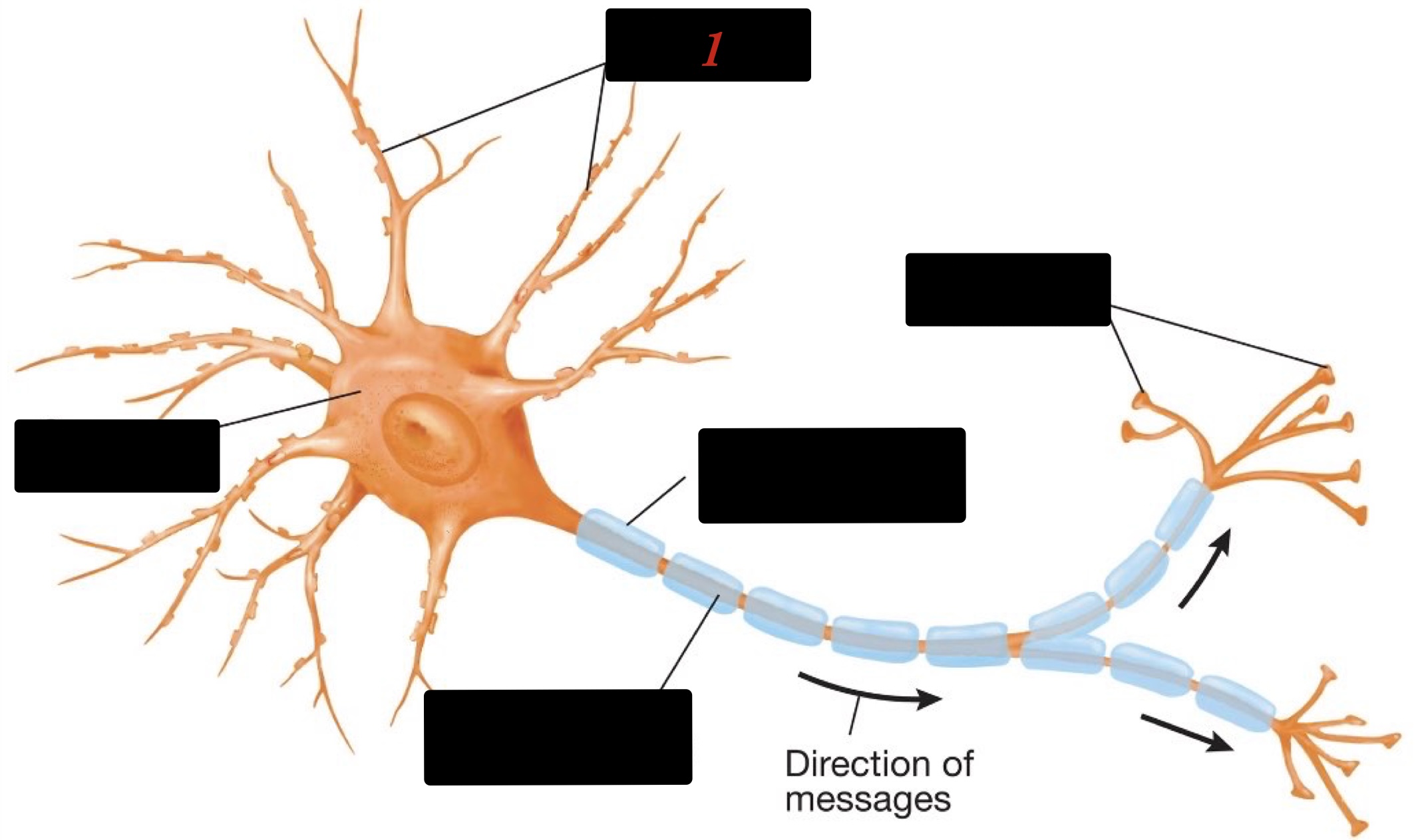
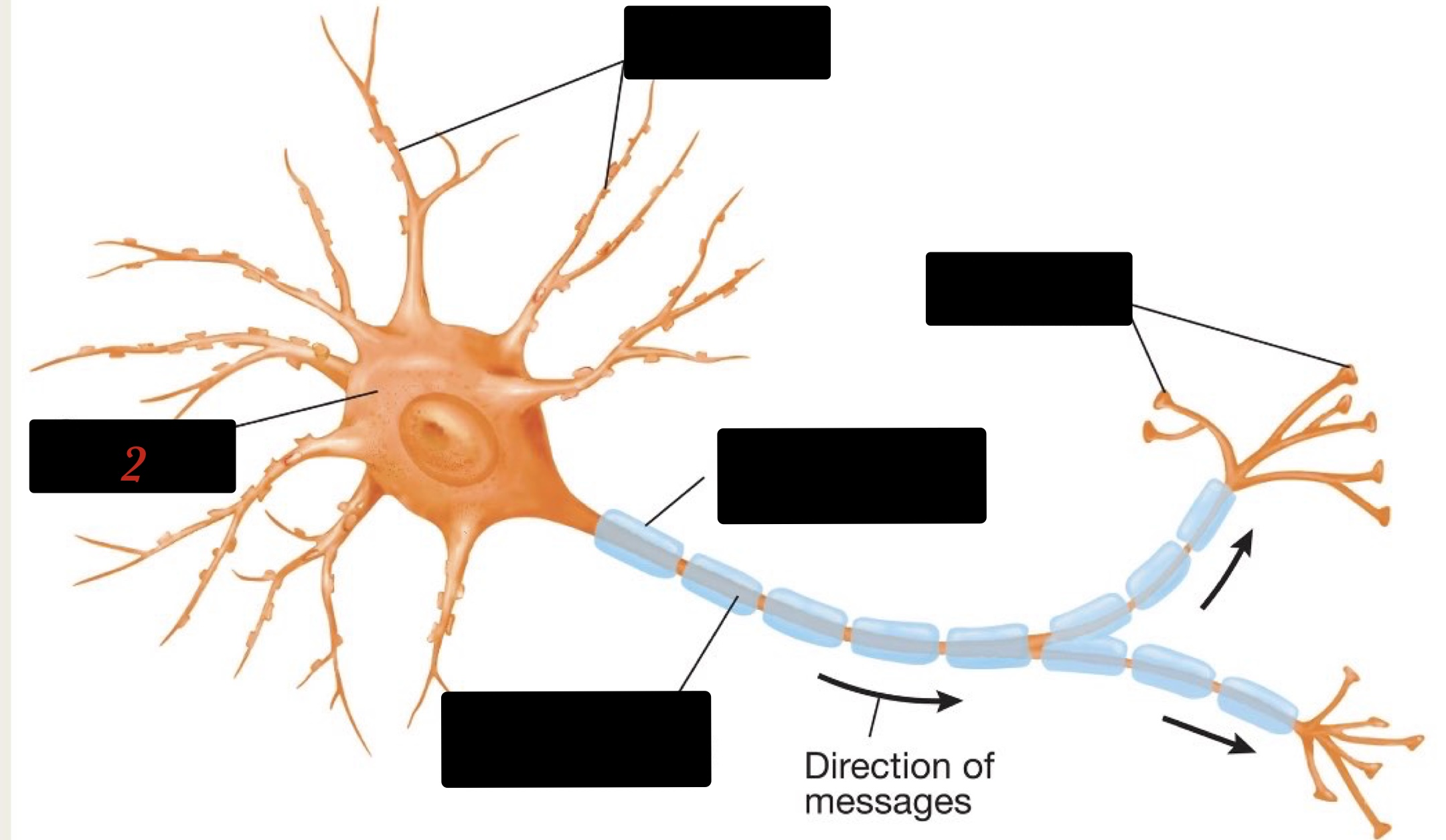
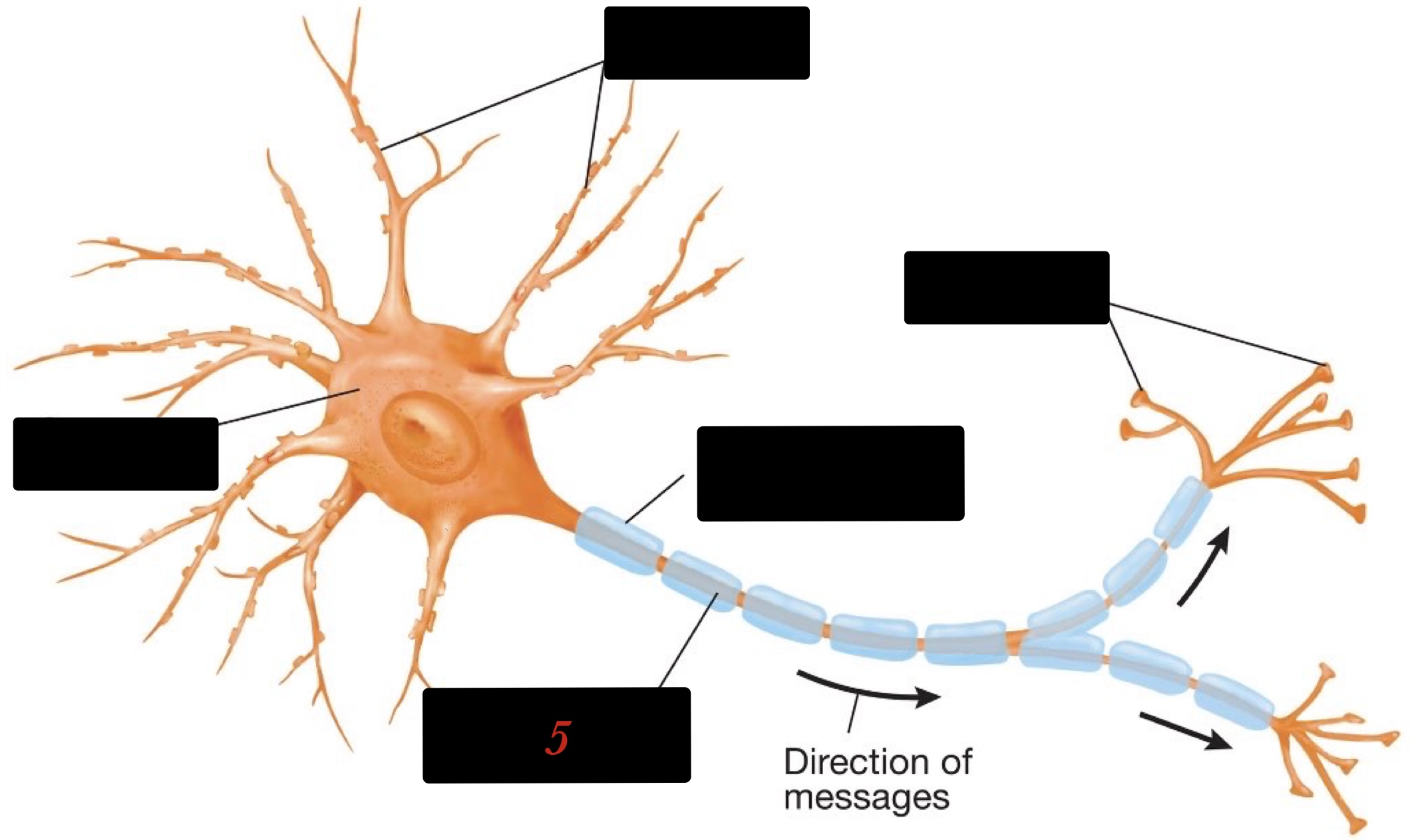
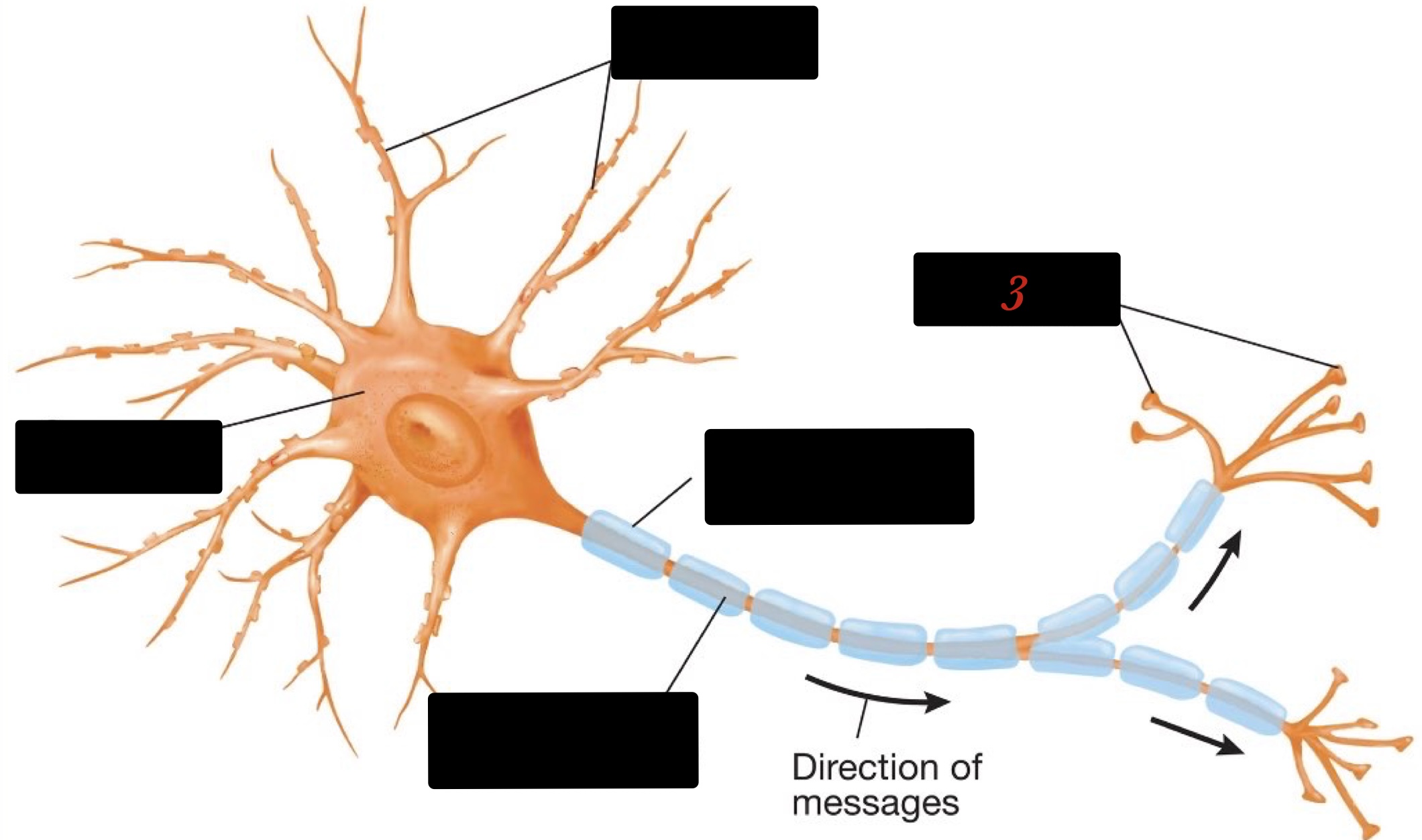
What are the structures of the neuron?
the cell body, dendrites, axon, and presynaptic terminal
44
New cards
dendrites
gather information from other neurons
45
New cards
dendritic spine
protrusion from a dendrite that greatly increases surface area and is the usual point of contact with axons of other cells
46
New cards
cell body
