Immigration & Industrialization Vocab
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
migrate
Two more specific definitions: 1) To move to one place to another WITHIN one's home country, 2) To move somewhere else TEMPORARILY

emigrate
the act of leaving one's home country in order to settle in another. (think E for EXIT)

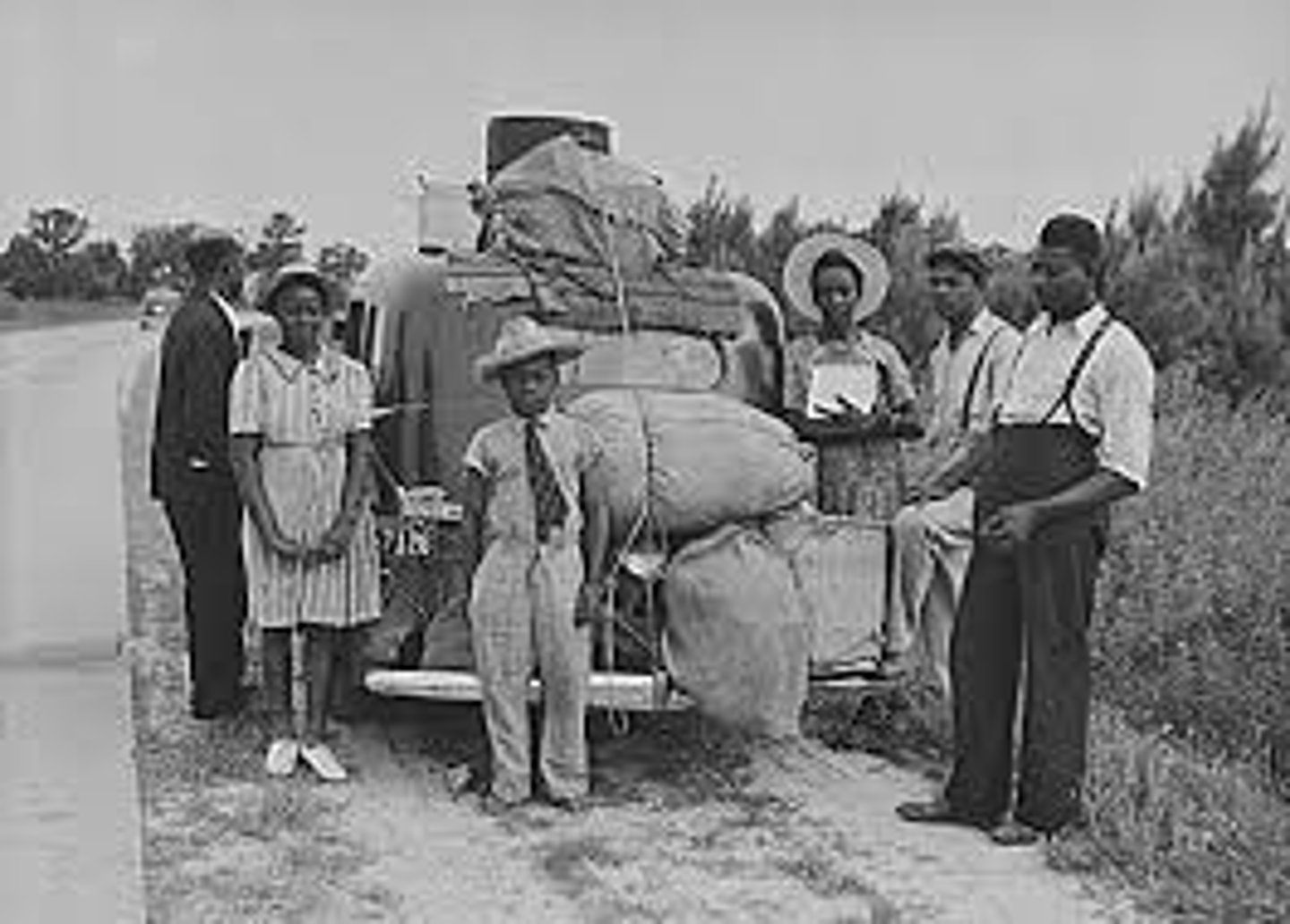
immigrate
the act of moving into a foreign country or region as a permanent resident (think I for IN)

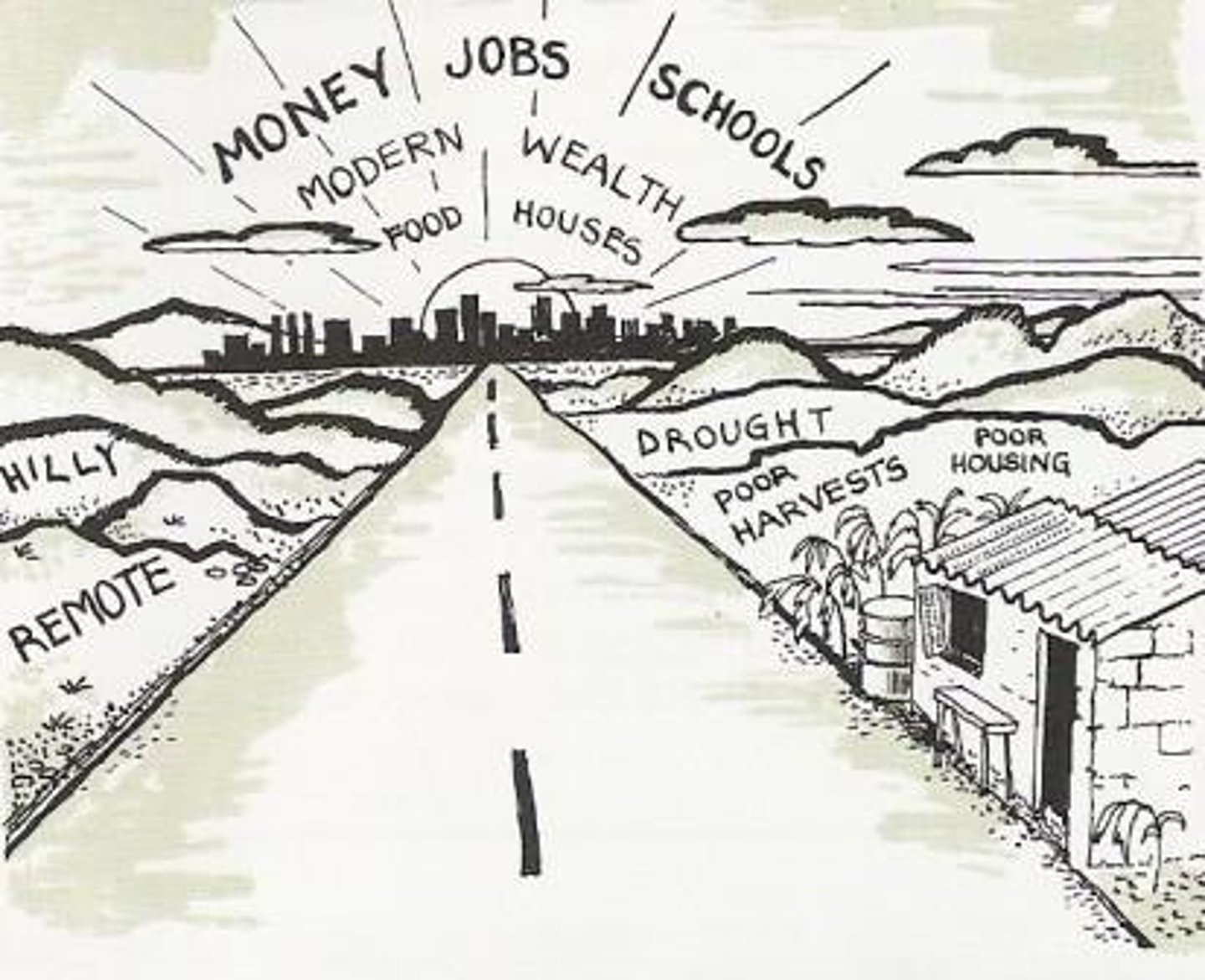
push factors
Negative conditions that causes people to leave their homelands and migrate to another region (poverty, violence, natural disaster, etc.)
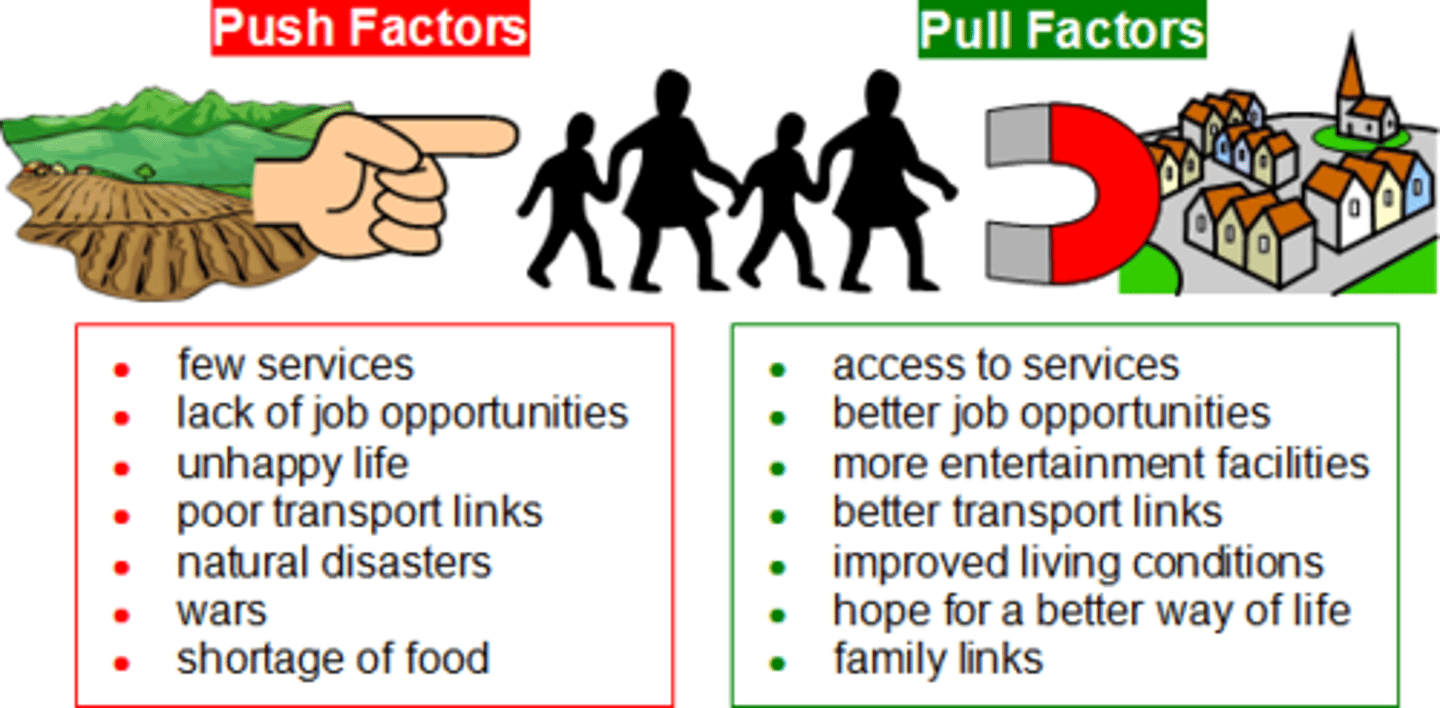
pull factors
Positive conditions that motivate people to move to a new location (higher pay, peace & security, voting rights & freedoms, etc.)
xenophobia
a fear/hatred of foreigners (pronounced zee-nuh-phobia or zen-nuh-phobia)

