2. Inhibitors of Cell Wall Synthesis
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Bacterial Cell Wall Characteristics
Gram +
Glycans cross-linked by peptides → THICK Peptidoglycan
β-Lactamases
Teichoic acids
Gram -
Peptidoglycan (THIN) surrounded by lipoprotein sandwich (Inner and outer plasma membrane)
LPS are lipophilic and prevent gram stain penetration
Porin channel proteins transport small hydrophilic zwitterions (both + and - charge)
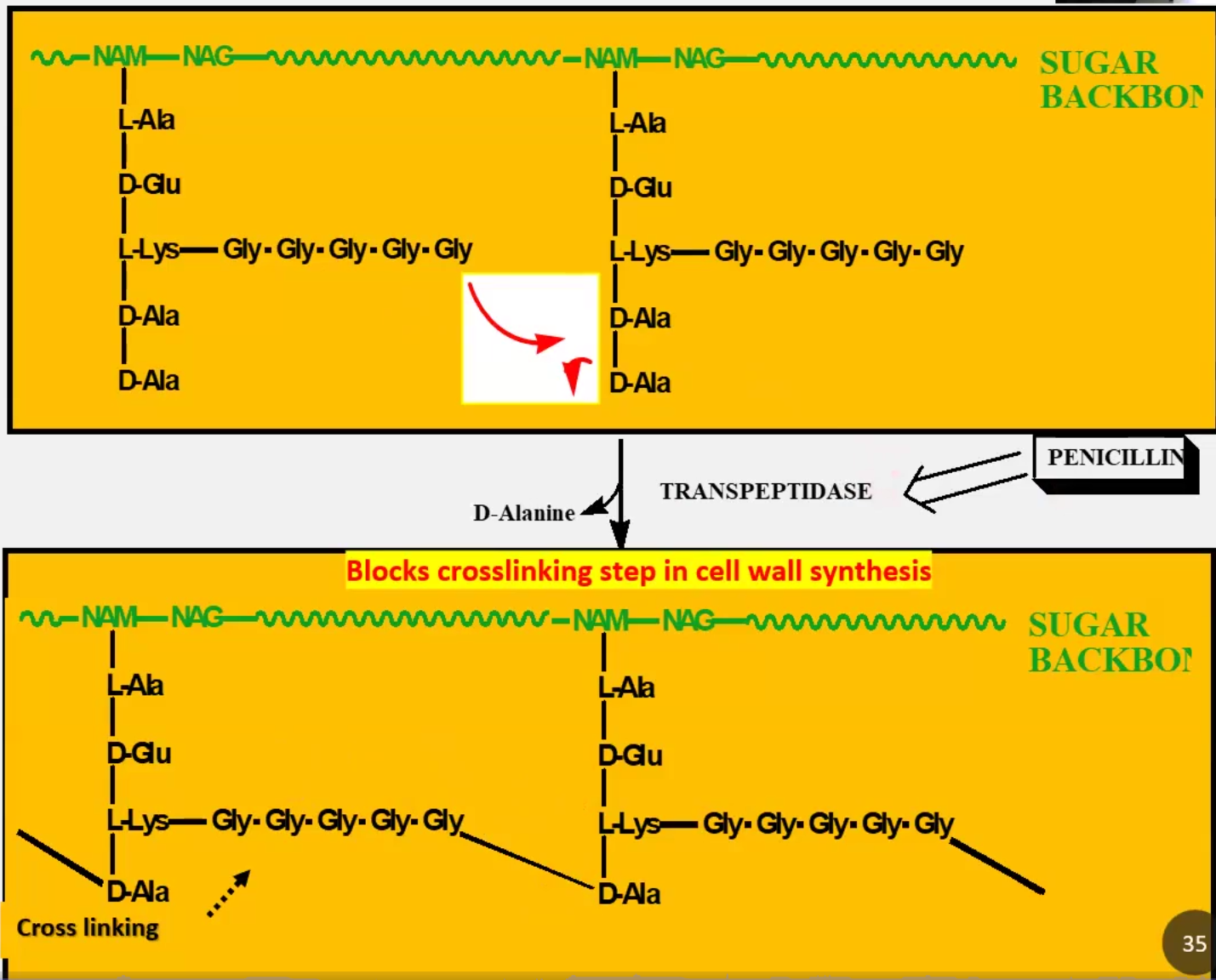
Explain Murein, NAM-NAG and Penicillin-Binding Proteins (PBPs)
Murein is a PG of repeating NAM and NAG units that crosslink via peptides
Transpeptidases remove alanine and help crosslink glycine to the previous alanine
PBPs = Transpeptidases because Penicillin binds to them and inhibit its activity → Results in loss of cell wall by autolysis → So Penicillin is an antibacterial
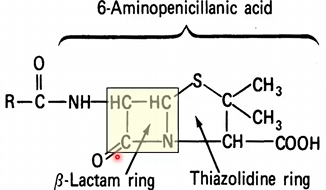
Characteristics of β-Lactam Rings
Originates from Penicillin (prototype)
5-membered ring
Substrate for β-lactamase hydrolyzation and breaking of ring
Unstable structure because it is acid labile → easily destroyed by immune system and stomach acid
What is the basis for Penicillin Hypersensitivity
β-lactam ring undergoes isomerization and then is able to bind a lysyl residue in a protein
This forms an immunogenic compound that triggers IgG Response
Pharmacokinetics of Penicillin and its derivatives
Acid labile and binds food proteins → must be administered 1-2hrs before meals
CSF Penetration is variable but possible
Plasma protein binding
Renal excretion of unchanged drug by glomerular filtration and tubular secretion
Probenecid BLOCKS secretion of penicillin and thus increases half-life
Penicillin Drug categories
MOA
Gram + or -
Susceptible pathogens
Adverse reactions
Resistance
Penicillin G (Prototype)
Block last step of cross-linking through β-lactam
Drug of choice for gram+ aerobes and anaerobes
Staph, Strep, Spirochetes, Treponema pallidum & few gram- such as Neisseria. gonorrhea and H. influenzae
