AQA Chemistry A-level: Atomic Structure Overview
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Plum Pudding Model
Early atomic model with positive sphere and negative charges.
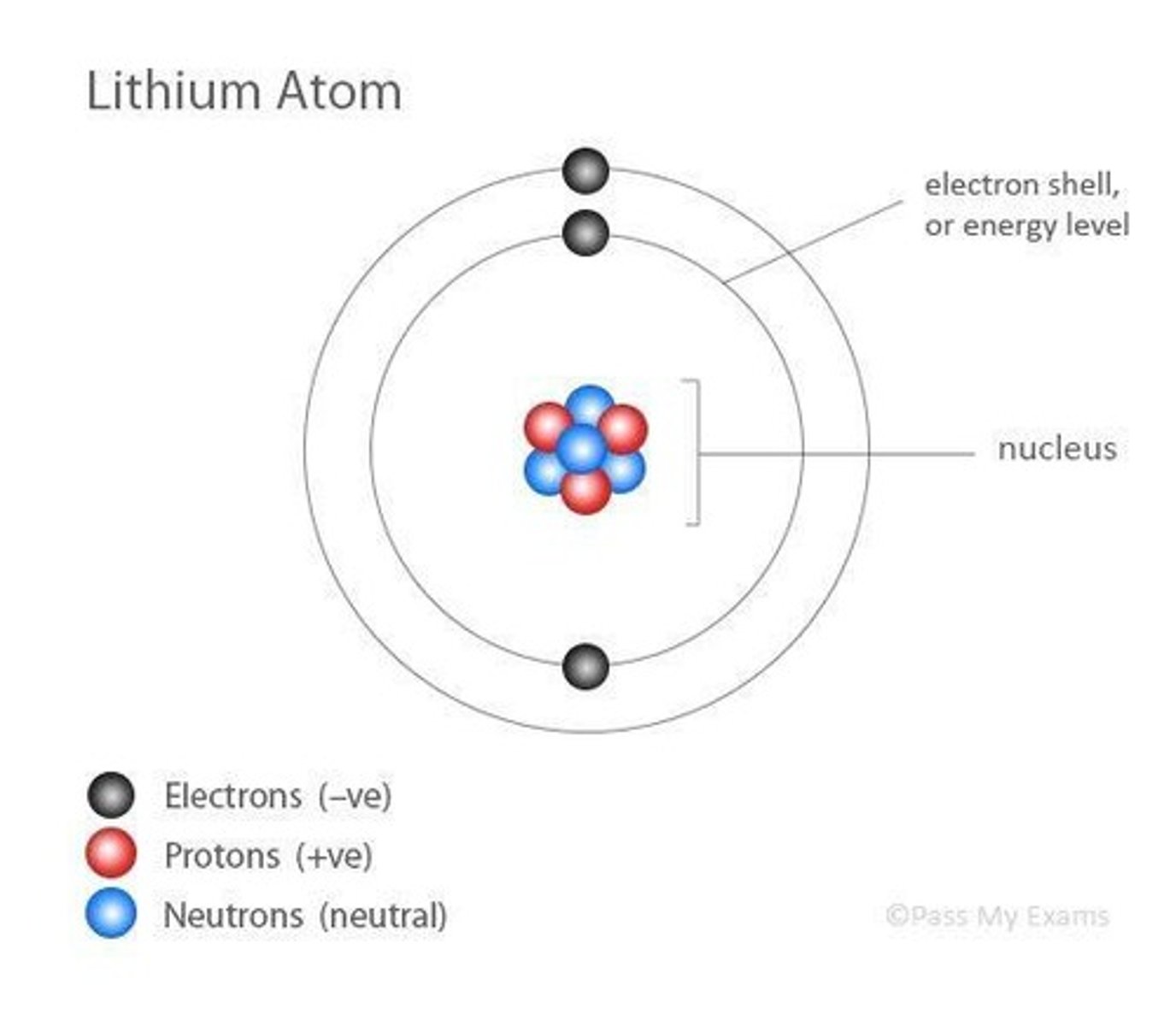
Electron Shell Model
Atoms have a dense nucleus with orbiting electrons.
Rutherford Scattering Experiment
1911 experiment confirming the atomic nucleus existence.
Nucleus
Central part of an atom containing protons and neutrons.
