CAP Mitchell Leadership
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
117 Terms
Warrior Spirit
Condition of the heart that is found in warriors who defend their personal honor.
Three things a warrior spirit guarantees:
Clear conscience, good reputation, environment of trust and respect.
Four basic qualities CAP expects all members to display at all times:
Core values: Integrity, Respect, Excellence, Volunteer Service.
Three skills to live the core values:
Self-awareness, self-discipline, attitude.
What are military customs and courtesies?
Expressions of politeness and mutual respect.
The CAP uniforms are a vehicle for learning what three things?
Self-discipline, personal responsibility, self-respect.
What is a unit's drill performance a measure of?
Its cadets' self discipline.
What is the chain of command?
The order of authority.
What does the chain of command encourage?
It encourages problems to be solved at the lowest level possible.
What is a prerequisite for leadership?
Character.
What is a goal?
A dream with a deadline.
Define future picture.
A clear, compelling description of what you want your life to look like at some point.
What are the seven steps to ethical decision making?
Define the problem, get the facts, brainstorm and list your options, weigh your options, consider your values, decide and act, and re-evaluate the decision.
Define time management.
Process of organizing and using time wisely.
Define efficiency.
Broad term that describes how well a leader is making use of time and resources.
Define procrastination.
Practice of putting off a task that should be done now for no good reason.
What is stress?
The body's response to change.
What is a stressor?
Anything that causes stress.
What is resilience?
The ability to bounce back and recover from adversity.
What is a team?
A collection of individuals who are committed to working together to achieve a common goal.
What is synergy?
The idea that working together, people can accomplish more than each individual could on their own.
Define mentor.
A close, trusted, experienced advisor.
Traits of a mentor-ready individual:
Humble, eager to learn, ambitious.
What is the biggest problem with communication?
The assumption that it has taken place.
Define listening.
An important communication skill that allows one to receive, decipher, and respond to spoken and non-verbal messages.
How often should we listen?
Twice as much as we speak.
Main goal of communication:
To share meaning.
What is feedback?
The act of returning to the speaker a portion of the message they shared.
Steps to reading critically:
SQ3R: Survey, Question, Read, Recall, Review.
What is the Air Force's definition of leadership?
The art and science of influencing and directing people to accomplish the assigned mission.
What does leadership require?
Imagination, creative skill, careful study, observation, and experimentation.
What is a mission?
The reason why the team exists.
Three components of leadership:
The leader, the followers, and the goal.
Define culture.
The attitudes, customs, and values of a civilization that influences how we approach leadership.
What are the facets of leadership?
Communication, inspiration, and mentorship.
What is the great man theory?
A poor theory that professes that to study leadership, one must focus on the stories of successful people.
Air Force doctrine states what about leadership?
It is built from experience, education, and training.
What is trait theory?
A theory that explains leadership in terms of the personality and character of the leader.
What is a major fault in trait theory?
No one can agree upon specific traits that make a leader great.
Why is flag etiquette important (See P. 91 Learn To Lead Vol. 1 for flag etiquette)?
The flag is our most important and recognizable national symbol.
What must leaders portray at all times?
Professionalism.
What is a standard?
An established requirement, a principle by which something can be judged.
What must NCO's do in the CAP?
They must epitomize the core values.
What are the jobs of NCO's in the CAP?
Epitomize core values, guide, instruct, mentor, reward, correct, counsel, and learn.
In what ways must NCO's be ready?
Technically, physically, and mentally.
What is servant leadership?
Leadership in which the leader sees themself as primarily a servant of the team.
What is often seen as a lazy, immature, and counterproductive way to lead?
Pulling rank.
What is coaching?
The process through which leaders try to solve performance problems and develop their people.
What are the four key elements to coaching?
Dialogue, empowerment, action, and improvement.
What does it mean to supervise; what are two cornerstones of supervision?
To observe and direct people in fulfillment of the mission; trust and fairness.
What is constructive discipline?
A learning process that provides an opportunity for positive growth.
What is the purpose of punishment?
To teach someone what not to do.
