KINS 1224 - Lab 4 - Blood Pressure
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
blood pressure
the pressure that is exerted by the blood against the walls of blood vessels
systolic pressure
Blood pressure in the arteries during contraction of the ventricles.
which number in BP is systolic pressure
top number on a blood pressure reading
diastolic blood pressure
the pressure in the arteries when the left ventricle is refilling
what number in BP is diastolic pressure
bottom number on a blood pressure reading
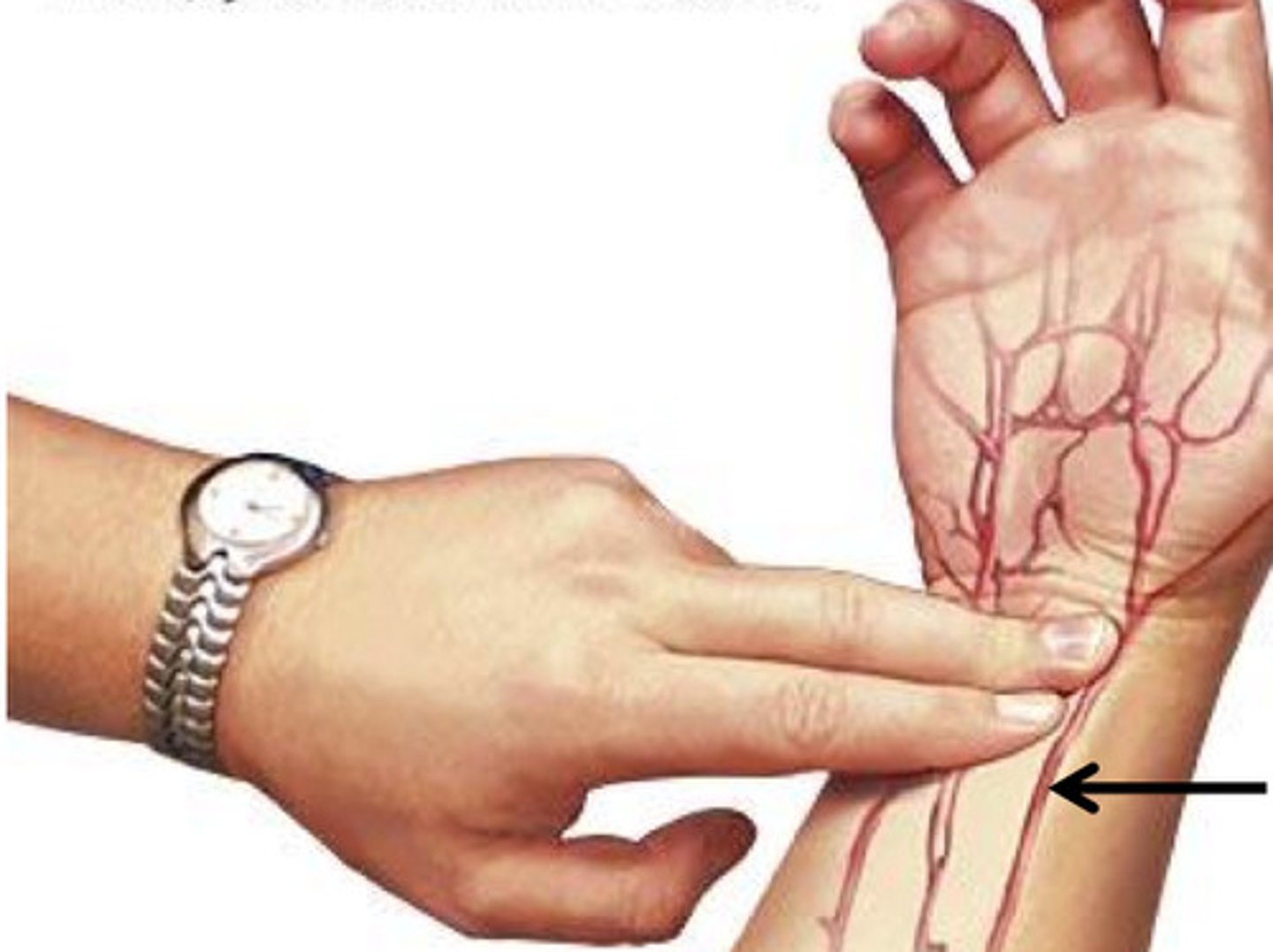
radial pulse
the pulse located on the inside of the wrist, where the radial artery runs just beneath the skin
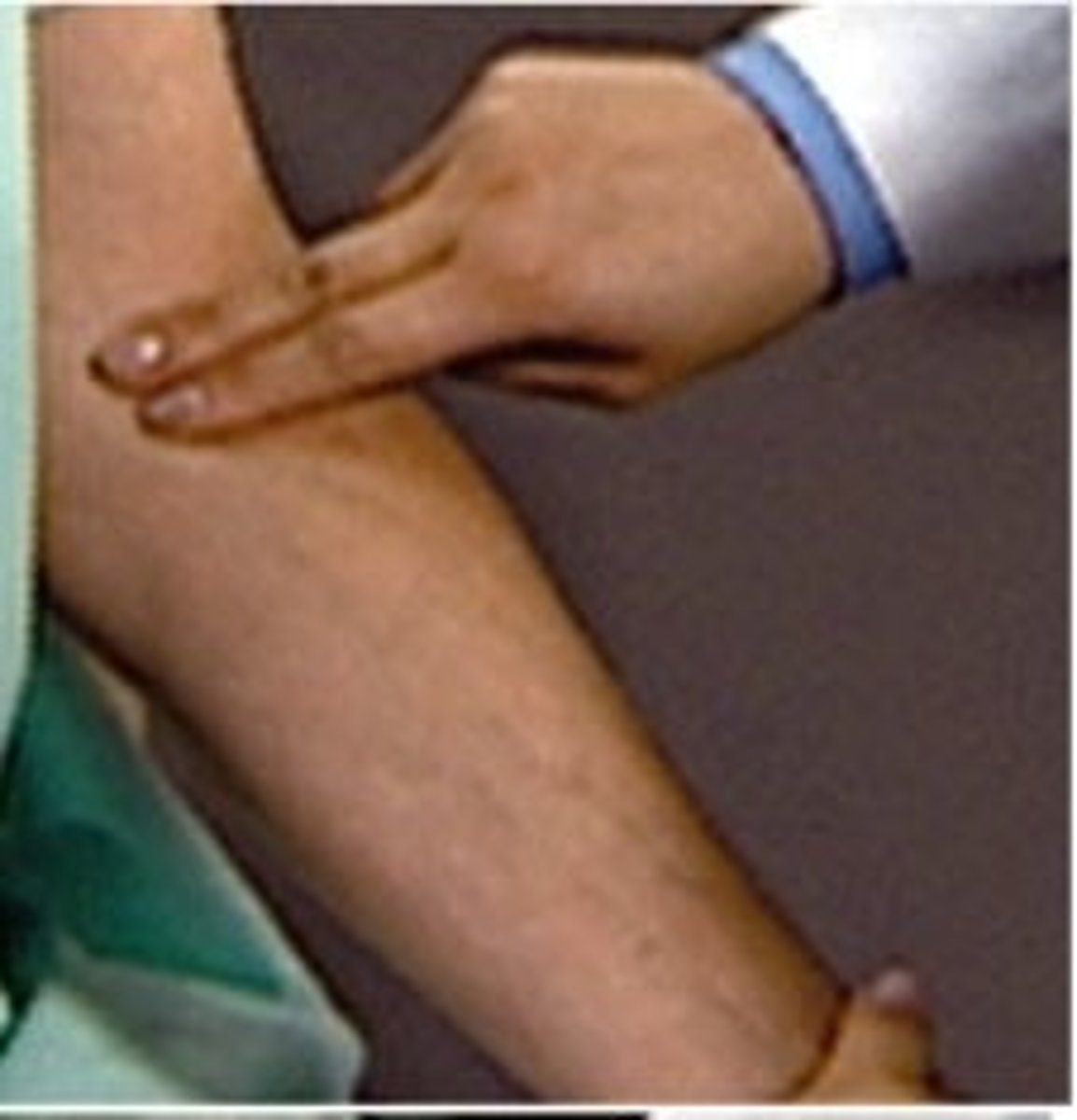
brachial pulse
the pulse felt in the upper arm
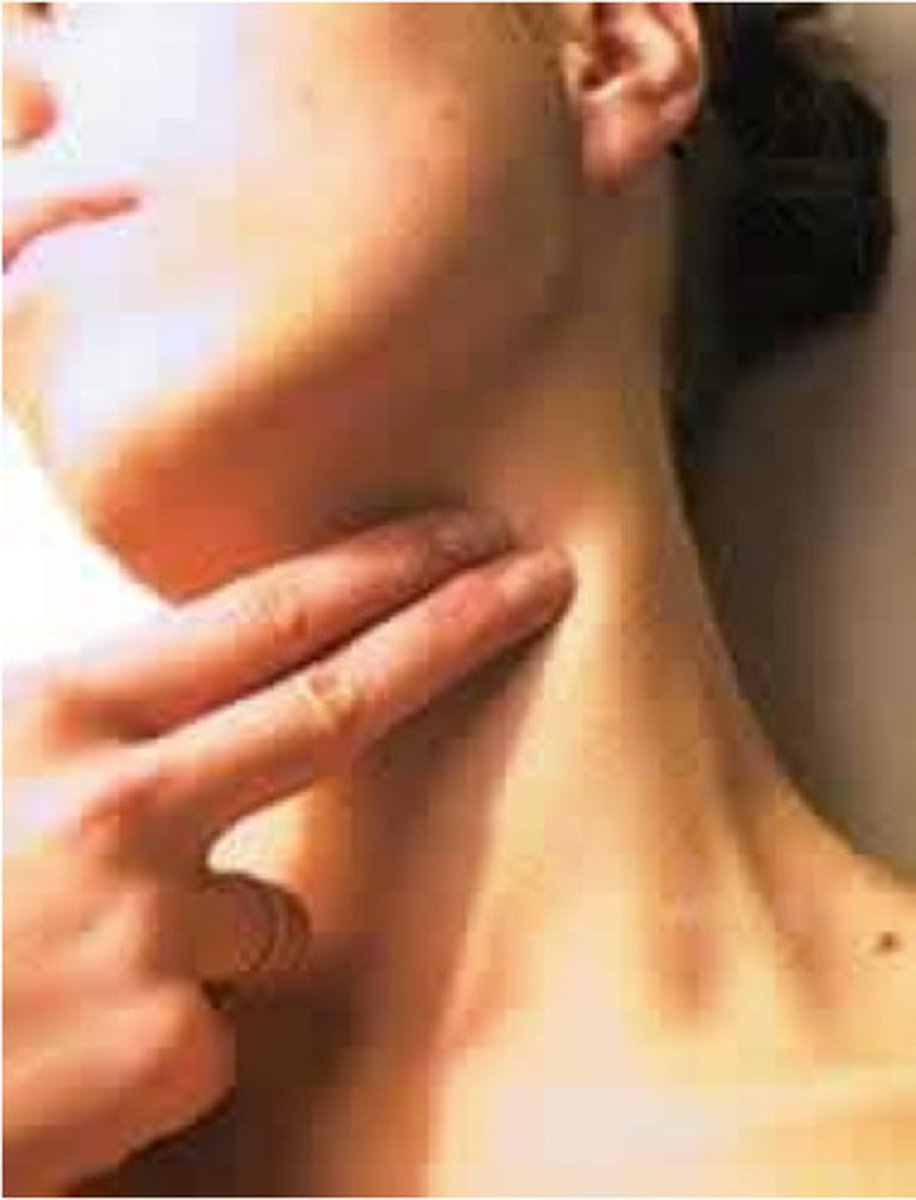
carotid pulse
the pulse felt along the large carotid artery on either side of the neck
mean arterial pressure (MAP)
