GB Week 2
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Chromatography
separation technique used to identify various components of mixtures based on the differences in their structure and/or composition.
Pigments
are substances that absorb visible light. Different pigments absorb light of different wavelengths
Photoexcitation
is the production of an excited state of a quantum system by photon absorption
Chloroplasts
are found only in plants and photosynthetic algae. (Humans and other animals do not have chloroplasts.) The chloroplast's job is to carry out a process called photosynthesis.
STRUCTURAL COMPONENTS OF CHLOROPLAST
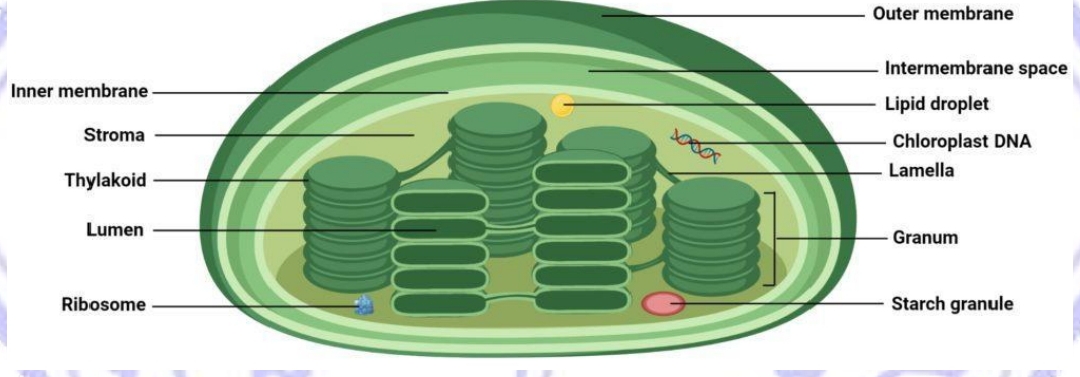
Chloroplast
disc-shaped organelles found in the cytosol of a cell. They have outer and inner membranes with an intermembrane space between them
Chloroplast
If you passed through the two layers of membrane and reached the space in the center, you’d find that it contained membrane discs known as thylakoids, arranged in interconnected stacks called grana (singular, granum).
membrane of a thylakoid disc
contains light-harvesting complexes that include chlorophyll
thylakoid space or lumen
the space inside a disc
stroma
the fluid surrounding the thylakoids
Light
Light, as it encounters an object, is either reflected, transmitted, or absorbed.
Visible Light Wavelength (380-750nm)
the segment in the entire range of electromagnetic spectrum that is most important to life on earth. It is detected as various colors by the human eye
Pigments
are the means by which plants capture sun’s energy to be used in photosynthesis.
4 main categories of Plant Pigments
chlorophylls, anthocyanins, carotenoids, and betalains.
Anthocyanins
particularly found in fruits such as grapes, purple grapes, black berries, strawberries, and raspberries.
Carotenoids
are Plant pigments that are responsible for their yellow, bright red, and orange color are carotenoids that play a key role in plant health. Different vegetables and fruits in which carotenoids are present: yams, carrots, sweet potatoes, watermelon, papaya, cantaloupe, spinach, mangos, kale, tomatoes, oranges, bell peppers,
Xanthophyll
molecules known as hydrocarbons and found in orange and yellow fruits and vegetables, for example, pumpkin, cantaloupe, sweet potatoes, apricots and carrots.
CHLOROPHYLL
the greenish pigment found in the thylakoid membrane inside the chloroplast of a plant cell.
CHLOROPHYLL
absorbs blue and red light while it transmits and reflects green light. This is why leaves appear green.
CHLOROPHYLL
It directly participates in converting solar energy to chemical energy.
Head and Tail
Structure of chlorophyll
Head
a flat hydrophilic head called porphyrin ring. It has a magnesium atom at its center. Different chlorophylls differ on the side groups attached to the porphyrin.
Tail
a lipid-soluble hydrocarbon tail.
HOW DOES PHOTOEXCITATION OF CHLOROPHYLL HAPPEN?
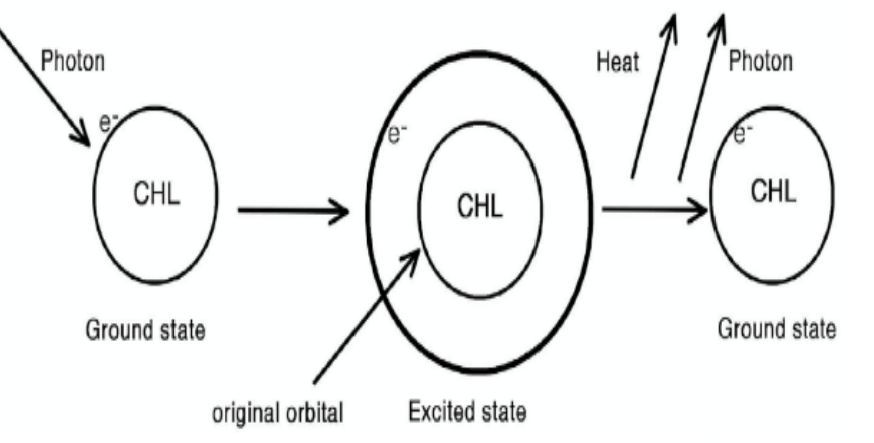
PHOTOSYSTEM
is an aggregate of pigments and proteins in the thylakoid membrane responsible for the absorption of photons and the transfer of energy and electrons.
LIGHT-HARVESTING COMPLEX
is also called the ‘antenna’ complex and is consisted of several different pigments (chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, and carotenoids) bounded with proteins
LIGHT-HARVESTING COMPLEX
When a pigment molecule absorbs a photon, energy is passed on from one pigment molecule to another pigment molecule until the energy reaches the reaction center.
REACTION-CENTER COMPLEX
is composed of a pair of chlorophyll a and a primary electron acceptor.
THERE ARE TWO TYPES OF PHOTOSYSTEM:
PHOTOSYSTEM II & PHOTOSYSTEM I
PHOTOSYSTEM II
was discovered later after the discovery of Photosystem I, but functions first in the light reaction of photosynthesis.
PHOTOSYSTEM II
The chlorophyll a in the reaction-center of Photosystem II effectively absorbs light with a wavelength of 680nm and thus called P680.
PHOTOSYSTEM I
was discovered first
PHOTOSYSTEM I
Its reaction-center has a chlorophyll a called P700 because it is effective in absorbing light with a wavelength of 700nm.