TERRESTRIAL BIOMES
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
Large-scale environments that are distinguished by characteristic temperature ranges and amounts of precipitation with specific set of biotic and abiotic features
Biomes
In his pioneering work on plant geography found a close relationship between climate and vegetation in geographically disjunct regions, exhibiting climatic similarity in similar regions
Alexander van Humboldt
Who developed the biome concept and what is it about?
Developed by Schimper (1903)
based on the idea that similar climates select for similar plant forms independent of differences in history
The land biomes of the world are controlled by?
The land biomes of the world are controlled by climate
Is the characteristic condition of the atmosphere near the earth’s surface at a certain place on earth. It is the long-term weather of that area (at least 30 years)
climate
Two of the most important factors determining an area’s climate are?
Two of the most important factors determine an area’s climate are air temperature and precipitation
What are Whittaker’s biome-types?
Tropical rain forests
Tropical dry forest
Savanna
Temperate grassland
Desert
Mediterranean Shrubland and Woodland
Temperate forest
Boreal forest (Taiga)
Tundra
the most biodiverse terrestrial biome
Have high net primary productivity
Cover about 6-7% of the earth’s land surface
Found in regions close to the equator
Tropical rain forests
warm and humid all year long
Always moist and lacking temperature seasonality
Average temperatures ranging from 20C to 34C
Annual rainfall ranges from 125-660 cm (50-200 in) with considerable seasonal variation
Climate: Tropical rain forests
highly acidic
The type of clay particles present in tropical rainforest has a poor ability to trap nutrients and stop them from washing away
Lack’s minerals and contains little remains of dead plants and animals
Decomposition is rapid on warm wet soil