Adverse rxns: Hypersensitivity may occur in allergic individuals
Resistance: Degradation by β-lactamases and most gram-
Penicillin V (Oral): same but acid resistant and administered orally
Penicillinase-resistant penicillin (PRPs/MSSA/methicillin susceptible staph aureus): Methicillin, Oxacillin and Nafcillin
MRSA Resistant: none
Aminopenicillins/Broad Spectrum: active against both gram+ and gram- because it gets into gram- through porin channels
Amoxicillin and Ampicillin
Anti-pseudomonas
Ticarcillin and Piperacillin
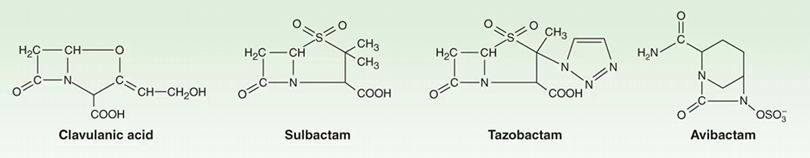
Combinations:
Augmentin: Amoxicillin + Clavulanic Acid (β-lactamase inhibitor)
Ampicillin + Sulbactam (β-lactamase inhibitor)
Piperacillin + Tazobactam (β-lactamase inhibitor)
Ceftazidime + Avibactam (β-lactamase inhibitor)
Explain modes of resistance through PBPs
Mutations in PBP genes result in resistance
MRSA: results from PBP 2A mutation that has less affinity to β-lactam ring on methycillin, all penicillins and almost all cephalosporins except Ceftaroline
Cephalosporins
Structure
MOA
Produced from what organism
Generations and how they are different
Structurally similar to penicillin but ring is 6-membered
Like penicillin, blocks final cross-linking step
Produced by fungi
Adverse reactions:
Super strong so superinfections and renal toxicity has been reported
Hypersensitivity just like Penicillin
Generations:
1st Gen (CEF/PH/A): Against gram+, but mostly strep and staph (not MRSA)
Cefazolin (injectable) and Cephalexin (oral)
2nd Gen (CEFO): gen1 and gram - anaerobes
Cefotetan and Cefoxitin
No pseudomona/ MRSA/ Enterococcus coverage
3rd Gen (CEFT): gen2 + pseudomonas coverage
Ceftazidime and Ceftriaxone (meningitis cause crosses BBB)
No MRSA or Enterococcus coverage
4th Gen (CEFI): same as 3 but more effective for pseudomonas
Cefipime
5th Gen (CEFTA): only one that targets MRSA
Ceftaroline
Carbapanems (-PENEM)
Structure
Derived from
Against what
Adverse reactions
