12.3 The Phillips Curve
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
The table below represents the relationship between unemployment rate and inflation rate in the United States.
The Phillips Curve shows the tradeoff between unemployment and inflation, demonstrating that if one is higher, the other must be lower. If the government attempts to reduce inflation, unemployment will rise, or if the government attempts to reduce unemployment, inflation will rise. When plotting points for the Phillips curve, unemployment rate is plotted as the x-variable and inflation rate as the y-variable. To draw a Phillips curve based off of the table above, plot the points for each year with unemployment as the x-coordinate and inflation as the y-coordinate, then connect the points.
A downward sloping Phillips curve that does not shift cannot explain _____________.
Select the correct answer below:
an inverse relationship between unemployment and inflation
expansionary policies leading to greater inflation
the double digit inflation accompanied by a decline in output, experienced in the 1970s
economic boom accompanied by a high inflation
the double digit inflation accompanied by a decline in output, experienced in the 1970s
The relationship between inflation and unemployment expressed by the traditional Phillips curve corresponds to changes in the aggregate demand curve. When demand increases, inflation goes up and unemployment goes down. However, this negative relationship between inflation and unemployment changes when supply shifts. When aggregate supply shifts left, we see both unemployment and inflation increasing, a situation referred to as stagflation.
In short, we should interpret a downward-sloping Phillips curve as valid for short-run periods of several years, but over longer periods, when aggregate supply shifts, the downward-sloping Phillips curve can shift so that unemployment and inflation are both higher (as in the 1970s and early 1980s) or both lower (as in the early 1990s or first decade of the 2000s).
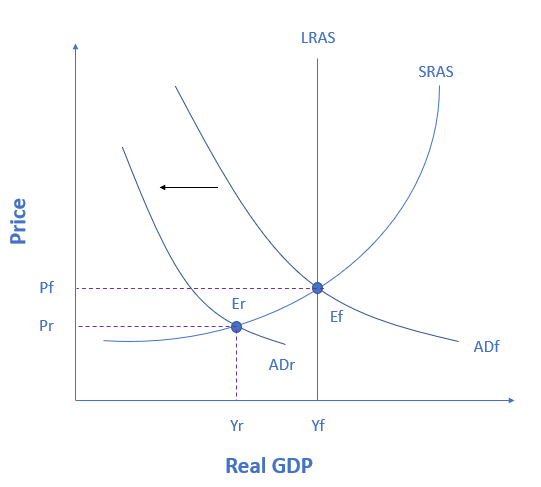
Using the Keynesian philosophy, identify the appropriate government response necessary to shift aggregate demand back to ADf. Select the correct answer below:
contractionary fiscal policy
expansionary fiscal policy
contractionary monetary policy
expansionary monetary policy
expansionary fiscal policy
When aggregate demand shifts leftward, that indicates a recessionary gap. Keynesian macroeconomics argues that the solution to a recession is expansionary fiscal policy, such as tax cuts to stimulate consumption and investment, or direct increases in government spending that would shift the aggregate demand curve to the right. The appropriate policy would be for government to shift aggregate demand to the right from ADr to ADf, where the economy would be at potential GDP and full employment.
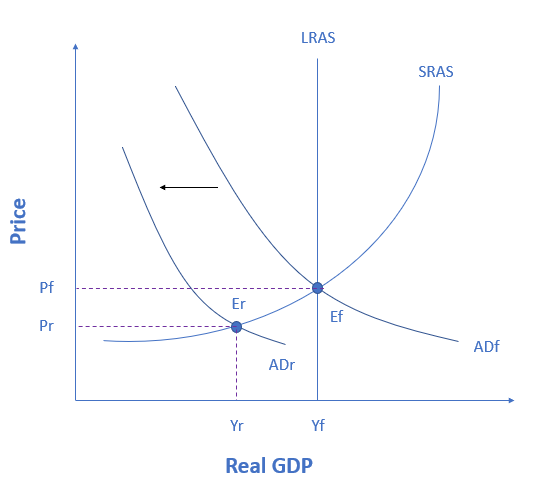
If the economy is currently producing at point Er, then the economy is experiencing a(n) _______ gap, which can be fixed by enacting fiscal policies that shift aggregate demand to the ______.
inflationary; right
recessionary; right
inflationary; left
recessionary; left
recessionary; right
The figure shows an economy experiencing a recessionary gap. When aggregate demand shifts leftward, that indicates a recessionary gap. Keynesian macroeconomics argues that the solution to a recession is expansionary fiscal policy, such as tax cuts to stimulate consumption and investment, or direct increases in government spending that would shift the aggregate demand curve to the right. The appropriate policy would be for government to shift aggregate demand to the right from ADr to ADf, where the economy would be at potential GDP and full employment. The government can shift aggregate demand to the right by increasing spending or enacting tax cuts.
