RLE 6F: DETERMINING TBSA AND FLUID REPLACEMENT COMPUTATION; PERITONEAL DIALYSIS; HEMODIALYSIS; ABG ANALYSIS; CYSTOCLYSIS
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Exsanguination
The action or process of draining or losing blood.
Ultrafiltration
Process whereby water is removed from the blood by means of a pressure gradient between the patient's blood and the dialysate.
Arteriovenous Graft
2 to 3 years or longer
compensation
The body likes the
pH to be 7.35-7.45
If it gets higher or lower than this, it tries to bring it back into normal range
metabolic and respiratory
two ways to compensate
Autograft
A transplant that comprises of an individual's own organ, tissue, or cells, transferred from one part of the body to another.
Collagen
The principal protein of the skin, tendons, cartilage, bone, and connective tissue.
Contracture
Fixed tightening of muscle, tendons, ligaments, or skin. It prevents normal movement of the associated body part. An injury such as a severe burn can cause contracture of the skin.
Cultured Epithelial autograft
involves obtaining full thickness biopsies of the patient's unburned skin that are cultured to promote growth of keratinocytes
Debridement
Removal of necrotic or infected skin tissue to help a wound heal, also to remove foreign material from tissue.
Donor site
An area where the surgeon has taken a layer of skin to create a graft.
eschar
Dead tissue that forms over healthy skin and then, over time, sheds. Caused by a burn or cauterization.
Heterograft
A graft obtained from an animal of a species other than that of the recipient; also termed xenograft, many grafts used today come from porcine grafts or pig.
Homograft
a graft transferred from one human to another human; also called allograft
Hydrotherapy
External use of water in the treatment of certain diseases. Burn units use hydrotherapy to soften and remove dead tissue to enable new healthy tissue to form.
Prosthetic
Artificial body part that replaces a missing part.
rule of nines
The most common method used to estimate the extent of burns in adults. This is based on anatomical regions, each representing approximately 9% of the total body surface area, allowing clinicians to quickly obtain an estimate of burn size
Arteriovenous fistula
Type of vascular access for dialysis and is created by surgically connecting an artery to a vein
Arteriovenous shunt
These are abnormal connections between coronary arteries and a compartment of the venous side of the heart
Dialysis
is a modality to remove sodium and fluid from the body if renal function is impaired and pharmacologic agents no longer work.
Dialysate
An electrolyte solution that circulates through the dialyzer in hemodialysis and through the peritoneal membrane in peritoneal dialysis
Dialyzer
May also be termed as an artificial kidney; this contains a semipermeable membrane through which particles of a certain size can pass
Diffusion
Natural tendency of a substance to move from an area of higher concentration to one of lower concentration.
Hemodialysis
Procedure during which a client's blood is circulated through a dialyzer to remove waste products from the blood.
Osmosis
The process by which fluid moves across a semipermeable membrane from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration; the process continues until the solute concentrations are equal on both sides of the membrane.
Peritoneal cavity
Serous membrane line cavity in the abdominopelvic cavity. Space in the body that contains the stomach, bowel, liver, bladder, etc.
Peritoneal dialysis
A procedure that uses the lining of a client's peritoneal cavity as the semipermeable membrane for exchange of fluid and solutes
Tenckhoff catheter
A long narrow tube inserted into the peritoneal cavity
Acid base homeostasis
Homeostatic regulation of the pH of the body's extracellular fluid. The proper balance between the acids and bases in the ECF is crucial for the normal physiology of the body and for cellular metabolism.
Bicarbonate
Chemically, HCO3, is a byproduct of the body's metabolism. The blood brings bicarbonate to the lungs, and then it is exhaled as carbon dioxide.
blood pH
The acidity or alkalinity of blood, the blood has a normal pH of 7.35 to 7.45.
hypoxemia
Decrease in arterial oxygen tension in the blood.
Hypoxia
Decrease in oxygen supply to the tissues and cells.
Metabolic acidosis
Low arterial pH due to reduced bicarbonate concentration; it is a common clinical disturbance characterized by a low pH, and a low plasma bicarbonate concentration. It can be produced by a gain of hydrogen ions or a loss of bicarbonate.
Metabolic alkalosis
A high arterial pH with increased bicarbonate concentration; It is a clinical disturbance characterized by a high pH and a high plasma bicarbonate concentration. It can be produced by a gain of bicarbonate or a loss of H+
Oxygen saturation
Percentage of hemoglobin that is bound to oxygen in the blood.
Oxyhemoglobin
The combined form of oxygen and hemoglobin; found in arterial blood; oxygen readily binds to hemoglobin in the lungs and is carried as oxyhemoglobin in arterial blood. Oxyhemoglobin is a brighter red than hemoglobin that is not bound to oxygen.
Partial pressure of carbon dioxide
is the measure of carbon dioxide within arterial or venous blood. It often serves as a marker of sufficient alveolar ventilation within the lungs, At equilibrium, the partial pressure of carbon dioxide in the blood and in alveolar gas is the same, 40mmHg.
Respiratory acidosis
A low arterial pH due to increased PCO2; Respiratory acidosis is a clinical disorder in which the pH is less than 7.35 and the PaCO2 is greater than 42 mmHg and a compensatory increase in the plasma HCO3 occurs.
