searching algorithms
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
linear search
can be used on an unsorted list
quick and easy to develop
the search takes anywhere between immediately finding the item, and checking every item in the list
if the item is not in the list you have to check every item
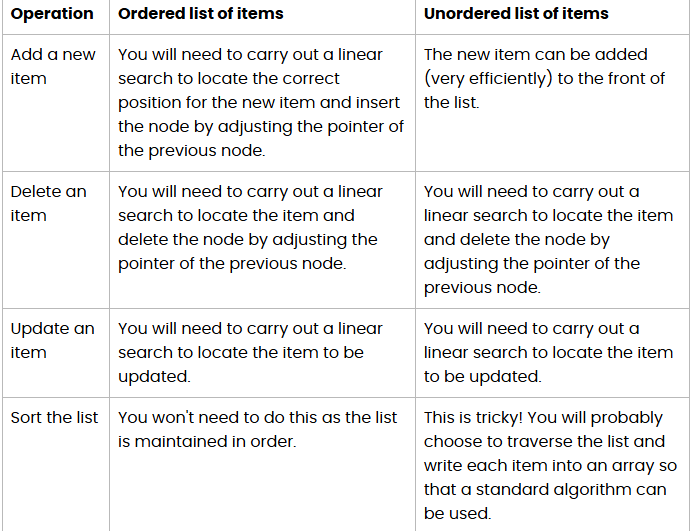
for loop linear search
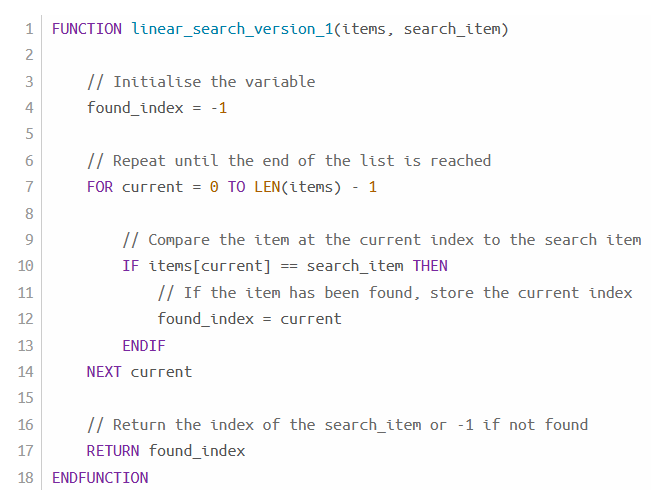
while loop linear search
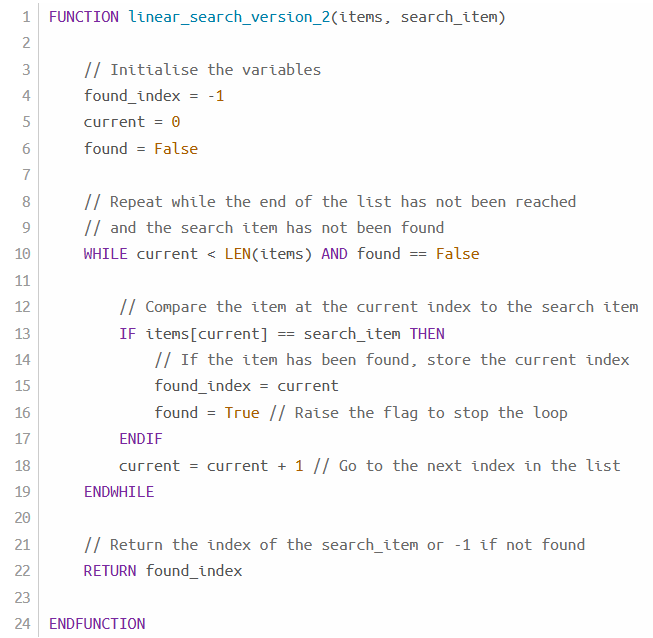
time complexity of linear search
for a for loop, the time is always n checks, in Big O notation this would be described as O(n). in a while loop it is at least O(1) and at most O(n). to find the average time is the sum up to n all divided by n, which simplifies to (n+1)/2, but this is still written as O(n) as n+1/2 tends to n as n gets larger.
binary search
needs an ordered list
the half chosen will change if the list is ascending or descending
checks the midpoint of the list and checks it. if the item is the item your looking for, then you have found it. if the item is greater than the item your looking for then pick the half that is lower. if the item is lower than the item your looking for then pick the half that is greater. repeat until you find the item.
