A2 Physics Medical Imaging
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
when does a piezo-electric crystal change shape
when a potential difference is applied across it
what happens if a piezo-electric crystal changes shape
the crystal generates an e.m.f.
how are ultrasound waves created
they are generated by a piezo-electric transducer which converts electric energy to ultrasound energy through the use of a piezo-electric crystal such as quartz
how are ultrasound waves detected by a piezo-electric transducer
when receiving it coverts sound waves to alternating p.d.
when transmitting it converts alternating pd to sound waves
how is the reflection of pulses of ultrasound used to obtain diagnostic information
sound waves are reflected at the boundaries to the transducer causing it to vibrate
vibration generates electrical signals
using speed of sound waves and time for it to reach back, the distance can be known
ultrasound tells us about depth and nature of the organ/bones
what is specific acoustic impedance of a medium
Z=pc, where c is speed of sound in the medium and p is the density
formula for intensity reflection coefficient of a boundary between two media
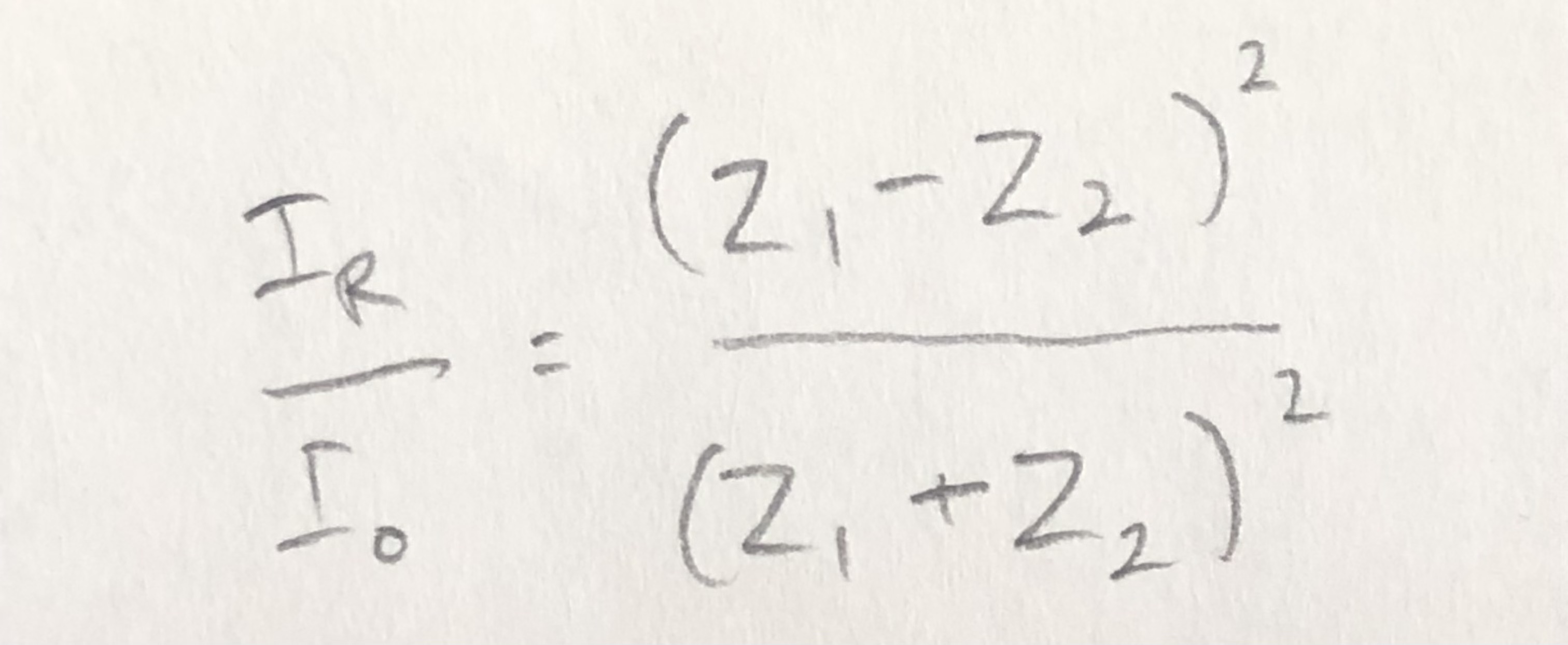
formula for attenuation of ultrasound in matter
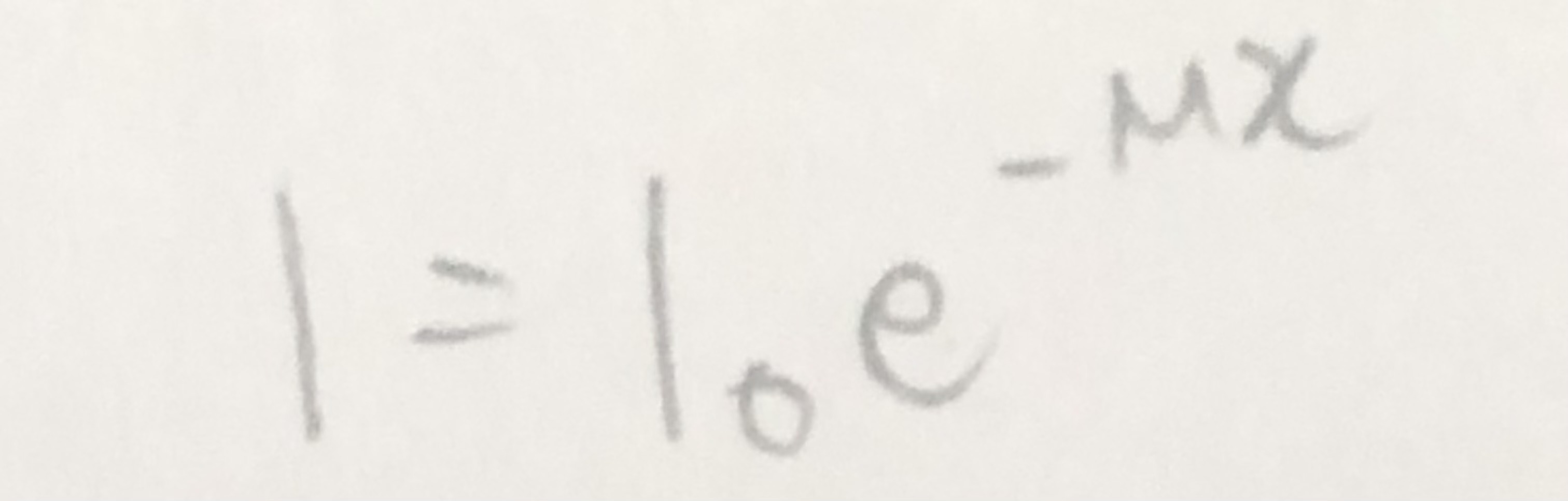
how are X-rays produced
electrons are accelerated by an applied p.d.
electrons hit the target
x-rays are produced when electrons decelerate
formula for minimum wavelength of X-rays produces from accelerating pd
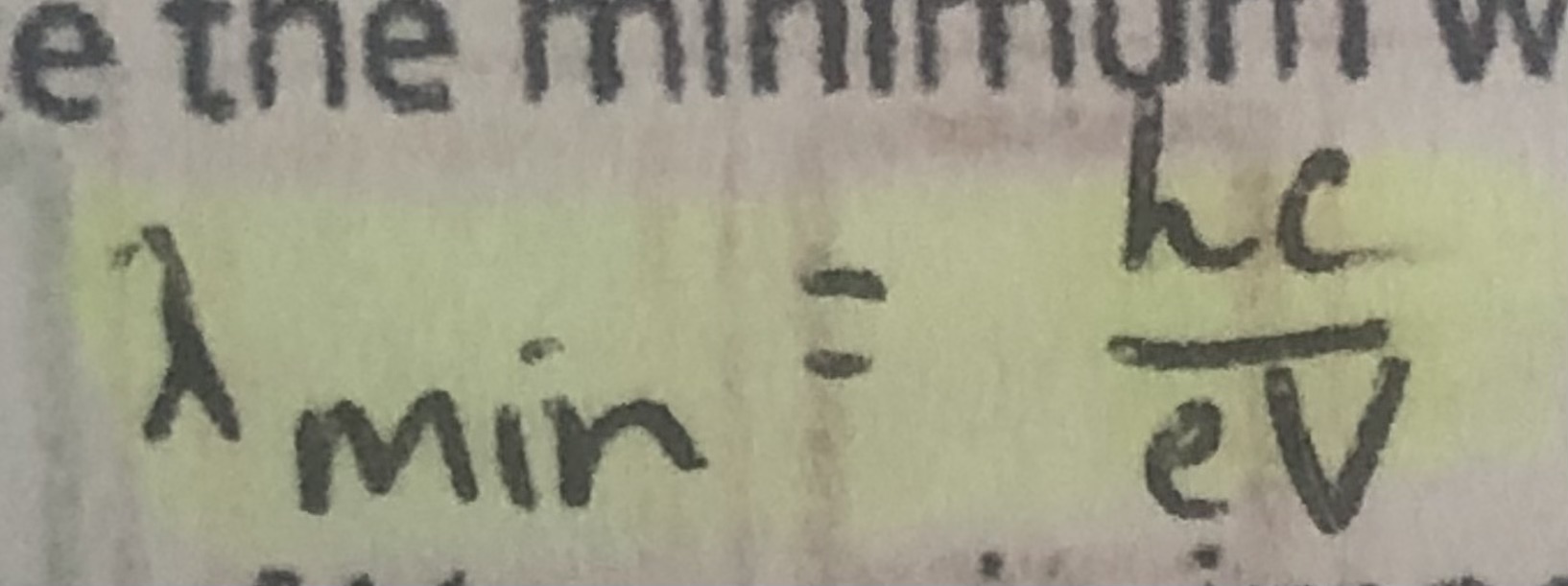
use of x-rays in imaging internal body structures
reduce exposure to radiation —> aluminum filters absorb long wavelengths which are more harmful to the body
improve contrast and sharpness of photos —> hard x-ray for bones, soft x-ray for tissues
what is contrast in x-ray imaging
difference in the degree of blackening between structures
how does computed tomography (CT) scanning produce a 3D image
it combines multiple x-ray images taken in the same section from different angles to obtain a 2D image of the section
repeating this process along an axis then combining 2D images of multiple sections