<1cm of topsoil; not very fertile
Mycorrhizae help gather nutrients
Soil: Tropical rainforest forests
characterized by vertical layering of vegetation and the formation of distinct habitats for animals within each layer
Dominated by a continuous canopy of tall evergreen trees rising to 30-40 m
Occasional emergent trees rise above the canopy to heights of 55 m or so
Climbing lianas, or woody vines, and epiphytes, plants that grow on the branches of other plants and are not rooted in soil are prominent in the forest canopy itself
Vegetation: Tropical rainforest forests
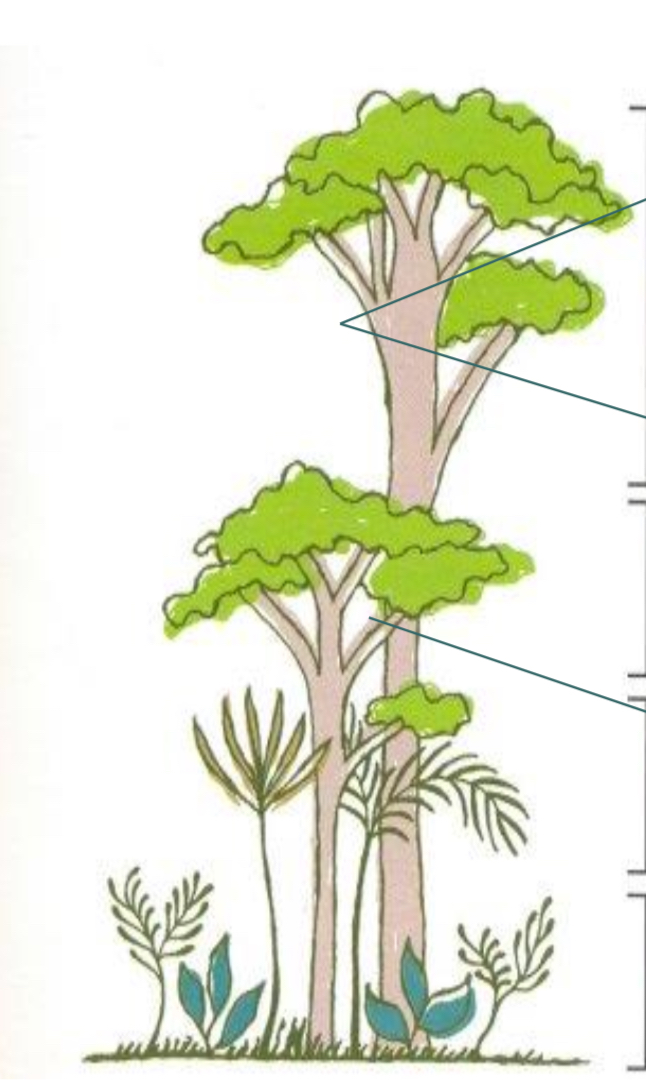
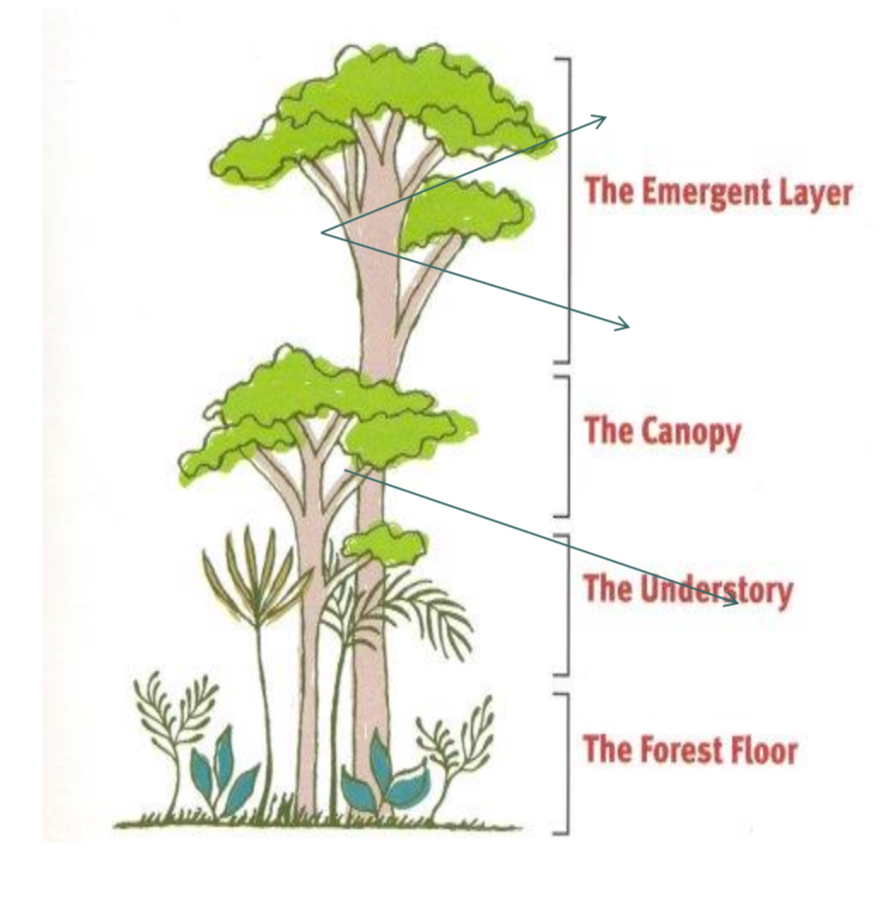
very tall trees that rise above the canopy
Gets lots of sunlight and strong winds
Birds and insects are common here
The emergent layer
thick, leafy roof formed by tall trees
Blocks most sunlight from reaching lower layers
Many animals like monkeys and birds live here
The canopy
layer above the forest floor
Small plants and young trees grow here
Very shady and humid
The understory
bottom layer
Very dark, little sunlight
Home to decomposes like fungi and insects
The forest floor
Plant adaptations: What is the major limiting factor of tropical rain forests?
Sunlight is a major limiting factor
shallow, wide roots since soil is so thin and poor in nutrients
Little sun reaches the floor
Plants grow in layers (canopy receives most light)
Examples of plants found in tropical rainforest forest
Ex: Bougainvillea and Bangul Bamboo
What are the dominant wildlife included in the animal life of tropical rainforest forests
Dominant wildlife includes:
herbivores ( sloths, tapirs, and capybaras)
Predators (jaguars); anteaters; monkeys
Birds (toucans, parrots, and parakeets)
Insects (butterflies, ants and beetles)
Piranhas and other freshwater fishes
Reptiles (frogs, caymans, boa constrictors, and anacondas)
What are the other animal adaptations of tropical rain forest animals?
