bio unit 1 test (9th grade)
1/257
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
258 Terms
“pro” in prokaryotic cells
prokaryotic cells evolved before eukaryotic cells and lack a true nucleus or membrane-bound organelles. Prokaryotic cells are simpler, typically smaller, and found in organisms like bacteria and archaea.
“karyo” in prokaryotic cells
The term "karyo" in "prokaryotic" comes from the Greek word karyon, meaning "nut" or "kernel," which refers to the nucleus. In prokaryotic cells, "karyo" indicates the absence of a true, membrane-bound nucleus, distinguishing them from eukaryotic cells, which do have a defined nucleus.
capsule
The capsule is a protective outer layer in some bacteria. It helps protect the bacteria and keeps it from drying out. (outside cell wall) (slimy)
cell wall
rigid/solid that give shape and support to prokaryotic cells (provides structure)
cell membrane
thin and flexible layer inside the cell wall which controls what goes in and out.
Pili
tiny hair like structures on the surface of most prokaryotic cells, they allow the cell to stick to surface/other cells and transfer genetic material
flagellum
long whip like structure; attached at back that acts like a tail to help prokaryotic cells move and swim through liquid
ribosome
small structure, in ALL cells, including prokaryotic cells, that make PROTEINS. they can be found floating in the cytoplasm or attached to cell-membrane
chromosomes/DNA
chromosomes are a structure that contains genetic information. In prokaryotic cells DNA is usually found in a single circular chromosome located in the cytoplasm, as there is no nucleus in prokaryotic cells.
CLassification of bacteria: Kingdom eubacteria
Kingdom Eubacteria includes most common bacteria. Here are some key points:
Cell Structure: Eubacteria have a cell wall made of peptidoglycan.
Shape: They can be round (cocci), rod-shaped (bacilli), or spiral (spirilla).
Reproduction: Eubacteria reproduce mainly by binary fission (splitting in two).
Nutrition: They can be autotrophic (make their own food) or heterotrophic (consume other organisms).
diverse bacteria that play essential roles in processes like decomposition, nutrient cycling, and digestion in living organisms.
CLassification of bacteria: Kingdom Archaebacteria
Kingdom Archaebacteria includes ancient bacteria that often live in extreme environments, such as hot springs or salt lakes, and have unique cell walls and membranes that allow them to survive in harsh conditions.
what is the main difference between the types of bacteria found in Kingdom eubacteria and Kingdom Archaebacteria
Eubacteria: Have cell walls made of peptidoglycan and are found in a wide range of environments, including soil and water. They include most common bacteria.
Archaebacteria: Have unique cell walls that do not contain peptidoglycan and often thrive in extreme environments, like hot springs or salty lakes. They are biochemically and genetically distinct from eubacteria.
“EU” in eukaryotic cells
In "eukaryotic," the prefix "eu-" means "true" or "good." It refers to the presence of a true nucleus and more membrane-bound organelles in these cells, distinguishing them from prokaryotic cells.
KARYO in eukaryotic cells
In "eukaryotic," the term "karyo" comes from the Greek word karyon, meaning "nucleus." It refers to the presence of a true, membrane-bound nucleus in these cells, which distinguishes them from prokaryotic cells that lack this feature.
classification of eukaryotic cells: Kingdom Animalia
Kingdom Animalia includes multicellular organisms that are heterotrophic (they consume other organisms for energy) and lack cell walls. Members of this kingdom are characterized by their ability to move at some stage in their life cycle and have specialized tissues and organs. Examples include mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and insects.
4o mini
classification of eukaryotic cells: Kingdom Plantae
Kingdom Plantae consists of multicellular organisms that are primarily autotrophic (they produce their own food through photosynthesis) and have cell walls made of cellulose. Members of this kingdom include flowering plants, conifers, ferns, and mosses, and they play a crucial role in ecosystems as producers.
classification of eukaryotic cells: Kingdom Protista
Kingdom Protista includes a diverse group of mostly unicellular organisms that can be autotrophic (produce own food)(like algae) or heterotrophic(get food from elsewhere) (like protozoa). They often live in aquatic environments and exhibit various forms of movement, such as using flagella or cilia. Examples include amoebas, paramecia, and diatoms.
classification of eukaryotic cells: Kingdom Fungi
Kingdom Fungi includes multicellular and unicellular organisms that are heterotrophic and absorb nutrients from their surroundings through external digestion. They have cell walls made of chitin and play essential roles in decomposition and nutrient cycling. Examples include mushrooms, yeasts, and molds.
What do all Eukaryotic Cells have which prokaryotic cells dont?
NUCLEUSSS
3 main differences between plant and animal cells
Cell Wall: Plant cells have a rigid cell wall made of cellulose, providing structure and support, while animal cells do not have a cell wall.
