Chem 501 All Exams & Quizzes
1/352
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
353 Terms
Catabolism
All the reactions by which complex molecules are broken down to simpler ones, energy-yielding reactions.
Conformation
The spatial arrangement of atoms free to assume different positions because of freedom of bond rotation.
Endergonic
A process that is accompanied by a positive change in free energy.
Weak interactions include:
Ionic bonds and hydrophobic interactions
A dynamic steady state results when the rate of synthesis or intake of a molecule equals the rate of its breakdown, consumption, or conversion into some other product.
True
The pKa for benzoic acid is 4.21. At a normal blood pH of 7.4 you would:
Expect mostly the basic form to be present
Hydrophobic interactions play an important role in micelle formation.
True
Name one amino acid that belongs to the polar, uncharged class using its one letter code.
S
Primary structure
The sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain.
Secondary structure
The local folding of the backbone of a polypeptide chain to form a regular, repeating structure.
Tertiary structure
The specific three-dimensional shape into which an entire polypeptide chain is folded.
Quaternary structure
The association of multiple polypeptide chains in a complete protein.
A 100 mL solution of 0.1 M alanine at pH 1.72 was titrated with 2 M NaOH solution. The pH was monitored and the results were plotted on a graph, as shown above. The key points in the titration are designated I to V. Identify the appropriate key point(s) in the titration where alanine is present predominantly as the species NH2-CH(CH3)-COO-
V
Consider the following two peptides:
I. Cys-Asp-Gln-Lys and II. Ser-His-Arg-Asn
Which peptide can be oxidized to produce a cystine linkage?
Answer I or II.
I
Reaction of the peptide, Glu-Met-Lys-Ala, with phenylisothiocyanate at pH 8.0 followed by mild acidification (first cycle of Edman chemistry):
would release phenylthiohydantoin-glutamate and the peptide Met-Lys-Ala.
Dialysis
process in which small molecules are removed from a complex mixture of molecules
Achiral
an object that is superposable on its mirror image
Isoelectric point
pH at which a solute has no net electric charge
Zwitterion
dipolar ion with spatially separated positive and negative charges
The amino acid sequence of a protein does not determine the tertiary structure adopted by the protein.
False
The peptide bond:
is rigid and planar
All of the following are types of secondary structures except:
domain
In an α helix, the R groups on the amino acid residues:
are found on the outside of the helix spiral
For the following statements, indicate whether they are true for myoglobin, hemoglobin or both.
Its function is to store O2 - Myoglobin
its O2 binding curve is sigmoidal - Hemoglobin
It binds O2 reversibly - Both
Proteins that do not perform any obvious chemical transformation, but control the ability of other proteins to carry out their physiological functions are:
regulatory proteins
For a reaction that can take place with or without catalysis by an enzyme, what would be the effect of the enzyme on the:
Activation energy of the reaction? Decrease
Standard free energy change of the reaction? No change
Cofactors
Inorganic ions or coenzymes required for enzyme activity.
Activation energy
The amount of energy required to convert all the molecules in 1 mol of a reacting substance from the ground state to the transition state.
Metal ion catalysis
Catalysis involving ionic interactions between a metal ion bound to an enzyme and the substrate.
In uncompetitive or mixed inhibition, an inhibitor:
binds reversibly at a site distinct from the active site
Allosteric enzymes function through irreversible, covalent binding of regulatory molecules called modulators.
False
Enzymes ensure that the product is more thermodynamically stable than the substrate.
