Unit14-2
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What type of wave is a sound wave, and how do particles move?
Longitudinal wave; particles oscillate parallel to propagation direction (compressions/rarefactions).
What is the speed of sound in air at 20°C?
~343 m/s (increases with temperature).
How does wavelength change if sound frequency doubles (same medium)?
Wavelength halves (λ=v/f; speed v is constant).
What are the conditions for standing waves in a closed-end tube?

A closed-end tube is 19.5 cm long. What is its fundamental frequency? (Use v=343 m/s)
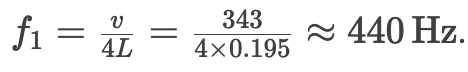
How does an open-end tube differ in harmonics?

What causes beats in sound waves?

A 440 Hz tuning fork and piano string produce 3 Hz beats. What are possible piano frequencies?
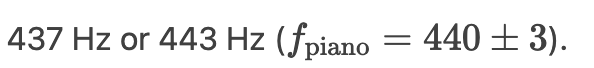
How does a piano tuner adjust a string if the frequency is too high?
Loosen the string (reduces tension FT, lowering wave speed v and frequency f).
What causes the Doppler effect?
Relative motion between wave source and observer. Motion toward = higher f; away = lower f.
Does the Doppler effect change wave speed?
No! Only perceived frequency/wavelength change; speed depends on the medium.
Qualitative example: An ambulance moves toward you. Describe the sound.
Pitch (frequency) increases as it approaches, decreases as it passes.
What is the speed of light in a vacuum?

How are electric/magnetic fields oriented in an EM wave?
Perpendicular to each other and to propagation direction (transverse wave).
What is the visible light spectrum order (low to high f)?
Red, Orange, Yellow, Green, Blue, Violet (ROYGBV; ~400–700 nm).
How does frequency relate to wavelength for EM waves?
λf=c. Higher f = shorter λ.
Write the universal wave equation for sound/light.

Formula for beat frequency.
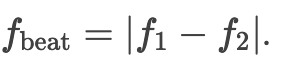
Harmonic frequencies for closed-end tube.
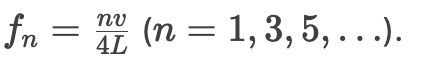
Mnemonics & Pitfalls