Proton
Positively charged particle in the atomic nucleus.
Neutron
Neutral particle in the atomic nucleus.
Electron
Negatively charged particle orbiting the nucleus.
Relative Charge
Charge comparison of particles: +1, 0, -1.
Relative Mass
Mass comparison: proton/neutron = 1, electron = 1/1840.
Maximum Electrons per Shell
Calculated using formula 2n², where n is shell number.
Mass Number (A)
Sum of protons and neutrons in an atom.
Atomic Number (Z)
Number of protons in an atom.
Relative Atomic Mass (Ar)
Mean mass of an atom relative to carbon-12.
Isotopes
Atoms with same protons, different neutrons and mass.
Ions
Charged particles formed by electron loss or gain.
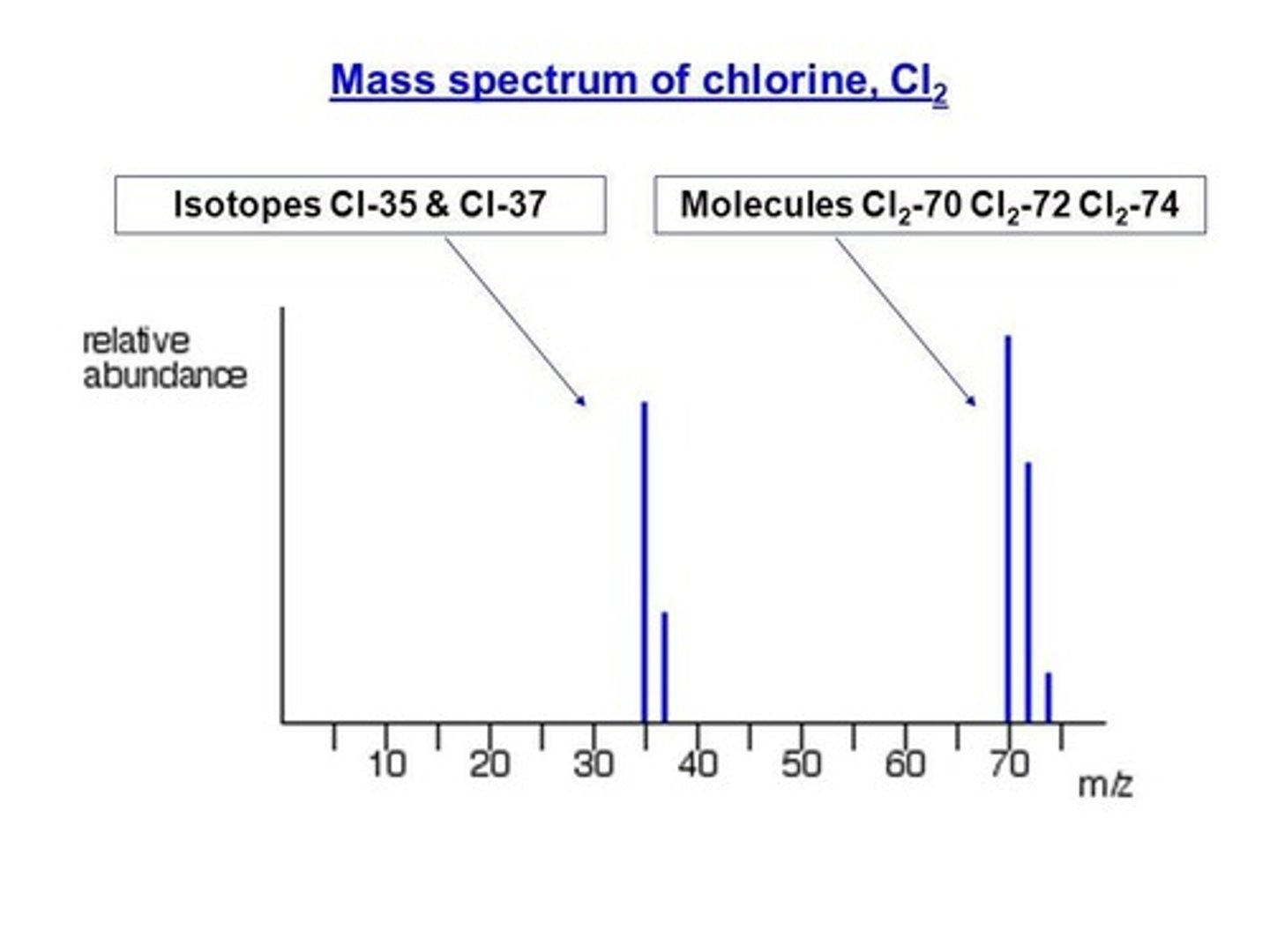
Mass Spectrometry
Technique to identify isotopes and relative atomic mass.