False
Aldose structure
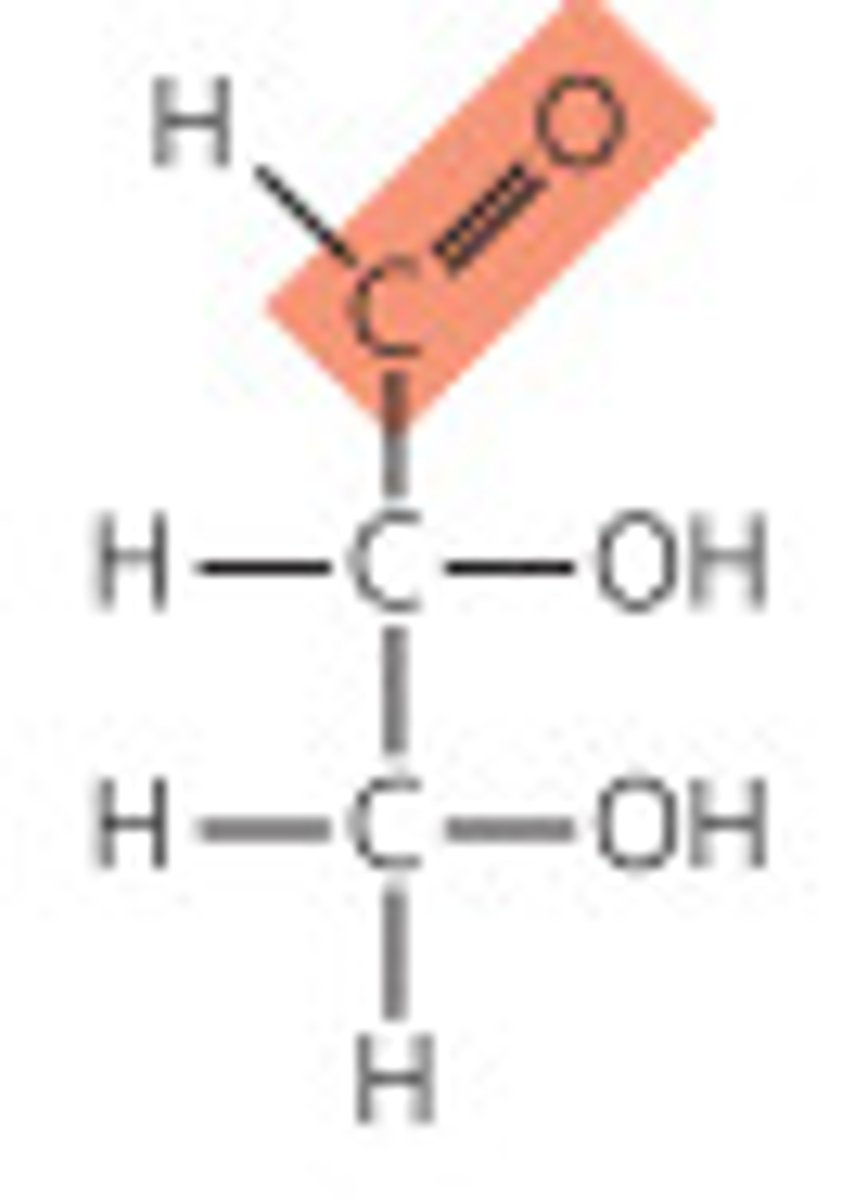
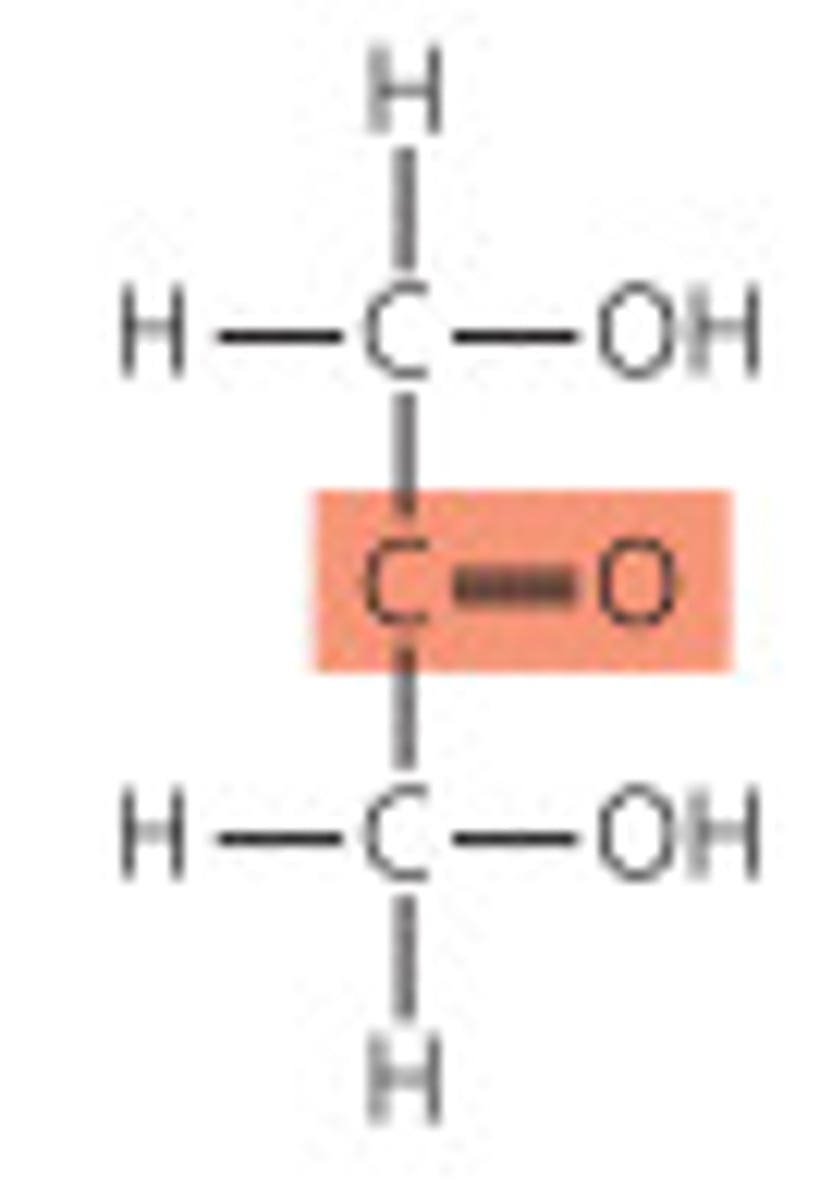
Ketose structure
Cellulose
Homopolymer of glucose linked β1→4 only
Diastereomer
Stereoisomers that are nonsuperposable, nonmirror images of each other
Ketose
Sugar containing a ketone group
Which of the following pairs is interconverted in the process of mutarotation?
α-D-glucose and β-D-glucose
Refer to the structures in the figure below. Which column contains the structure for guanine?
Column B
All of the following are important characteristics of DNA except:
Susceptibility to alkaline hydrolysis.
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is different from ribonucleic acid (RNA) in that:
DNA contains a 2′ H, whereas RNA contains a 2′ OH.
Which of the following is true concerning a DNA double helix found inside cells?
The bases are exposed through the major groove.
Mirror repeat
A segment of duplex DNA in which each strand exhibits a symmetric sequence of itself.
Sterol
A lipid molecule containing a four fused carbon ring.
Triacylglycerol
An ester of glycerol with three molecules of fatty acid.
Z-form DNA
Left-handed helical structure.
The fatty acid 18:1(Δ9) has a lower melting temperature than the fatty acid 18:0.
True
Which statement is true about the difference between fats and sugars as a source of stored energy?
Sugars are a quicker source of energy because they are more soluble in water.
