Topic 8 - Energy Production
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Definitions for Topic 8 - Energy production: 8.1 - Energy sources 8.2 - Thermal energy transfer
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Primary energy source
An energy source that has not been converted before a consumer uses it
Secondary energy source
An energy source that results from the transformation of a primary energy source
Renewable energy source
An energy source that is either continually generated or can be replenished in a relatively short amount of time (on the scale of a human lifetime)
Non-renewable energy source
An energy source that can only be replenished over a very long period of time
Specific energy
The energy per unit mass that is stored in a fuel
J/kg
Energy density
The energy per unit volume that is stored in a fuel
J/m^3
Energy transfers in a thermal power station
Examples of primary energy sources that are converted in a power station include fossil fuels (coal, oil, natural gas), biomass, and nuclear fuel.
Energy from the primary source is used to boil water in a pressure vessel, so energy from the primary source is converted into the internal energy of the steam particles.
Steam from the pressure vessel is used to turn the blades of large turbines, so the internal energy of the steam particles is converted into the kinetic energy of the turbines.
The turbines are connected to an electricity generator, so the kinetic energy of the turbines is converted into electrical energy.
Fossil fuel power stations
Fossil fuel power stations are thermal power stations.
Fossil fuels (coal, oil, natural gas) are burnt and chemical energy stored in these fuels is converted into the internal energy of the steam particles.
Fossil fuels are non-renewable, so it takes a very long time for fossil fuel storage to be replaced.
Burning fossil fuels releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, leading to the greenhouse effect.
Moderator
High-speed neutrons are released during fission.
The role of the moderator is to slow down fast-moving neutrons.
As a result, the kinetic energy of the neutrons is reduced.
Slow-moving neutrons are more likely to cause further fission.
Moderators are poor absorbers of neutrons.
Control rods
The role of control rods is to absorb neutrons.
As a result, fewer neutrons are available and fission slows down.
Control rods moderate power output and stop fission when necessary.
Control rods are good absorbers of neutrons.
Heat exchanger
The heat exchanger transfers energy from the reactor to the turbines.
This energy transfer is achieved through a closed water system.
Safety issues and risks in nuclear power plants
The reactor vessel is made of steel to withstand high temperatures and pressure.
The reactor vessel is surrounded by thick concrete that absorbs radiation.
The reactor can be shut down quickly in case of an accident.
Safe radioactive waste disposal technologies are still being developed.
It is costly to safely decommission a nuclear power plant at the end of its lifetime.
Solar heating panels
Solar heating panels are used to heat water through a water circulation system.
The panels convert solar energy into thermal energy.
Solar photovoltaic panels
Solar photovoltaic panels are made by connecting several photovoltaic cells together.
The panels convert solar energy into electrical energy.
The efficiency of solar photovoltaic panels is around 20%.
Black body
Absorbs all the wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum and does not reflect any of the radiation that falls on it.
Emissivity
The ratio of the power radiated by an object to the power radiated by a black body with the same surface area and at the same temperature as the object.
Solar constant
The amount of solar radiation that is incident in one second on one square metre at the top of the Earth’s atmosphere.
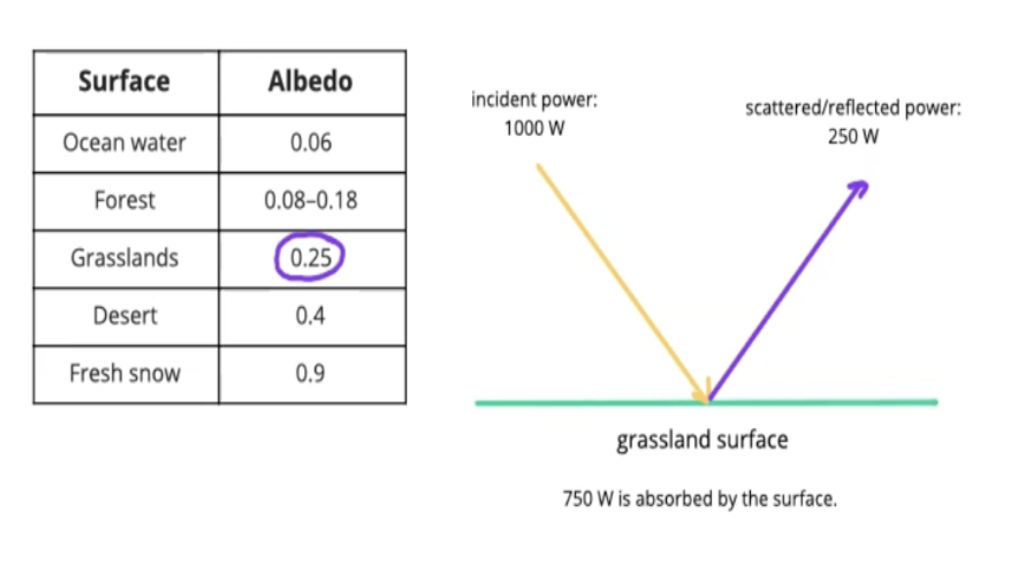
Albedo
The proportion of incident radiation that is reflected by a surface
Greenhouse effect
The warming of the Earth’s surface and the lowest level of the atmosphere due to the energy trapped by greenhouse gasses.
CH4, H2O, CO2, N2O
These gases have natural and man-made origins.
Energy absorption by greenhouse gases
The surface of the Earth absorbs incident energy from the Sun.
Then the surface re-radiates energy which is in the infrared section of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Some of this infrared energy is absorbed by greenhouse gases in the atmosphere due to an effect called resonance.
Resonance means that the frequency of the radiation that is incident on a greenhouse gas molecule is equal to one of the vibrational frequencies (vibrational states) of the molecule.
At a later point, the gas molecules re-emit the absorbed energy in all directions, some of which remains trapped in the atmosphere.