When should one correct; when should one praise?
Praise in public, correct in private.
Define motivation.
The reason for an action; the "why."
What are intrinsic motivators?
Motivators at work within you.
What are extrinsic motivators?
Motivators at work outside of you.
What are the three leadership arenas, in order of lowest to highest?
Tactical, operational, and strategic.
What are the three types of leadership associated with the leadership arenas?
Personal (tactical), Team (operational), and Institutional (strategic).
What is a command intent?
A leader's concise expression of purpose.
What are the seven needs of teams?
Common goals, leadership, involvement, communication, respect, and a fair way to resolve conflict.
What is a free rider?
One who receives the fruits of the team's labor without doing their fair share of work.
Define groupthink.
Occurs when team members seek unanimous agreement in spite of facts that point to another conclusion.
List (in order) the stages of the team's life cycle.
Forming, storming, norming, performing.
What are the components of the L.E.A.D model?
Lead with a clear purpose (L), empower to participate (E), aim for consensus (A), direct the team (D).
Define critical thinking.
Self-guided, self-disciplined thinking which attempts to reason at the highest level of quality in a fair-minded way.
What are the seven universal intellectual standards?
Clarity, accuracy, precision, relevance, depth, breadth, and logic.
What is big-picture thinking?
The practice of stepping back from an issue so as to take more of it in.
What is focused thinking?
The practice of intensely studying an issue and not becoming distracted with other similar issues.
What is realistic thinking?
An approach where the leader tries to see the world for what it actually is.
Define intellectual honesty.
Honesty in the acquisition, analysis, and transmission of ideas.
What are the tools for creative thinking?
Brainstorming, mindmapping, the five "whys", reversal, headlines of the future, and flowcharts.
What are the tools for decision making?
Multi-voting, weighted pros and cons, and gradual voting.
What are learning objectives?
Specific and measurable statements that describes what what students should know, feel, or be able to do at the end of a lesson.
What are the different learning styles?
Visual, auditory, tactile, and kinesthetic.
What are the teaching and training methods?
Lecture, guided discussion, demonstration-performance, experiential and simulation.
Describe the birth order theory.
Contends that a person's rank within their family can have an effect on their personality and intelligence.
Define charisma.
The sparkle in people that money cannot buy; an invisible energy with visible effects.
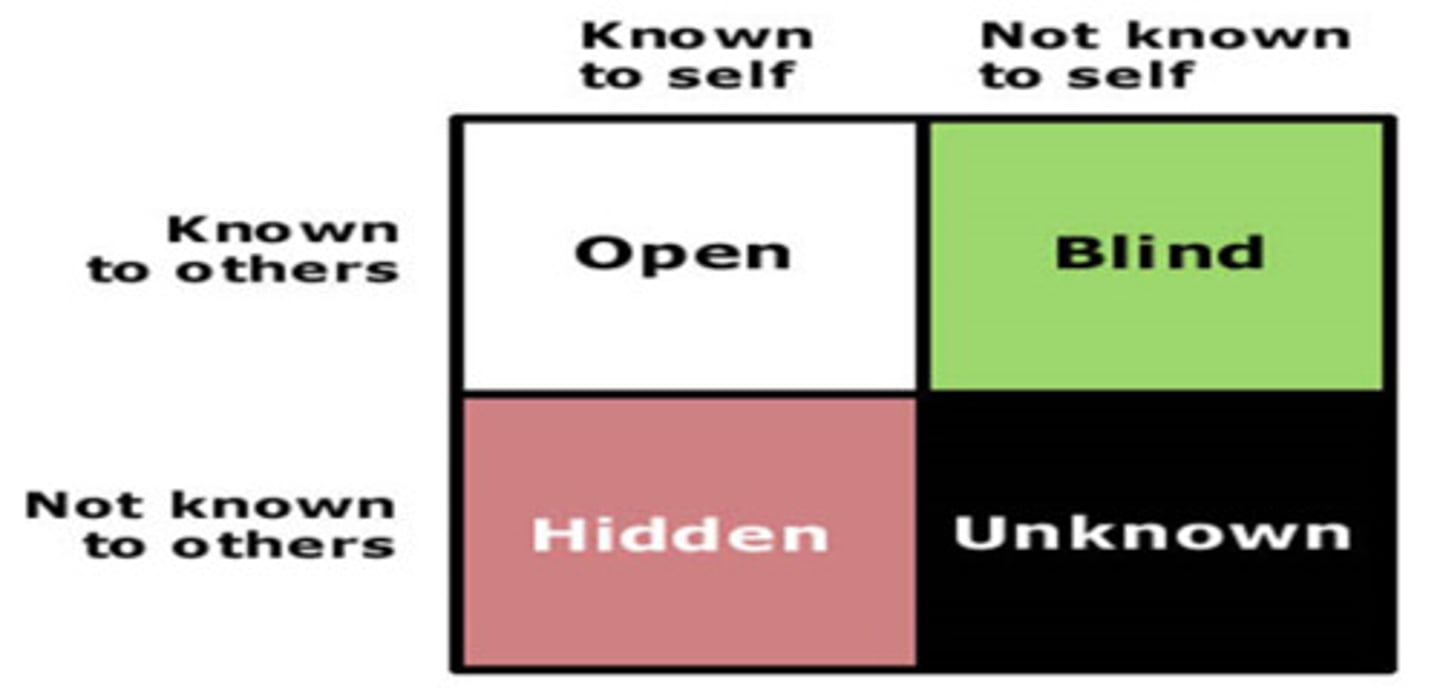
Describe the Johari Window.
A tool for exploring self-perception made of four arenas (Public, blind, private, and unknown).
Describe the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI).