Sinophobia
fear or dislike of China, its people, and culture (pronounced sigh-noh-phobia)

Chinese Exclusion Act of 1882
This federal law prohibited any additional Chinese laborers to enter the country while allowing students and merchants to immigrate.

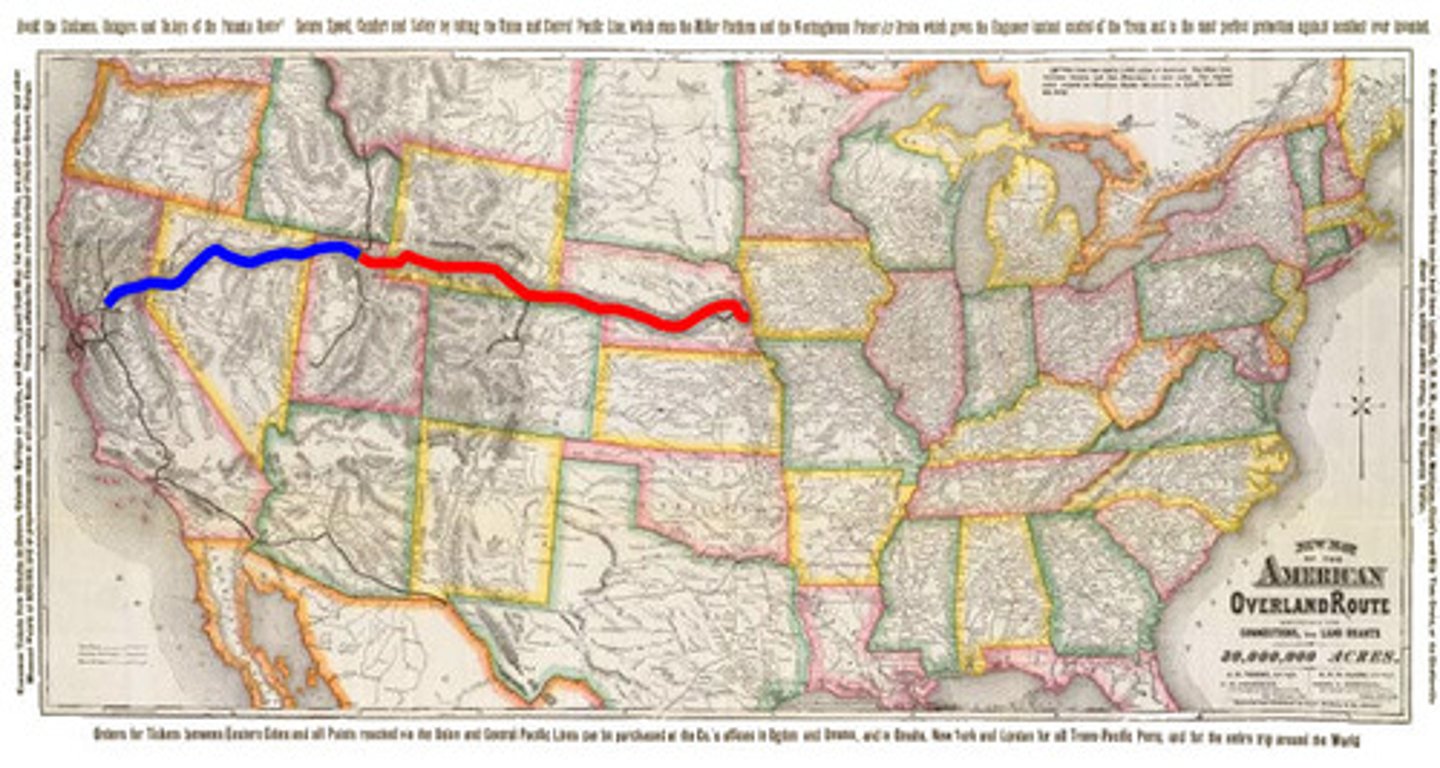
Transcontinental Railroad
This path was completed in 1869, linking the eastern railroad system with California's railroad system, revolutionizing transportation in the west. Built mostly by Irish & Chinese immigrants.
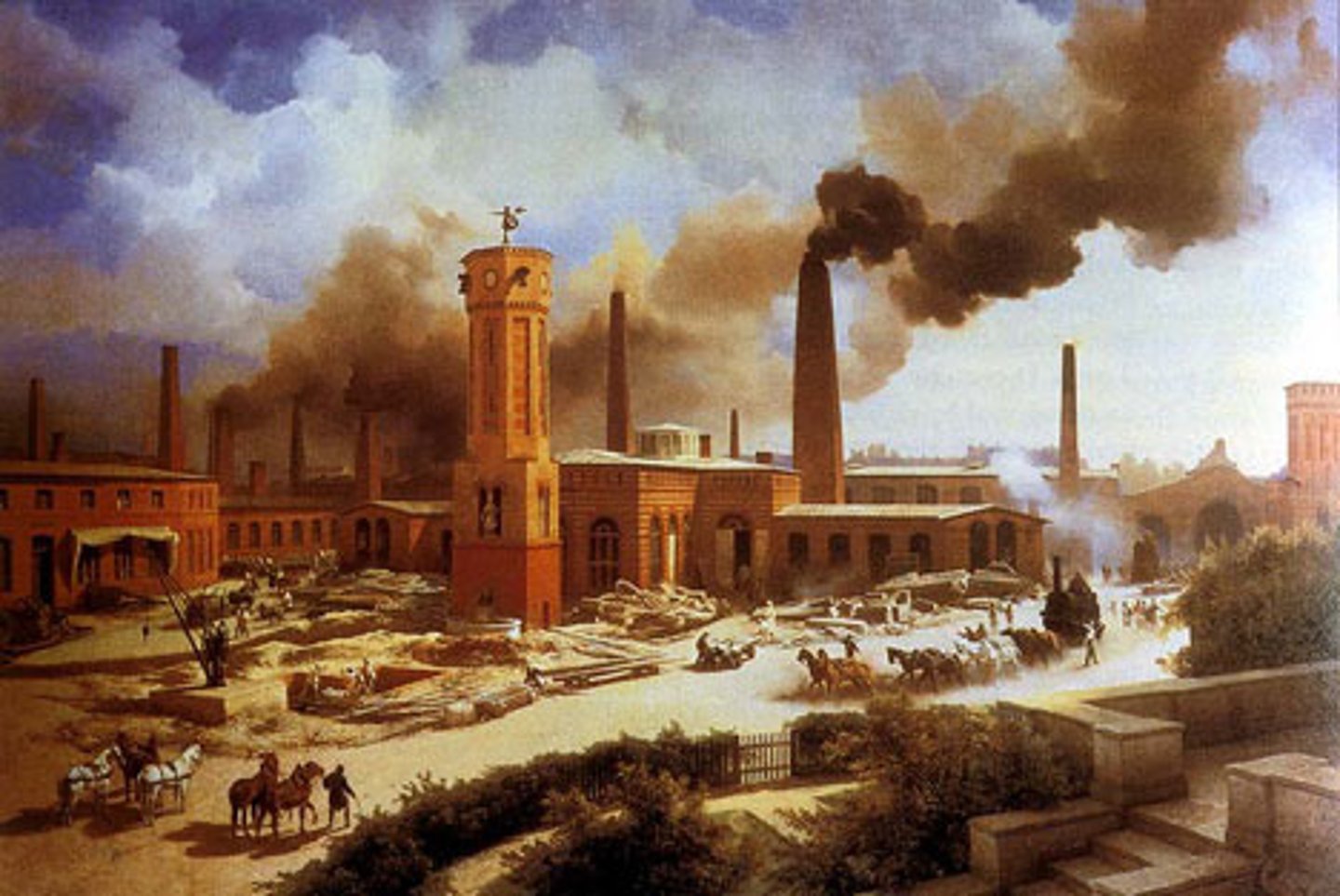
Industrialization