Lipids that spontaneously form micelles, monolayers and bilayers have what property?
Amphipathic
As the temperature is lowered, lipids in the bilayer change from a highly ordered gel state to a more fluid liquid-crystalline state.
False
Molecules can only move down a concentration gradient in active transport.
False
Types of reactions that can be catalyzed by enzymes in cells include:
Free radical, group transfer, redox, and isomerization
The phenomenon of coupling always involves oxidation and reduction reactions.
False
Metabolism takes place in stages:
To allow for efficient production and use of energy.
Autotroph
An organism that can synthesize its own complex molecules from very simple carbon and nitrogen sources.
Catabolism
All the reactions by which complex molecules are broken down to simpler ones, energy-yielding reactions.
Entropy
The extent of randomness or disorder in a system.
Mark all of the following that are substrates for step 6 of glycolysis.
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate, NAD+
Mark all of the following that are substrates or products for step 9 of glycolysis.
2-phosphoglycerate, phosphoenolpyruvate
Rapidly dividing cells have a high need for nucleotide precursors, which are provided by:
The pentose phosphate pathway.
Gluconeogenesis consists entirely of the reactions of glycolysis, operating in the reverse direction.
False
The first committed step in the glycolytic pathway is the conversion of fructose-6-phosphate to fructose-1,6-bisphosphate.
