Microscopic Examination of Urine
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
114 Terms
to detect and identify insoluble elements present in the urine specimen
What is the purpose of microscopic exam of urine?
Microscopic Exam
Third part of urinalysis
most time-consuming and the least standardized part
confirms physical and chemical analysis
Routine Techniques
Special Techniques
Automated microscopy
What are the 3 methods of microscopic examinations?
Quantitative estimation of urinary sediments
Hausser’s method
Long Coefficient method
Addis count
Application of stains
What are the special techniques of microscopic examination?
10—15 ml urine
What is the recommended volume of urine in microscopic examination?
5 minutes (1,500-2,000 rpm)
How many minutes is the centrifugation of urine in microscopic examination?
0.5-1.0 ml
What is the volume of sediment in microscopic exam after discarding the supernantant?
RCF (Relative Centrifugal Force)
What is the preferable to use that can produce minimal damage to cells?
Braking mechanism
What mechanism that slow centrifugation that cause disruption of sediments?
Prevent biohazardhous aerosols
What is to purpose of centrifuge in capped tubes?
uniform amount of sediment - aspirate rather than poured off
resuspend sediment by gentle agitation
Use of pipettes in measuring the drop of sample
How do you prepare sediment?
Use of pipettes
What material should we use in measuring the drop of sample?
Conventional coverslip method (20ul)
22mmx22mm coverslip
What method of coverslip shoul be used and what size?
prevent sediment to flow outside the coverslip (loss of heavier elements)
What should be prevented in the preparation of sediment?
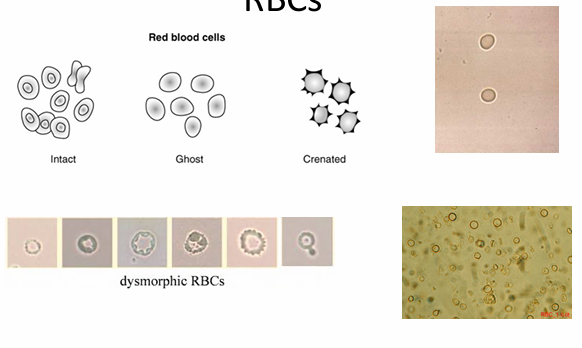
Organized sediments
Unorganized sediments
What are the 2 types of urine sediments?
Cells
Casts
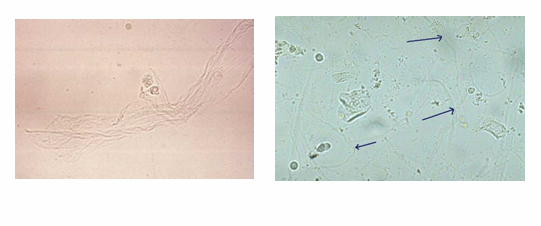
Mucus Thread
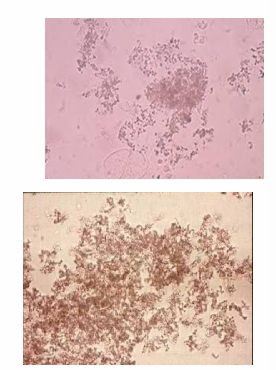
Microorganisms
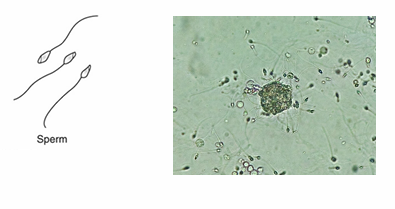
Sperm Cells
What are the organized sediments?
Crystals
normal crystals in acid urine
normal crystals in alkaline urine
Abornal crystals
What are the unorganized sediments?
abnormal crystals of Iatrogenic origin (drugs)
abnormal crystals of Metabolic origin
What are the 2 types of abnormal crystals?
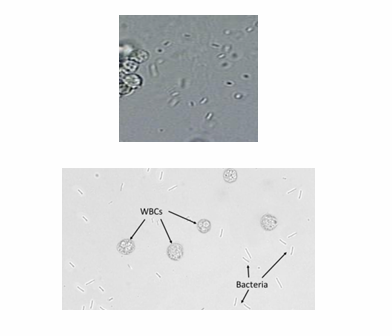
RBC
WBC
Epithelial cells
Enumerate the cells found in the sediment
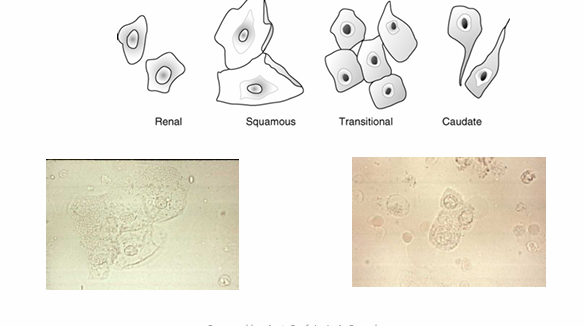
Squamous epithelial cells
Transitional epithelial cells
Renal Tubular epithelial cells
Enumerate Epithelial cells
RBCs
WBCs

