Media Lab Blood Bank Questions
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
Storage lesion, or the biochemical changes in red blood cells during storage, will result in:
Decreased hemoglobin
Increased plasma sodium
Decreased plasma potassium
Decreased plasma pH
Decreased plasma pH
In blood banking, the DAT is used in the investigation of which of the following clinical conditions?
1 HDFN
2 IgA deficiency
3 HTR
4 Zika virus infections
1 3
Which of the following antigen groups is closely related to the ABO antigens on the RBC membrane?
Rh
Kell
I,i
Duffy
I, i
Which of the following statements regarding the ABO phenotype A2 is true?
A2 cells contain more antigens per RBC than A1 cells
A2 antigens are linear while A1 antigens are branched
A2 RBCs will agglutinate with anti-A1 lectin (Dolichos biflorus)
A2 cells will not agglutinate with anti-A antisera used for ABO blood typing
A2 antigens are linear while A1 antigens are branched
What is the Indirect Antiglobulin Test (IAT) usually used to detect?
Antibodies coating red cells
Antibodies in the plasma
Antigens coating red cells
Antigens in the plasma
Antigens in the plasma
The lectin Dolichus biflorus agglutinated which types of cells?
B
A1B
A2
Both A1B and A2
A1B
A D positive mother with a D negative fetus eliminates the possibility of HDFN due to the:
D antigen
ABO antigen system
Lewis antigen system
Rh antigen system
D antigen
Which of the following D variants has the best likelihood to recieve D positive RBCs without any adverse effects?
Del
Partial D
Partial weak D
C in Trans to RHD
C in Trans to RHD
What is Weak D testing not performed on pregnant women?
Weak D should be performed
Weak D is not required as part of a prenatal evaluation, as it’s not possible to differentiate weak D from partial D serologically
Weak D testing is no longer used in blood banking
Weak D testing is not reliable
Weak D is not required as part of a prenatal evaluation, as it’s not possible to differentiate weak D from partial D serologically
In the Coombs phase of a crossmatch, what is the proper procedure to follow if the Check cells give a negative reaction?
Repeat procedure with new AHG reagent and check the cell washer
Add additional Check cells and dilute with 100 % distilled water
Add additional AHG reagent plus proteolytic enzymes to enhance the reaction
Accept the crossmatch results as correct
Repeat procedure with new AHG reagent and check the cell washer
Which best describes an A1 individual?
A antigens on RBCs and anti-B antibodies in serum, which may also contain anti-A1 antibodies
A, A1 and B antigens on RBCs and no antibodies in serum
B antigens on RBCs and anti A antibodies in serum
A and A1 antigens on RBCs and anti B in serum
A and A1 antigens on RBCs and anti B in serum
for granulocyte concentrations, all of the following lab tests must be performed on the unit by the donor center except?
ABO and Rh
Red Cell antibodies
Infectious disease markers
Lymphocyte enumeration
Lymphocyte enumeration
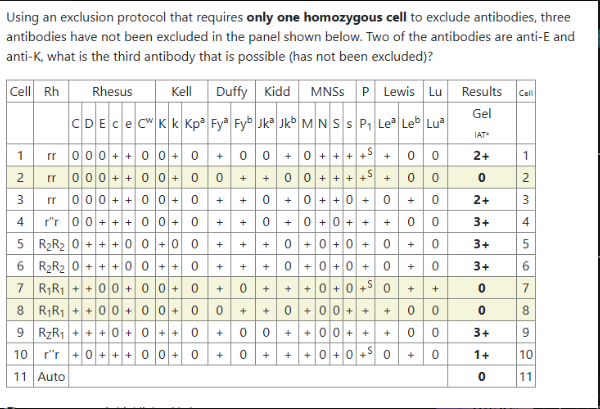
What is the third antibody that has not been excluded? (Anti E and K are the other two antibodies?
Anti c
anti Jka
anti Jkb
anti C
anti Jkb
What kind of immunoglobulins are predominantly found in Rh immune globulin?
IgM anti-D
IgG anti-D
IgM anti-A,B
IgG anti-AB
IgG anti-D
Before testing, all cord cells should be thoroughly washed in order to:
Remove Lea substances
Remove H substances
Remove Wharton's jelly
Hemolyze contaminating maternal cells
Remove Wharton's jelly
A sample has reactions occurring at immediate spin and AHG in a panel that show varying reaction strengths. There is no obvious pattern that matches a particular panel cell or single antigen profile and the auto-control was negative. Which of the following is the most likely cause?
An IgM and an IgG antibody
An IgG antibody only
An IgM antibody only
An autoantibody
An IgM and an IgG antibody
Which of the following blood smear observations would support the diagnosis of Multiple Myeloma if a patient demonstrated plasma cells in his bone marrow and had an elevated serum IgG?
Anisocytosis
Target cells
Microcytic RBC's
Rouleaux formation
Rouleaux formation
Which of the following is the most common reagent source for anti-Al?
Group A1 plasma
Dolichos biflorous seed extracts (lectins)
Bandeiraea simp[icifolia seed extracts (lectins)
Ulex europaeus seed extracts (lectins)
Dolichos biflorous seed extracts (lectins)
Delayed hemolytic transfusion reactions are usually caused by antibodies directed against what blood group system?
MNS
Kidd
Kell
ABO
Kidd
At many hospitals, patients with sickle cell disease are given phenotypically matched units of blood. This policy is often used to help prevent alloimmunization to common RBC antigens in patients who are regularly transfused. A patient who regularly comes to your hospital demonstrates the following phenotype on her RBCs: C antigen positive; E antigen-negative: K antigen positive. The patient's doctor requests a single unit of crossmatched packed RBCs. Based on the antigen prevalence indicated below, how many units of ABO compatible packed RBCs will you phenotype to find one to transfuse to this patient?
Antigen_freguencies:
C antigen positive: 68%
E antigen positive: 22%
K antigen positive: 9%
7 units
77 units
4 units
1 unit
1 unit
78% are neg for E antigen=.78 reciprocal: 1/.78=1.3=1 unit
or 100/78 =x x=1.28= 1 unit
Which of the following represents the approximate percentage of the Caucasian population that is Rh-positive?
35%
65%
85%
95%
85%
In the interest of safety, it is the policy at XYZ hospital to always add one extra 300 pg vial of RhlG, regardless if the dosage calculation is rounded up or rounded down.
After performing a Kleihauer-Betke test, a technologist in the laboratory at XYZ hospital calculates the fetomaternal hemorrhage to be 45 mL of fetal whole blood. How many 300 pg vials of RhlG should be administered to this woman?
One
Two
Three
Four
Three
(45/30=1.5=2 +1=3)
Which of the following statements is correct regarding blood bank adverse event reporting to the FDA?
All patient deaths while being transfused must be reported to the FDA, even when it has been confirmed that the death was not related to the transfusion.
When a transfusion reaction is the result of an error it must be reported to the FDA in writing.
A transfusion-related death must be reported to the FDA within 24 hours of the patient's death.
The initial notification to the FDA of a transfusion-related death must be made by fax, telephone, express mail, or electronically as soon as possible after the death is confirmed to be associated with the transfusion.
The initial notification to the FDA of a transfusion-related death must be made by fax, telephone, express mail, or electronically as soon as possible after the death is confirmed to be associated with the transfusion.
A spectrophotometric scan of amniotic fluid may be valuable in the determination of which of the following conditions:
Neural tube defects
Maternal hypertension
Hemolytic disease of the newborn
Maternal diabetes
Hemolytic disease of the newborn