L14 Ruminant Trichostrongyle abomasum | Parasitology Exam 2
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
What is the most important parasite of adult cattle in USA
Ostertagia ostertagia (brown stomach worm)
What is the preferred environment for Ostertagia osteragia and predilection site
cool, wet climates
predilection site: abomasum
What is the egg characteristics of Ostertagia ostertagia
egg have dark brown numerous blastomeres 80-40micrometers (indistinguishable to Haemonchus)
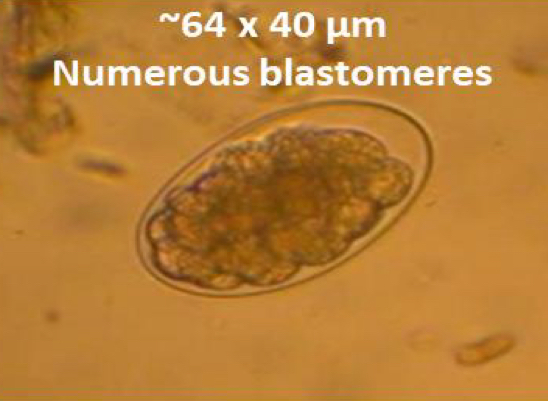
What is the PPP of Ostertagia ostertagia
2 wks
What are the seasonal transmission characteristics of Ostertagia in warm temperate climates
highest transmission in winter-spring
larvae acquired in late spring become hypobiotic (arrested)
(to survive hot summers)
What are the seasonal transmission characteristics of Ostertagia in cool temperate climates
highest transmission in summer-fall
larvae acquired in late fall become hypobiotic
to survive too cold winter in host
What are the difference in grazing patterns of cattle in warm temperate climates vs cool temperate climates; and how does Ostertagia arrest depending on the climate
warm temperate climates - freq grazing all-year; L4 stage arrest over summer
cool temperate climates - seasonal grazing; L4 arrest over winter
What life stage does ostertagia arrest (hypobiosis) and why
early L4 stage arrest for 3-4 mo to avoid adverse environmental conditions
In warm temperate, the L4 stage of Ostertagia will arrest when
over the summertime in the host
In cool temperate, the L4 stage of Ostertagia will arrest when
over wintertime in host
What is the difference between clinical type I disease vs clinical type II disease of Ostertagia ostertagia
Clinical type I - ingested of large number of L3 stages in summer
Clinical type 2 - L4 develops and emerges as adult in late winter causing type 2 dz
In summer ostertagiosis, what is the primary lifecycle of Ostertagia ostertagia to develop clinical type I disease
as temp inc in summer, pasture larval contamination inc reaching infective L3 stage
In winter ostertagiosis, what is the primary lifecycle of Ostertagia ostertagia to develop clinical type II disease
as temp dec in winter, L3 becomes arrested at early L4 stage in abomasal mucosal glands
What is the primary pathology of ostertagia ostertagia
disruption of abomasal mucosa by development of larvae leading to gastric gland destruction
What is the post-mortem pathology of ostertagia ostertagia
abomasum has putrid smell bc of bacterial overgrowth, high pH
abomasum mucosa has nodules
abomasum mucosa edematous and hyperemic
What are the Ostertagia clinical feature involving abomasal gastric glands
larvae develop disrupting abomasal gastric glands
high pH in abomasum due to replacement of HCL-secreting cells
What is the clinical feature of Ostertagia infection relating to pepsin
pepsin inhibits digestion of protein
What is the clinical feature of Ostertagia relating to albumin
albumin leakage thru abomasal mucosa
What is the tx of Ostertagiosis
ML is drug of choice
What species is infected by Teladorasagia circumincinta (and its predilection site)
sheeps/goats in abomasum
What is the egg characteristics of teladorsagia circumcinta
reddish-brwon w numerous blastomeres (~80-40micrometers)
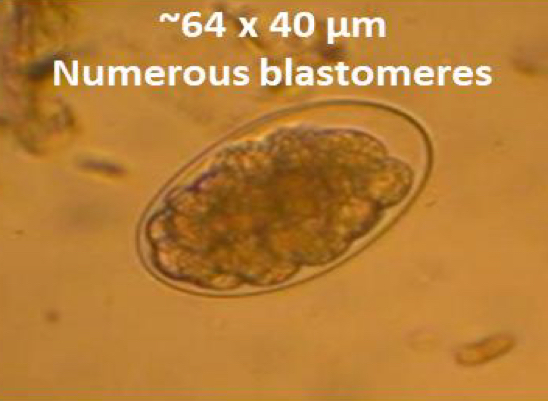
What is the PPP of Teladorsagia circumcinta
2 wks
What causes loss of weight and appetite in Teladorsagosis dz (caused by T. circumcinta infection)
hyperplastic inflammation of abomasal mucosa (abomasitis)
What causes hypoprotinaemia in Teladorsagosis dz (caused by T. circumcinta infection)
leakage across damaged mucosa
What causes loss of weight and appetite WITH watery diarrhea in Teladorsagosis dz (caused by T. circumcinta infection)
impaired abomasal func associated w alteration in pH
What is the appearance of abomsal mucosa of Teladorsagia infection
morocco leather apperance
What is the tx of teladorsagosis
Benzimidazole + ivermectin DOC
What are the six sustainable control programs of teladorsagosis
build up infection in host
farming system
seasonal appearance
pasture contamination
TST and refugia management
dx tests
What is the host and predilection site of trichostrongylus axei
hosts: cattle, small ruminants, horses, pigs
predilection site:
abomasum - ruminants
stomach - horses pig
What is the smallest trichostrongyle
T. axei
What trichostrongyle nematode has unique characteristic of cross-infection in mixed species grazing situation
Trichostrongylus axei
Trichostrongylus axei is not usually a _____ pathogen by itself and is part of the ruminant ____ complex
primary; PGE