Epithelial cells
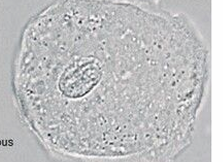
Squamous
Transitional
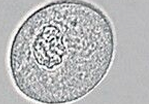
Renal

Oval Fat Bodies
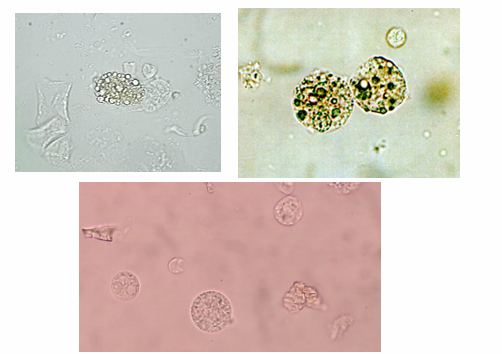
Bubble cells
distal convoluted tubule and collecting tubules
Where does the casts formed?
cylindrical with rounded or flat ends and are classified according to the substance observed in them
What is the shape of the casts and what are its classification?
representative of the tubular lumen
What does the shape of the casts represents?
Tamm-Horsfall mucoprotein or uromodulin
What is the major constituent of casts?
hyaline cast
cellular cast
Enumerate the type of casts
RBC casts
WBC casts
Epithelial casts
What are the types of cellular casts?
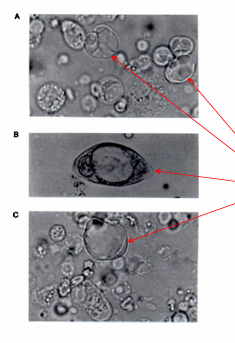
Hyaline cast
RBC casts
WBC Cast
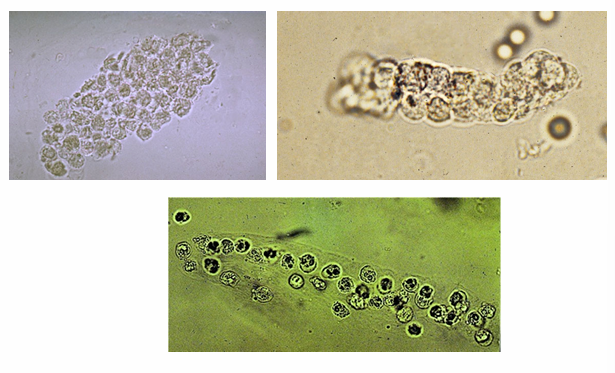
Transitional EC casts
Renal Tubular EC cast
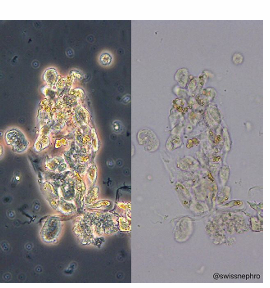
Granular cast - fine or coarse
What type of cast that contain remnants of disintegrated cells that appear as fine of coarse granular embedded in the protein?
Waxy cast
What type of cast that is not normally seen in the urine but are associated with renal stasis?
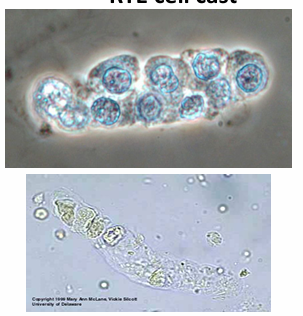
Fatty cast
What type of cast that the important pathologic findings in the urine which indicate severe renal dysfunction?
Coarse granular
Fatty cast
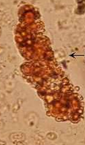
Oval Fat Body Cast
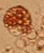
Waxy casts