Related to penicillin’s and cephalosporins, have β-lactam ring
Compound of bacterial origin
Increased effectiveness against gram - bacteria and increased effectiveness against most β-lactamases
Reserved for life-threatening diseases with resistance
Names:
Imipenem (prototype) + Cilastatin (Renal dehydropeptidase inhibitor /DHPI)
Also Meropenem, Doreipenem, Ertapenem → These do not require a DHPI
Adverse effects:
Renal disease requires decreasing dose due to decreased renal clearance
Toxicity leads to CNS toxicity (seizures in elderly)
Can only be prescribed by
Monobactam (AM)
Structure
Against what
Adverse reactions
Name
Structure: Monocyclic β-lactam
Narrow Spectrum: Similar to 3rd gen cephalosporins including pseudomonas, but not gram + and anaerobes
Highly resistant to β-lactamases
Adverse effects: Superinfections and GI disturbances
Aztreonam: used when pt can’t tolerate aminoglycosides due to renal insufficiency and when resistant to 3rd gen cephalosporins
Bacitracin
Structure
MOA
Against
Adverse effects
Structure: cyclic peptide
MOA: Inhibits bacterial cell wall formation
Against gram + bacteria and mostly used as a topical ointment, derm or ophthalmic
Adverse effects:
Poor absorption
Excretion by glomerular filtration
IM use discontinued due to toxicity
Vancomycin
Structure
MOA
Against
Resistance
Adverse effects
Structure: glycopeptide, acid labile and hydrophilic (IV use only)
MOA: Hydrogen bonds to D-ala and prevents transpeptidase from binding and cross linking of NAM-NAG units
Bypasses PBP2 mutations so it can kill MRSA
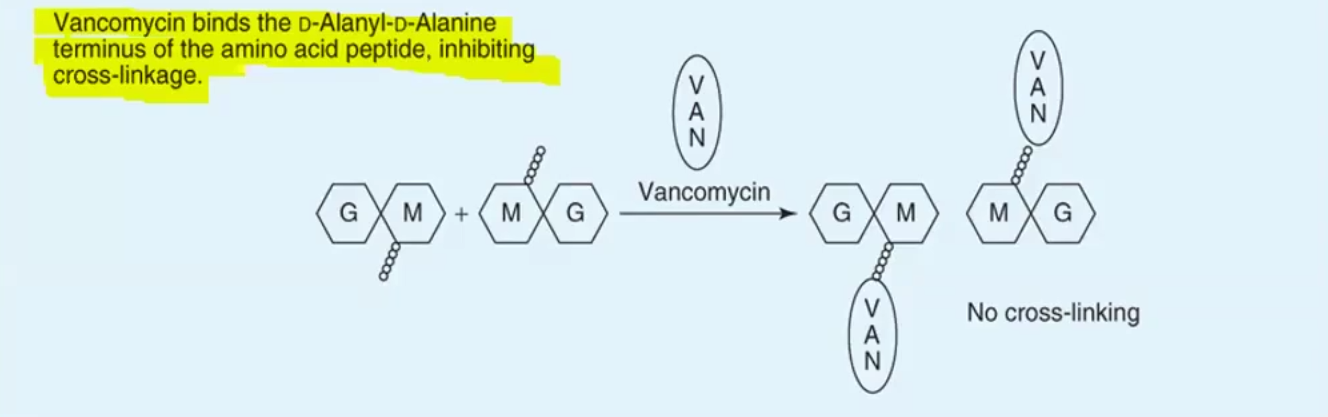
Also blocks trans-glycosylase mediated polymerization
Against:
Narrow spectrum: gram + bacteria including MSSA and MRSA; too large to kill gram -
Drug of choice for: MRSA, endocarditis, sepsis, pneumonia, osteomyelitis and cellulitis
Resistance:
Vancomycin Intermediate S. aureus (VISA) and Vancomycin Resistance S. aureus (VRSA)
Vancomycin Resistant Enterococcus (VRE): substitutes D-ala with D-lactate so vancomycin cannot block cross-linking
