Chapter 13 - the Properties of Solutions and Colloids
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
What is the difference between a solution and colloid?
solution - homogeneous mixture, individual single phase
colloid - heterogeneous mixture, multiple phases
Define “solubility”
the maximum amount of solute that dissolves in a fixed quantity of solvent
describe the phrase “like dissolves like”
substances w/ similar intermolecular forces dissolve in each other
describe the intermolecular force: ion-dipole
polar
between charged ion and molecular dipole
40-600
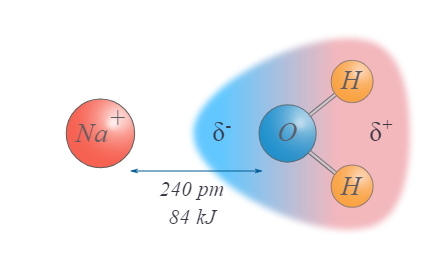
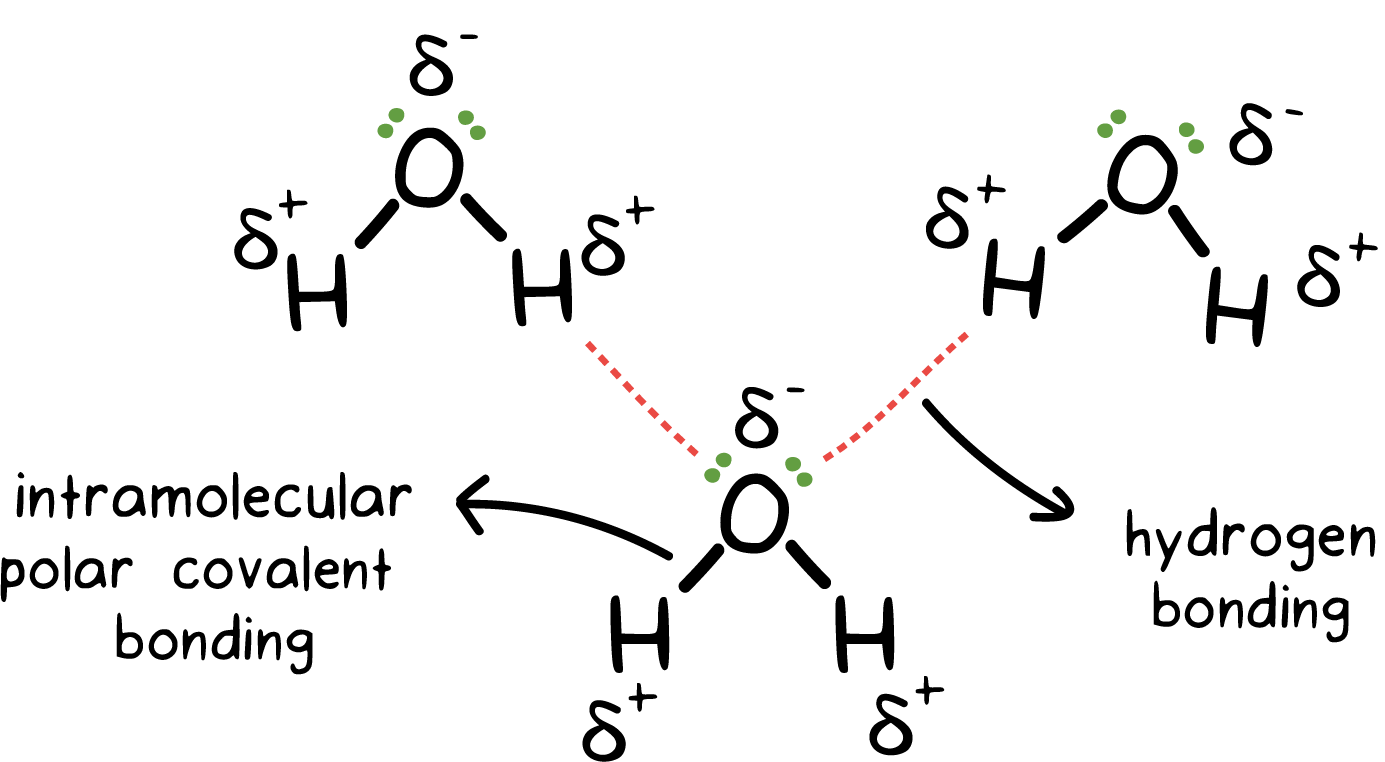
describe the intermolecular force: hydrogen-bond
polar bond w/ a hydrogen
high electronegativity of N, O, F
10-40
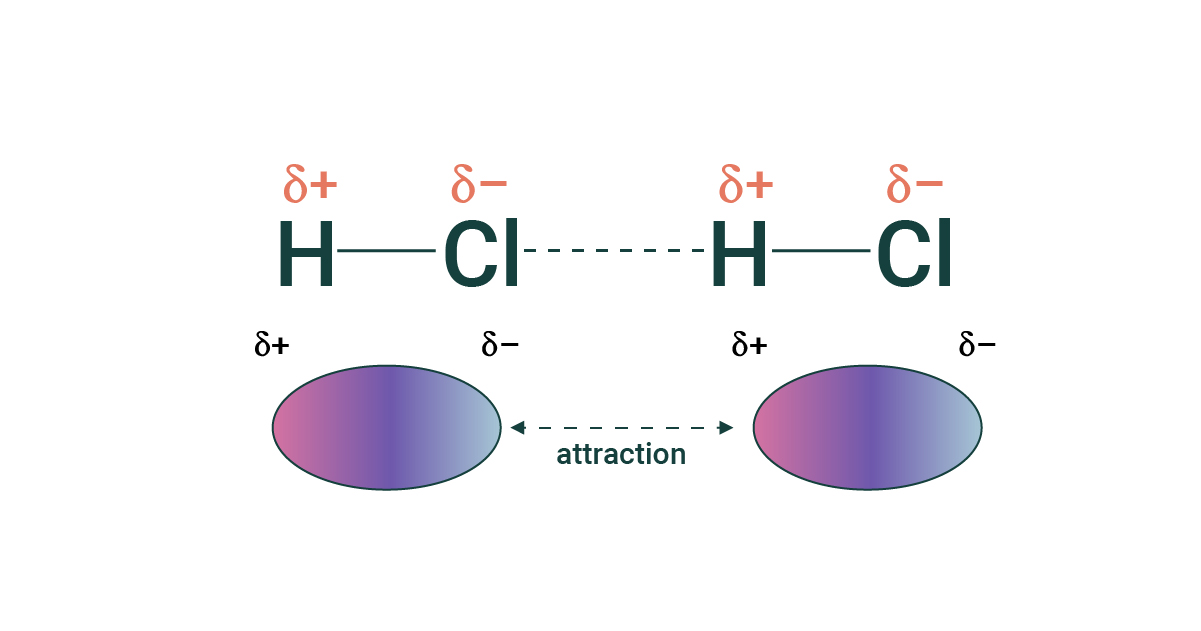
desribe the intermolecular force: dipole- dipole
dipoles attracted to each other
5-25
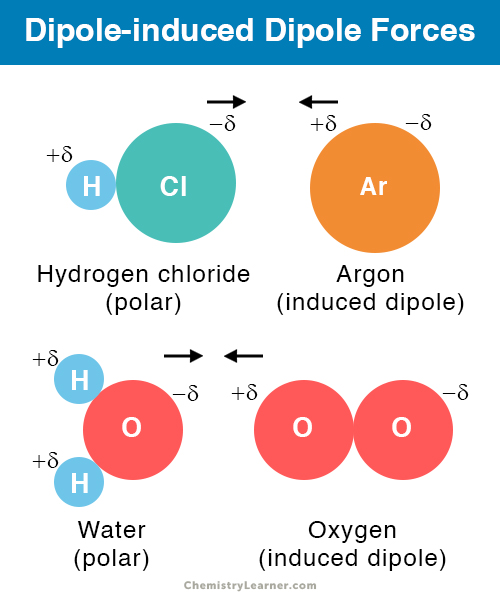
describe the intermolecular force: dipole-induced dipole
polar
permanent dipole & temporary dipole
2-10
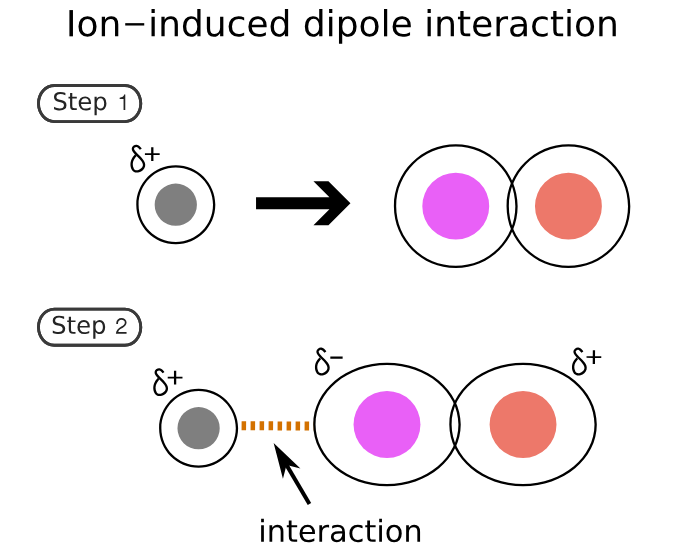
describe the intermolecular force: ion-induced dipole
polar
charged ion & temporary dipole
3-15
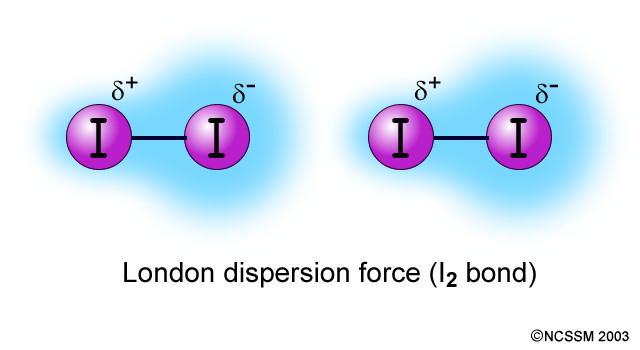
describe the intermolecular force: dispersion