Many animals are specialists and require special habitat components to survive (Silvery Gibbon)
Camouflage is common (Wagler’s pit viper)
Many symbiotic relationships
Live in different level of canopy (Slender Loris)
usually located between 10 to 25 latitude
Heavily settled by humans within each layer extensive clearing for agriculture
Tropical dry forest
climate more seasonal ( with a pronounced dry season during part of the year) than tropical rainforest
Responds to the rhythms of the annual solar cycle which drive the oscillation between wet and dry seasons
Characterizes by little change in temperature (alternation of wet and dry season)
Climate: Tropical dry forest
soils generally less acidic and richer in nutrients than tropical rainforests
The annual pulses of torrential rain make the soil highly vulnerable to erosion, particularly when deforested and converted to agriculture
Soil: Tropical dry forest
height of trees is correlated with average precipitation. Tallest trees are found in wettest areas
Over 50% of trees are evergreen in wetter areas
Have deciduous species of trees that lose their leaves at the onset of the dry season
Many plants produce animal-dispersed seeds
Vegetation: Tropical dry forest
many birds, mammals, and even insects make seasonal migrations to wetter habitats along rivers or to the nearest rainforest
Many animals reduce their need for water by entering long periods of inactivity called estivation
Animal life: tropical dry forest
found in parts of the tropics where there is not enough rainfall throughout the year to create a rainforest
Transitional between tropical rain forest and desert
Located closer to the equator than prairies
Grasslands with scattered trees and are found in Africa, South America, and northern Australia
Savanna
rainy and dry season
With seasonal drought
Rain comes in summer accompanied by intense lightning starting fire
Climate : Savanna
soil layer with low water permeability
Impermeable subsoil keeps surface soil waterlogged during the wet season
Nutrients in soil are present mainly due to a thin layer of humus
Soil: savanna
grasses with few scattered trees
Fire and grazing undoubtedly play important roles in maintaining the character of the ??? Biome
The woody trees are very limited and usually do not get very tall
Vegetation: savanna
grows in tufts
Resistance to drought
Many plants have thorns and sharp leaves to protect against predation
Plant adaptations: savanna
Ex: whistling thorn, umbrella thorn, kangaroos paws
adapt for short rainy season-migrate as necessary
Reproduce during rainy season-ensures more young survive
Animal adaptations: savanna
Ex: zebras, chacma baboon
largest biome in North America
The major manifestations are veldts of South Africa, the puszta of Hungary, the pampas of Argentina, the steppes of the former Soviet Union and the prairies of Central America
Temperate Grassland
hot summers and cold winters
Rainfall is moderate (300-1000mm). the amount of annual rainfall influences the height of the grass land vegetation with taller grasses in other regions
Maximum precipitation occurs in summer
Climate: Temperate grassland
the soil is deep and dark with fertile upper layers
It is nutrient-rich from the growth and decay and many branched grass roots. The rotted roots hold the soil together. The soil is fertile because of the remains of plants and animals and dried leaves of plant fell on the ground
Soil: Temperate grassland
Why is the soil fertile in temperate grassland?
soils are fertile because the subsurface of the soil is packed with the roots and rhizomes (underground stems) of these grasses
The roots and rhizomes act to anchor plants into the ground and replenish the organic material (humus) in the soil when they die and decay
the dominant vegetation tends to consist of grasses
The treeless condition is maintained by low precipitation, frequent fires, and grazing. The vegetation is very dense due to fertile soil
Vegetation: Temperate grassland
what are the plant adaptations of the Steppe?
most abundant are plants called Bunch grasses, fine bladder grasses that grow in clumps to preserve water
Ex: Tumbleweed, Sweet Vernal

What are the adaptations of Prairie plant adaptations
sod-forming grasses that won’t dry out or blow away in wind
Ex: Fleabane, Buffalo grass

supported huge herds of roving herbivores (bison, pronghorns and wild horses)
Herbivores band together in social groups in open grasslands just like predators in steppe and prairie wolves
Smaller animals such as grasshoppers and mice are more numerous than the large herbivores
Animal life: Temperate grassland
What are the adaptations of steppe animals?

What are the adaptations of Prairie animals?