the list must be in some form of ascending or descending order
iterative binary search
this works for list in ascending order. div returns a whole number, if the input is even div will round down to the middle left
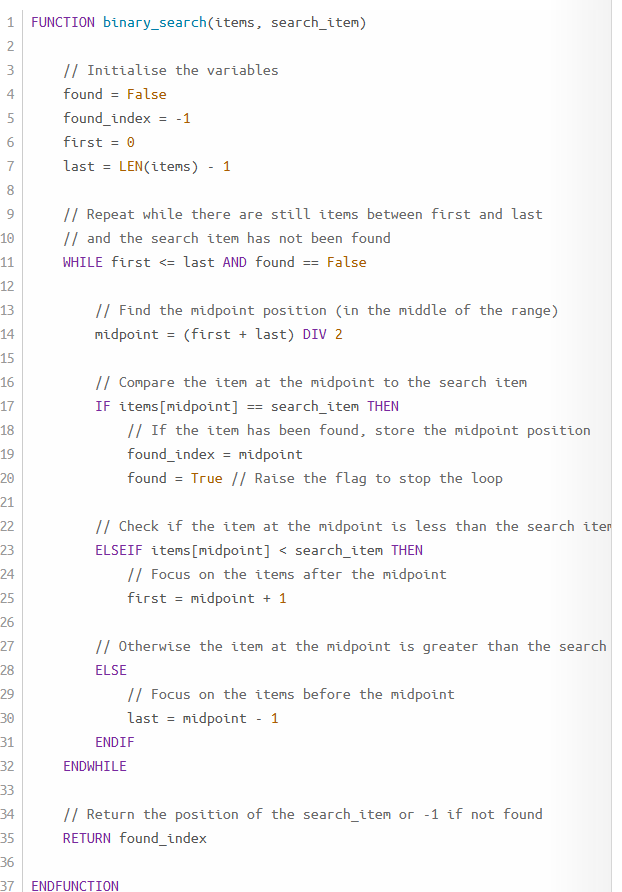
recursive binary search

binary search efficiency
the best case scenario is when the first midpoint is the item
worst case happens when the item is either index 0 or index n, or isn’t in the list. in this case the algorithm goes through all possible midpoints.
a list with 10 items has at most 4 comparisons (3 midpoints and 1 to check at the end), but a 52 item list has only 6 comparisons. the number of searches is log2(n) comparisons + 1 (final comparison)
binary search time complexity
In the worst case, the main operation will be carried out log2(n)+1. the time complexity in big O notation is this time complexity is defined as O(logn) because the cost of the final comparison is negligible when searching large data sets because the final check is negligible for large n, this is known as logarithmic complexity
In the best case, the time complexity will be O(1).
the average case has O(logn) time complexity.
binary search space complexity
For the iterative version of binary search have a space complexity of O(1) since the only additional memory used will be a few variables to keep track of the elements being checked.the recursive version of binary search has a higher space complexity, as recursion places more demand on the call stack. Therefore, the space complexity will depend on the recursion method, and at its most efficient is O(logn).
binary search tree
a search tree of ordered nodes, where each node has at most 2 nodes
to be as efficient as a binary search, the tree must be balance: every final node (leaf node) is about the same distance from the root
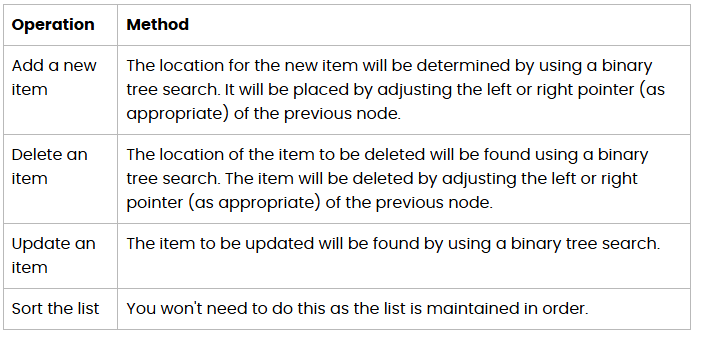
recursive binary search tree
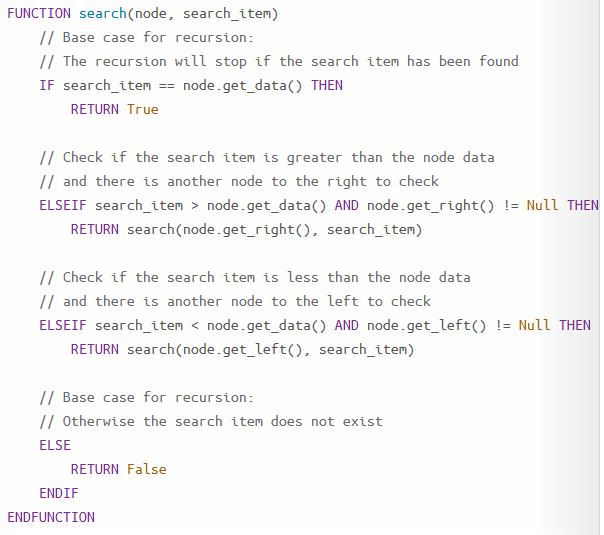
binary search tree time complexity
depends on the balance of the tree
balanced tree:
In the best case, the time complexity will be O(1)
In the worst case, the maximum number of comparisons needed will be O(logn)
unbalanced tree
In the best case, the time complexity will be O(1).
