Biological Science Freeman Chapter 2
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Theory of chemical evolution
-explains the origin of life on Earth
-inputs of energy created complex carbon-containing molecules
-the molecule could replicate itself
Functional Group
a specific configuration of atoms commonly attached to the carbon skeletons of organic molecules and involved in chemical reactions
Catalyze
speed up chemical reactions
atomic mass
Number of protons and neutrons
non polar covalent
equal sharing of electrons
atomic number
-the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
-written as a subscript to the left of its symbol
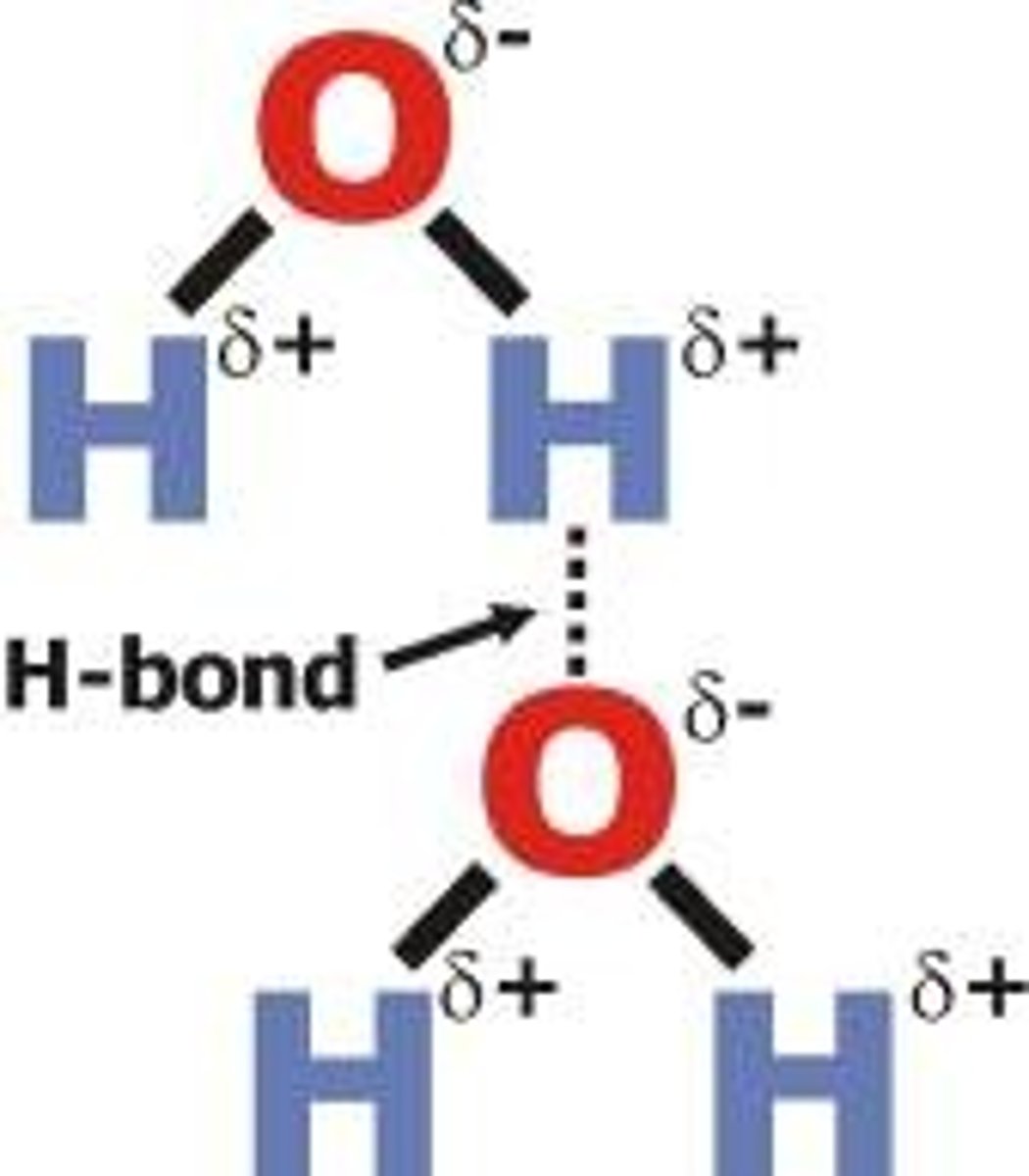
hydrogen bond
weak attraction between a hydrogen atom and another atom
Valance
-number of unpaired valence electrons
-atoms are most stable when valence shells are full
covalent bond
sharing of electrons between atoms
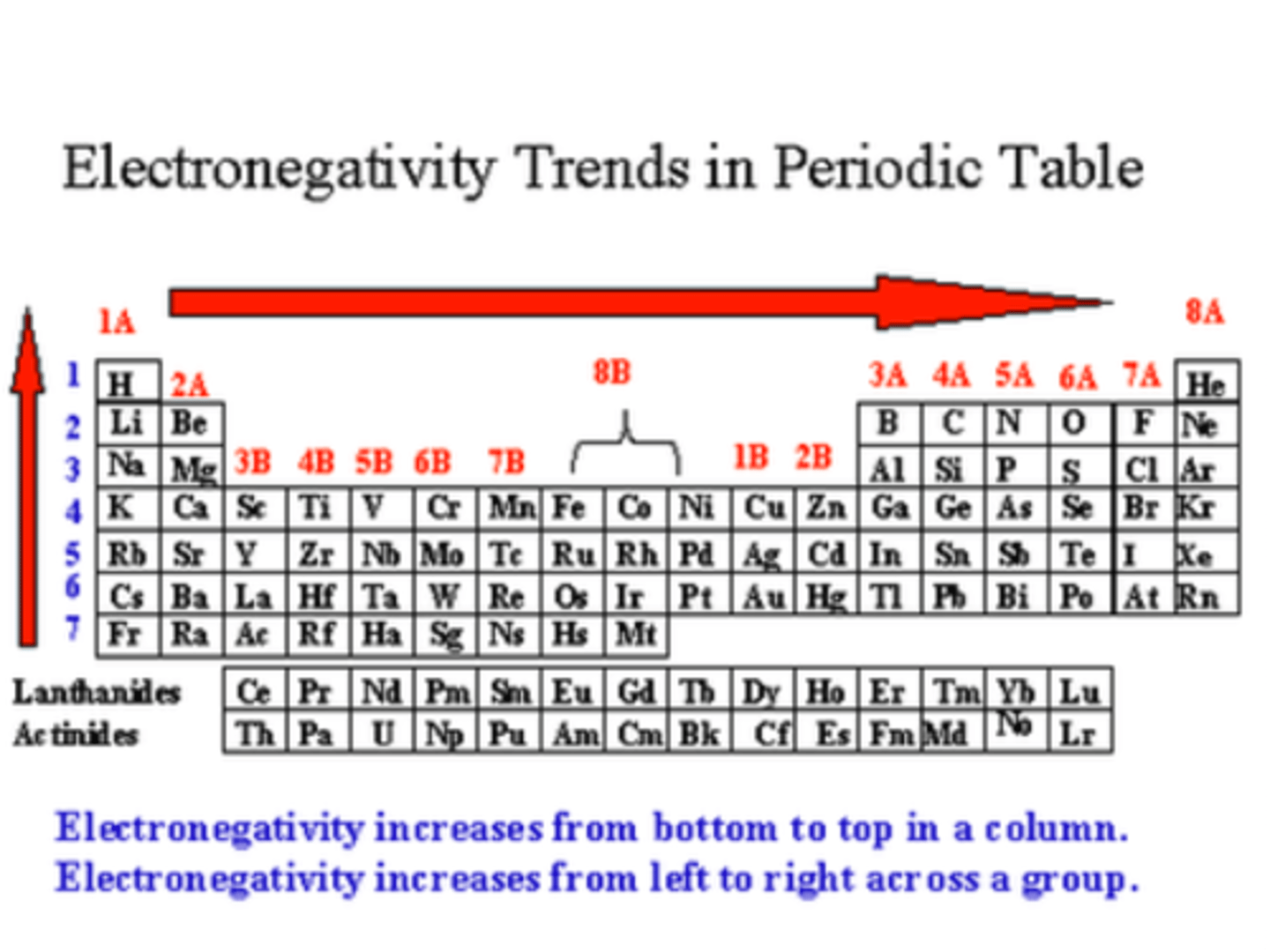
Electronegativity
-the strength with which atoms pull electrons toward themselves
-O>N>S, C, H, P
Molecule
A group of atoms bonded together, covalent
polar covalent bond
not shared equally
Cohesion
-binding between like molecules
- = high surface tension
-Example: water binds to itself by hydrogen bonding
Adhesion
-binding between unlike molecules
-Example: water binds to glass (meniscus formation)
valance shell
outermost shell
Ions
charged atoms that have gained or lost electrons
chemical reaction
substances that are combined or broken down
endothermic reaction
A reaction that absorbs thermal energy in the form of heat
exothermic reaction