occupy 20% of land surface
Low species diversity
Low water vapor content
Evaporation and transpiration exceed precipitation
Desert
very hot and dry
Receive less than 25 cm of rain per year while some receive NO precipitation at all during one year
Receive more than twice as much incoming solar radiation as humid regions
Often undergo large shifts in temperature during the course of a day
Climate: desert
sandy, dry and loose; contains minerals like calcite
Course-textured, shallow, rocky or gravely with good drainage and have no subsurface water
Little to no topsoil due to high winds
Minerals not deep in soil
Too dry for decay (like OM)
Soil: desert
What are the plant adaptations of desert

What are the animal adaptations of desert?

What are the 4 major types of desert?
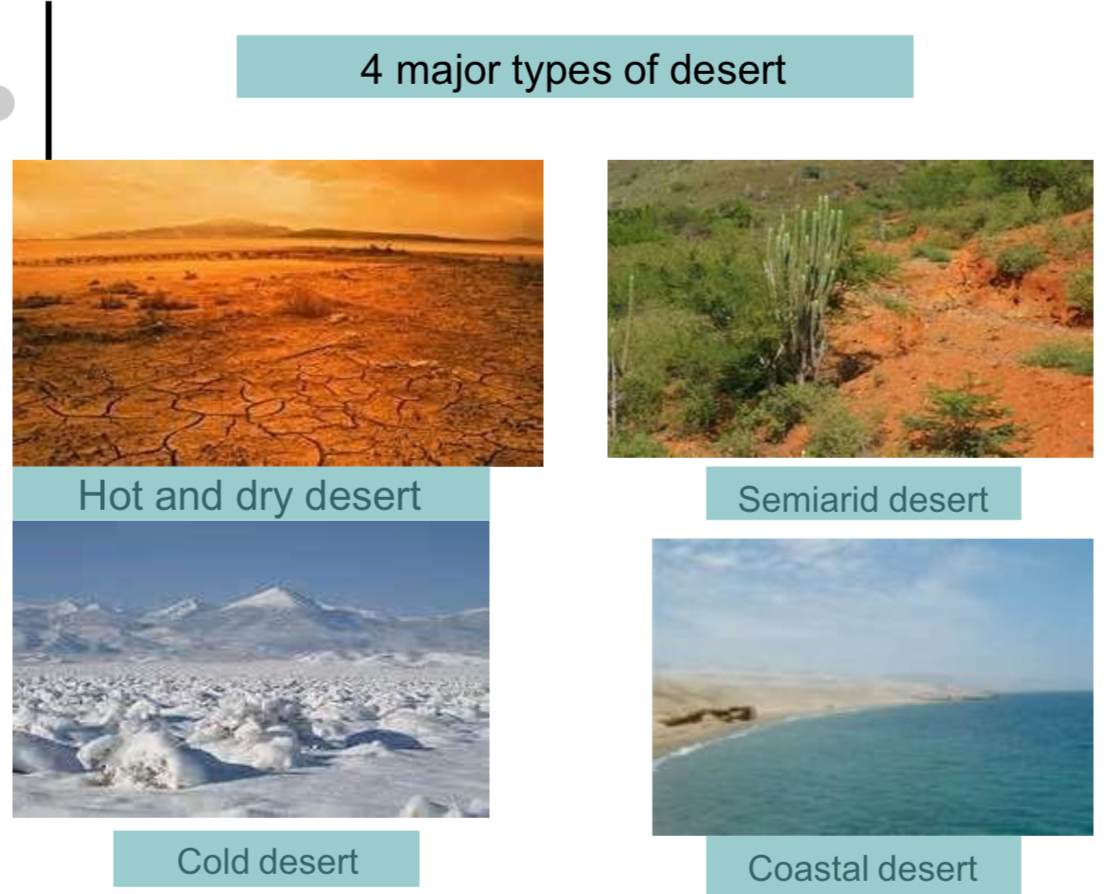

the seasons are generally warm throughout the year and very hot in the summer. The winters usually bring little rainfall
Hot and dry desert
What are the 4 major North American the hot and dry desert?

How is the vegetation in hot and dry desert?
vegetation is very rare
Plants are almost all ground-hugging shrubs and short woody trees. All of the leaves store nutrients
Some of the adaptations in this case are the ability to store water for long periods of time and the ability to stand the hot weather
What animals are included in hot and dry desert?
animals include small nocturnal carnivores
The dominant animals are burrowers. The animals stay inactive in protected hideaways during the hot day and come out to forage at dusk, dawn or at night, when the desert is cooler
characterized by cold winters with snowfall and high overall rainfall throughout the winter and occasionally over the summer
Have a short, moist and moderately warm summers with fairly long, cold cactus winters. Usually occur in Antarctic, Greenland and Nearctic realm
Cold desert
How is the vegetation in cold desert?
there are no trees and shrubs present at all. The only vegetation able to survive are liverworts, lichens and mosses.
