fear arousal model
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
fear arousal theory of persuasion
theory that suggests that when emotion is aroused by fear the audience will become highly motivated to accept the recommendations given. by changing our behaviour we avoided the feared outcome and the unpleasant state is reduced.
fear-behaviour relationship
janice and feshbach argue that the relationship between fear arousal and behaviour change is not a straight line they expected a curvilinear relationship
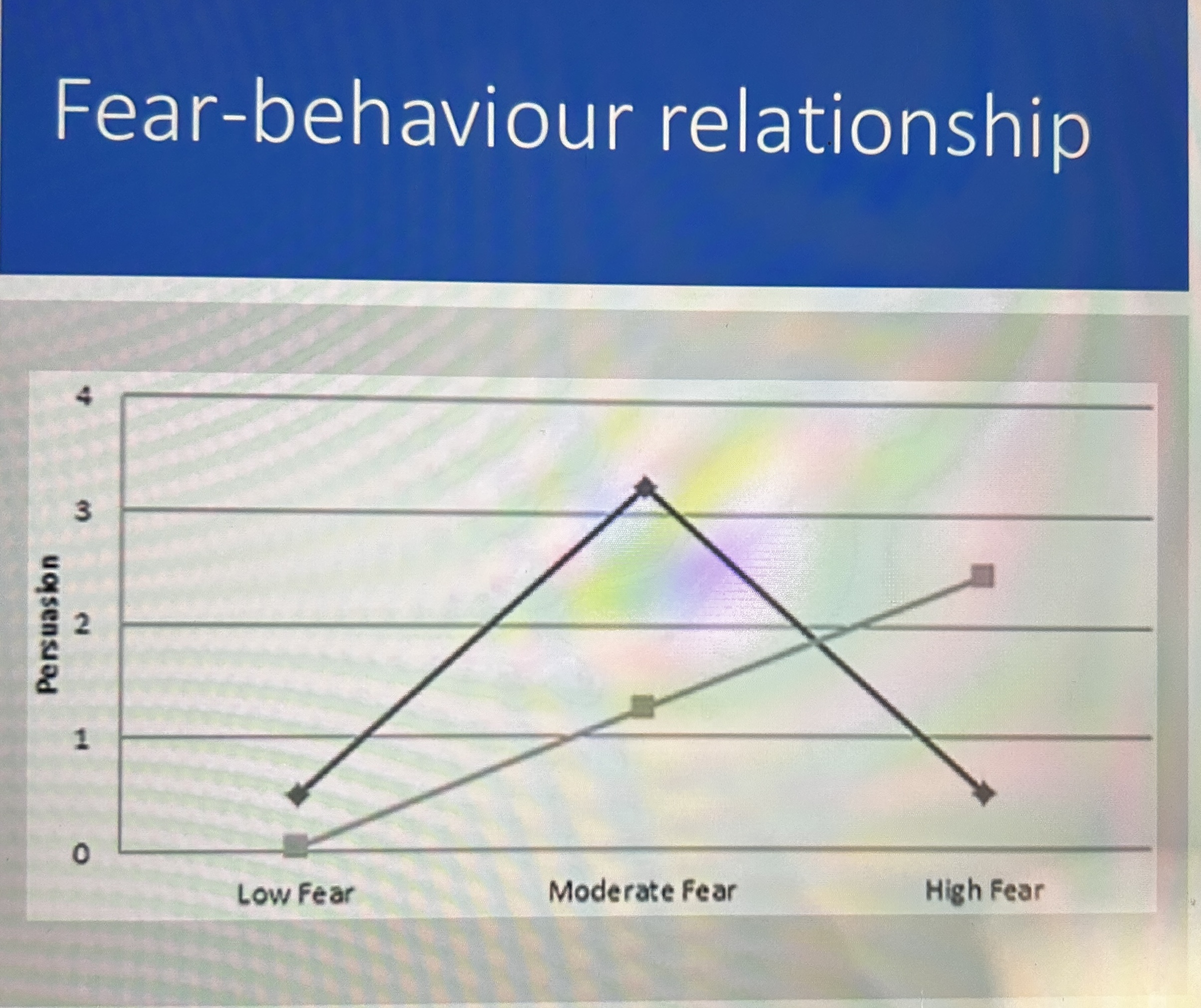