what is a tracer
a substance containing radioactive nuclei that can be introduced into the body and is then absorbed by the tissue being studied
what particles are decayed in a tracer used in positron emission tomography (PET scanning)
beta plus decay
what is annihilation
a particle interacting with its antiparticle so that mass is converted into energy
what particles are involved in the annihilation process
electrons and positrons
what is conserved in the annihilation process
mass, energy and momentum
in PET scanning, what happens when positrons emitted by the decay of the tracer annihilate when they interact with electrons in the tissue
it produces a pair of gamma-ray photons traveling in opposite directions
formula for energy of gamma-ray photons emitted during annihilation
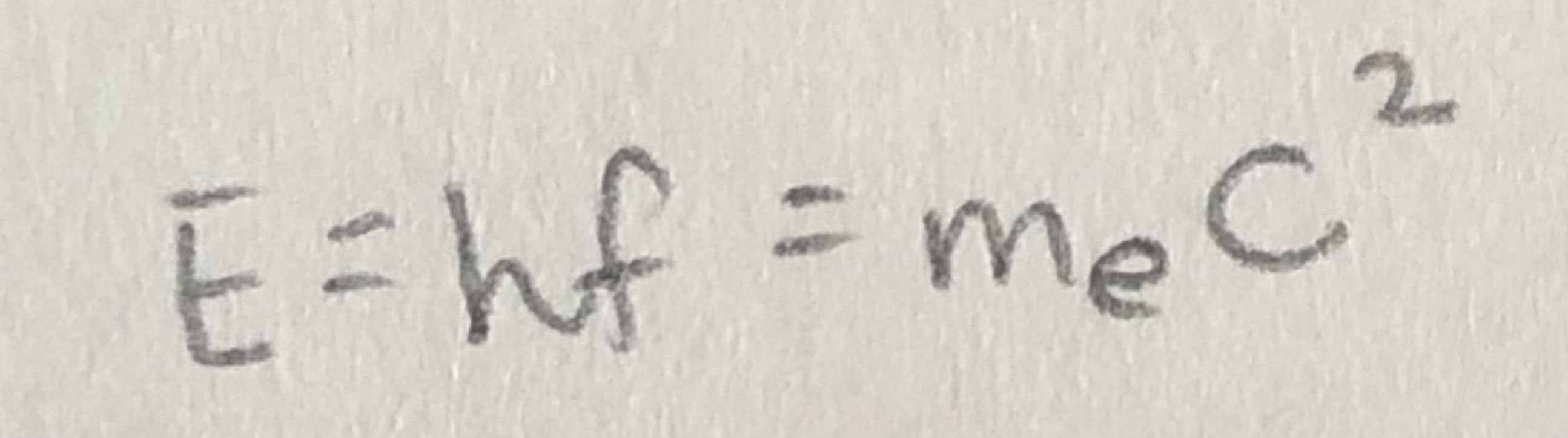
how are gamma photons used to produce an image
two gamma photons travel in opposite directions
gamma photons are detected and arrive at different times
this helps determine the location of production of gamma
the image of tracer concentration in tissue is then produced