The process of moving from an agricultural society, in which most goods are handmade, to a society that thrives on machine-manufactured goods.
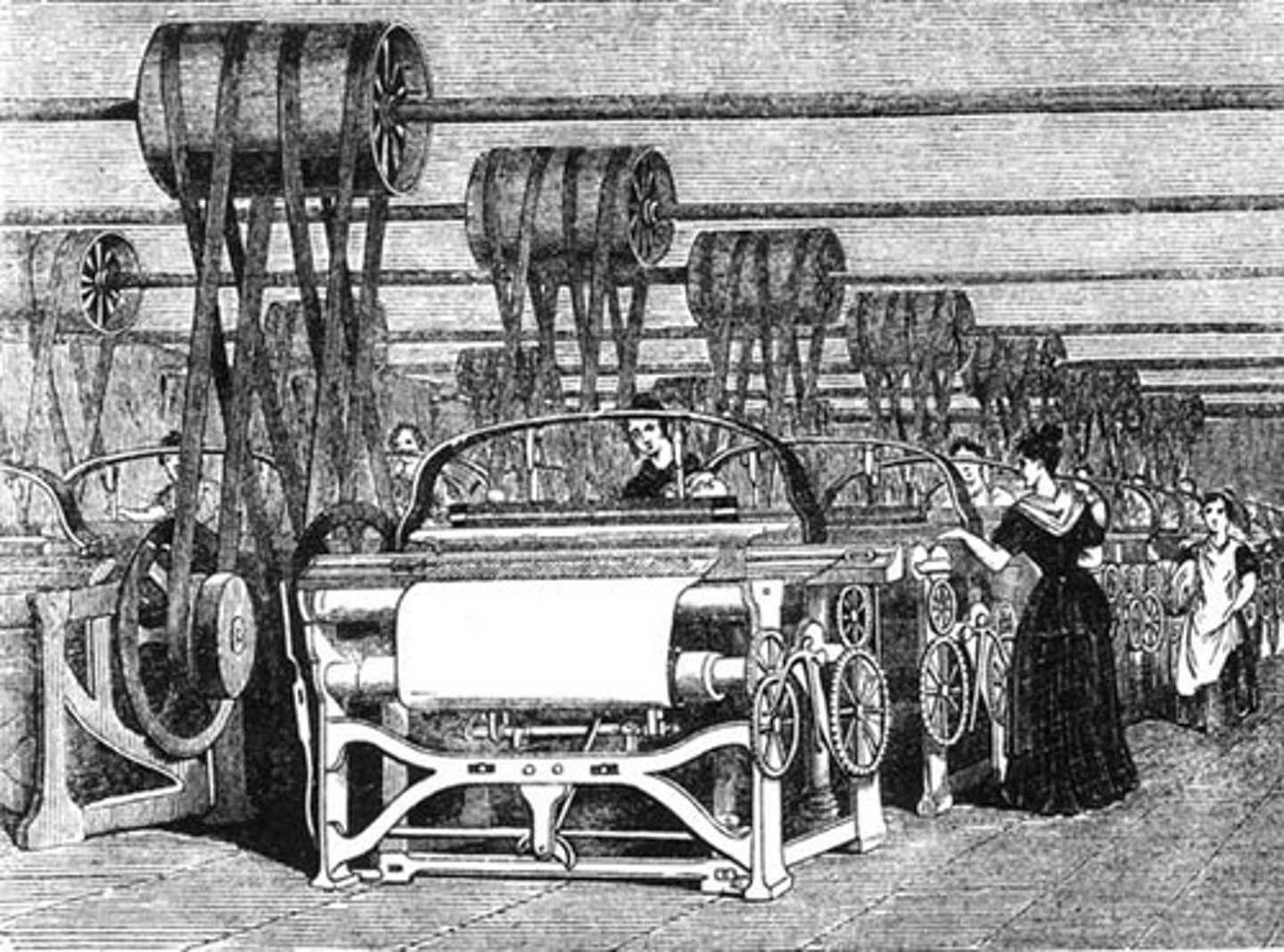
Industrial Revolution
This was a period of change in the 1700s & 1800s that transformed the economy and society of much of the world.
Many countries industrialized, transitioning from producing solely farmed and handmade goods to using new manufacturing technology.

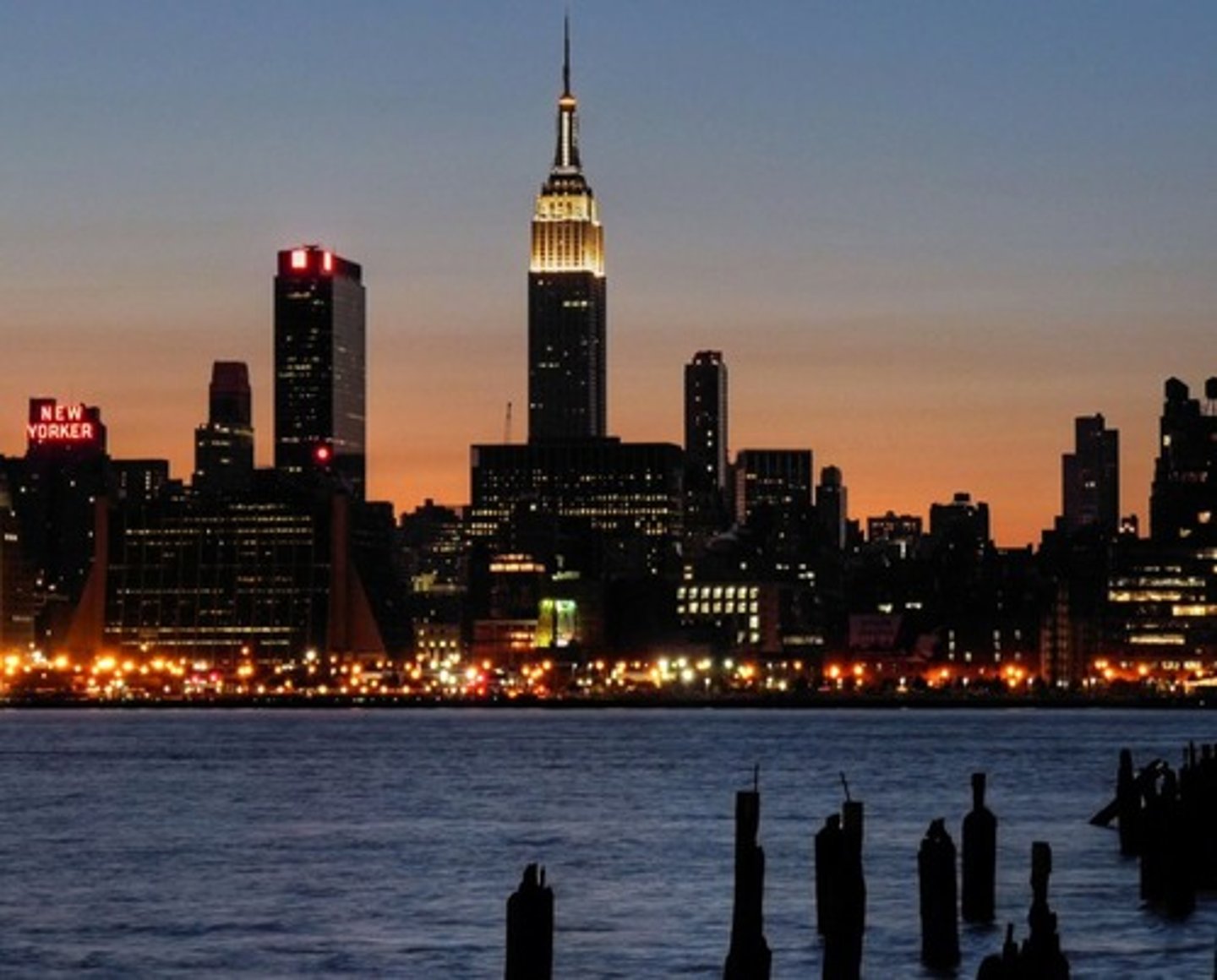
urban
Describing a place that has the characteristics of a city or town. These are dense centers of population, business, and culture.