the average blood pressure over a single cardiac cycle
MAP formula
DBP + PP / 3
Pulse pressure
difference between systolic and diastolic pressure
pulse pressure formula
systolic pressure - diastolic pressure
baroreceptor
a sensory receptor that responds to changes in pressure; for example, there are baroreceptors in the carotid arteries and the aortic arch that monitor blood pressure
heart rate
number of beats per minute
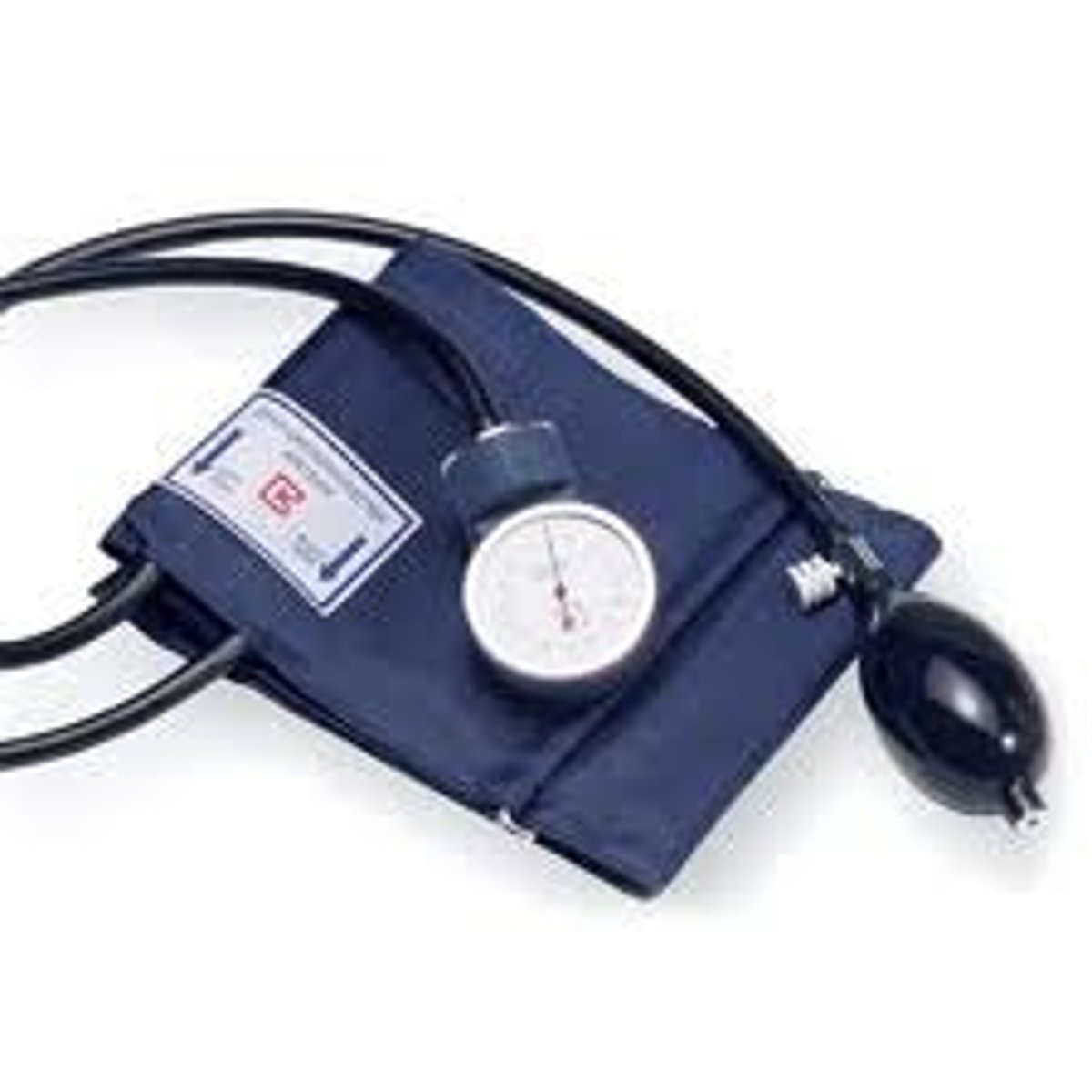
sphygmomanometer
instrument to measure blood pressure
korotkoff sounds
series of sounds that correspond to changes in blood flow through an artery as pressure is released
korotkoff sounds - systolic
first clear, repetitive tapping sound
korotkoff sounds - diastolic
point of silence when all sounds disappear
Stroke Volume (SV)
The amount of blood pumped out of the heart with each contraction.
Stroke volume equation
SV = EDV - ESV (end diastolic volume - end systolic volume)