nonpolar & nonpolar
describe the enthalpy of hydration
the energy released when an ion is surrounded by water molecules
depends on the charge density!
(1) describe the solute-solute energy change in solution formation
endothermic, takes in energy to break lattice
solute (aggregated) + heat → solute (separated)
enthalpy of hydration solute > 0
(2) describe the solvent-solvent energy change in solution formation
endothermic
solvent (aggregated) + heat → solvent (separated)
enthalpy of hydration solvent > 0
(3) describe the solute-solvent energy change in solution formation
exothermic; extra energy in formation
solute (separated) + solvent (separated) → solution + heat
enthalpy of hydration mix< 0
HEAT OF SOLUTION:
what is the formula for the enthalpy of hydration solution?
enthalpy hyd. solution = (1) enthalpy hyd. solute !POSITIVE! + (2) enthalpy hyd. solvent !POSITIVE! + (3) hyd. mix !NEGATIVE!
→ endothermic (+) when heat enthalpy of solution > 0
→ exothermic (-) when heat enthalpy of solution < 0
Define/describe solvation
a solute particle surrounded by solvent particles
the hydration of an ion is always exothermic
change in heat enthalpy of solvation = heat enthalpy solvent + heat enthalpy mix
(for water) → change in heat enthalpy of solution = heat enthalpy of solute + heat enthalpy hydration
Describe enthalpy hydration & its trend on the periodic table
depends on charge density
charge/vol.
charge density & enthalpy hydr. decrease down a group
depends across period (metals = CD increases; nonmetals = CD decreases)
what would an increase in charge density do to the enthalpy of hydration?
more exothermic (negative)!
what would a decrease in charge density do to the enthalpy of hydration?
more endothermic (positive)!
the higher the charge density & smaller its radius…
STRONGER ATTRACTION!
the closer the ion is to the oppositely charged pole
ppm?
10^6
the # of units of mass of solute per million units of solution
ppb?
10^9
the # of units of mass of solute per billion units of solution
what are the factors that affect solubility?
temperature: @ higher temp.. solids more & gases less
pressure: @ higher pressure.. gases more
what is an unsaturated solution?
contains less than the equilibrium concentration of solute WATER IS HUNGRY!!
what is a saturated solution?
equilibrium: maximum amount of dissolved solute in the presence of undissolved solute
what is a supersatuated solution?
contains more than the equilibrium concentration of solute, unstable!
henry’s law?