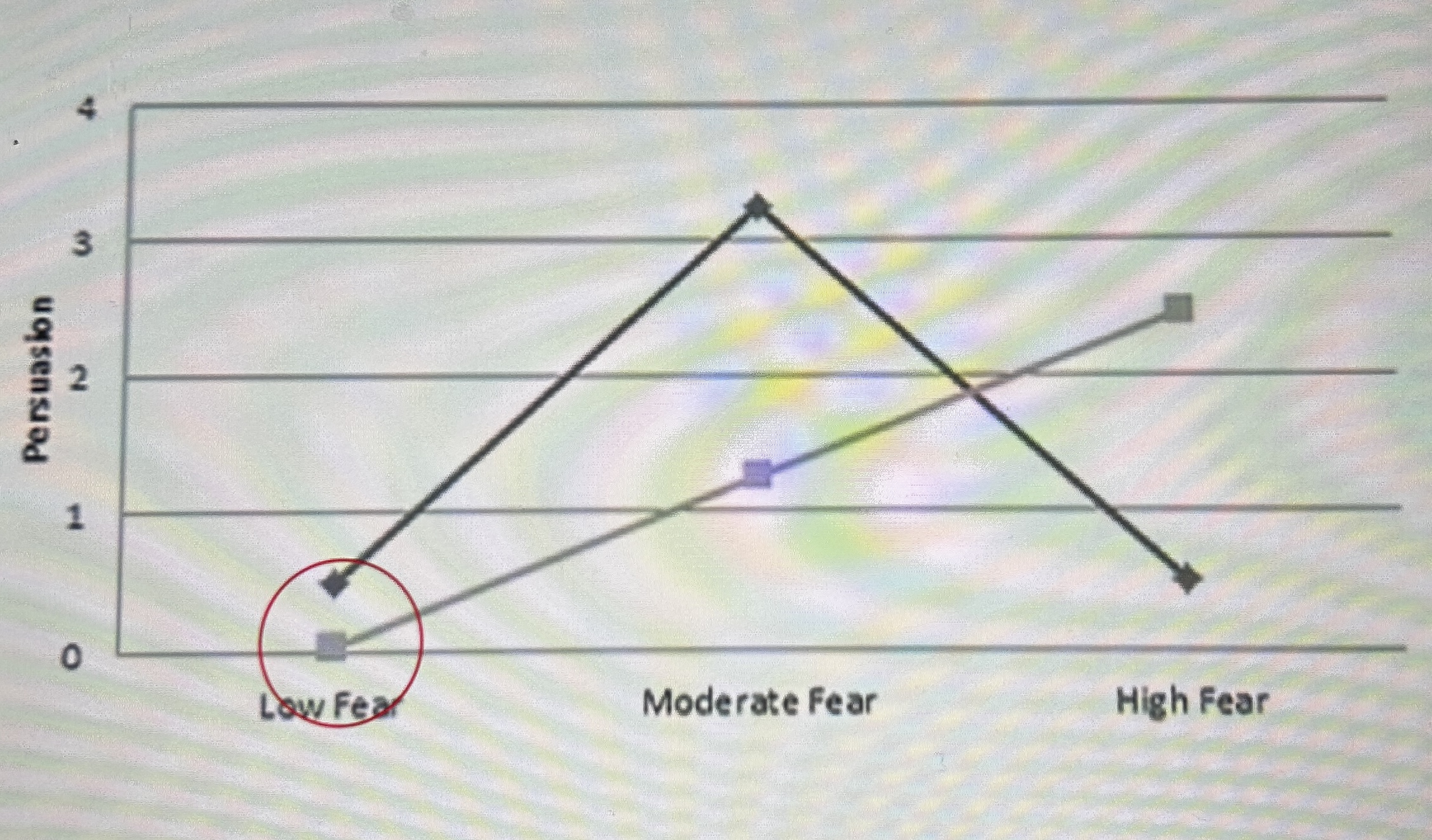
fear behaviour relationship (low fear)
a message that arouses no fear does not change behaviour. the arousal is too weak to produce the motivation to change
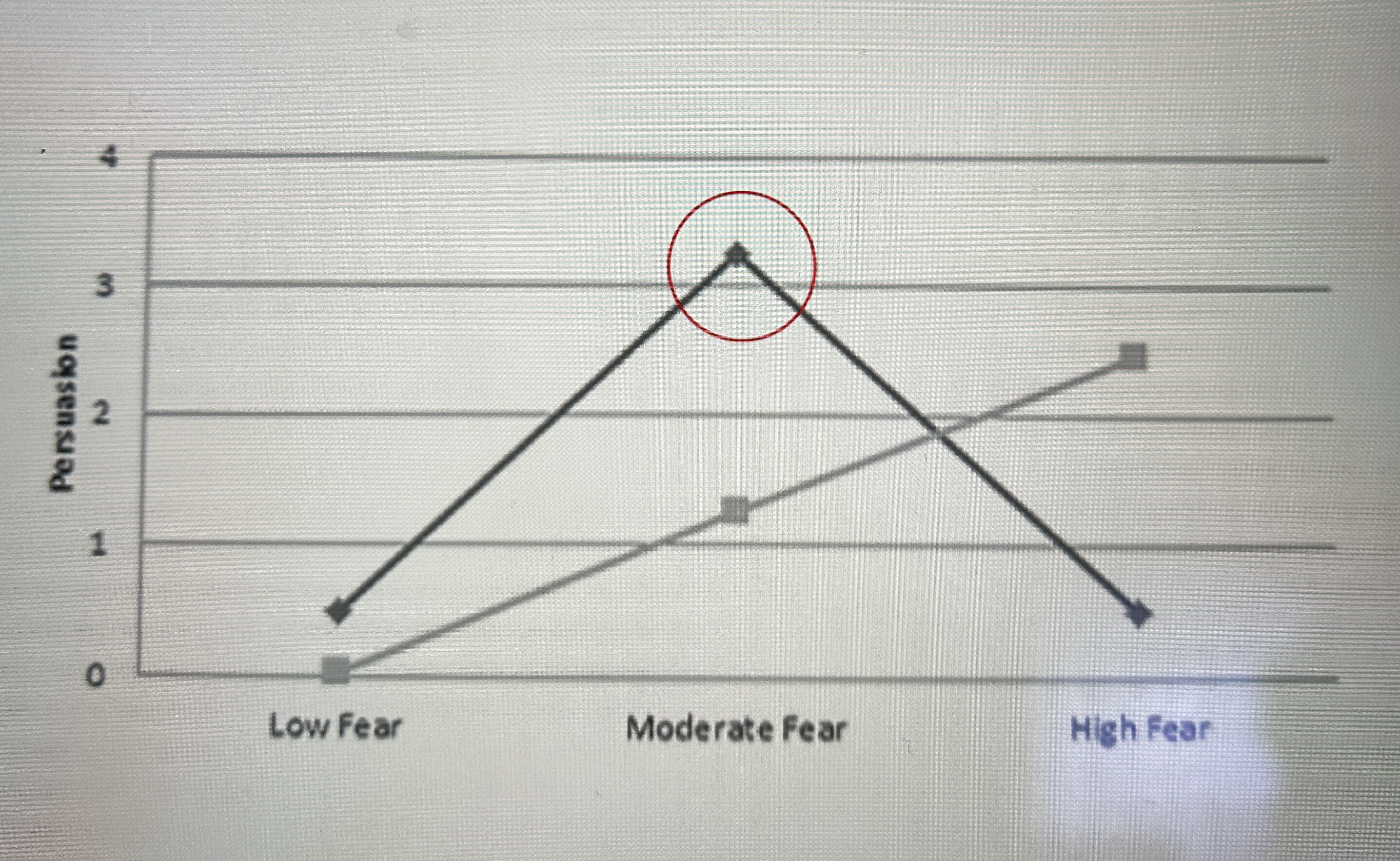
fear behaviour relationship (moderate fear)
moderate fear does produce this motivation so is likely to change behaviour
fear behaviour relationship (high fear)
high levels of arousal are counterproductive so much fear is produced that the recipient believes changing their behaviour is not enough to change their unpleasant state
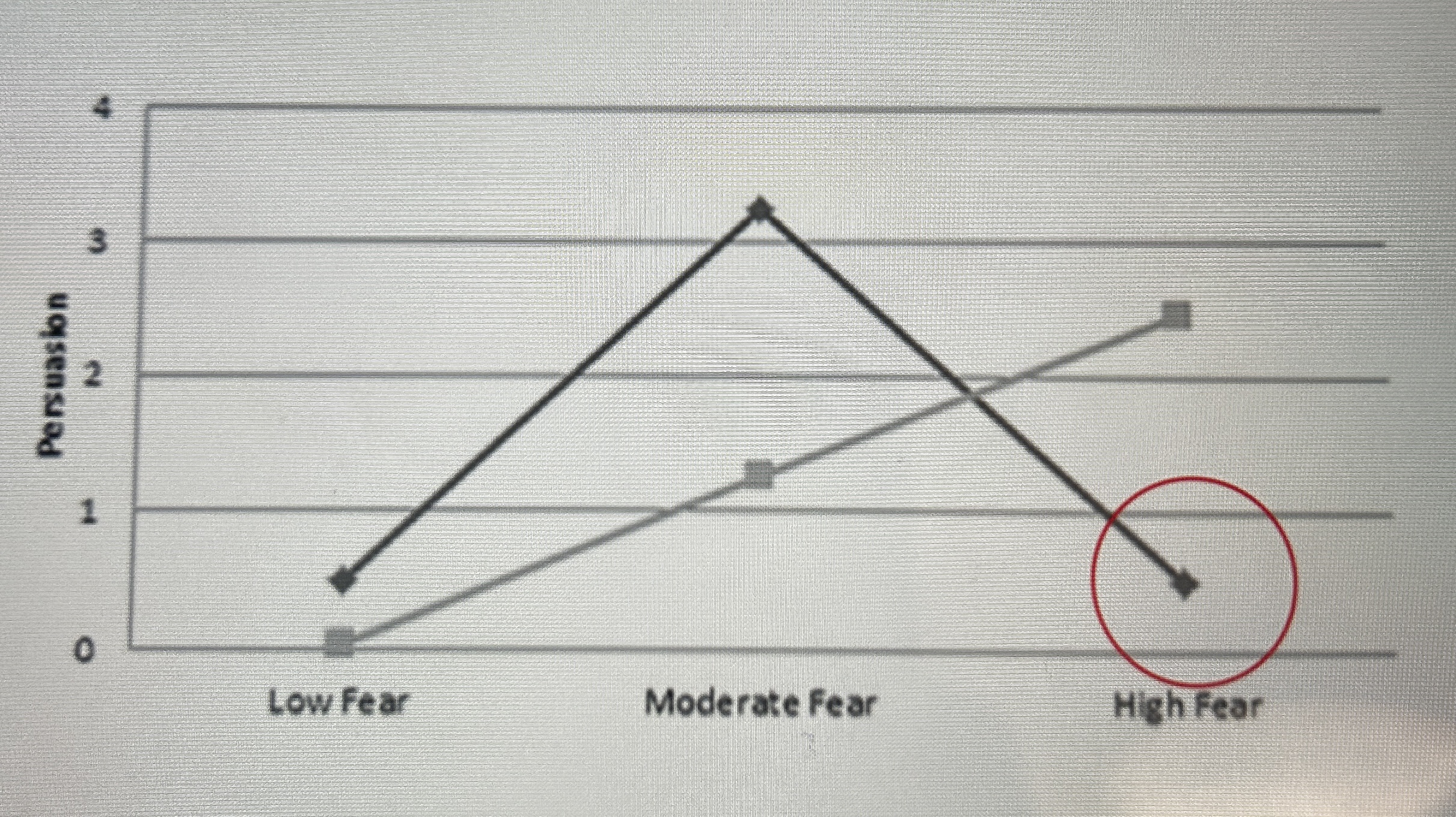
how is fear instead reduced with high levels of arousal and fear
through denial as it removed the fear state so negatively reinforces denial but behaviour does not change- the opposite of the desired outcome.
dabbs et al (1966)
studies the effects on students of fear arousing commutations on not being vaccinated against tetanus. they found that arousing fear did have a positive effect in the likelihood of students to either get vaccinated (behaviour) or intent (attitude) to get vaccinated. even so high fear arousal produced the most change suggesting it is not always counterproductive.
is the fear arousal model still used
yes widely as part of health campaigns showing that the theory can be applied to real life situations to improve public health
limitation of fear arousal model
too simplistic as it only considers fear arousal in relation to the recipients intention to change without considering other factors like social support or personality suggesting some individuals may experience fest at different levels to one another meaning it doesn’t explain indictable differences and therefor lacks validity to some extent