1) Core content: key terms
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
demographic movement
the way in which the population’s structure changes, for example as a result of an ageing community or migration into an area
enterprise
a business, particularly one started by someone who shows initiative by taking a risk setting up, investing in, and running it
crowd funding
a method of raising funds from many people for an enterprise via online platforms
sustainability
the ability to meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs
pollution
the release of contaminating substances that are likely to harm the natural environment
recycling
the process of converting waste material into other usable products, such as glass bottles made from recycled glass
consumer
a person who uses goods and services
apprenticeship
a job with training that allows people to gain nationally recognised qualifications
automation
using control systems to operate equipment
culture
The way a group of people behave, dress, eat and live their lives. Culture can be influenced by anything from religion, tradition and history to local food sources, climate and artistic expression.
critical evaluation
A process that identifies positives and negatives from a range of areas to assess the sustainability of concepts such as a design, process or material.
global warming
an increase in the temperate of the Earth’s atmosphere, caused by greenhouse gases
ethics
balancing behaviour with moral principles when carrying out an activity
carbon footprint
The amount of CO² emissions that can be directly or indirectly attributed to an individual’s or company’s activities. The larger the carbon footprint, the greater the environmental impact.
life cycle analysis
An analysis of all the environmental impacts related to a product from the extraction of the raw material to its use and disposal.
photovoltaics
using solar cells to generate electrical power by converting energy from the sun
Compressive strength
the ability of a material to resist squashing
tensile strength
the ability of a material to resist stretching
veneers
slices of wood that are 3mm or less, used to build up manufactured boards or to protectively coat other woods
lever
a fixed rigid beam requiring a fulcrum, load, and effort to provide a mechanical advantage
force
a push or pull upon an object that, when unopposed, will change the object’s motion
cam
a mechanism for converting rotary motion into reciprocation or oscillating (up and down/back and forth) motion
follower
a device that follows the movement of a cam profile to provide a desired output in a connecting part
friction
The resistance to movement between two surfaces that are trying to slide against each other. Friction generates heat.
Torque
a measure of system’s turning power
input device
Something that can give an input signal to the system.
Output device
Something that responds to an instruction of change in control elements.
Input signal
information given to the system by an input device
Output signal
an instruction the system gives to an output device
program
A set of instructions the system controller has been given to make the electronic system do what it is supposed to do. If a transistor is used, there is no program, just a simple switching action due to the rise in voltage on the base of the transistor above 0.6 volts.
transistor
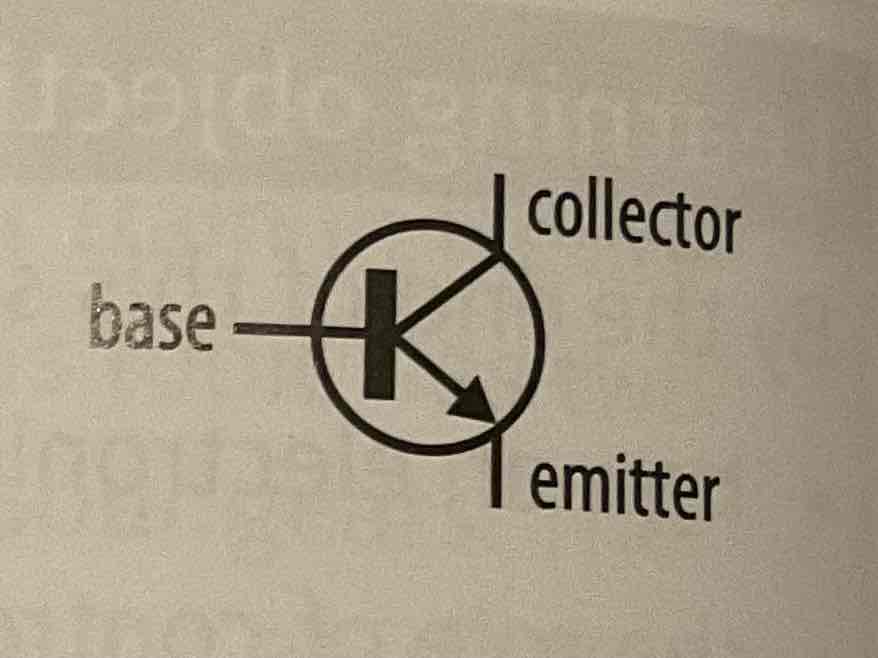
a transistor is a semi-conductor that acts like an electronic switch depending upon the voltage across the base and emitter. has three connections, a small voltage at the base connection turns it on and lets a larger current flow into the collector and out of the emitter. transistors are useful in sensing circuits to amplify the small current you get from some sensors.