True
Match the correct biochemical function with each of the cofactors listed.
Biotin - carrier of activated CO2
NAD+ - oxidation of hydroxyl groups
NADH - reduction of carbonyl groups
TPP - decarboxylation of α-ketoacids
General functions of hormones include:
Maintaining homeostasis, mediating a response to external stimuli and regulating growth and development are all functions of hormones.
Acidosis is a pathological condition in which the pH of the blood rises above its normal value of 7.4.
False
Glycogen synthesis is decreased in response to insulin.
False
Match the following receptor classes to the description that best describes its function.
Act through a second messenger - G protein-coupled receptors
Open and close in a response to a signal - Gated ion channels
A receptor that is also an enzyme - Receptor enzymes
Triacylglycerols are a principal component of cell membranes.
False
Fatty acid synthesis requires the formation of malonyl-CoA.
True
CO2 (or bicarbonate) is a required substrate of acetyl-CoA carboxylase.
True
Oxidative phosphorylation requires O2.
True
The reducing equivalents of NADH generated by glycolysis in the cytosol are transported across the inner mitochondrial membrane by an NADH shuttle.
True
The chemiosmotic hypothesis requires an intact inner mitochondrial membrane.
True
Which of the following is not part of the electron transport chain?
Coenzyme A
Oxidative phosphorylation
The synthesis of ATP driven by electron transfer from NADH and FADH2 to oxygen.
Respiratory inhibitor
Molecule which blocks the flow of electrons in the electron transfer chain.
Thermogenesis
The biological generation of heat by muscle activity (shivering), uncoupled oxidative phosphorylation, or the operation of futile cycles.
The complete degradation of stearoyl-CoA (C18) through the β-oxidation pathway produces:
8 FADH2, 8 NADH, and 9 acetyl-CoA.
The first three reactions in the β-oxidation of saturated fatty acids produce:
1 mole of both NADH and FADH2
Ketone bodies are synthesized in the mitochondria of liver cells.
True
Fatty acids are transported into the mitochondrion via:
Carnitine.
All of the following statements about β-oxidation are true except:
The pathway is reversible.
Pyruvate dehydrogenase requires each of the following cofactors except:
PLP.
During seed germination, the glyoxylate pathway is important to plants because it enables them to:
Carry out the net synthesis of glucose from acetyl-CoA.
Which of the following statements regarding the four "dehydrogenases" of the citric acid cycle is incorrect?
GTP is generated from one of them via substrate level phosphorylation.
The anaplerotic reactions associated with the citric acid cycle are a result of the:
Use of many of the citric acid cycle intermediates in biosynthesis.
Of the enzymes in the following list, indicate whether they are subject to allosteric feedback inhibition or not subject to allosteric feedback inhibition.
Aconitase - subject
Malate dehydrogenase - not subject
Pyruvate dehydrogenase - no subject
Citrate synthase - subject
Metabolic pathways can be regulated through the use of allosteric enzymes.
True
Glycogen phosphorylase:
Removes glucose from the non-reducing ends of the glycogen chain, cleaves α(1→4) bonds but not α(1→6) bonds, responds differently to allosteric effectors in its phosphorylated and dephosphorylated forms, and exists in two forms phosphorylase a and phosphorylase b
DNA in a closed-circular, double-stranded molecule with no net bending of the DNA axis on itself is:
Relaxed.
In a nucleosome, eukaryotic DNA is wrapped around histone proteins.
True
Topoisomerase
Enzyme that changes the supercoiling of DNA.
Supercoiling
A process that either allows a DNA molecule to be compacted for storage or allows strand separation to occur.
Histones
Small, basic proteins that participate in forming the nucleosomal structure of chromatin.
Functional DNA is not found in:
Lysosomes.
All DNA polymerases synthesize DNA in a 3' → 5' direction.
False
E. coli replication on the lagging strand:
Is initially synthesized as Okazaki fragments.
DNA polymerase I has 3' → 5' but not 5' → 3' exonuclease activities.
False
3' → 5' exonuclease
Activity that allows the removal of an improperly base-paired nucleotide from the 3' end of a nucleic acid.
Leading strand
During DNA replication, the strand that is synthesized continuously in the same direction as the direction of movement of the replication fork.