Few amphibians, reptiles or mammals are native to cold deserts, but humans have introduced some animals, such as rats and mice
Native fauna includes spiders, earthworms, beetles and the Arctic fox
summers are moderately long and dry and like hot deserts
Winters normally bring low concentration of rainfall
Summer temperatures usually average between 21-27C does not go above 38C and evening temperatures are cool at around 10C
Semiarid desert
What are the major deserts in Semiarid desert?
Major deserts of this type include the sage brush of Utah, Montana and Great Basin
The cool winter’s coastal deserts are followed by moderately long, warm summers
The average summer temperature ranges from 13-24C winter temperatures are 5C or below
These deserts occur in moderately cool to warm areas such as the Nearctic and Neotrophical realm. A good example of this Atacam and Chile
Coastal desert
What is the maximum annual temperatures of coastal desert?
The maximum annual temperatures are about 35C and the minimum is about -4C
occur in all continents except Antarctica
Most extensive around Mediterranean Sea; extend from California into northern Mexico; also found central Chile, southern Australia, and Southern Africa
Chaparral (western North America); mayoral (Mediterranean); fynbos (South Africa); mallee (Australia)
Mediterranean shrubland and woodland
cool and moist during fall, winter and spring
Summers are hot and dry
Usually get more rain than deserts and grasslands but less than forested areas
The combination of dry summers and dense vegetation, rich in essential oils, creates ideal conditions for frequent and intense fires
Climate: Mediterranean shrubland and woodland
generally low to moderate fertility and fragile
Soil erosion can be severe following fire
Soil: Mediterranean shrubland and woodland
fire coupled with overgrazing has stripped the soil from some Mediterranean woodland and shrubland landscapes
Describe the vegetation of Mediterranean shrubland and woodland
dense low plants that contain flammable oils make fire a constant threat
Trees and shrubs are evergreen and have small, tough leaves, which conserve both water and nutrients
Sclerophyllous (hard-leaved) vegetation
Most herbaceous plants grow during the cool, moist season and die back in summer, avoiding both drought and fire
Describe the animal life of Mediterranean shrubland and woodland
animals tend to be browsers
Some prominent wildlife are coyotes, wild goats, mule deer, and the Mediterranean gecko
Camouflage is common in exposed shrubland
found mid-latitude regions
Harbor ancient trees
The second largest terrestrial biome
Most of the human population lives in this biome
Temperate forest
temperatures are not extreme
Annual precipitation averages from 650-3000mm
Receive more winter precipitation
Climate: temperate forest
soils are usually fertile
Most fertile develops in deciduous forests with generally neutral or slightly acidic and rich in OM and inorganic nutrients
Soil: temperate forest
lower diversity of trees compared to tropical forests
Vertically, stratified (herb layer, shrub layer, shade- tolerant understory trees and canopy)
More sunlight reaches the ground compared to a rainforest so more ground dwelling plants are found on the floor
May either be deciduous (more dominant) or coniferous
Vegetation: Temperate forest
birds, mammals , and insects make use of all the forest strata
Fungi, bacteria, microscopic invertebrates consume large quantities of wood stored on the floor of old-growth temperate forest
The activities of these organisms recycle nutrients
Animal life: temperate forest
found only in northern hemisphere (northern parts of Alaska, Canada, Asia and Europe)
The NPP is lower than that of temperate forests and tropical wet forests
The above- ground biomass is high because these slow- growing tree species are long-lived and accumulate a large standing biomass over time
Boreal forest (Taiga)
warm, and rainy summers
Very long and cold winter lasting to about half a year; precipitation is in the form of snow about. 60cm
Below -20C in winter and about 15C in summer
Climate: boreal forest (taiga)
soil is not fertile. It takes very long for needlelike leaves to decompose and decomposition is very slow in cold weather
A layer of now covers the ground during much of the year
Soil beneath the snow is grayish on top and brown below and lacks minerals needed by plants to grow
Soil: boreal forest (taiga)
mostly contains evergreen coniferous trees like pines, spruce, and fir, which retain their needle shaped leaves year-round
Evergreen trees can photosynthesize earlier in the spring than deciduous trees because less energy from the sun is required to warm a needle- like leaf than a broad leaf
Vegetation: boreal forest (taiga)
What are the plant adaptations of boreal forests?