A reaction that releases thermal energy in the form of heat
chemical equilibrium
In a chemical reaction, the state in which the rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the reverse reaction
Acidic reaction
Lose electrons
Basic reaction
Gains an electron
Chemical Evolution Theory
Simple molecules present on ancient Earth reacted to create larger, more complex molecules.
*This may have happened in:
-The atmosphere
-Deep-sea vents
potential energy
stored energy
kinetic energy
active energy of movement
first law of thermodynamics
-Energy can be transferred and transformed, but it cannot be created or destroyed.
-Energy is conserved
Entropy
measure of disorder
second law of thermodynamics
-entropy always increases
-chemical retractions result in products with
-less ordered energy
-less usable energy
-physical and chemical processes proceed in the direction that results in lower potential energy and increased disorder
surface metabolism model
-air came in contact with minerals in deep-sea vents (in water)
-formed more complex organic molecules
Photons
-high-energy light energy formed from experiments
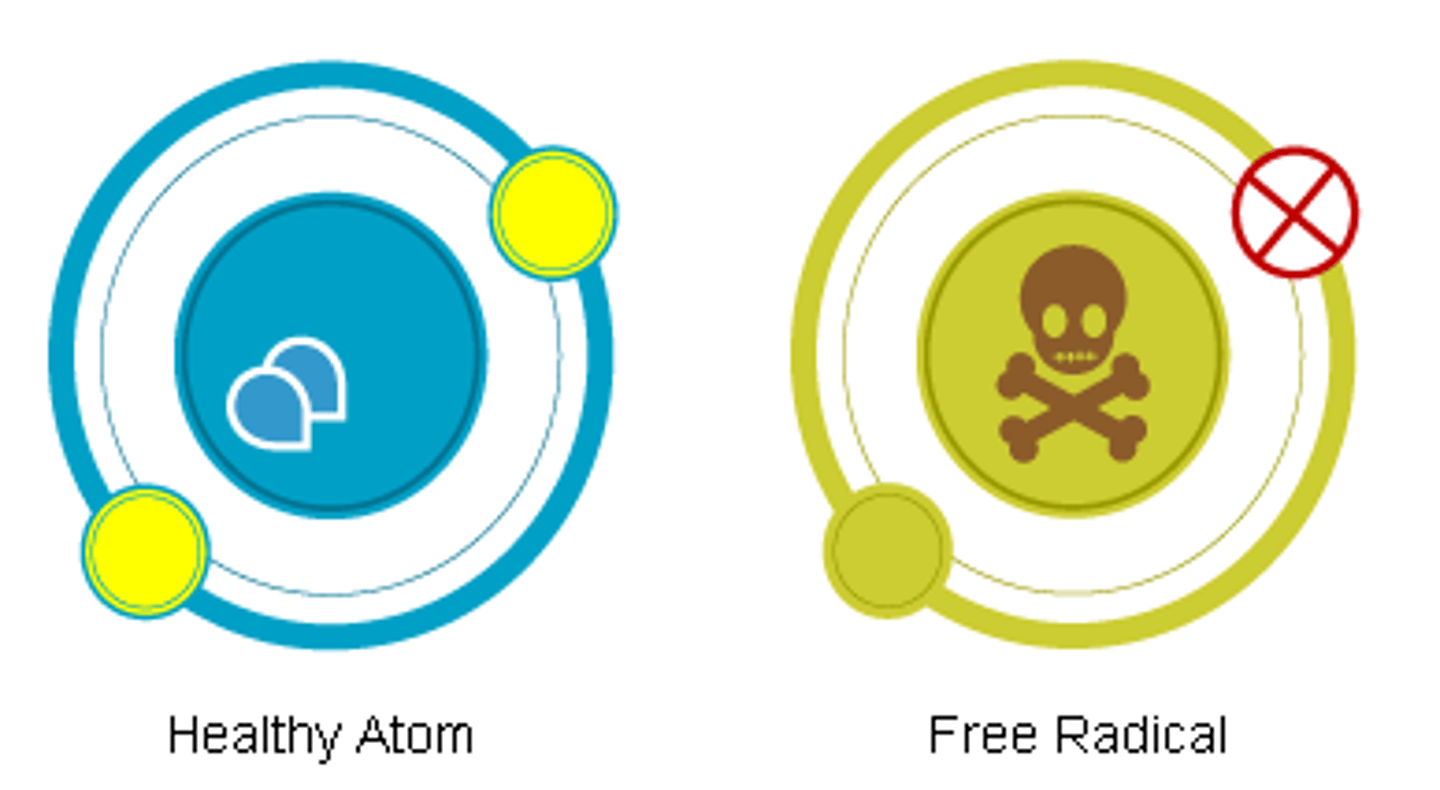
free radicals
-highly reactive unpaired electrons
-created from photons
chemical energy (type of PE)
-molecule's potential to form stronger bonds
4 Types of Matter in Organisms
-make up 96% of matter in organisms
1. Hydrogen
2. Carbon
3. Nitrogen
4. Oxygen
Basic Atomic Structure
Atoms are composed of
-Protons (positive)
-Neutrons (neutral)
-located in nucleus
-Electrons (negative)
-located in orbitals (outside of nucleus)
Atoms with same atomic number...