A model that attempts to describe different flavors of personality made up of four dimensions (Extroversion/introversion, intuition/sensing, thinking/feeling, judging/perceiving).

What are the five basic needs in Maslow's hierarchy of needs in order?
Physiological needs, safety needs, love/belonging needs, esteem needs, and self-actualization needs.
What is the lesson we take from the Hawthorne studies?
When leaders pay attention to their and treat them as partners, people feel appreciated and perform better.
What did Milgram conclude from his study?
Obedience to authority is a powerful motivator; leaders bear some responsibility for the actions of their subordinates.
List the types of defense mechanisms.
Displacement, projection, rationalization, intellectualization, denial, suppression, and withdrawl.
What is conflict?
A disagreement through which individuals perceive a threat to their needs, interests, or concerns.
What must leaders do when there is conflict?
The must respond because it is their duty.
What are the basic approaches to managing conflict?
Avoidance, denial,suppression and smoothing, compromise, the zero-sum game, and mediation.
Define prejudice.
The act of pre-judging someone.
Define harassment.
Unwelcome conduct.
Define retaliation.
When someone seeks revenge against someone who objects harassment or discrimination.
What are the five ways to fight hate?
Rise up, pull together, speak out, support the victims, and teach tolerance.
Define emotional intelligence.
Intelligent use of emotions; when one makes their own emotions work for themselves by using them to helpguide behavior and thinking positively.
What are the ways to motivate yourself?
Motivational statements, mental imagery, right-sized goals, and go with the flow.
What is empathy?
Understanding, being aware of, and being sensitive to feelings, thoughts, and experiences of another.
Define interpersonal skills.
The ability to maintain and develop positive relationships with others
What is transformational leadership?
Leadership in which a person strives to heighten the motivation and morality of themself and their followers.
Describe transactional leadership.
Leadership in which an exchange takes place between a leader and follower.
Describe idealized influence
A form of transformational leadership in which the leader's principles and standards have the power to attract followers.
Describe inspirational motivation.
A form of transformational motivation in which leadrs communicate high expectations to followers, inspiring them to become committed to a shared vision of an organization.
Describe intellectual stimulation.
A form of transformational leadership in which leaders encourage team members to challenge the leader's, organization's, and their own beliefs.
Describe individualized consideration.
A form of transformational leadership in which the leader is supportive of followers, listens closely to them, and acknowledges their unique needs.