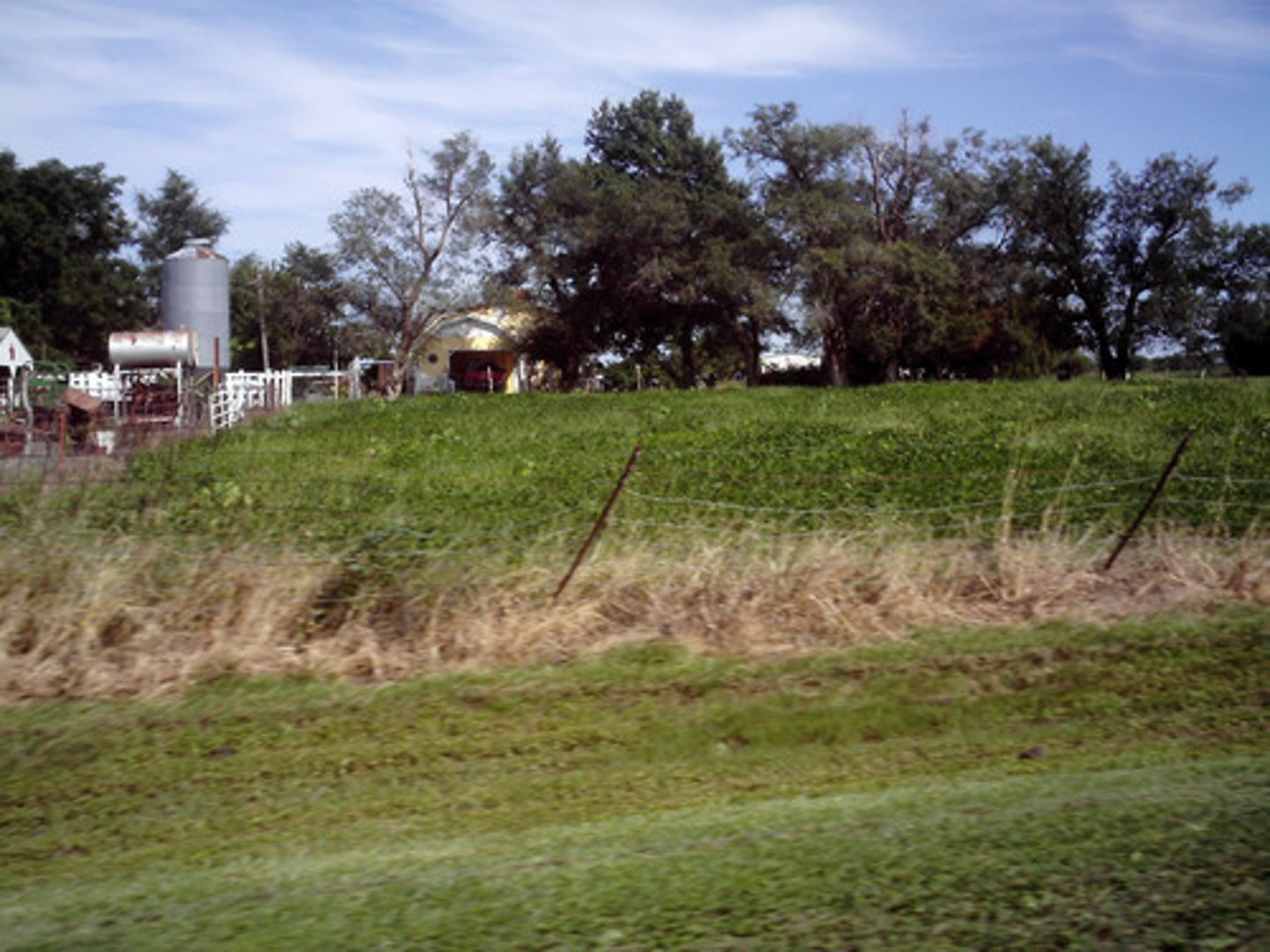
rural
Describing places in the countryside, usually some distance away from cities and suburbs.

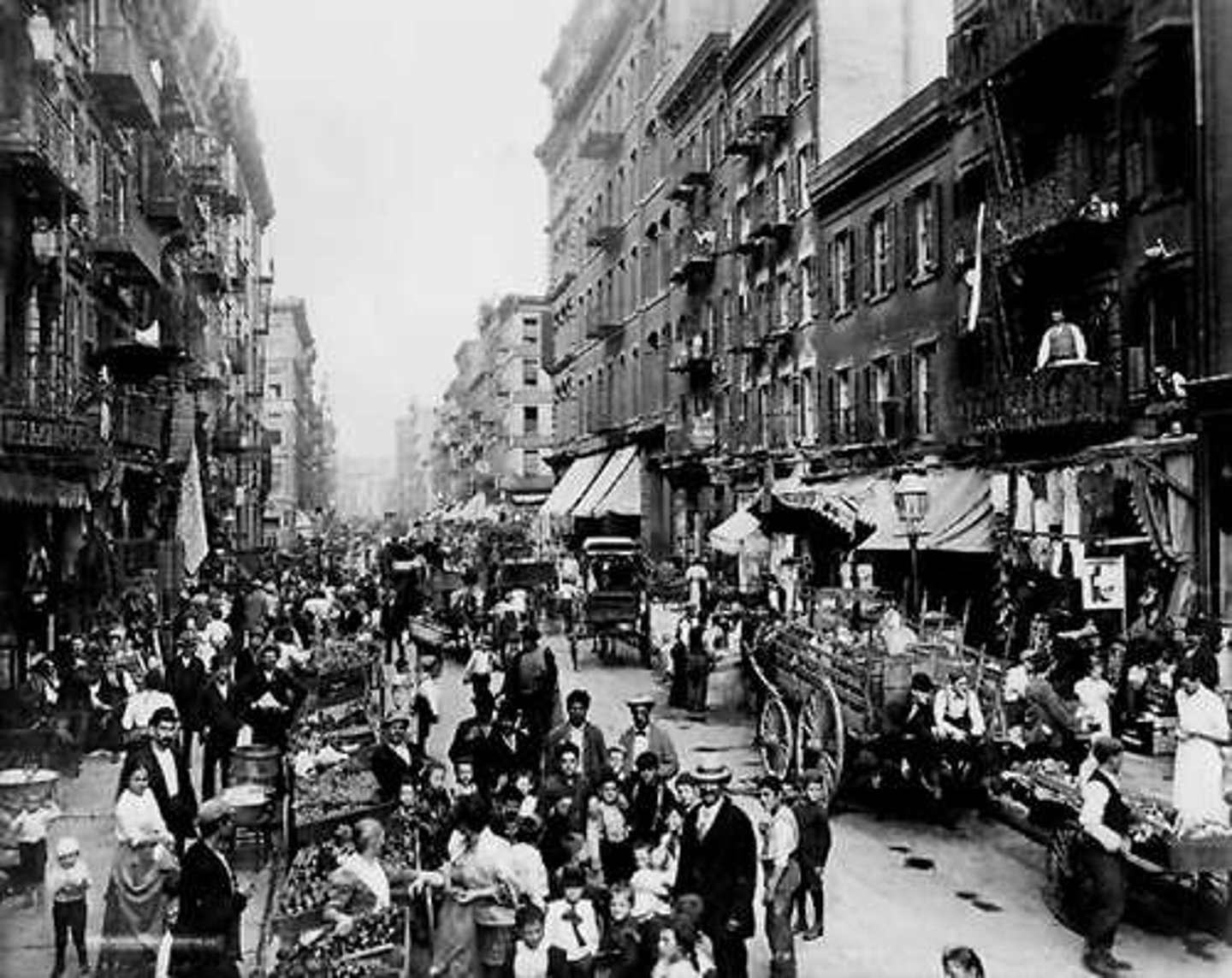
Urbanization
This is the rapid expansion of cities due to a large movement of people to the city from the country.