Are the same element
mass number
-# of protons and neutrons
-superscript to the left of symbol
mass of electron
-so small (can be ignored)
Mass of atom =
Mass Number
Atomic weight
-average of all the masses of the naturally occurring isotopes based on their abundance
radioactive isotope
isotope that decays over time
Orbitals
-what electrons move in
-each orbital holds up to 2 electrons
-orbitals are grouped into levels called electron shells
Electron shells
-levels orbitals are grouped into
-shells are numbered
-smaller numbers are closer to the nucleus
-inner most shells fill first
Valence shell
-outermost shell of an atom
-contains valence electrons
valence electrons
-Electrons on the outermost energy level of an atom
-located in the valence shell
chemical bonds
attractions that bind atoms together
Covalent Bond
-unpaired valence elections are shared by two atoms
-example: H2
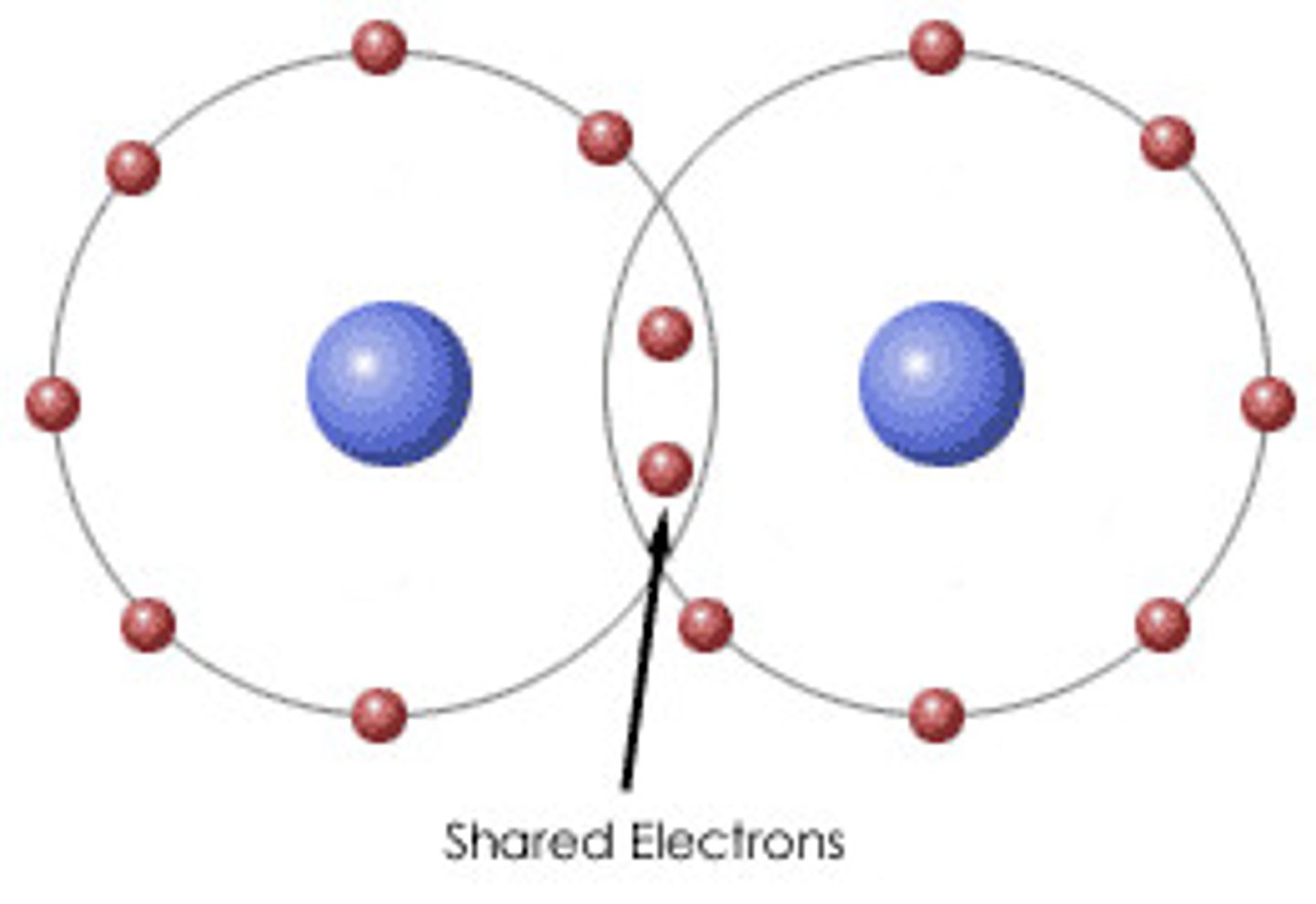
Molecules
substances held together by covalent bonds
Compounds
-molecules in which atoms of different elements are held together
Ionic Bonds
-electrons are transferred from one atom to another to give both atoms full valence shells
Cation
atom loses electron and becomes positively charged
Types of covalent bonding
-polar
-don't share well (unevenly)
-O-H Bond
-non polar
-shared perfect (evenly)