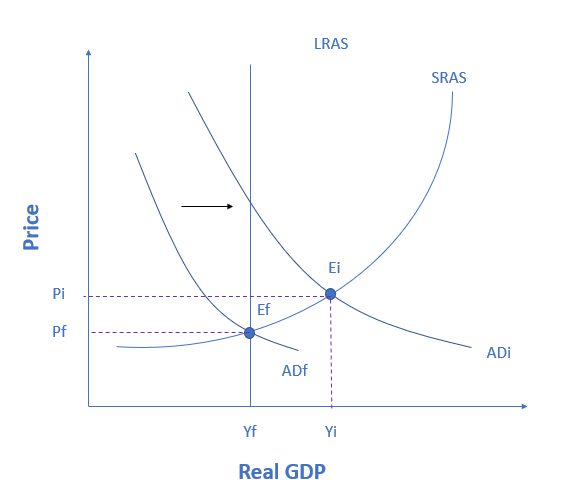
The figure below shows an economy that is currently producing beyond its full employment output level at point Ei. This economy is experiencing a(n) __________ gap, which can be closed by ___________.
Select the correct answer below:
recessionary; increasing government spending
recessionary; decreasing government spending
inflationary; increasing government spending
inflationary; decreasing government spending
inflationary; decreasing government spending
The figure shows an economy experiencing an inflationary gap, which occurs when the economy is operating above potential GDP. In this situation, unemployment is low, but inflationary rises in the price level are a concern. The Keynesian response would be contractionary fiscal policy, using tax increases or government spending cuts to shift AD to the left. The result would be downward pressure on the price level, but very little reduction in output or very little rise in unemployment. If aggregate demand was originally at ADi in the figure, so that the economy was experiencing inflationary rises in the price level, the appropriate policy would be for government to shift aggregate demand to the left, from ADi toward ADf, which reduces the pressure for a higher price level while the economy remains at full employment.
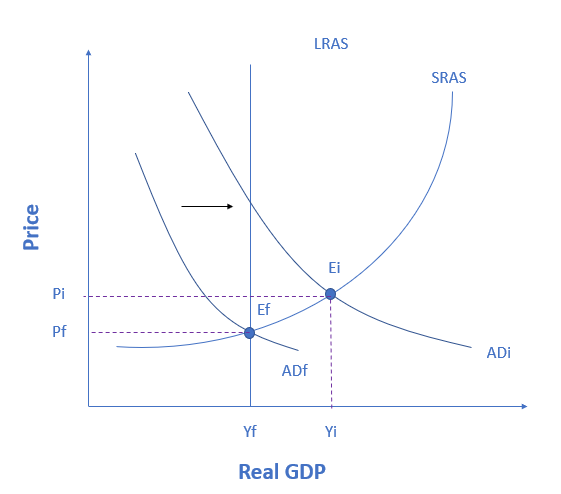
True or false?
If an economy is currently producing at point Ei, then the figure below shows a recessionary gap, which can be closed using contractionary fiscal policy.
False
The figure shows an economy experiencing an inflationary gap, which occurs when the economy is operating above potential GDP. In this situation, unemployment is low, but inflationary rises in the price level are a concern. The Keynesian response would be contractionary fiscal policy, using tax increases or government spending cuts to shift AD to the left. The result would be downward pressure on the price level, but very little reduction in output or very little rise in unemployment. If aggregate demand was originally at ADi in the figure, so that the economy was experiencing inflationary rises in the price level, the appropriate policy would be for government to shift aggregate demand to the left, from ADi toward ADf, which reduces the pressure for a higher price level while the economy remains at full employment.
What kind of conditions can lead to stagflation?
Select the two correct answers below.
Select all that apply:
Workers have just received wage increases that reflect expectations of future inflation. A few months later, however, prices rise faster than expected.
A military conflict results in a sharp and unexpected rise in the cost of oil.
Prices tend to remain sticky even though wages have risen.
Over the course of a year, unemployment falls at a rate directly proportional to the rise in inflation.
Workers have just received wage increases that reflect expectations of future inflation. A few months later, however, prices rise faster than expected.
A military conflict results in a sharp and unexpected rise in the cost of oil.
Stagflation can occur when there's a supply shock (such as the unexpectedly high rise of the price of oil) or when the rate of inflation rises higher than expected. Prices drive wages up and wages drive prices up in a vicious circle.
During a recession, a government decides to use fiscal policy to provide incentives for companies to increase production overseas, where labor and manufacturing costs are lower, and import these products into the domestic economy for sale. What is the effect of this government fiscal policy on the economy?
Select all that apply:
It will contribute to a recessionary gap.
It will contribute to an inflationary gap.
It will increase aggregate demand.
It will decrease aggregate demand.
It will have no effect.
It will contribute to a recessionary gap.
It will decrease aggregate demand.
Importing manufactured products will lead to greater spending on imports than exports and thus to lower aggregate demand. Furthermore, Keynesian macroeconomics argues that the solution to a recession is expansionary fiscal policy, such as tax cuts to stimulate consumption and investment, or direct increases in government spending that would shift the aggregate demand curve to the right.