resistance
An electrical quantity that is a measure of how the device or wire reduces the electric current flow through it.
component
an individual piece of a circuit
circuit
individual components are joined up with a conductive material so electricity can flow through them and perform a task
voltage
the amount of potential electrical force available that could make electricity flow
current
the amount of electricity that is flowing through a circuit
semi-conudctor
a material that allows electricity to flow under certain conditions, it can behave as an insulator or conductor
analogue
a signal that can vary up and down through a range of values
feedback loop
a loop in a program that goes back to an earlier point to keep repeating that part of the program
alloy
a mixture of two or more metals or elements, which has improved properties and characteristics
ductility
ability of a material to deform by bending, twisting, or stretching; ability to be drawn out without breaking. ductility in metals increases with temperature
malleability
ability of a material to be permanently deformed in all directions without fracture. it increases with temperature
hardness
ability of a material to resist deformation, indentation, or penetration. hard materials can resist abrasion, drilling, impact, scratching, and wear and tear
paper
thin, flat material made from natural fibres, weighing less than 220 grams per square metre (gsm)
board
thick paper or layers of paper more than 220 grams per square metre (gsm)
synthetic polymer
a synthetic material made mostly from oil; normally referred to as plastic
thermoforming polymer
a material that can be reshaped by application of heat. this type of material can be recycled and made into other products
thermosetting polymer
a material that cannot be reshaped by reheating. this type of material cannot be recycled
HIPS
high-impact polystyrene: a thermoplastic commonly used for vacuum forming
glass reinforced plastic (GRP)
a composite material made from polyester resin and glass fibres. moulds can be laid up by hand or using a spray on technique
insulator
a material with low conductivity preventing electrical current or heat to flow
polyvinyl chloride (PVC)
a thermoplastic containing chlorine and carbon
fibres
thread-like elements that can be formed into yarns and fabrics
fabric
a length of flexible material constructed from fibres
staple
the length of a fibre
monomer
a molecule that can be bonded to similar molecules to form long chains
hardwood
comes from a tree with broad leaves
grain
fibres run the length of a tree trunk, which give it its strength and make the distinctive patterns you see on timber
softwood
a tree with needle like leaves and seeds in a cone
evergreen
a tree that keeps its leaves all year round
veneer
a thin slice of wood, about 1mm thick. used as a decorative surface and to make plywood
hard
how well materials resist deformation, indentation, or penetration. hard materials can resist abrasion, drilling, impact, scratching, and wear and tear
touch
how well a material withstands being hit
durable
how well a materials lasts
mechanical properties
elements of a material that resist deformation from external forces or loads
physical properties
elements of a material that can be defined and measured, such as colour, size, and weight
prototype
a full size, three dimensional model of the finished design, created for testing before production is started
modular
a design featuring parts of standard sizes so they can be constructed in different ways
anthropometric data
measurements of the human body
styrofoam
a modelling form commonly shaped with a hot wire cutter
stripboard/breadboard
electronics prototyping board
computer modelling
using computer aided design (CAD) software like ProDesktop to visualise your idea
simulation
a computer model that represents how something would work in real life, such as how the screw on an adjustable spanner could be altered so that it would allow different nut sizes to be tightened or loosened
construction lines
faint sketched lines that help you build up the rough shape of a product before creating your design within them. They should not be rubbed out.
vanishing point
a point in the distance where the construction lines project to. it can be positioned to the right or left, above or below, depending on how you would like your image to appear
disassemble
to take apart a product so that you can identify the parts that it consists of
patent
a license that is applied for to protect the way that a design works. once a product has been patented, no one else can use that exact design for a similar product
ergonomics
designing products that take into account the strengths and limitations of people so that the product fits well, reduces effort and increases performance
CAM
computer aided manufacture, such as using a laser cutter or 3D printer
CNC
computer numerically controlled, for example using a CNC router