AP Econ Unit 1 Vocab
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
Positive Economics
Economic statements that are testable through empirical evidence.
Normative Economics
Subjective opinions that cannot be proven true or false.
Product Market
“Place” where goods and services produced by businesses are sold to households.
Resource (Factor) Market
“Place” where resources (land, labor, capital, entrepreneurship) are sold to businesses.
Economics
The science of scarcity - the study of choices.
Scarcity
The limitedness of resources - unlimited wants, limited resources - forces us to make choices.
Microeconomics (mostly US)
Study of small economic units such as individuals, firms, and markets - how they work/coexist
Macroeconomics (US and Global)
Study of large economy as a whole - more headline and government stuff
Tradeoff
The entire list of alternatives to a decision
ALL decisions involve trade-offs
Opportunity Cost
Most desirable alternative given up when you make a choice
Price
Amount buyer/consumer pays (consumer perspective)
Cost
Amount seller pays to produce a good (producer perspective)
Investment
The money spent by businesses to improve their production
Consumer Goods
Created for direct consumption (ex: pizza)
Capital Goods
Created for indirect consumptions (ex: oven)
5 Key Economic Assumptions:
Society has unlimited wants and limited resources (scarcity exists)
Due to scarcity, choices must be made. Every choice has a cost (a tradeoff)
Everyone’s goal is to make choices that maximize their satisfaction. Everyone acts in their own “self interest” (rational actors)
Everyone makes decisions by comparing the marginal costs and marginal benefits of every choice (cost/benefit analysis)
Real-life situations can be explained and analyzed through simplified models and graphs (makes easier to understand with a tradeoff of absolute accuracy)
4 Factors of Production
Land - All natural resources used to produce goods and services
Labor - Effort a person devotes to a task for which that person is paid
Capital - Physical: human made resources used to create other goods and services. Human: skills or knowledge gained by a worker through education and experience.
Entrepreneurship - Ambitious leaders that combine the other factors of production to create goods and services.
Economic System
Method used by society to produce and distribute goods and services
3 Economic Questions
What goods and services should be produced?
How should these goods and services be produced?
Who consumes these goods and services?
Command Economy
Government owns all resources and answers the 3 economic questions (Ex: North Korea)
Free Market Economy
Little to no government involvement in the economy, individuals own resources and answer the 3 economic questions
Laissez Faire
Let it be (relates to free market economies)
Mixed Economies
A system with free markets but also some government intervention (almost all countries)
Private Sector
Part of the economy that is run by individuals and businesses
Public Sector
Part of the economy run by the government
Factor Payments
Payment for the factors of production; rent, wages, interest, and profit
Transfer Payments
When the government redistributes income (Ex: welfare, social security)
Subsidies
Government payments to businesses (Ex: agricultue, airlines)
Production Possibilities Curve (PPC)
A model that shows alternative ways that an economy can use its scare resources
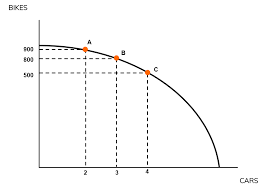
Concave PPC
Shows increasing opportunity costs
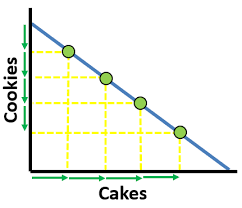
Constant Opportunity Cost PPC
Resources are easily adaptable for either good
Convex PPC
Decreasing opportunity cost, specialization
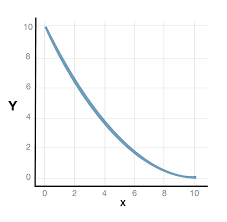
3 Shifters of PPCs
Change in resource quantity or quality
Change in technology
Change in trade
Per Unit Opportunity Cost
Opportunity costs / Units gained
Productivity
A measure of efficiency that shows the number of outputs per unit of input
Absolute Advantage
The producer that can produce the most output OR requires the least amount of inputs (resources)
Comparative Advantage
The producer with the lowest opportunity cost of production
Terms of Trade
The agreed upon conditions that would benefit both countries
What are the advantages of specialization and trade?
Being able to specialize in 1 item and trade for another allows for higher production and overall more products gained
Why do businesses and countries work to improve their productivity?
Since all resources are scarce, improving productivity allows us to produce more stuff with fewer resources
Output Question
Amount of input is the same for both countries, only the OUTPUT is different.
OOO = Output: Other goes Over
Input Question
The amount of output is the same for both countries, only the INPUT is different.
IOU = Input: Other goes Under
How should absolute and comparative advantage be used to inform decisions about specialization and trade?
Countries should specialize and trade when they see a relatively lower opportunity cost
How do you find the terms of trade?
The terms of trade has to be in between the 2 countries opportunity costs
Explicit Costs
The traditional out of pocket costs associated with making a decision
Implicit Costs
The value of the opportunity costs of making a decision
Utility
The amount of satisfaction or enjoyment consumers receive from the goods or services they consume
Total Benefits
The total amount of satisfaction people receive from all the goods and services they use
Total Costs
Include the time, effort, and expense spent to obtain the goods and services
Optimal Choice
The level at which you receive the greatest benefit for the least cost
Total Net Benefits
Total benefit - Total costs
Marginal Analysis
Making decisions based on increments
Marginal Benefit
The amount of satisfaction people receive from increasing their consumption by 1 unit of the good or service
Marginal Cost
The time, effort, and expense spent to obtain 1 additional unit of the good or service
Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility
As you consume anything, the additional satisfaction that you’ll receive will eventually start to decrease
Utility Maximization Rule
Consumers money should be spent so that the marginal utility per dollar of each goods equal each other
Utility Maximization Rule Equation
MUx/Px = MUy/Py