-C-H Bond
Ion
-atom or molecule that carries a charge
-attraction occurs between oppositely charged Ions
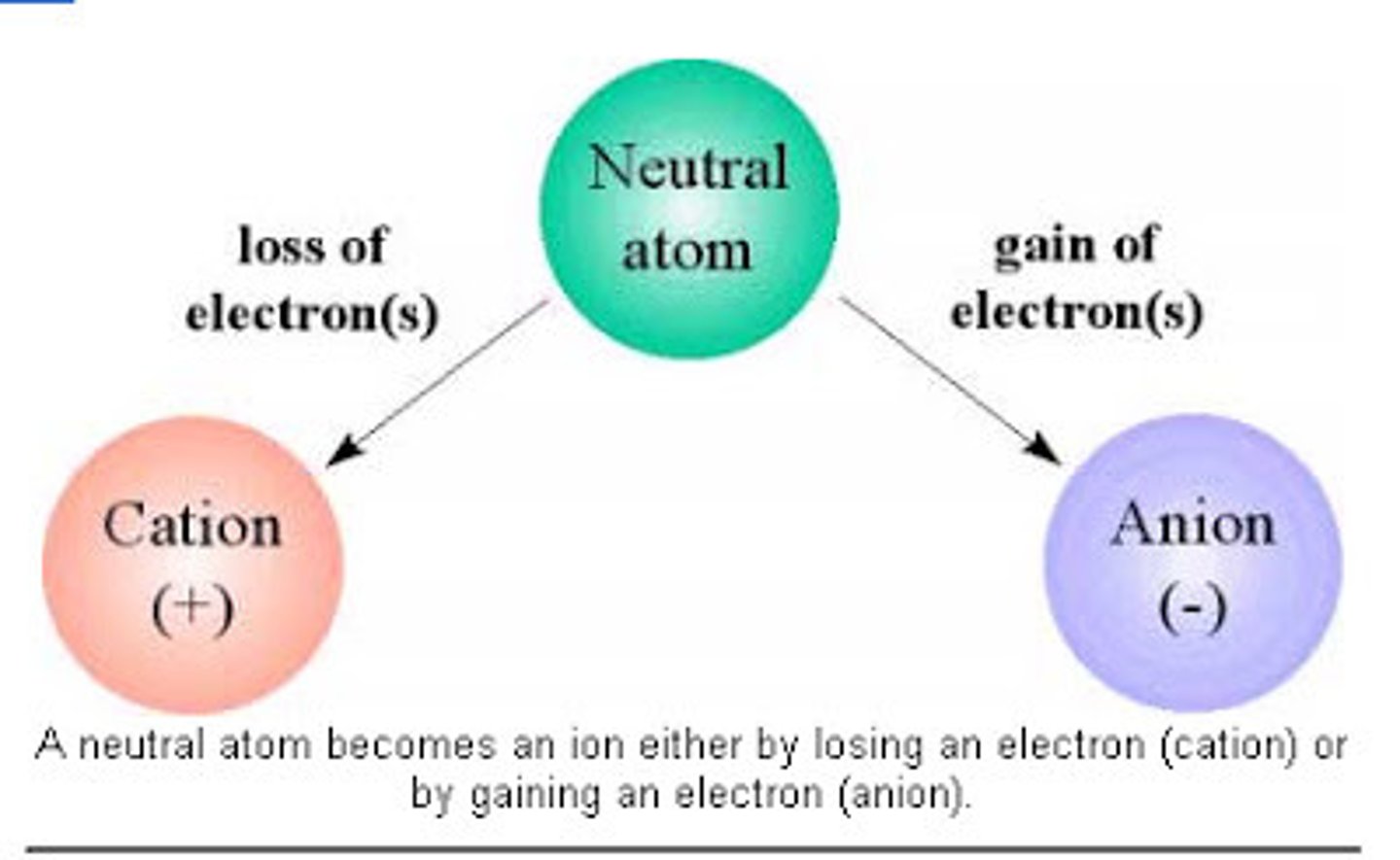
Anion
atom gains an electron and becomes negatively charged
Strength of bonds (strongest to weakest)
Covalent Non polar>Covalent Polar>Ionic>Hydrogen
How are the number of Bonds determined?
-They are determined by the number of unpaired electrons
Number of bonds (strengths and lengths)
-triple bonds (shortest and strongest)
-single bonds (longest and weakest)
Molecules Shape
-dictates its behavior
-are different
-determined by geometry of bonds
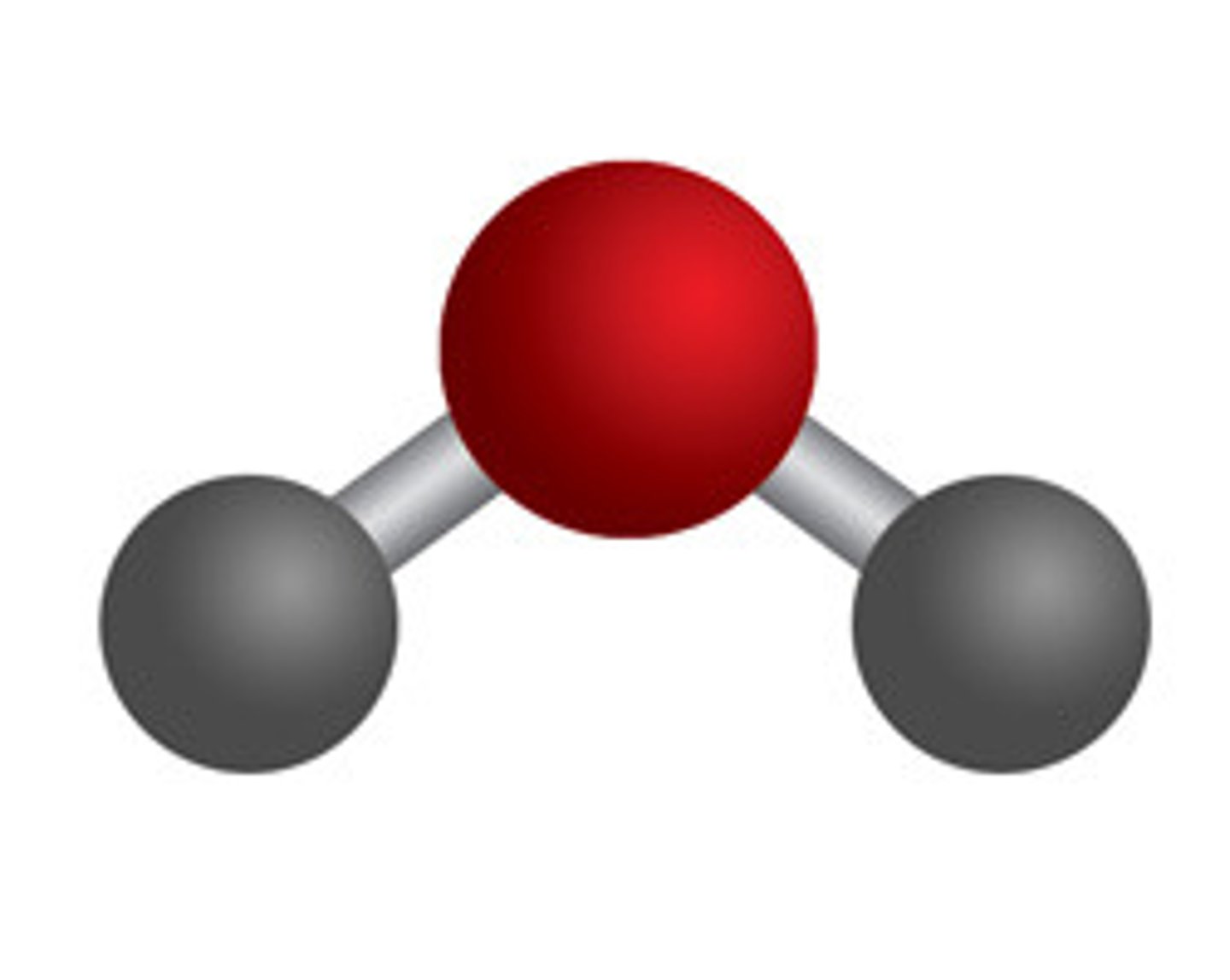
molecular formula
-indicate number and types of atoms
-Example: (H2O)
structural formula
-indicate what atoms are bonded together
ball and stick model (space-filling models)
-3D geometry
Solute
the substance that is dissolved
Solvent
the substance in which the solute dissolves
Hydrogen Bonds
-weak electrical attractions
Hydrophilic
-water-loving atoms and molecules
-ions and polar molecules that stay in solution
hyrdrophobic
-water-fearing molecules
-uncharged and non polar compounds
Polar
-charges are at opposite ends of water molecule
-oxygen atoms
-partial negaitive charge
-hydrogen atoms
-partial positive charge
Water is unique due to its structure because of...