integrates the information
47
New cards
axon
carries information to be passed to other cells
48
New cards
axon hillock
juncture of the soma and the axon where action potential begins
49
New cards
presynaptic terminal
uses neurotransmitters to transport neurons
50
New cards
What are the three types of neurons?
sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons
51
New cards
sensory neurons
carry information from the sensory receptors in or on the body to the spinal cord (afferent)
52
New cards
bipolar neurons
a sensory neuron that transmits afferent sensory information from the retina's light receptors to neurons that carry information into the brain’s visual centers
53
New cards
interneurons
associate sensory and motor activity within the CNS
54
New cards
motor neurons
send signal from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles (efferent)
55
New cards
glial cell
the nervous system’s support cells
56
New cards
What are the five types of glial cells?
ependymal, astrocyte, microglia, oligodendroglia, and schwann cells
57
New cards
ependymal
makes and secretes cerebrospinal fluid
58
New cards
astrocyte
keep neurons healthy and heals if injured
59
New cards
microglia
originates in the blood, aids in cell repair, and scavenges debris in nervous system
60
New cards
oligodendroglia
cells in the CNS that myelinate axons
61
New cards
schwann cells
cells in the PNS that myelinate axons
62
New cards
How does the cell membrane act as a barrier and a gatekeeper?