Time of Flight (TOF)
Mass spectrometry measuring ion travel time to detector.
Ionisation
Process of creating charged ions from neutral atoms.
Acceleration
Positively charged ions are accelerated towards detection.
Ion Drift
Ions follow curved paths due to magnetic fields.
Detection
Current produced when ions hit detection plate.
Analysis
Current values used to produce isotope abundance spectra.
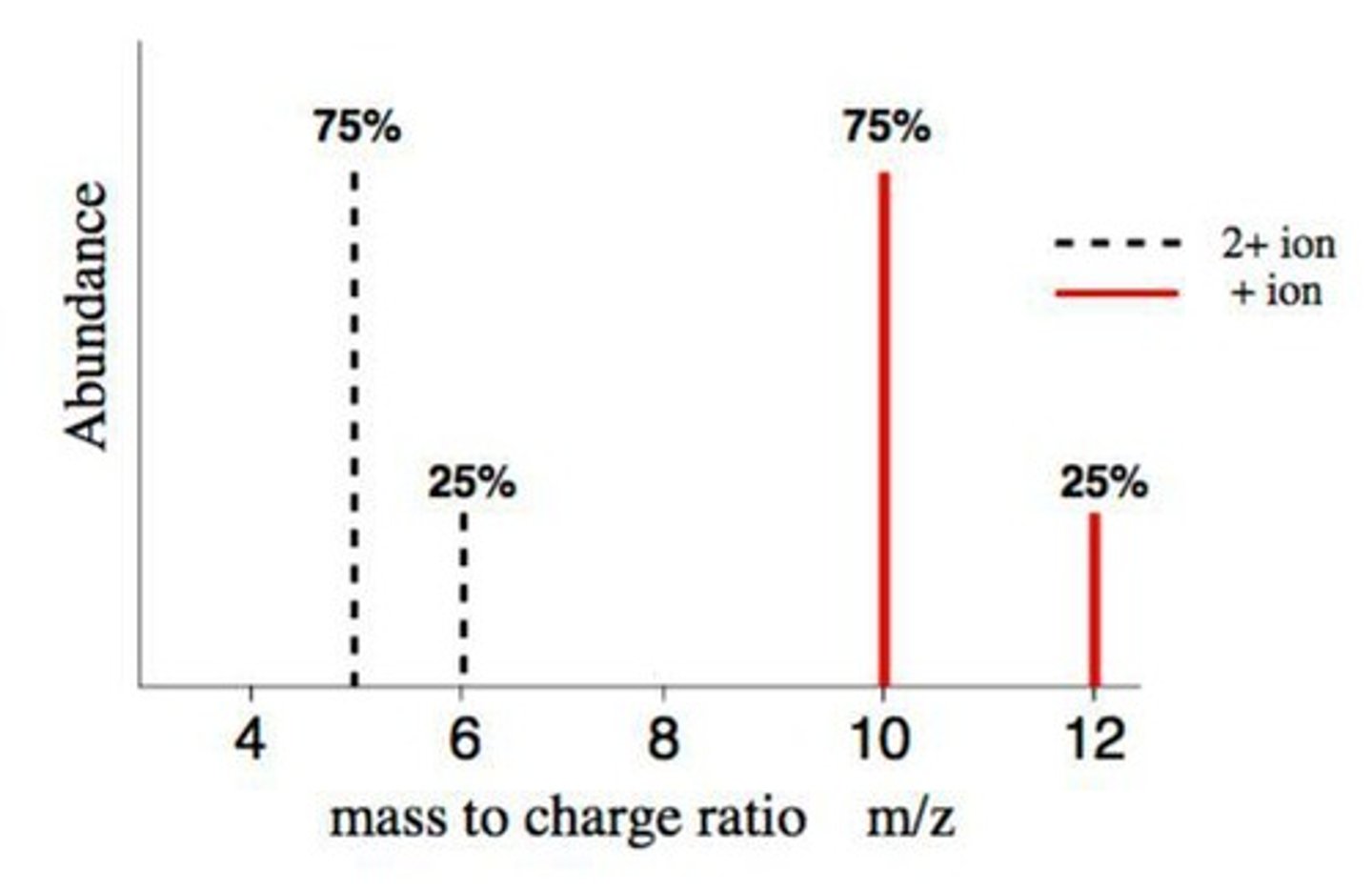
Mass to Charge Ratio (m/z)
Ratio affecting ion path curvature in mass spectrometry.