In the worst case, the maximum number of comparisons needed will be O(n) because all nodes will be on one branch and you are looking for the leaf node
binary search tree space complexity
The standard binary search tree algorithm is recursive. This will effect the space complexity since recursion places more demand on the call stack than an iterative algorithm. Therefore, the space complexity will depend on the recursion method, and at its most efficient is O(logn).
linear vs binary
the binary search is much more efficient because it checks for a range where the item might be, and looks through that so the number of maximum checks is less that checking every item.
the binary search only works on ordered lists.
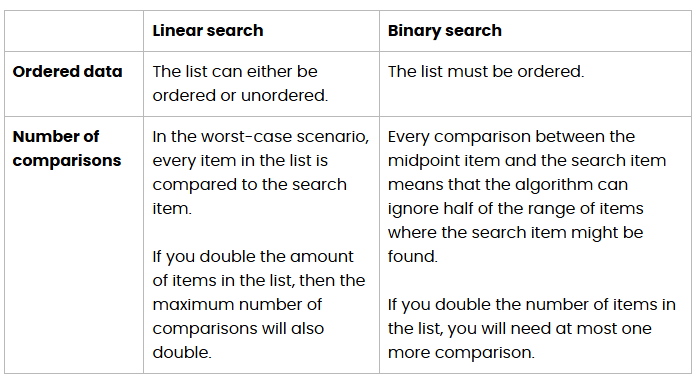
search arrays
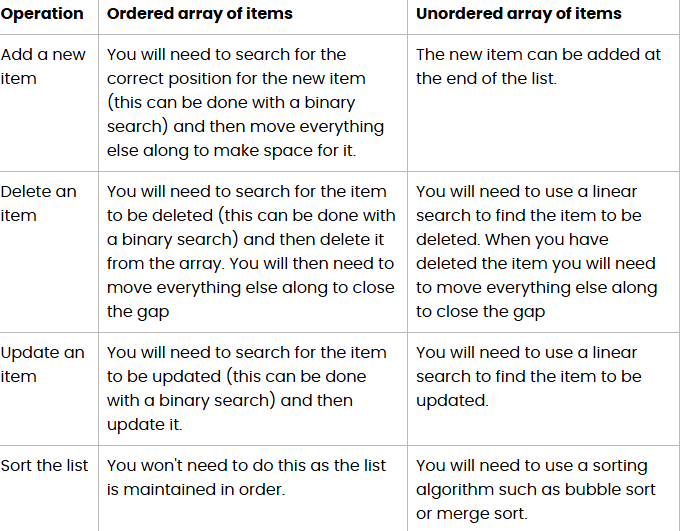
search hash maps
When you want to find a single item in a hash table, you generate a hash value for the key. The hash value is then used to directly locate the item in the hash table. In the best case, where there have been no collisions, and the item is where you expect to find it or the position is empty, a hash table allows searching, adding and deleting an item in constant time O(1).
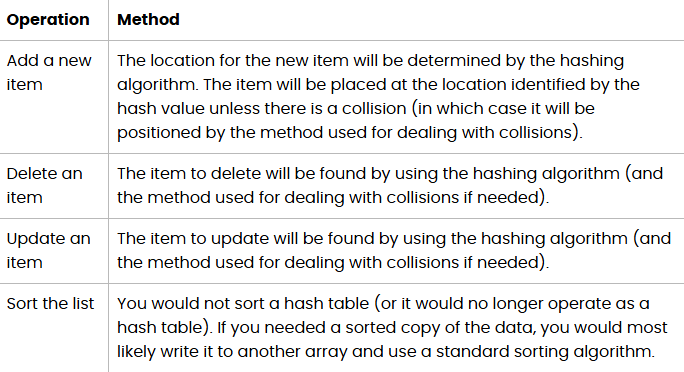
search linked lists