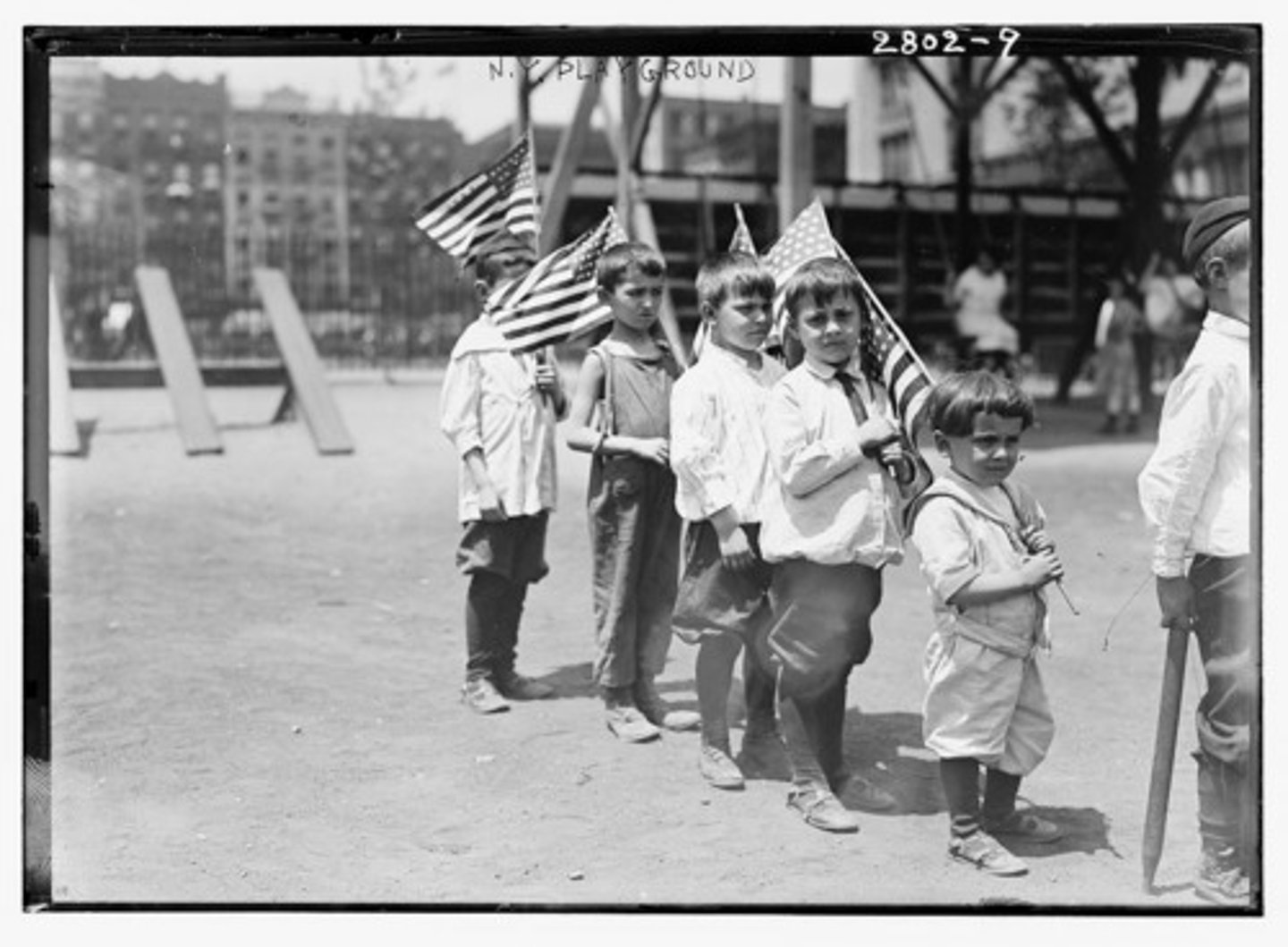
assimilation*
the process of becoming more similar to the dominant cultural group to "fit in" (ex: some immigrants might learn English in order to assimilate into an English-speaking society) BONUS*

Americanization*
the process of acquiring or causing a person to acquire American traits and characteristics (ex: some immigrants change their names to be more easily pronounced by Americans)* BONUS

culture shock*
the feeling of disorientation experienced by someone who is suddenly surrounded by an unfamiliar culture, way of life, or set of attitudes. * BONUS

citizen
A person with certain official rights and responsibilities in their country or community.

Manufacturing*
Combining raw materials (ex: cotton) and processed goods into finished products (ex: clothing)* BONUS

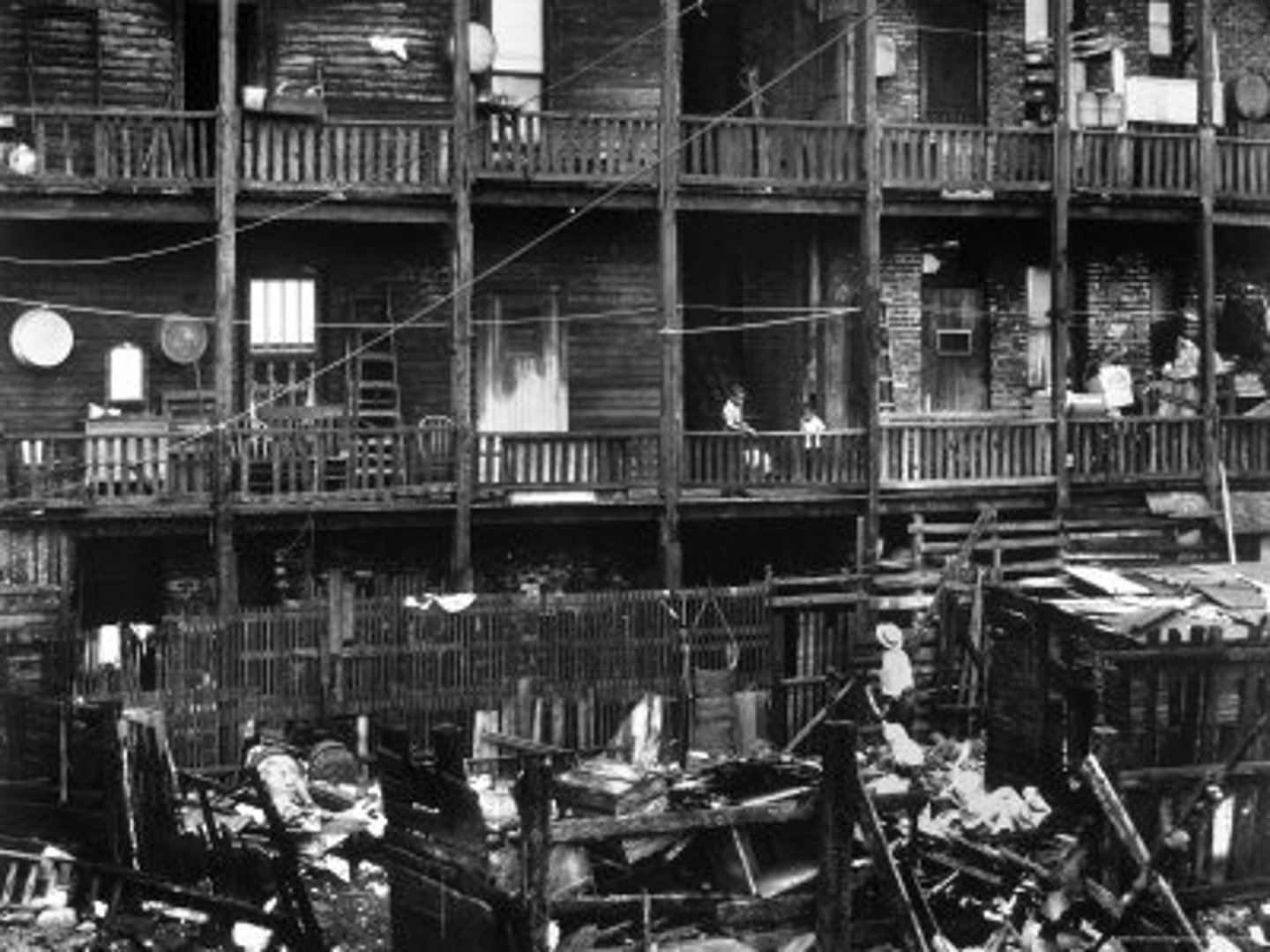
Tenement
A building in which several families rent rooms or apartments, often with little sanitation or safety

