AP Human Geo - Unit 5 (Agriculture)
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Agriculture
Raising animals or growing crops on tended land for consumption by the farmer's family or sale.
Agricultural practices influenced by…
Physical environment
Climate conditions
First Agricultural revolution
Started farming
Created agricultural hearths
Led to owning land
Second agricultural movement
Through mechanization began to be able to create and transport more crops - being able to transport crops
Aligned with industrial revolution
Third agricultural revolution
Advancements in science - maximizing plant
fertilizers - GMO’s
Norman Borlaug made wheat stock stronger
Pros —> producing more food
Cons —> environmental issues
Domestication
Process of adapting plants and animals for human use
Subsistence Agriculture
Primary focus is to feed family or local community - not for sale
found in developing countries
Commercial Agriculture
Form of agriculture to generate product for sale off of the farm
Vertical Integration of Agriculture (Vertical Agriculture)
A company maximizing profit by buying multiple steps in the value chain
Cereal grain
A grass yielding grain for food
Monoculture
Mass producing of one type of crop
May change from season to season
Can be susceptible to disease
Monocropping
Mass producing of one crop in the same place year after year
Food Sercurity
When people have access to enough food to stay healthy
Transhumance
Seasonal movement of livestock from one area to another
Pastoralism / pastoral nomadism
A practice where animals are herded across lands too dry to grow crops - for agriculture
irregular movement
Plantation
Production of one or more usually cash crops in a area of land
Shifting Cultivation
is a form of extensive subsistence farming done in areas with low population density – especially in the tropics.
People rotate fields in order to allow soil to replenish nutrients
Not the same as crop rotation — when farmer rotates crop type
“Slash-and-burn” farming
Burning portion of the forest so the soil can be used for agriculture
Intensive Agriculture
Hard: involves a lot of manual labor/or financial commitment per amount of land
Continuously produce crops → can take a toll on the land
Extensive Agriculture
Smaller amounts of labor/tech and science over a large amount of space
Spending a little amount of money/work for a large amount of land
Double Cropping
Harvesting from the same field twice a year
Terrace farming
The practice of cutting flat areas out of a hilly or mountainous landscape in order to grow crops
Commodity chain
A linked system of processes that gather resources, convert them into goods, package them for distribution, disperse them, and sell them on the market.
Value chain (increases value with every step)
Production to retail
Export Commodity
Primary reason for growing is to gain money (cash crop)
Economies of Sale
As corporations buy smaller farms, they have enough capital to purchase equipment and produce more for a cheaper price
More you buy the cheaper it is per product
Crop rotation
system developed during the Second Agricultural Revolution in order to preserve the mineral health of soil used in agriculture and prevents patches of land from being exhausted.
Farmer rotates crop type
Aquaculture
Farming/cultivation of aquatic species (fish)
Agribusiness
Refers to entire process and entire value chain of all agricultural process
From seed to grocery store
Companies, transportation, etc.
Increase large commercial farms (a lot more food) → independent small farms and decreasing (especially in developing countries)
3rd agricultural revolution
Horticulture
growing of fruits, vegetables, and flowers
Von Thünen’s model
Focused on where certain types of agriculture would be best located because of land and transportation
Ex: higher cost closer to the city (horticulture/forestry)
Desertification
the process by which previously fertile lands become arid and unusable for farming.
Soil Salinization
Increased salinity of land, once fertile land can no longer produce land → leads to more deforestation to create more land
When watering land the salt and minerals are in the water. The water evaporates but the minerals don’t, and have an increased concentration of salt being left.
Intertillage
Mixing different seeds together
Genetically Modified Organism (GMO)
When crop has been modified to keep some characteristics and leave negative ones (protect against pests)
Undernourishment
a dietary energy consumption continuously below minimum requirement for maintaining healthy life and carrying out light physical activity
Organic Farming
approach to farming and ranching that avoids the use of herbicieds, pesticides, growth hormones, and other similar synthetic inputs
Farm Subsidies
government is protecting price of something
Government can pay amount so that farmers get a certain price for something they do
Ex: crop is really bad for a few years only $20 need $30, government paying extra $10
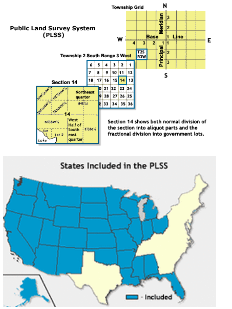
Township and Range
Created after American revolution
Makes the land look like graph paper/grid system
Common in Midwest
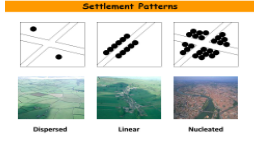
Clustered Settlement Pattern
Have a focused nuclear area in the middle
Occur in areas where resources are focused in small areas
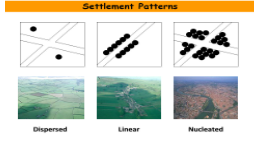
Dispersed Settlement Pattern
Spread out
Found in areas that have a strong agricultural base
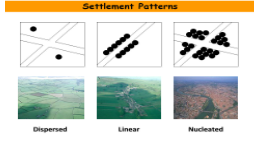
Linear Settlement Pattern
Has a pattern
Develop in areas where the most important economic reasons for settlement exist in lines
Ex: River
Long lot
Divides land into narrow areas stretching from river, roads, or canals
Metes and Bounds
Uses natural feature to create areas of land
Used in early colonies
Columbian Exchange
Massive trade between Europe and the Americas
Relocation diffusion
Greatly influenced parts of the world