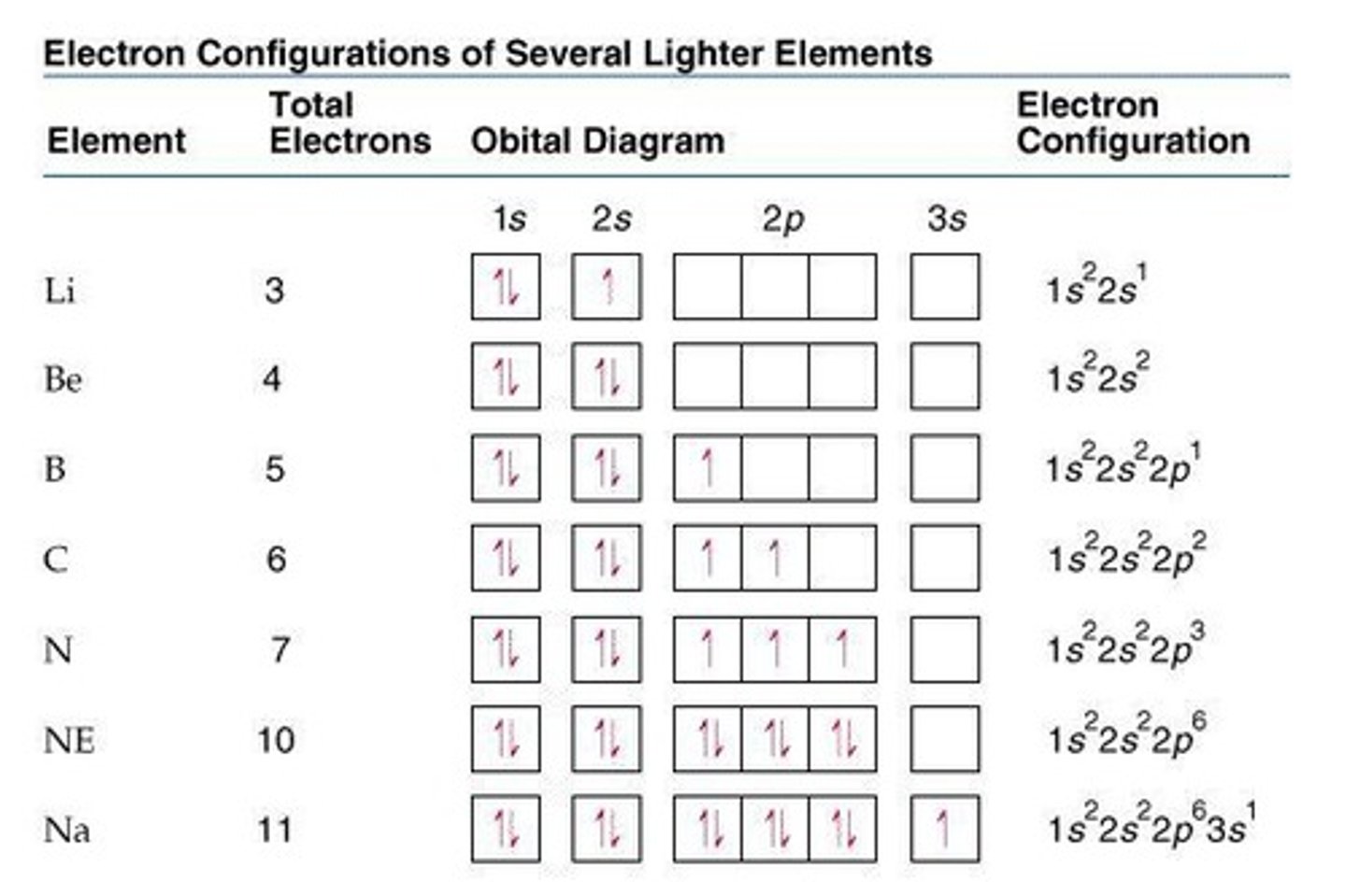
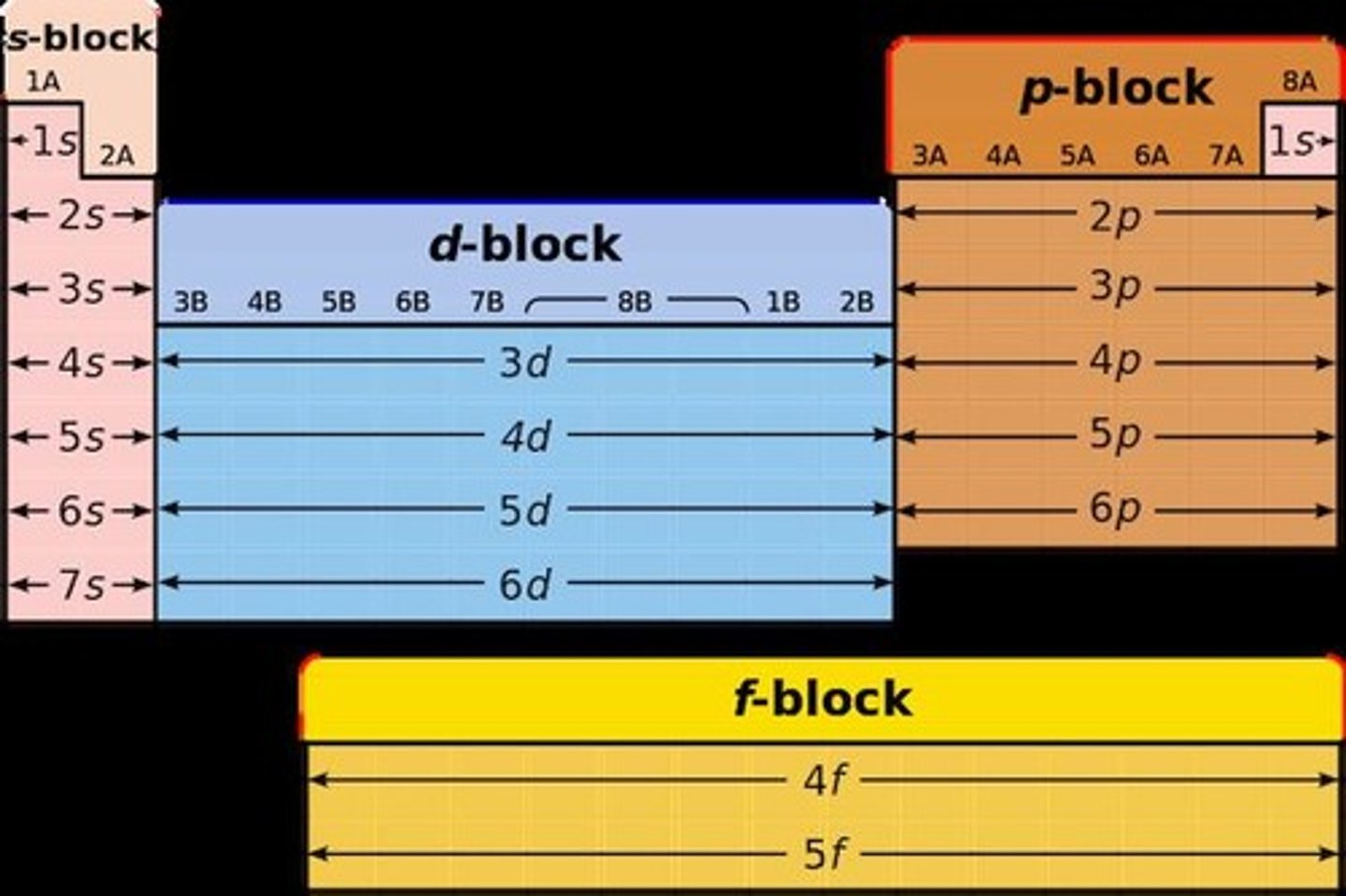
Electron Configuration
Arrangement of electrons in atomic orbitals.
Electron Orbitals
Regions where electrons are likely to be found.