refugee*
A person who has been forced to leave their country in order to escape war, oppression, or natural disaster. (This is different than choosing to move to get a higher paying job) * BONUS
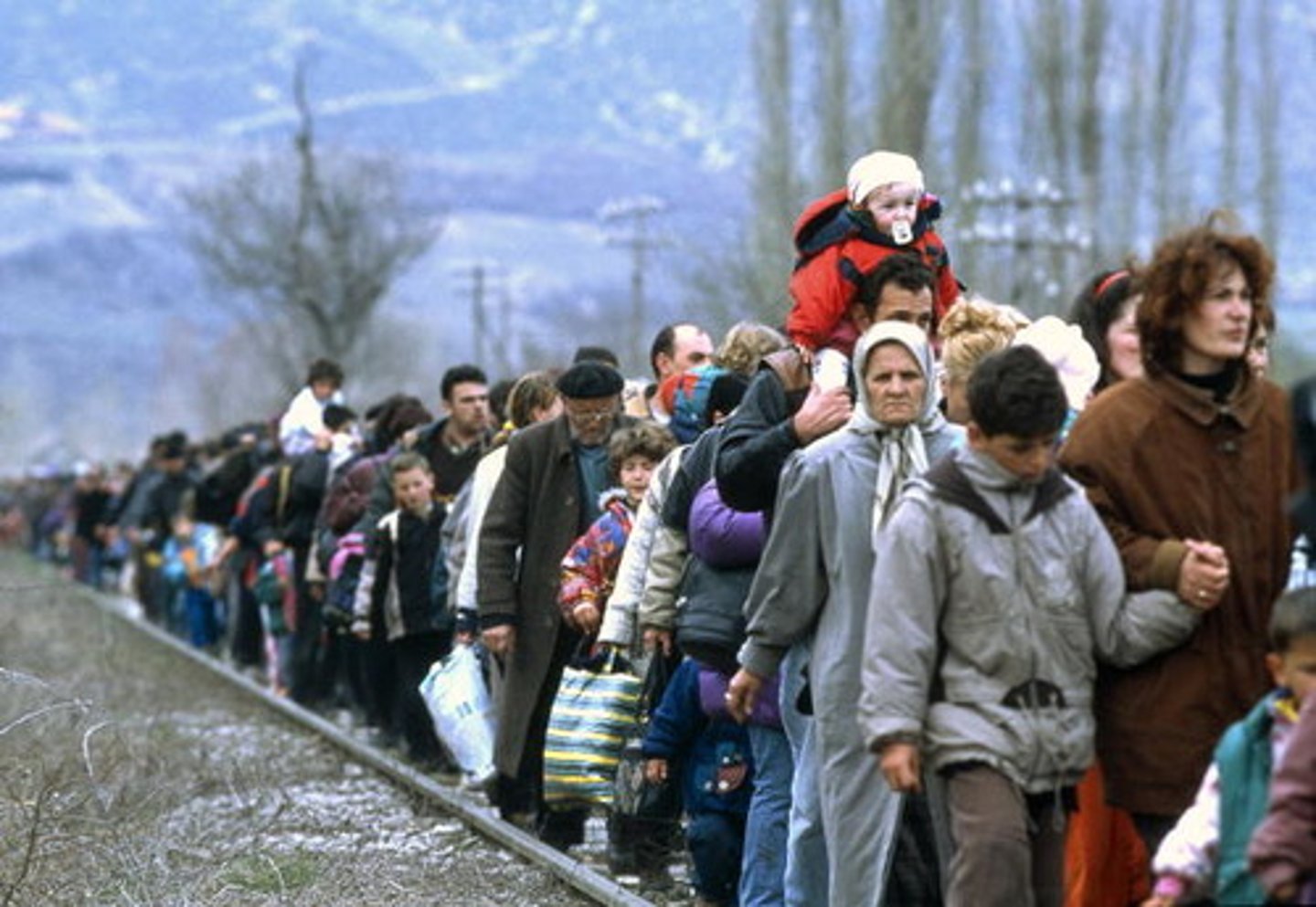

asylum*
This is a temporary legal designation given to some migrants who are let into a country on an emergency basis for their safety. One must apply for asylum status at a U.S. port of entry, and it may be denied. (a refugee could apply for asylum) * BONUS

The "American Dream" *
The widespread belief that the United States is a land of opportunity and that individual initiative and hard work can bring economic success to anyone. * BONUS

Nativism*
favoring the interests of native-born people over foreign-born people * BONUS

Nativist*
a person who favors those born in his country and is opposed to immigrants * BONUS


Gilded Age
a period of rapid economic growth and industrialization in the United States during the late 19th century, marked by corruption and social inequality.
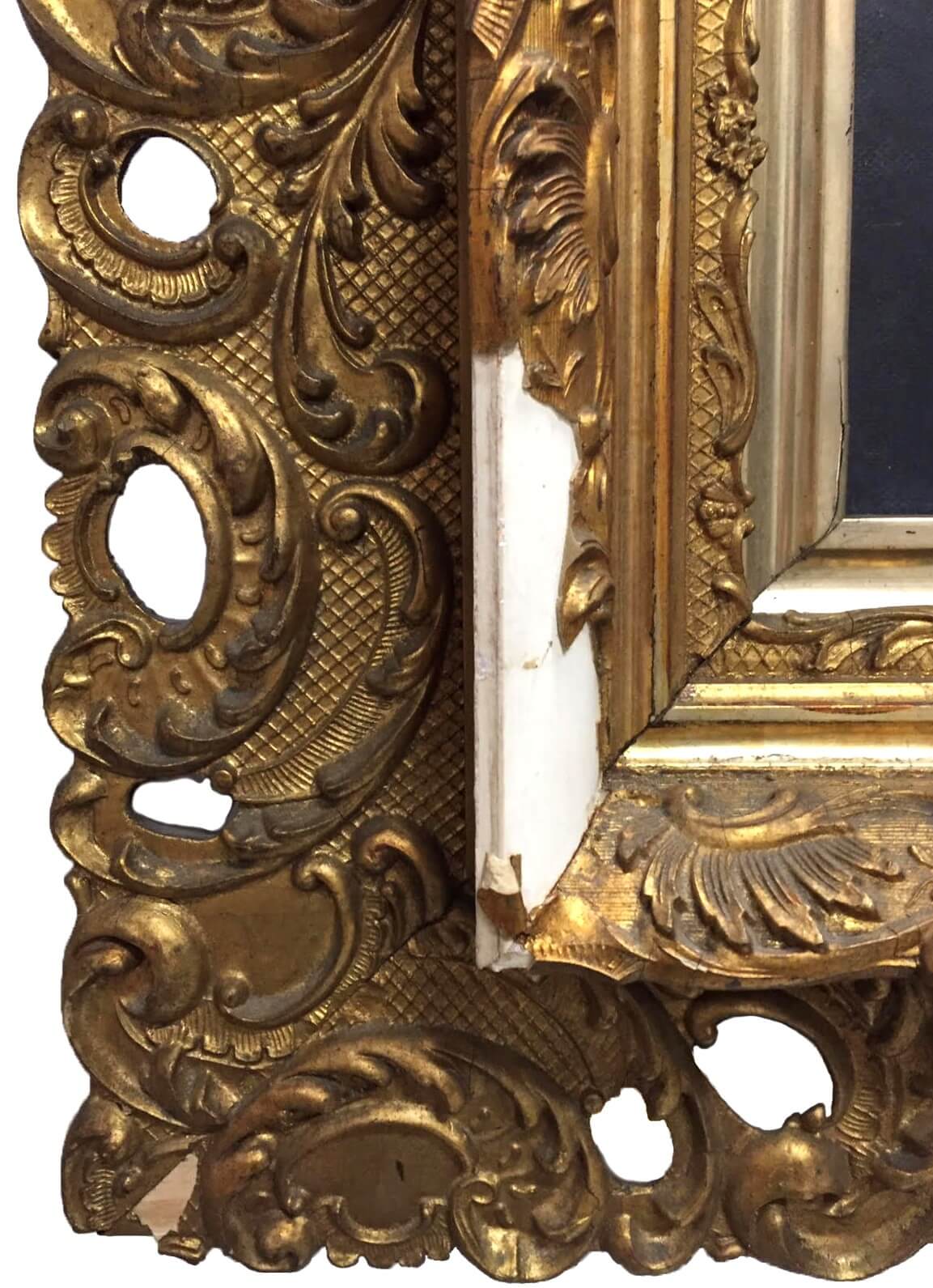

gilded
covered in a thin layer of golden material, with a cheaper material underneath

corrupt
“Being willing to act dishonestly or abuse power in order to get money or other personal gain.” Political leaders & government officials during the Gilded Age often behaved in a manner that could be described this way.