Respiratory Alkalosis
A high arterial pH due to reduced PCO2;
Cystoclysis
Also known as bladder irrigation may be defined as the process of flushing the bladder with normal saline continuously to prevent or treat clot formation, allowing urine to flow freely and maintain IDC patency.
emergent/ resuscitative
From onset of injury to completion of fluid resuscitation
acute/ intermediate
From beginning of diuresis to near completion of wound closure
true
t/f
peritoneal dialysis can be done at home
Peritoneal Dialysis
This type of dialysis uses the peritoneum, a lining in your abdomen, as a filter. A solution called dialysate is put into your abdomen through a catheter.
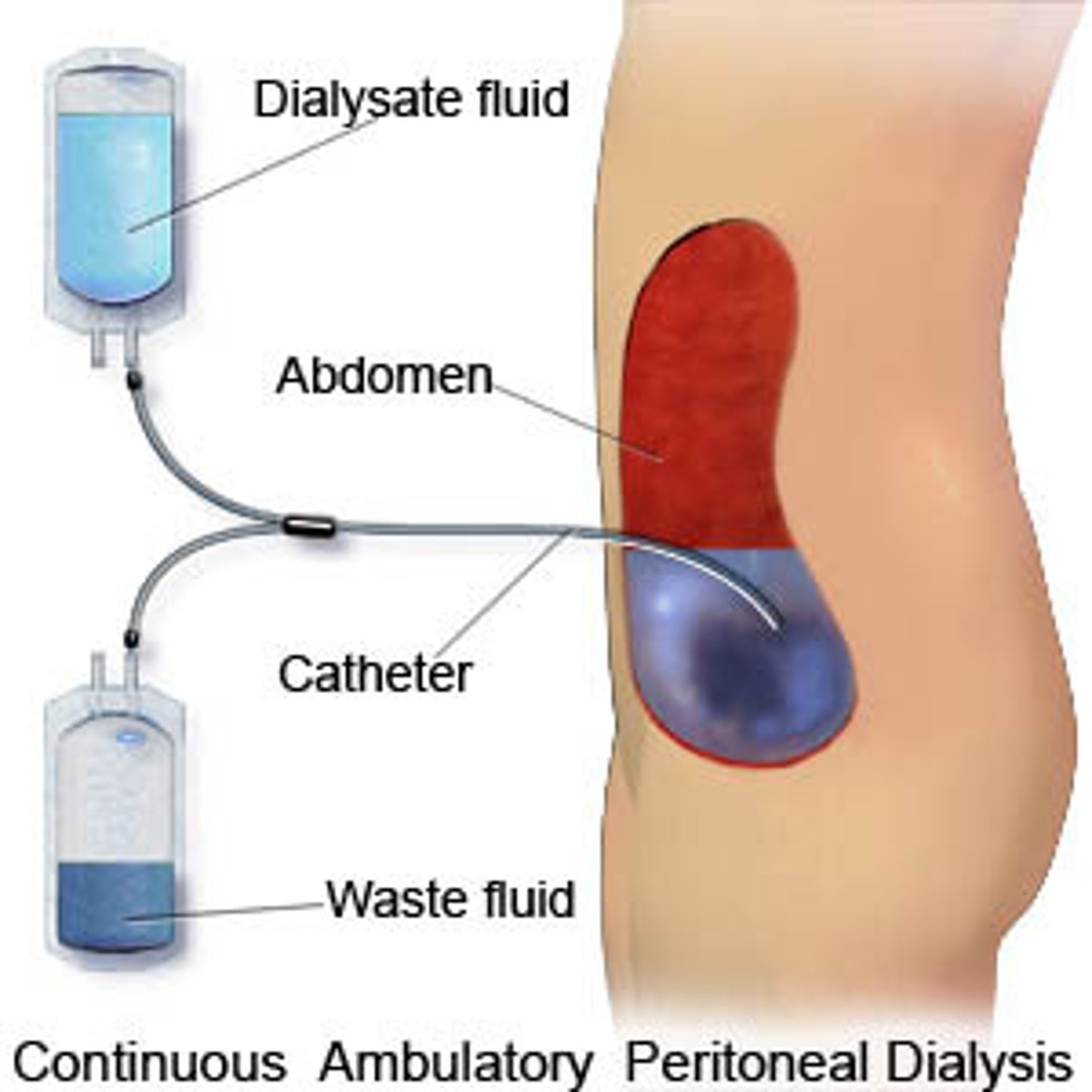
peritonitis
It is the most common and serious complication of PD. The first sign of ____ is cloudy dialysate drainage fluid. Diffuse abdominal pain and rebound tenderness occur much later.
Arteriovenous Fistula
2 to 3 months to mature
metabolic
Kidneys make bicarbonate - a base
respiratory
Lungs either retain, or blow off, CO2
respiratory acidosis
Hypoventilation
-Overdose
respiratory acidosis
COPD
-Asthma
Respiratory alkalosis
Hyperventilation
-Panic attack
Metabolic acidosis
Loss of bicarb
Metabolic acidosis
Diarrhea
Metabolic acidosis
-Diuretics
Metabolic alkalosis
-Too much sodium bicarb
Metabolic alkalosis
Antacids
-Renal disease
Metabolic alkalosis
Vomiting