by separating intercellular and extracellular fluid, regulating movement of substance into and out of the cell, and regulating the differing concentrations of salts and other chemicals on its inside and outside
63
New cards
How is the electrical activity of a neuron generated?
neurons convey information as a wave and those waves send ions down a voltage gradient from an area of higher charge to an area of lower charge
64
New cards
action potential
rapid rise and subsequent fall in voltage of membrane potential across a cellular membrane with characteristic patters
65
New cards
neuron, axon
_____ reaches the threshold to start the action potential down the _____ .
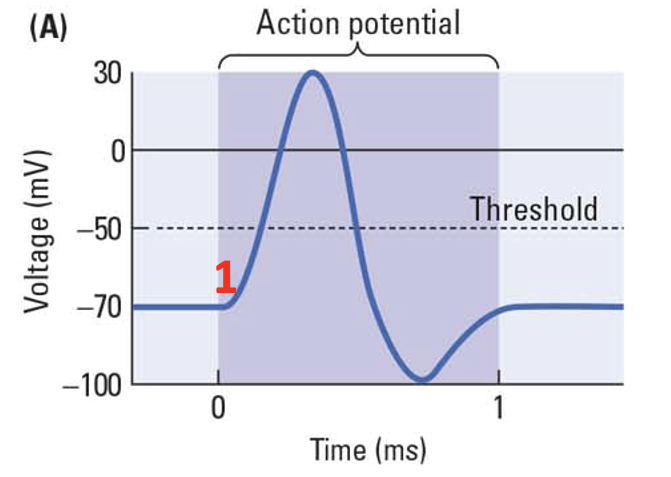
66
New cards
Na+ channels, Na+ rushes
___ _____ open and __ _____ out
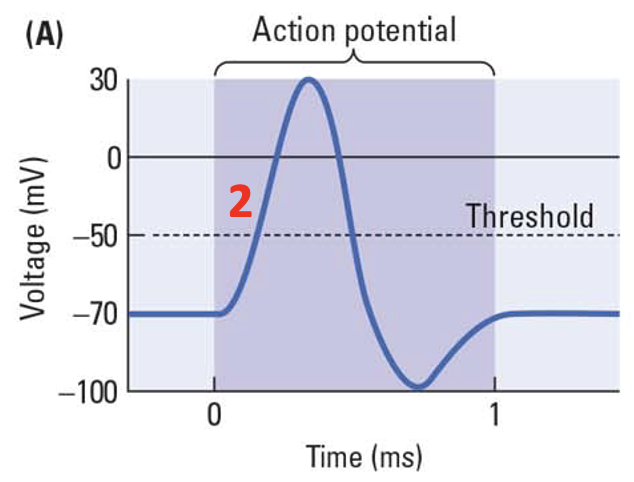
67
New cards
close
Na+ channels _____.