Fine granular

Bacterial cast
What type of casts that contain bacteria often associated with pyelonephritis?
Broad cast
What type of cast that is associated with renal failure cast?
Bacterial cast
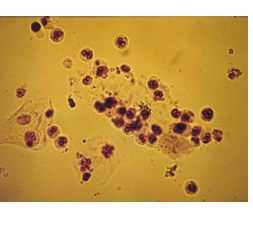
Broad cast
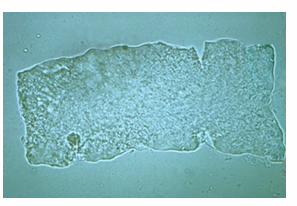
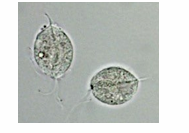
bacteria
protozoa (flagellates)
yeasts
What are the types of microorganism?
Bacteria
because of the movement of the flagella
How does protozoa usually recognized in urine sediment?
Trichomonas vaginalis
In protozoa, what is the most frequently seen parasite in urine?
Protozoa
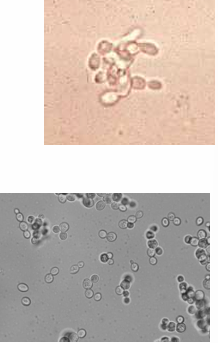
smaller than RBC
What is the size of yeast cells?
ovoid
What is the shape of yeast cell?
in budding or in chains
How can we observe yeast cells?
Candida albicans
What is the most common yeast found?
Yeast cells
Sperm cells
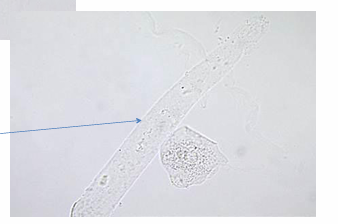
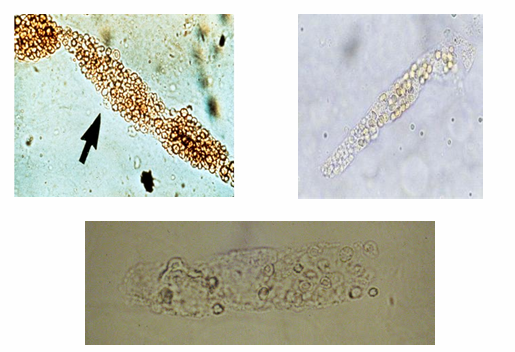
Mucus Threads
urine pH
urine solubility
The identifcation of the types of (unorganized sediments) crystals depends on, what?
Amorphous urates
Uric acid
Sodium urates
Calcium oxalates
Hippuric crystals
What are the normal crystals in acid urine?
Amorphous phosphates
Calcium carbonates
Ammonium biurate
Triple phosphate
Calcium phophates
What are the normal crystals in alkaline urine?
Cystine
Tyrosine
Leucine
Cholesterol
Bilirubin
Hemosiderin granules
What are the abrnomal cyrstals of metabolic origin?
appear as fine granules with no specific shape
sediment may appear pink in the urine container but under the microscope the appear yellowish
What is the appearance of amporhous urates?
Amorphous urates
Uric acid
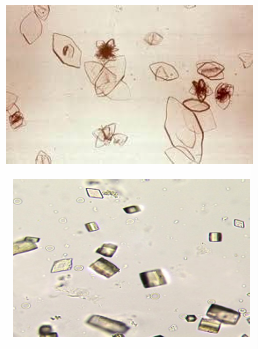
appear as yellowish brown crystals that have a variety of shapes: irregular, rhombic clusters or rosettes
large amount may be seen in patients with gout
What is the appearance of uric acid?
patients with gout
Where can we see large amount of uric acid?
irregular
rhombic clusters
rosettes
What are the variety of shape of uric acid?
Sodium urates
appear as light-yellow slender prisms may be single or in clusters
no clinical importance
What is the appearance of sodium urates?
Calcium oxalates
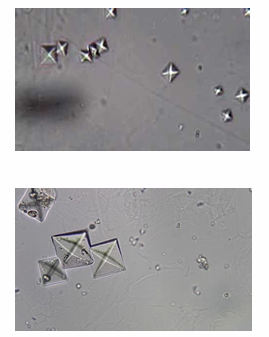
appear as colorless, octahedral crystals which are refractile and variable in size
looks like “envelopes” having an X intersecting
What is the appearance of calcium oxalates?
Hippuric crystals
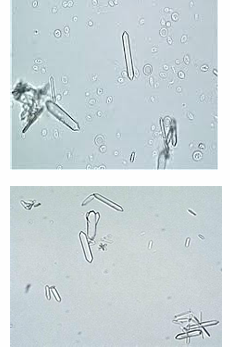
rarely seen
yellow-brown or clear
resemble needle-like prisms or plate
What is the appearance of hippuric crystals?
Amorphous phosphates
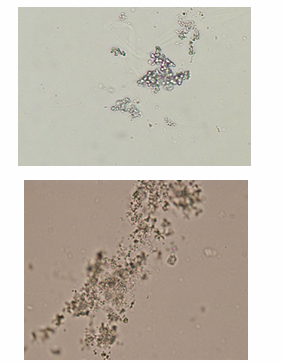
may appear as colorless, amorphous, granular masses in urine sediment
solube in 10% acetic acid
What is the appearance of amporphous phosphates?
Calcium carbonates
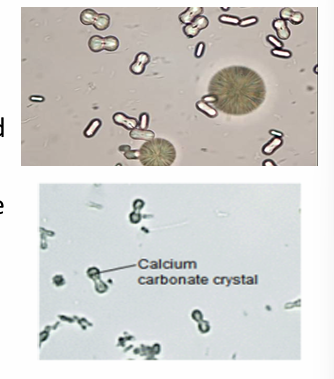
appear as small, colorless, dumbbell-shaped or leaf-shaped crystals
no clinical significance
What is the appearance of calcium carbonates?
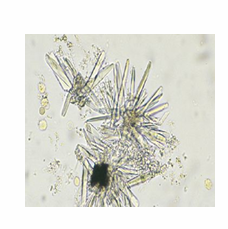
Ammonium biurate