Adverse effects
Renal elimination dependent on creatinine clearance
Red man syndrome: pseudo-allergy due to rapid IV infusion
Nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity
Daptomycin
Structure
MOA
Against
Resistance
Adverse effects
Structure: cyclic peptide
MOA: Depolarizes bacterial cell membrane by binding Ca2+ and causes ion leakage, leading to cell death (NOT LYSIS)
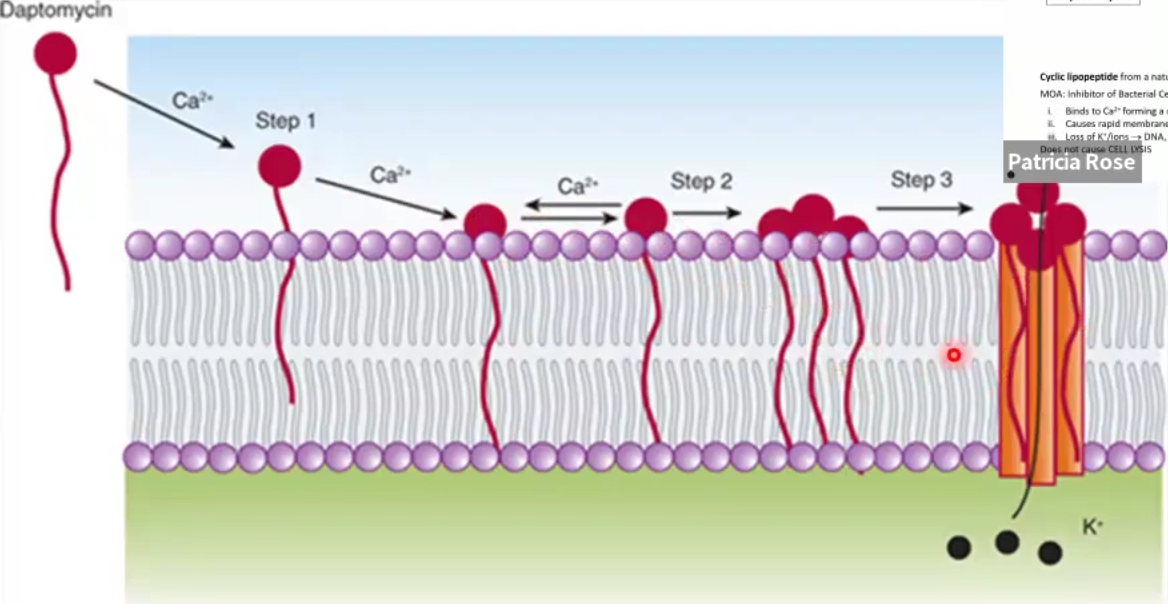
Against: Gram +, MRSA, VRSA, VISA, VRE
Same use as vancomycin: skin, eye, osteomyelitis, bacteremia, sepsis, endocarditis
Resistance: bacteria find a way to reset membrane potential
Adverse effects:
Don’t use for pneumonia: Inactivated by lung surfactants
Myopathies and rhabdomyolysis:
Stop taking statins at the same time because risk for myopathy increases
Fosfomycin
Structure
MOA
Against
Structure: phosphoenolpyruvate analog
MOA: Inhibits transferase in early stage of bacterial cell wall synthesis
Against both gram + and negative
Synergistic with β-lactams, aminoglycosides and fluoroquinones
Use for UTI’s, one dose for females and 9-21 Sundays for males
Cycloserine
Structure
MOA
Against
Adverse effects
Structure: structural analog of D-ala
MOA: transpeptidase binds it instead of D-ala, prevents cross-linking
Against both gram + and - bacteria
Only used as a second-line treatment for treatment of tuberculosis resistant to first-line agents
Administered orally, can enter CSF
Adverse effects: Dose-related CNS toxicity and peripheral neuropathies
Polymyxin B
Structure
MOA
Against
Adverse effects
Combinations
Structure: group of cationic basic peptides
MOA: Imitates cationic detergents and disrupts cell membrane, causing leakage
Similar MOA to Daptomycin
Against only gram - bacteria
Adverse effects:
Only B polymyxin is available in the USA
Restricted for topical use only
Combinations:
Polymyxin B + Trimethoprim = for both gram - and gram +
Polymyxin B + Hydrocortisone
Triple antibiotic has what 3 drugs
Neomycin, Bacitracin and Polymyxin B