rp1 - solution + titration
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
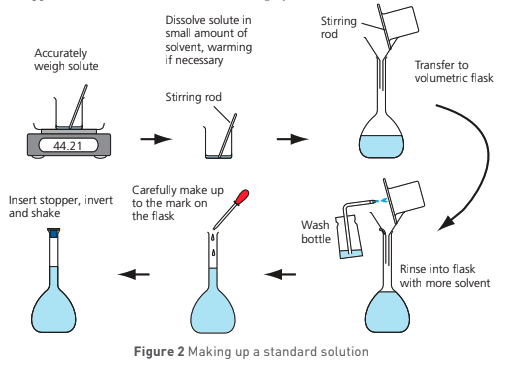
describe the method for 1a - making up a standard solution (250 cm³ of NaHSO4 w/ a conc of approx 0.100 mol dm-3):
calculate mass of NaHSO4 solid needed using mol = conc x vol and mol = mass/Mr
weigh a clean, dry weighing boat w/ mass balance
place weighing boat and use a spatula to transfer approximately the calculated mass of NaHSO4
use mass balance to weigh weighing boat and contents and record precise mass
pour contents into beaker and reweigh weighing boat
calculate mass of NaHSO4 transferred
add approx 100 cm³ of deionised/distilled water to beaker containing solid and stir until dissolved w/ glass road
using a funnel, pour contents of beaker into a 250 cm³ volumetric flask and using the wash bottle, rinse beaker, funnel and glass rod into same volumetric flask
make volumetric flask up to graduated mark w/ deionised/distilled water from wash bottle
stopper and shake volumetric flask thoroughly to mix contents
calculate exact conc of solution in mol dm-3 and use this to label flask
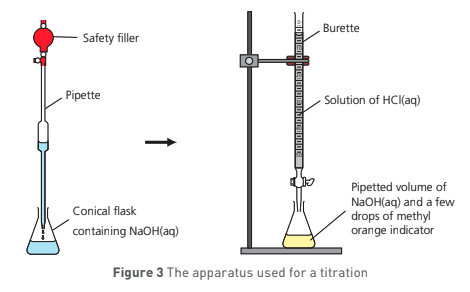
describe the method for 1b - titration:
pour approx 100 cm³ of NaHSO4 solution into clean, dry, labelled beaker and use a small vol of this solution to rinse the burette
pour approx 100 cm³ of NaOH into a second clean, dry, labelled beaker
rinse a 25 cm³ pipette w/ NaOH and use a pipette filler to pipette exactly 25 cm³ NaOH into a 250 cm³ conical flask (rinsed w/ distilled water)
add 2-3 drops of phenolphthalein in solution in conical flask
record initial burette reading
titrate contents of conical flask by adding NaHSO4 solution from burette slowly, then dropwise near end point, swirling flask gently
when titration has been completed and solution has turned colourless from pink, record final reading on burette and use this to calculate vol of NaSO4 needed to neutralise NaOH
this is your rough titre - repeat until concordant results are obtained and calculate mean vol of NaSO4 used
does rinsing the burette w/ NaHSO4 instead of water increase or decrease precision? why?
increases precision
prevents dilution of NaHSO4 solution by any residual water left in burette, which would decrease precision of titration
does rinsing the pipette w/ NaOH instead of water increase or decrease precision? why?
increases precision
prevents dilution of NaOH solution by any residual water left in pipette, which would decrease precision of titration
what are concordant results?
results that are w/in 0.1 cm³ of each other
what is a standard solution?
a solution for which the concentration is accurately known
what is the purpose of ‘washing’ the beaker/glass rod into the solution in the volumetric flask?
ensures there is no solute left behind in the beaker or on glass rod
why must the tip of the burette be filled w/ liquid before the titration begins?
to prevent any air bubbles being present, which would produce an inaccurate volume
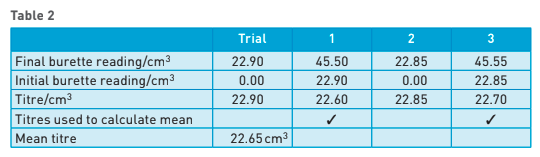
give a suitable table for the titration results to be recorded in:
how can we calculate the uncertainty and % error of the equipment used?
uncertainty = no. of readings taken x smallest increment/2
% error = uncertainty/reading x 100
does rinsing the sides of the conical flask with water increase or decrease the accuracy? why?
increases accuracy
ensures all the alkali is at the bottom of the conical flask and can react, because as you swirl the alkali can travel up the sides of the flask
why do we use a pipette to transfer the acid into the conical flask instead of a measuring cylinder?
increases precision as uncertainty is smaller
why is adding alkali solution until the indicator “just” changes colour a mistake? how can this be rectified?
acid may not have fully reacted as mixture not swirled
add alkali solution until a permanent colour change seen
why is it important to add 2-6 drops of indicator?
adding too much indicator may cause the indicator to react with the solution, affecting the endpoint reading