Orbital Types
s, p, d, and f orbitals with distinct shapes.
Spin
Electrons in orbitals must have opposite spins.
Ionisation Energy
Energy needed to remove one mole of electrons.
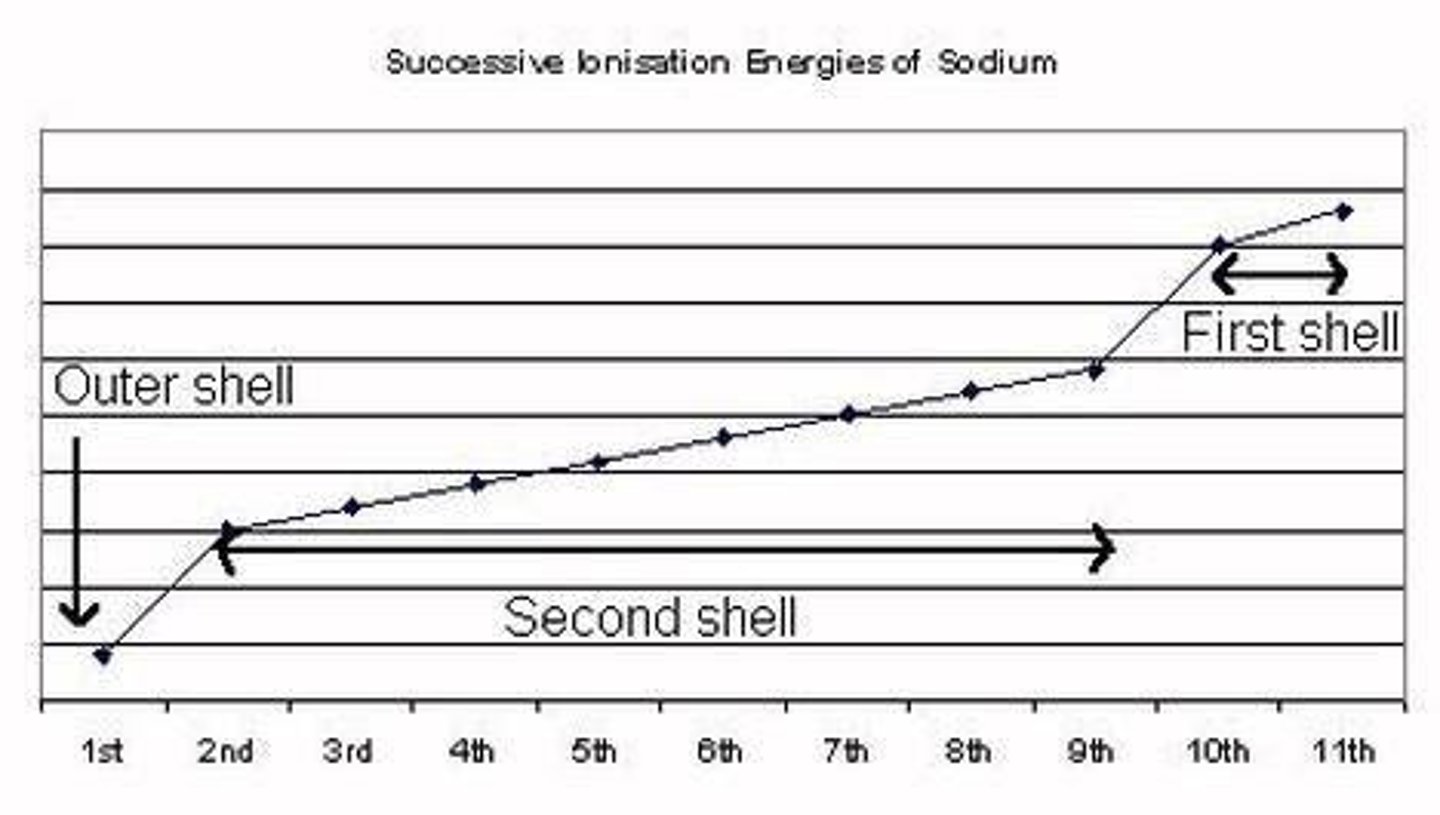
Trends in Ionisation Energy
Varies across periods and groups in the periodic table.
Exceptions to Electron Configuration Rules
Unpaired electrons may rearrange for stability.