seen in old urine samples
yellow to brown spheres with striation on the surface & also can show irregular projection called “thorny apple” crystals
What is the appearance of ammonium biurate?
Triple phosphates

ammonium magnesium phosphate
What is triple phosphates also known as?
appear as colorless, highly refractile prisms having 3 -6 sides
“coffin’lid” appearance
What is the appearnace of triple phosphates?
Calcium phosphates
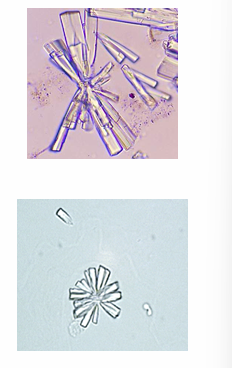
colorless and may appear as star-like or needle-like, through may also form plates
show up alone or clusters
What is the appearance of calcium phosphates?
Cystine

colorless, refractile, flat, hexagonal crystals, usually having unequal sides
presence in the urine indicates cystinuria
What is the appearance of cystine?
Tyrosine
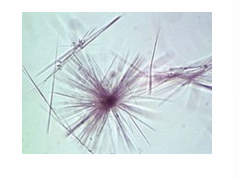
colorless or yellow fine, delicate needles arranged in sheaves
What is the appearance of tyrosine?
Liver disease or kidney damage
What does the presence of tyrosine in the urine means?
Leucine
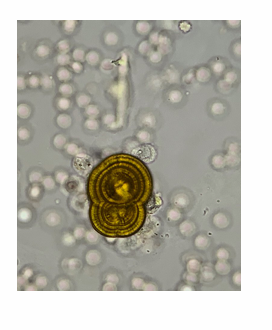
appear as oily spheres that may be yellow-brown in color and are refractive
What is the appearance of leucine?
liver disease or damage
maple syrup urine disease (MSUD)
What indicates the presence of leucine in the urine?
Cholesterol
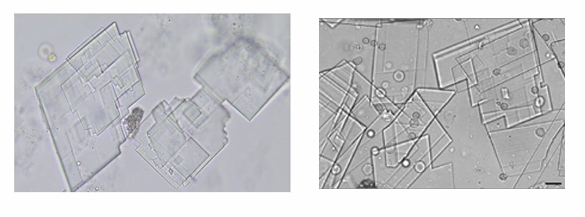
colorless, flat, rectangular plates with notched corners
What is the appearance of cholesterol?