coniferous (needle-bearing) trees are abundant
Roots long to anchor trees
Needles long, thin and waxy (low sunlight and poor soil keeps plants from growing on forest floor)
Ex: Balsam Fir
What are the animal adaptations on boreal forest?
adapt for cold winters
Burrow, hibernate, warm coat, insulation etc
Ex: great grey owl, moose, deer, mosquito, bear, hares, porcupine, squirrel
found north of the arctic circle
Treeless plain
Coldest biome
“Permafrost”
Tundra
extremely cold and dry biome
Usually receives NO more precipitation than a desert biome (<25 in/year)
Short growing season
Limited sunlight
Average temperature is. 23F or 5C
Climate: Tundra
ground covered with little snow
Below the surface soil is permanently frozen (permafrost)
During summer, the top layer of soil thaws, but the rest remains frozen
Decomposition is very slow because of the extreme cold
Soil: Tundra
biodiversity of plant is very low
Lichens, mosses and short shrubs are dominant
Plants are dwarf, prostrate woody shrubs grow low to the ground to gain protection under the winter blanket of snow and ice
Vegetation: Tundra
What are the plant adaptations of tundra?
growing close to the ground
Having shallow roots to absorb the limited water resources
Trees grow less than 1 m high
Ex: Reindeer lichen, cottongrass
Many birds that occur in Arctic tundra are?
Many birds that occur in Arctic tundra are migratory (summer)
The main animal population in the Arctic tundra consists of?
The main animal population in the Arctic Tundra consists of reindeer, polar bears, arctic fox, arctic hare, snowy owls, lemmings and musk ox
Animals living in the alpine tundra are?
Animals living in the alpine tundra are, pikas, marmots, mountain goats, sheep elk, grouse like birds, springtails, beetles, grasshoppers, and butterflies
Describe the animal adaptations of tundra

What are the types of tundra

a layer of permanently frozen subsoil (permafrost) exists consisting mostly of gravel and finer material
The growing season ranges from 50-60 days
The Arctic tundra
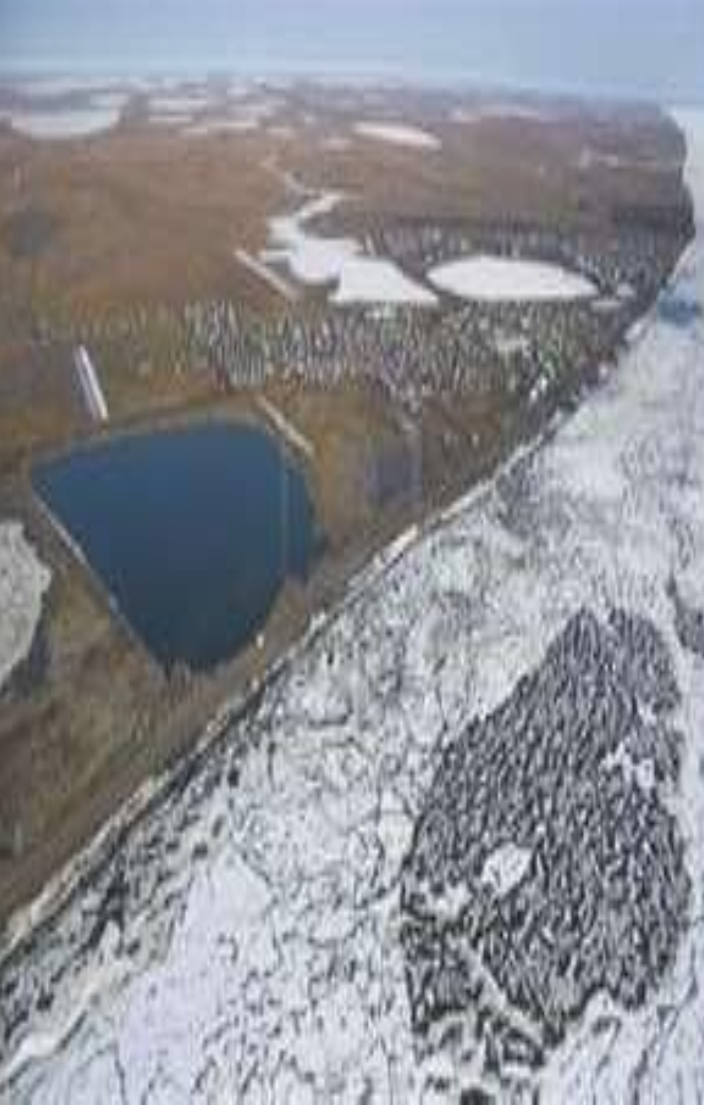

Where is the Arctic tundra located?