cardiac output
Volume of blood pumped by the heart per minute.
cardiac output equation
CO = HR x SV
cardioacceleratory center
controls sympathetic neurons that increase the heart rate
cardioinhibitory center
controls the parasympathetic neurons that slow the heart rate
vasomotor center
adjusts blood vessel diameter for blood pressure regulation
vasodilation
Widening of blood vessels to increase blood flow.
vasoconstriction
decreasing the diameter of blood vessels to reduce blood flow
what is the unit of measurement for blood pressure
mmHg (millimeters of mercury)
Which of the following is the average blood pressure value when the ventricles contract and blood is ejected into the aorta?
systolic BP
You measure a patient's blood pressure and get a reading of 118/72. What is the diastolic BP?
72
3 multiple choice options
You measure a patient's blood pressure and get a reading of 118/72. What is the pulse pressure?
46
3 multiple choice options
You measure a patient's blood pressure and get a reading of 118/72. What is the mean arterial pressure? (note: round to the nearest whole number)
87
3 multiple choice options
Which artery should be used to measure blood pressure?
Brachial
Calculate the cardiac output (CO) given the following information? Heart rate (HR): 70 bpmSystolic BP: 124 mmHgDiastolic BP: 82 mmHgStroke volume (SV): 70 mL
4,900 mL/min
3 multiple choice options
A baroreceptor in the aortic arch senses an increased stretch in the aorta. Which of the following would be a response to this stimulus?
cardioacceleratory center is inhibited, cardioinhibitory center is excited, vasomotor center is inhibited
3 multiple choice options
A baroreceptor in the aortic arch senses an increased stretch in the aorta. Which of the following would be a response to this stimulus?
Decreased HR, decreased CO, vasodilation
3 multiple choice options