Chloroplasts: Plant cells contain chloroplasts, which are necessary for photosynthesis, whereas animal cells do not have chloroplasts.
Vacuoles: Plant cells typically have a large central vacuole for storing water and maintaining turgor pressure, while animal cells have smaller vacuoles that are more involved in storage and transport.
what does DNA stand for
DNA stands for Deoxyribonucleic Acid. It is the molecule that carries the genetic instructions for living organisms.
two main functions of DNA
Genetic Information Storage: DNA contains the instructions needed for the development, functioning, growth, and reproduction of all living organisms.
Protein Synthesis: DNA guides the process of making proteins through transcription and translation, determining the traits and functions of cells.
what is a nucleotide?
A nucleotide is the basic building block of DNA and RNA. It consists of three components: a sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. Nucleotides link together to form the long chains of DNA or RNA, carrying genetic information.
three big characteristics in a nucleotide
Sugar: Specifically, deoxyribose in DNA and ribose in RNA.
Phosphate Group: A molecule that contains phosphorus and oxygen.
Nitrogenous Base: One of four types (adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine in DNA; uracil replaces thymine in RNA).
fill in the blank:fill in the blank: the backbone of the double helix has alternating ______________________ and ______________________
sugar, phosphate groups
fully labeled DNA
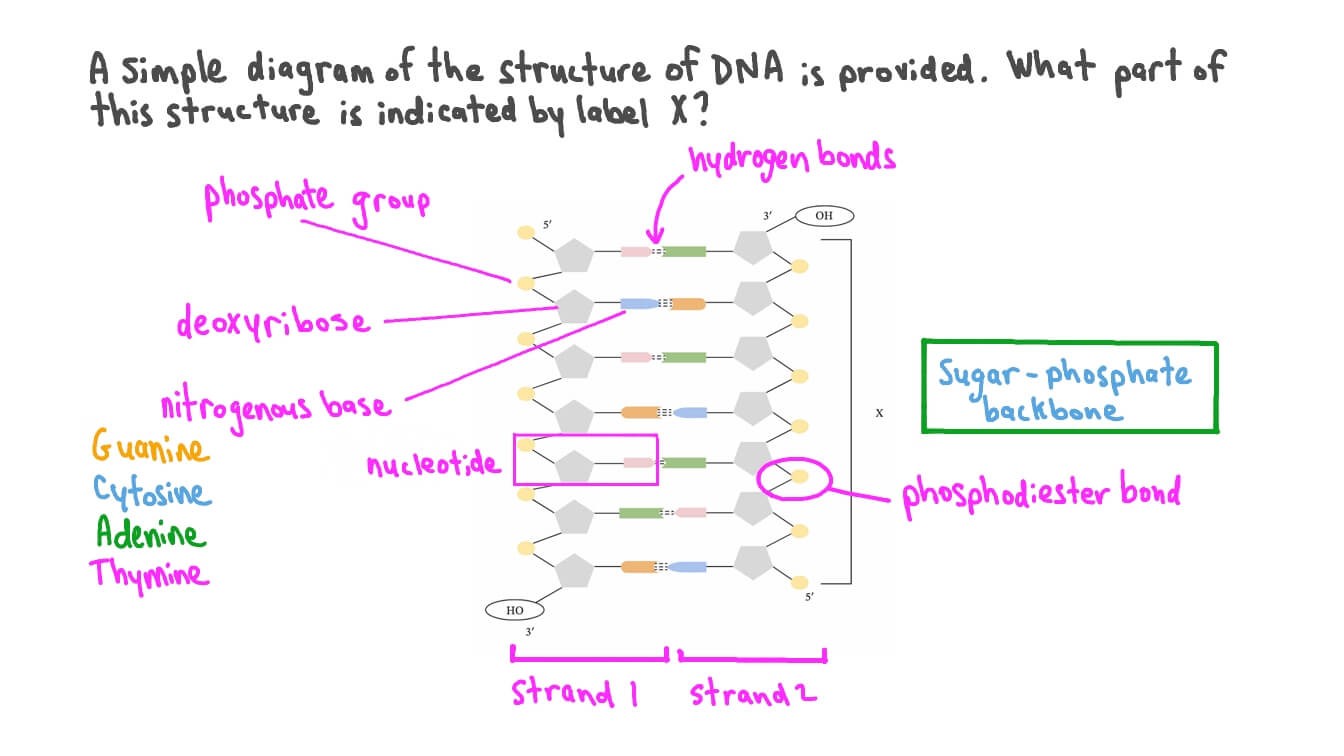
G pairs with? IN DNA
GUanine pairs with Cytosine
Thymine (T)pairs with? IN DNA
Adenine (A)
what bond (dotted lines) holds complementary bases of DNA together?
hydrogen bonds
In a DNA molecule, the number of cytosines (C) equals the number of?