1.small size
2.bent shape
3.highly polar covalent bonds
4.overall polarity
Water is denser as a liquid than a solid
-ice floats
-water expands as it freezes
-it forms a relatively open crystal structure
Isotopes
-form of element with different number of neutrons
-have different masses
Water has high capacity for absorbing energy
-can absorb large amounts of energy
specific heat
-The amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of a substance by 1 degree celcius
-high in water
heat of vaporization of water
-very high in water
Chemical reactions
-substance is combined or broken down into another substance
Acids
-give up protons during chemical reactions
Bases
-acquire protons during chemical reactions
molecular weight
the sum of the atomic weights of all the atoms in a molecule
mole
6.022 x 10²³ molecules
Molarity (M) (mol/L)
-concentration of a substance in a solution
pH
-proton concentration in a solution
-Basic (8-14)
-Acidic (1-6)
-Neutral (7)
Buffers
-protect against changes in pH
-help maintain homeostasis
Homeostasis
-constant conditions
Chemical Evolution may have begun in:
1. the atmosphere:
-dominated by volcanic gases
-mostly water vapor, carbon dioxide (CO2), and nitrogen (N2)
2. Deep-Sea Hydrothermal Vents
-extremely hot rocks
-gases such as CO2 and H2
-minerals with reactive metals
System
-set of interacting components
Energy
-the capacity to do work or supply heat
thermal energy
-kinetic energy of molecular motion
Temperature
-measure of the thermal energy in a molecule
Heat
-measure of the thermal energy in a molecule