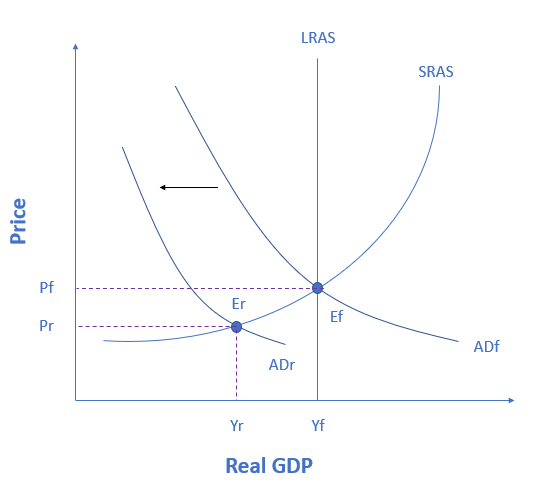
An economy is currently producing at point Er. What policy should the government of the economy take?
Select all that apply:
increase government spending
decrease government spending
raising taxes
lowering taxes
increase government spending
lowering taxes
The figure shows an economy experiencing a recessionary gap. When aggregate demand shifts leftward, that indicates a recessionary gap. Keynesian macroeconomics argues that the solution to a recession is expansionary fiscal policy, such as tax cuts to stimulate consumption and investment, or direct increases in government spending that would shift the aggregate demand curve to the right. The appropriate policy would be for government to shift aggregate demand to the right from ADr to ADf, where the economy would be at potential GDP and full employment. The government can shift aggregate demand to the right by increasing spending or enacting tax cuts.
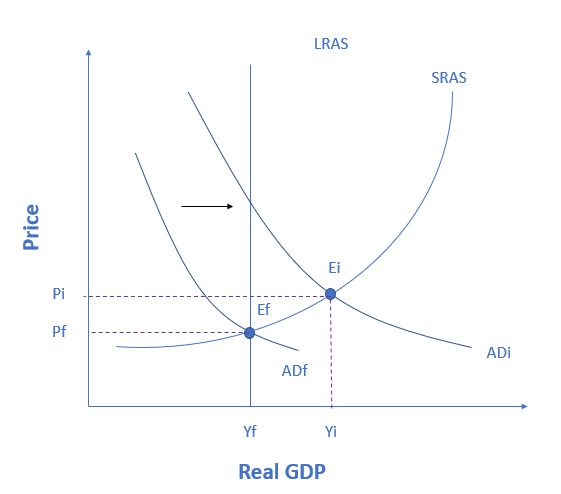
If an economy is producing at point Ei, then the figure below shows an economy experiencing a(n) __________ gap, which a government can fix by ___________.
recessionary; raising taxes
recessionary; lowering taxes
inflationary; raising taxes
inflationary; lowering taxes
inflationary; raising taxes
The figure shows an economy experiencing an inflationary gap, which occurs when the economy is operating above potential GDP. In this situation, unemployment is low, but inflationary rises in the price level are a concern. The Keynesian response would be contractionary fiscal policy, using tax increases or government spending cuts to shift AD to the left. The result would be downward pressure on the price level, but very little reduction in output or very little rise in unemployment. If aggregate demand was originally at ADi in the figure, so that the economy was experiencing inflationary rises in the price level, the appropriate policy would be for government to shift aggregate demand to the left, from ADi toward ADf, which reduces the pressure for a higher price level while the economy remains at full employment.
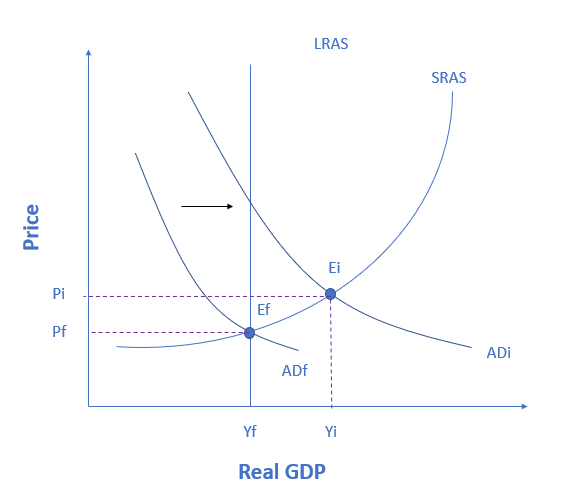
If the economy below is currently producing at point Ei, then the economy is experiencing a(n) _____________ gap, which can be fixed by using _________.
Select the correct answer below:
recessionary; expansionary fiscal policy
inflationary; expansionary fiscal policy
recessionary; contractionary fiscal policy
inflationary; contractionary fiscal policy
inflationary; contractionary fiscal policy
The figure shows an economy experiencing an inflationary gap, which occurs when the economy is operating above potential GDP. In this situation, unemployment is low, but inflationary rises in the price level are a concern. The Keynesian response would be contractionary fiscal policy, using tax increases or government spending cuts to shift AD to the left. The result would be downward pressure on the price level and reduction in real GDP. If aggregate demand was originally at ADi in the figure, so that the economy was experiencing inflationary rises in the price level, the appropriate policy would be for government to shift aggregate demand to the left, from ADi toward ADf, which reduces the pressure for a higher price level while the economy remains at full employment.