Guanines (G)
In a DNA molecule, the number of adenines (A) equals the number of
Thymines (T)
what psrt of the nucleotide cobtains the genetic code
The part of the nucleotide that contains the genetic code is the nitrogenous base. The specific sequence of these bases (adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine) encodes the genetic information.
the sequence of nitrogen bases is __________ for alsmost all organisms
universal
how many strands does DNA have
DNA has two strands that form a double helix structure.
The term used to describe how the two sides of the DNA molecule compare to one another is called______
complimentary/anti parallel
the process of which DNA is amde into RNA is called
transcription
The process by which RNA is made into protein is called:
The process by which RNA is made into protein is called translation.
Protein synthesis takes place on the ____
Protein synthesis takes place on the ribosomes.
This molecule takes the message from DNA to the ribosomes: __
This molecule that takes the message from DNA to the ribosomes is messenger RNA (mRNA).
A section of DNA that codes for a protein is a
A section of DNA that codes for a protein is called a gene.
A base found in RNA but not DNA: __
A base found in RNA but not in DNA is uracil (U).
Amino acids join together to make
proteins
This type of RNA, brings individual amino acids to the ribosome:
This type of RNA that brings individual amino acids to the ribosome is called transfer RNA (tRNA).
A set of 3 bases on a strand of mRNA is called
a codon.
Three bases on tRNA that match the codon is called the:
anticodon
5.Any change in DNA is called a ___
mutation
transcription and translation
look
What is the role of mRNA in the process?
In summary, mRNA acts as a messenger that conveys genetic information from DNA to the ribosomes, where proteins are synthesized.
.What is the role of tRNA in the process?
Role of tRNA in Protein Synthesis: tRNA (transfer RNA) transports specific amino acids to the ribosome and matches them with the corresponding codons on the mRNA, facilitating the assembly of the polypeptide chain during translation.
.What is the role of the ribosome in the process?
The ribosome is responsible for translating the mRNA sequence into a protein during translation, facilitating the binding of tRNA that brings amino acids to form the growing polypeptide chain.
.Where is the anticodon located?
The anticodon is located on the tRNA (transfer RNA) molecule. It is a set of three nucleotides that pairs with a complementary codon on the mRNA during protein synthesis.
Where does transcription take place?
Transcription takes place in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells, where the DNA is located. In prokaryotic cells, transcription occurs in the cytoplasm since they lack a defined nucleus.
Where does translation take place?
Translation takes place on the ribosomes, which can be found in the cytoplasm or on the endoplasmic reticulum in eukaryotic cells. In prokaryotic cells, translation occurs in the cytoplasm.
Summarize the relationship between proteins and genes.
The relationship between proteins and genes is that genes contain the genetic instructions for synthesizing proteins. Each gene encodes the sequence of amino acids that make up a specific protein, determining its structure and function. In summary, genes are the blueprints for proteins, and proteins perform essential roles in biological processes.
study this pic:
isotonic in blood cells meaning
EQUAL IN AND OUT: Isotonic in the context of blood cells refers to a solution that has the same concentration of solutes (such as salts) as the inside of the cells. When blood cells are in an isotonic solution, there is no net movement of water into or out of the cells, allowing them to maintain their normal shape and function.
hypotonic in blood cells meaning
LESS GOING IN MORE ALREADY IN. SWELL: Hypotonic in the context of blood cells refers to a solution that has a lower concentration of solutes compared to the inside of the cells. When blood cells are placed in a hypotonic solution, water moves into the cells, causing them to swell and potentially burst (a process called lysis) due to the increased internal pressure.
hypertonic in blood cells meaning
MOSTLY BOTH LEAVING DEFLATIONNN: Hypertonic in the context of blood cells refers to a solution that has a higher concentration of solutes compared to the inside of the cells. When blood cells are placed in a hypertonic solution, water moves out of the cells, causing them to shrink and become dehydrated (a process called crenation).
Movement across the cell membrane that does not require energy is called
passive transport
If there is a concentration gradient, substances will move from an area of high concentration to an area of
low concentration
The cell membrane is
selectivley permeable *:Permeable means that a substance can pass through a material or barrier. In the context of cell membranes, it refers to the ability of certain molecules to enter or exit the cell while preventing others from doing so.
_____________is the simplest type of passive transport.
diffusion
.The diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane is called
osmosis
A solution that causes a cell to swell is called a
hypotonic solution
In ________ diffusion, membrane proteins help molecules across the membrane.
facilitated
In diffusion, molecules______
spread out
Facilitated diffusion moves substances_________ using the cell's energy.
without