Chemical Reactions are Spontaneous if...
-they occur without continuous external influence
-no energy is needed
Spontaneity of a reaction is determined by...
1. Products are less ordered than the reactants
-Entropy (disorder) increases
2. Products have lower potential energy than the reactants
-(shared electrons are held more tightly in the reactants)
prebiotic soup
-molecules are already in atmosphere gases
-rained > ended in the ocean
-ended in "organic soup" > created more complex molecules
Carbon
-most versatile atom on Earth
-4 valence electrons
-can form many covalent bonds
Stanley Miller
-found complex molecules could be formed from simple molecules
-using heat and electrical charges
-formed precursors to life molecules
fuctional groups
-amino
-carboxyl
-carbonyl
-hydroxyl
-phosphate
-sulfhydryl
amino group
-attracts a proton, acts as bases
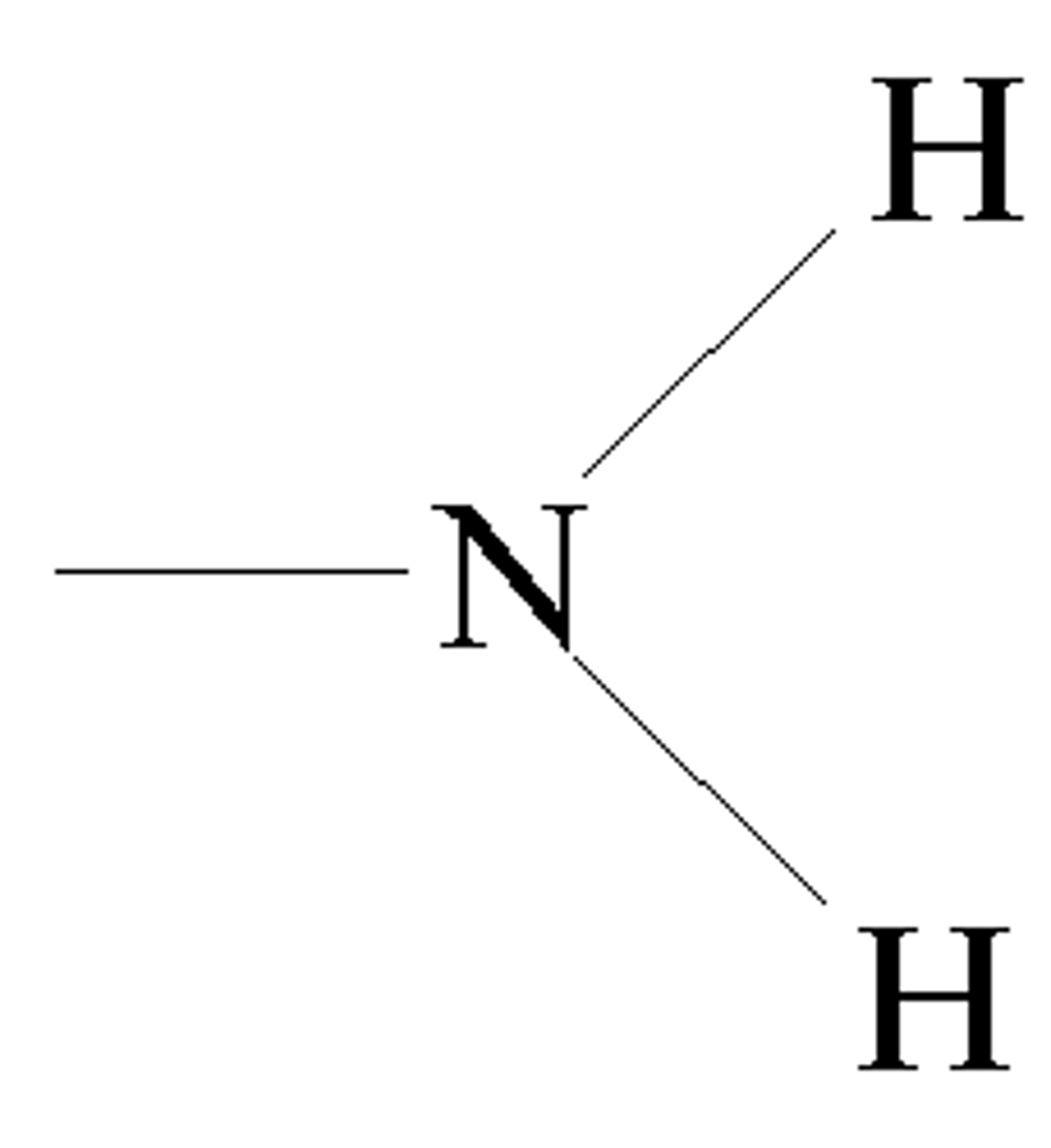
organic compounds
-molecules that contain carbon bonded to other elements
-many molecular shapes and combinations of single and double bonds
-formation of carbon-carbon bonds was an important event in chemical evolution
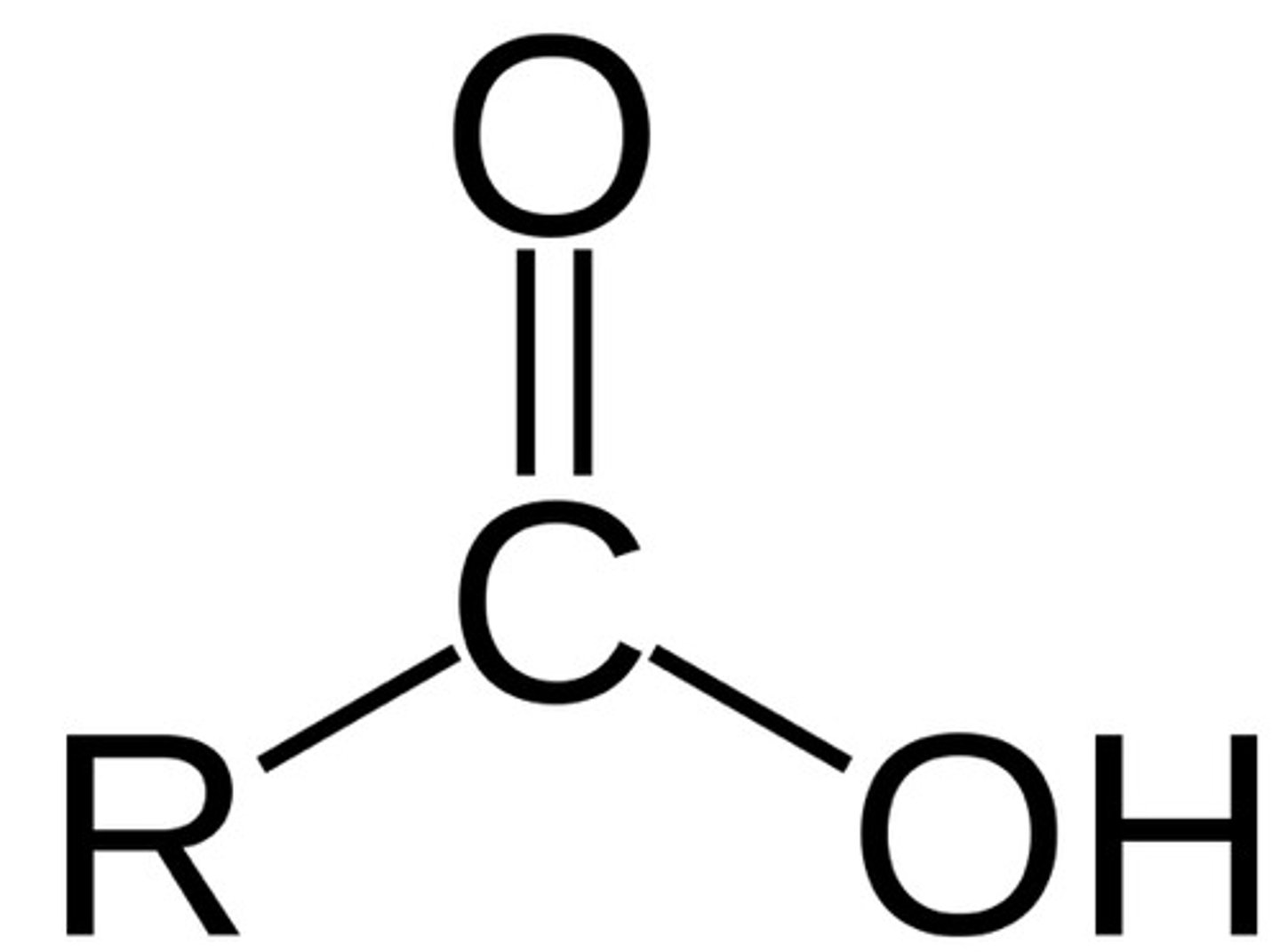
carboxyl group
-drop a proton, acts as acids
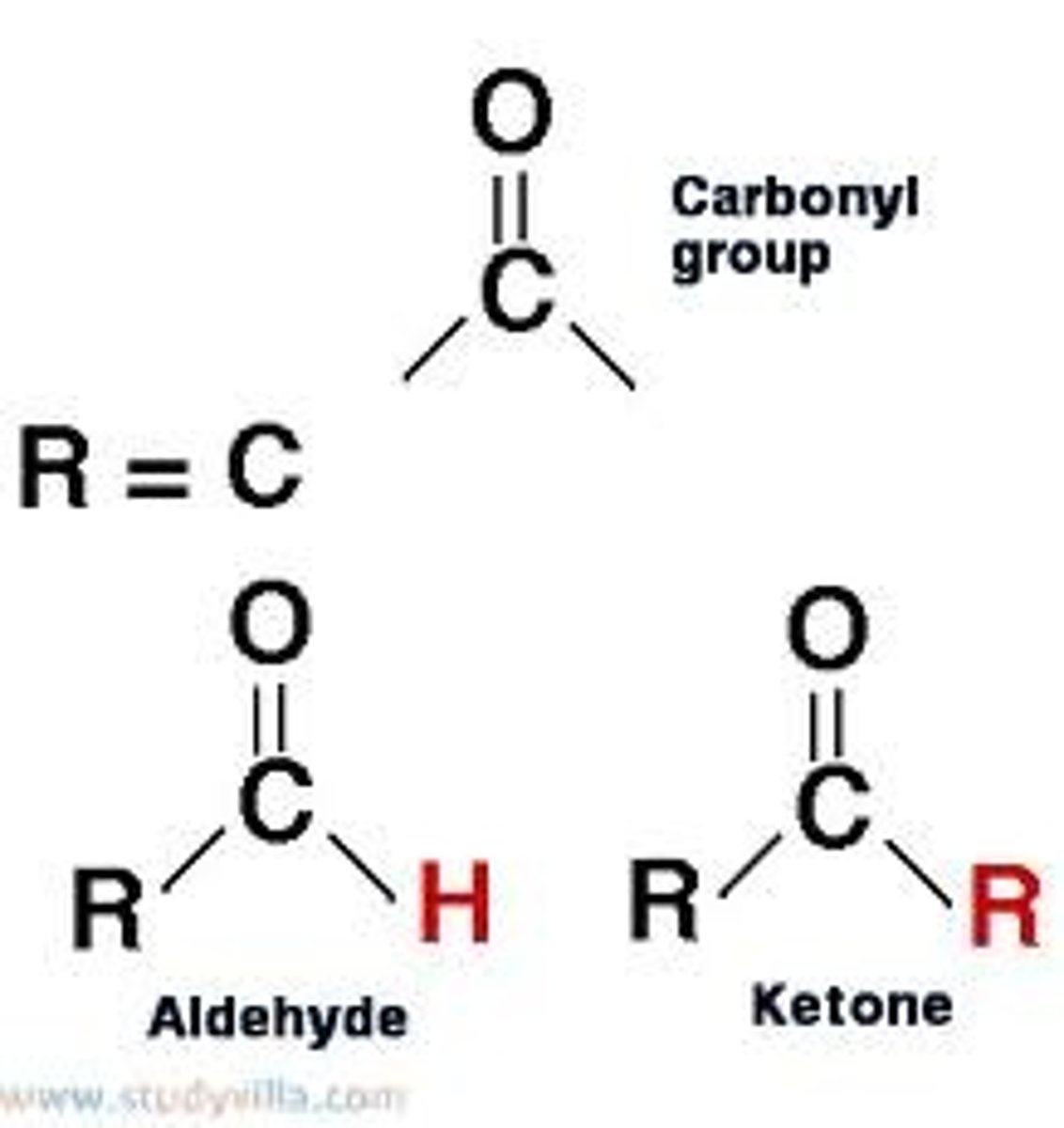
carbonyl group
-sites link molecules into more-complex compounds
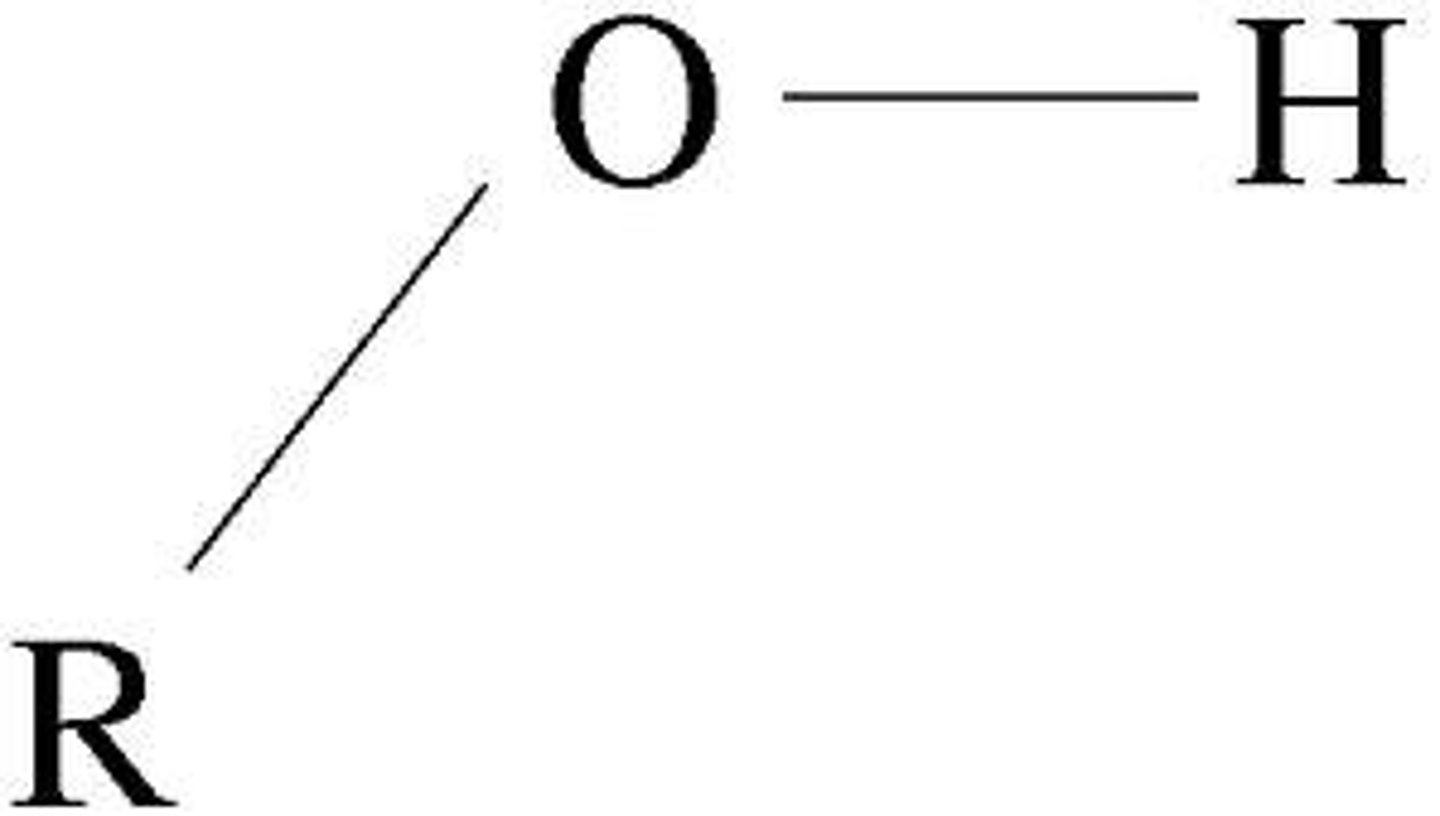
hydroxyl group
-act as weak acids
phosphate group
-two negative charges
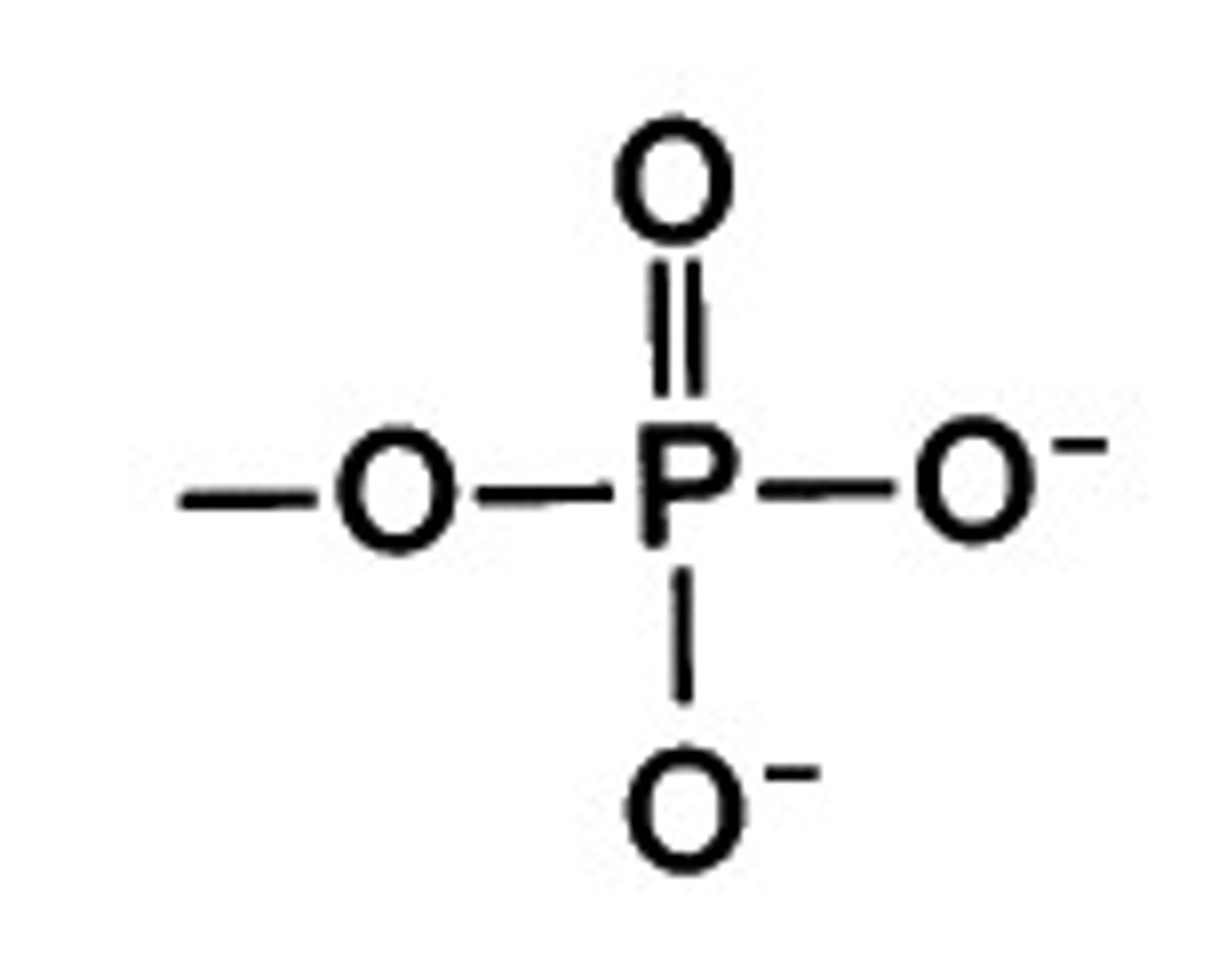
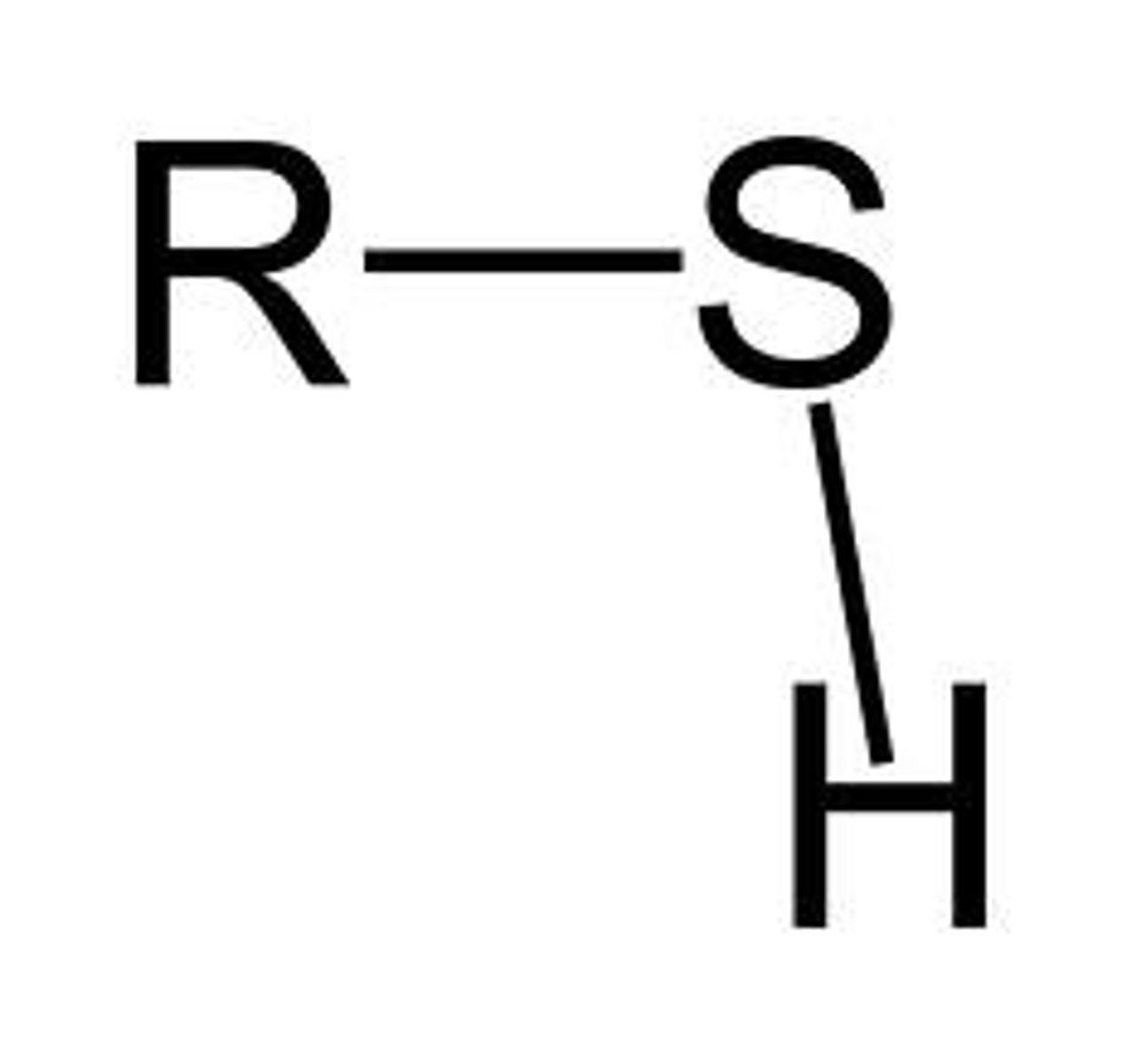
sulfhydryl group
-link together via disuflide bonds