unions
Organizations of workers who come together to fight and negotiate for better working conditions & pay from their employer.

working class
Workers who are often paid hourly or by how much they produce, often doing difficult, unsafe, or underpaid work. They typically include laborers, factory workers, and service industry employees.
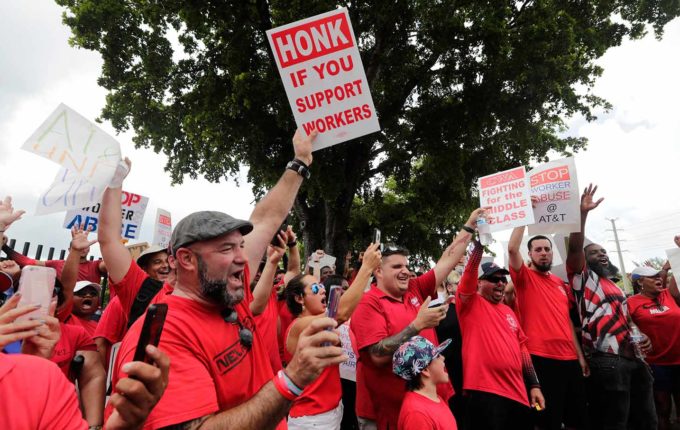

strike
When workers who are unhappy decide together to temporarily stop working for their employer until meaningful improvements are made to their working conditions.

laissez-faire economics*
“When the government has minimal interference and involvement with the economy or businesses.” During the Gilded Age, this approach allowed for rapid industrial growth, often at the expense of workers' rights and safety. * BONUS
monopoly*
When one company effectively has full control over a market for a certain product, without any significant competitors. This can lead to higher prices and reduced choices for consumers. * BONUS
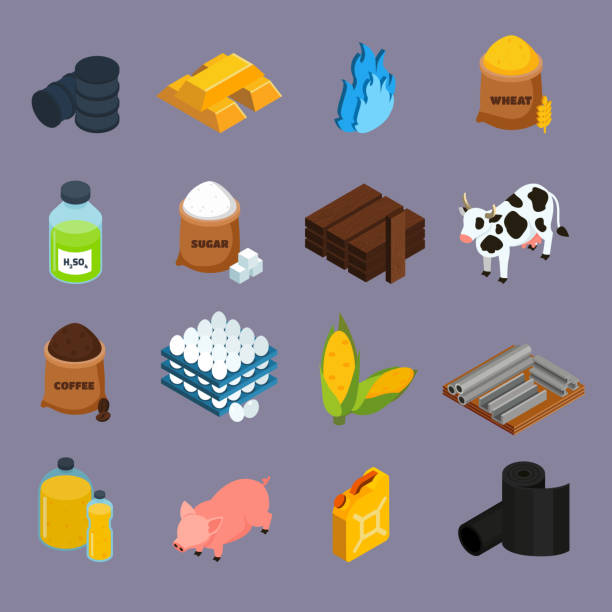


raw materials*
Natural resources that can be transformed into other goods, such as cotton → clothing * BONUS

corporation*
A large company or business. Individual consumers can purchase small "shares" of ownership in these big companies through stocks. * BONUS

Triangle Shirtwaist Factory Fire
A tragic factory fire disaster in 1911 that resulted in the deaths of 146 garment workers, many of whom were immigrant teenagers. This event highligted unsafe working conditions and led to improvements in labor laws. The name of this NYC factory was...

Titans of Industry/Robber Barons*
powerful industrial leaders in the Gilded Age who made huge fortunes and influenced economic policies & were often criticized for mistreatment of workers. They were key figures in sectors like railroads, oil, and steel (Carnegie, Rockefeller, etc.)
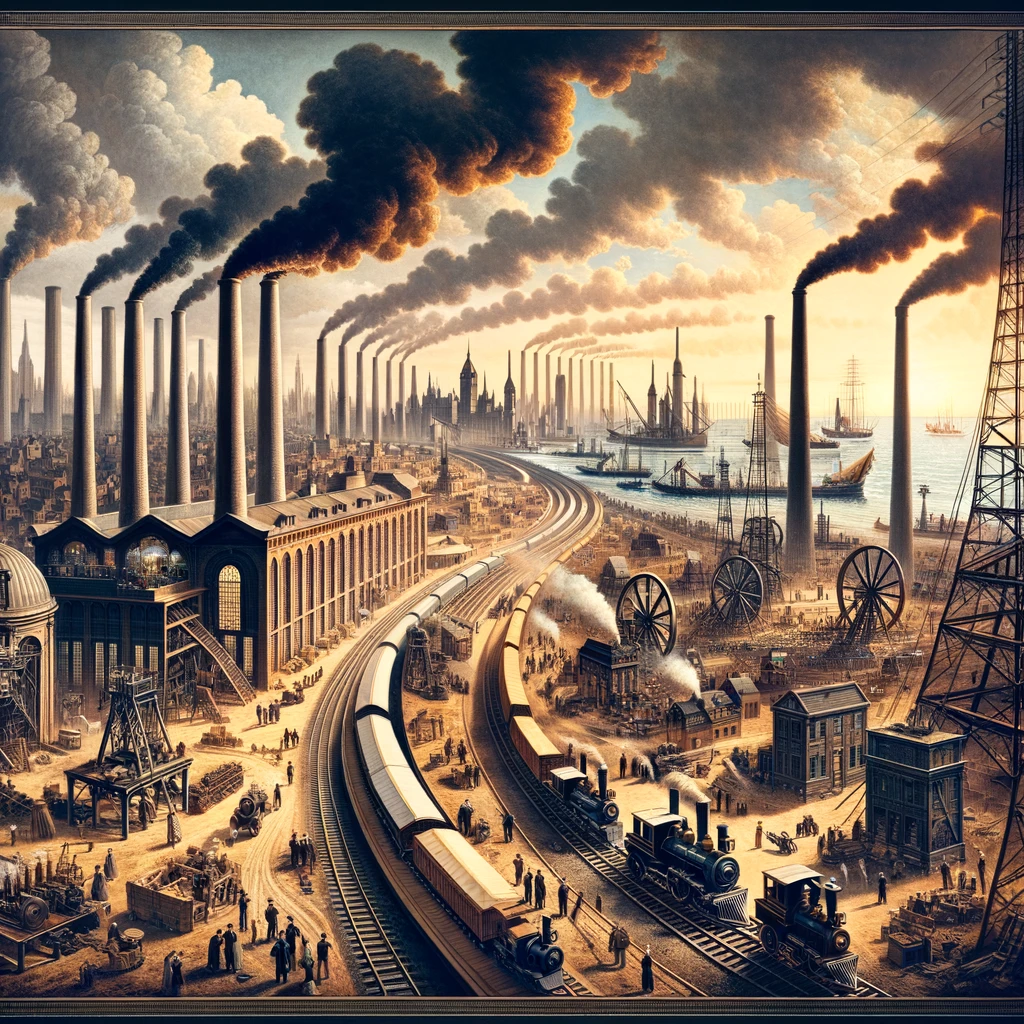

industrialization
The process of moving from an agricultural society, in which most goods are handmade, to a society that thrives on machine-manufactured goods.