Located between the North Pole and Coniferous forest or taiga region. It is extremely cold temperatures and land that remains frozen year-round
North America- Nothern Alaska, Canada Greenland, Northern Europe- Scandinavia Northern Asia- Siberia
the growing season is approximately 180 days
Very windy
Typically covered in snow for most of the year
Alpine tundra
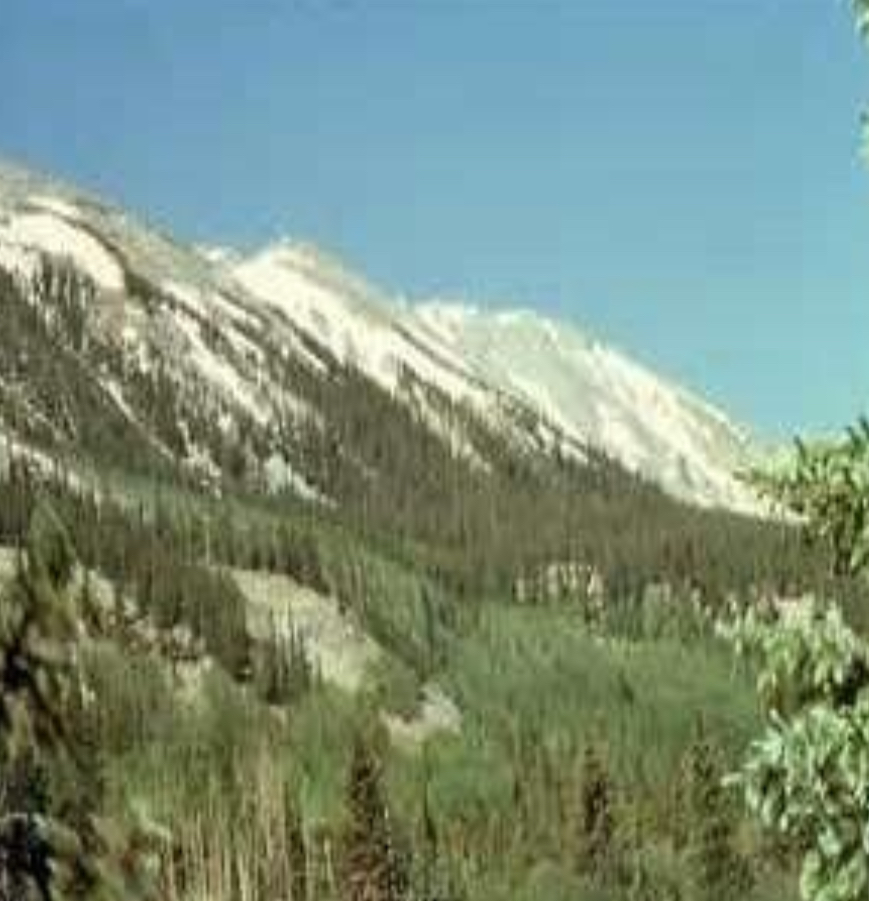

Where is the alpine tundra located?
Located on mountains throughout the world at high altitude where trees cannot grow
North America-Alaska, Canada, U.S.A and Mexico
Northern Europe- Finland, Norway, Russia, and Sweden
Asia- Southern Asia (Mt. Himalayan) and Japan. (Mt. Fuji)
Africa- Mt. Kilimanjava
South America- Andes Mountains
Why is the conservation and preservation of biomes should be a major concern to all?
Because we share the worlds with many other species of plants and animals, we must consider the consequences of our actions. It is important to preserve all types of biomes as each houses many unique forms of life