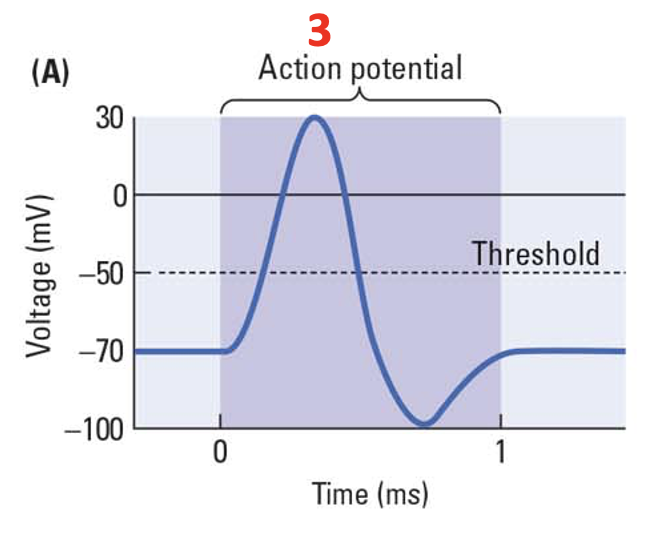
68
New cards
K+ channels, K+ rushes
__ _____ open and __ _____ out.
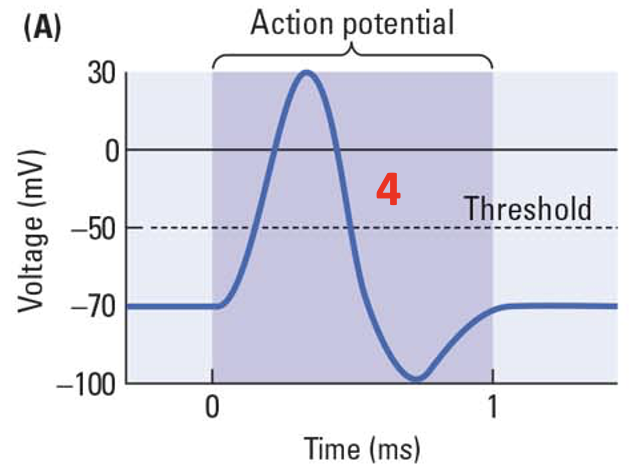
69
New cards
Na+, K+, on
__/__ pumps turn ___.
70
New cards
resting membrane potential
electrical charge across the cell membrane in the absence of stimulation
71
New cards
Why does the electrical gradient maintain resting potential?
because the membrane is relatively impermeable to large molecules they negatively charged proteins remain inside the cell
72
New cards
How does the concentration gradient use channels and gates to maintain resting potential?
ungated potassium and chloride channels allow potassium and chloride ions to pass freely, but gates on sodium channels keep out positively charged sodium ions
73
New cards
How does the pumps maintain resting potential?
Na+--K+ pumps extrude Na+ from the intracellular fluid and inject K+
74
New cards
excitatory postsynaptic potential
brief depolarization of a neuron membrane in response to stimulation
75
New cards
inhibitory postsynaptic potential
brief hyperpolarization of a neuron membrane in response to a stimulation
76
New cards
How do neurons communicate?
a chemical message via neurotransmitters
77
New cards
neurotransmitter
chemical released by a neuron onto a target with an excitatory or inhibitory effect
78
New cards
synapse
the junction where the messenger molecules are released from one neuron to excite or inhibit the next neuron
79
New cards
presynaptic membrane (axon terminal)
where the action potential terminates to release a chemical message
80
New cards
postsynaptic membrane (dendritic spine)
the receiving side of the chemical message where EPSPs or IPSPs are generated
81
New cards
synaptic cleft
small gap where the chemical message travels from the presynaptic membrane to the post synaptic membrane
82
New cards
synaptic vesicles (presynaptic)
small membrane-bound sphere that contains one or more neurotransmitters
83
New cards
What are the four classes of neurotransmitters?
small-molecule transmitters, peptide transmitters, lipid transmitters, and gaseous transmitters
84
New cards
small-molecule transmitters
class of quick acting neurotransmitters
85
New cards
peptide transmitters
hormones that respond to stress, oxytocin, regulate eating and drinking, and contribute to learning
86
New cards
lipid transmitters
synthesized “on demand” when an action potential reaches the axon terminal
87
New cards
endocannabinoids
lipophilic (fat loving) molecules associated with appetite, pain-sensation, mood, and memory
88
New cards
gaseous transmitters
synthesized cells as needed to easily cross the cell membrane
89
New cards
What are the four activating systems of the CNS?
cholinergic, noradrenergic, dopaminergic, and serotonergic
90
New cards
cholinergic activating system
normal walk behavior and is thought to function in attention and memory
91
New cards
noradrenergic activating system
plays a role in learning by stimulation neurons to change structure
92
New cards
dopaminergic activating system
plays a role in motor movements and behavior
93
New cards
serotonergic activating system
plays a role in wakefulness and learning
94
New cards
depolarization
decrease in electrical charge across a membrane (more positive)
95
New cards
diffusion
movement of ions from one area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration
96
New cards
electrical stimulation
passing an electric current from one uninsulated tip to produce behavior
97
New cards
GABA
main inhibitory transmitter
98
New cards
hyperpolarization
increase in the electrical charge across a membrane (more negative)
99
New cards
myelin
insulating sheath around nerve fibers
100
New cards
nerve
signals that travel to and from the brain via neurons