Progressive Era
A period of social activism and political reform in the United States from the 1890s to the 1920s, aimed at addressing issues caused by the industrialization, urbanization, and political corruption of the past Gilded Age.

reform
The process of making changes to improve a system, organization, or law, often associated with social and political movements to address injustices and inefficiencies.
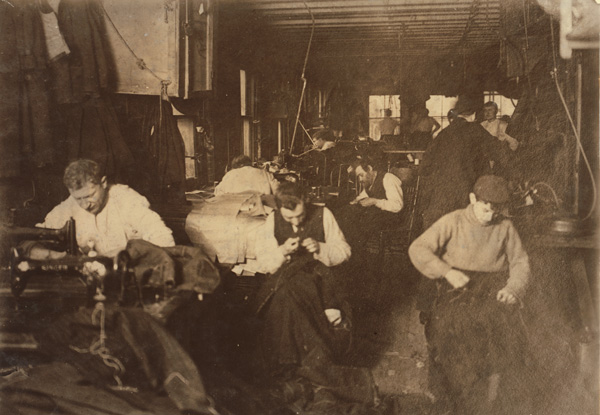

sweatshop*
A factory or workshop, often in poor conditions, where workers, including children, are employed for long hours and low wages, typically in the garment industry. * BONUS

wealth inequality
When there is a significantly unequal distribution of financial assets and unequal access to resources in a society.

child labor
This practice was very common during the Gilded Age, involving using young children & teens as workers in mines, factories, and farms for long hours w/ often unsafe conditions & little pay.

capitalism*
An economic system where private individuals (rather than the gov’t) own and control property and businesses, aiming to maximize profit ($$$) through competition. * BONUS
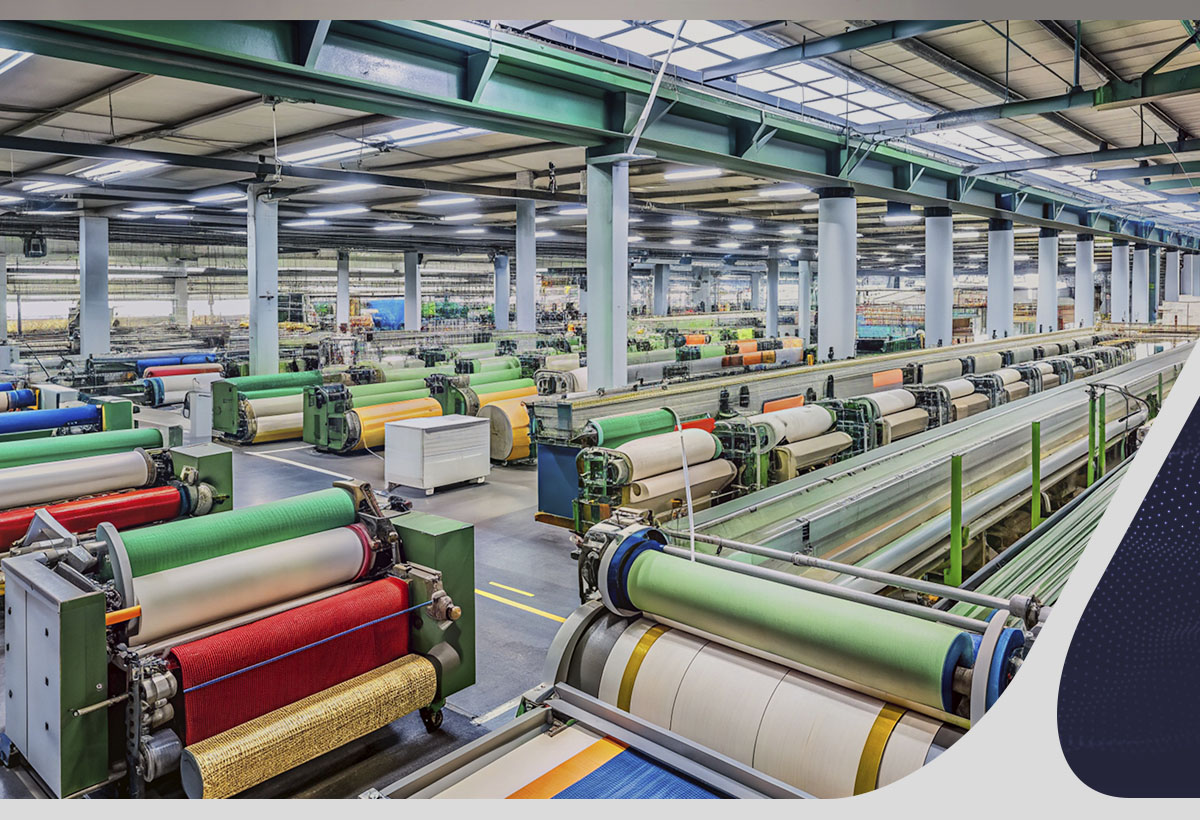

textile/garment industry*
The sector of the economy that produces clothing and fabrics. This industry employed a lot of children during the Gilded Age, often in sweatshops. * BONUS

Progressives/Reformers
A group of activists and politicians in the 18902-1920s who fought to address social issues and promote reforms in response to the challenges of industrialization and urbanization.

Temperance*
The social movement aimed at reducing or prohibiting the consumption of alcoholic beverages, advocating for moral and health improvements in society. * BONUS

Prohibition*
The banning of alcohol manufacture, sale, and transportation during the 1920s under the 18th Amendment. * BONUS

Regulation
A rule or law that controls how something is done or used. For example, after the Triangle Shirtwaist Fire, many new fire safety rules were put in place to protect workers.

Bootleggers*
Individuals who illegally produced or distributed alcohol during Prohibition. * BONUS

Settlement House*
Community centers founded during the Progressive Era in poor neighborhoods, providing services like education, healthcare, and social support to immigrants and others * BONUS
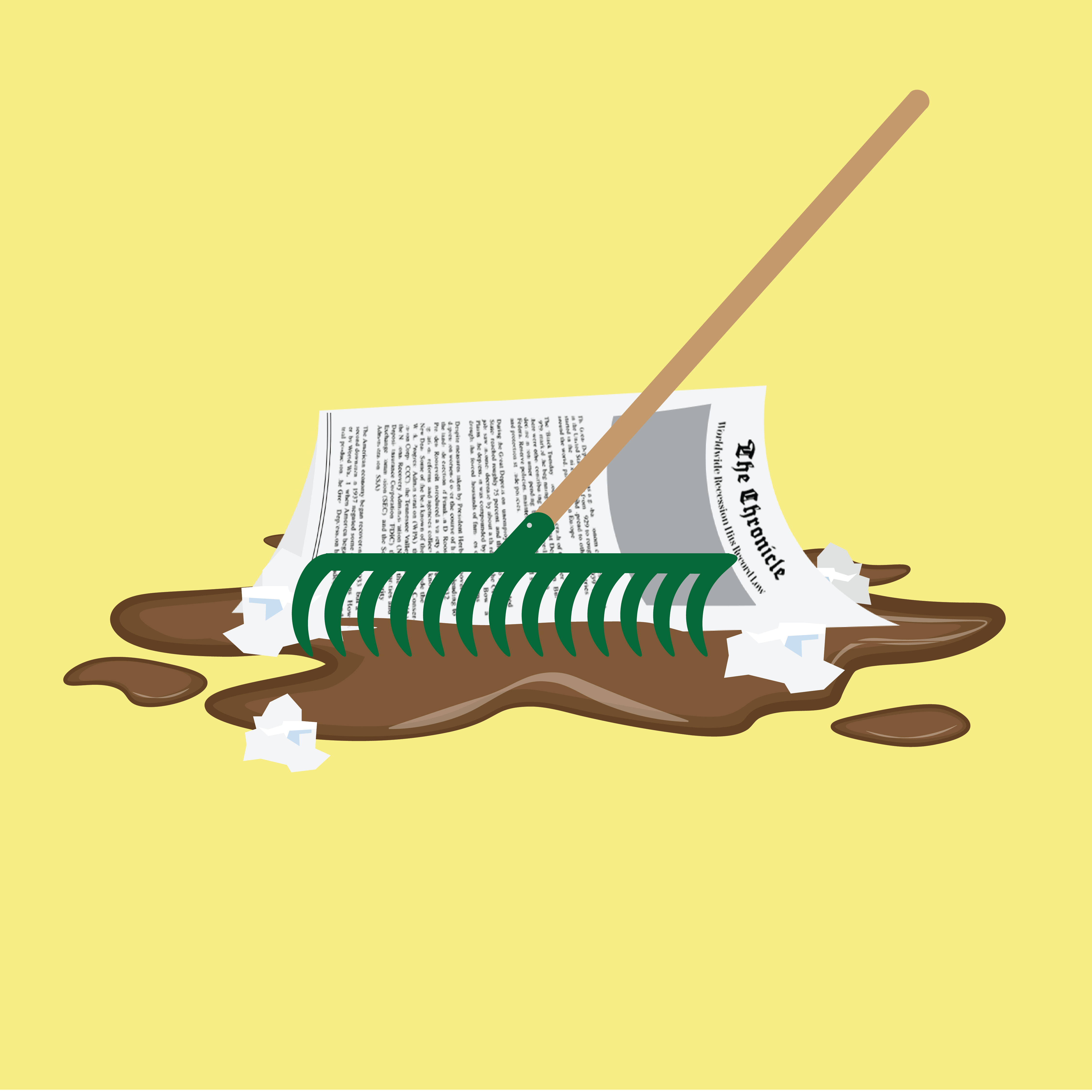

Muckrakers*
Journalists who exposed corruption and social injustices during the Progressive Era, aiming to bring about reform & changes. * BONUS
progress
The process of improving or developing over time.

Immigration Act of 1917