Sgas = kH x Pgas
solubility of a gas is directly proportional to its partial pressure
molarity f(M):
mol/vol.
molality (m):
mol (solute)/mass,kg (solvent)
parts by mass:
mass (solute)/mass (solution)
parts by volume:
vol.(solute)/vol.(solvent)
mole fraction (X):
mol(solute)/(mol, solute + mol, solvent)
conversion for ppm
mass(solute)/mass(solvent) x 10^6
conversion for ppb
mass(solute)/mass(solvent) x 10^9
what are colligative properties?
properties that depend on the NUMBER of solute particles
difference between electrolytes and non-electrolytes?
electrolytes → dissociate into ions in water
non-electrolytes → don’t dissociate
what are the colligative properties of electrolyte solutions?
vapor pressure lowering ∆𝑃 = 𝑖 𝑋𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑡𝑒 × 𝑃𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑣𝑒𝑛𝑡
freezing point depression ∆Tf = i(Kbm)
boiling point elevation ∆Tb = i(Kbm)
osmotic pressure π = MRT
i= Van’t Hoff’s factor; the # of particles a formula breaks up into
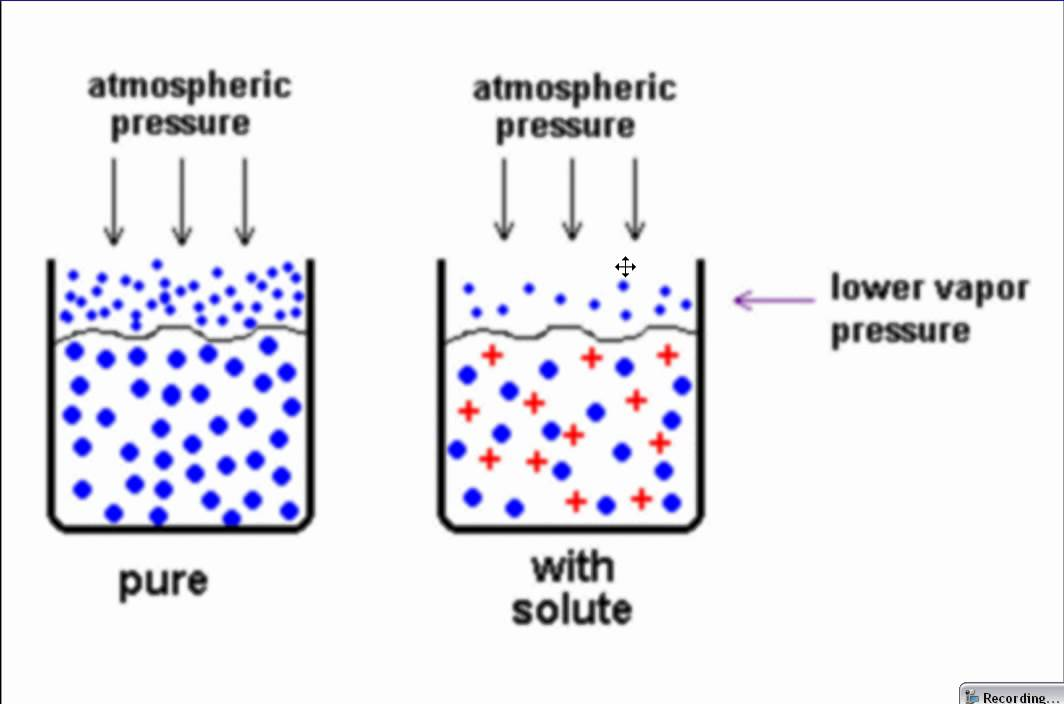
Describe the colligative property: Vapor pressure lowering
∆𝑃 = 𝑖 𝑋𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑡𝑒 × 𝑃𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑣𝑒𝑛𝑡
vapor pressure of solution < vapor pressure of pure solvent
Raoult’s law → the vapor pressure of the solvent ABOVE the solution is proportional to the mole fraction of the solvent present: P_solvent = X_solvent * P°_solvent
ONLY DILUTE SOLUTIONS
the vapor pressure LOWERING is proportional to the mole fraction of the solute present: ∆P_solvent = X_solvent * P°_solvent
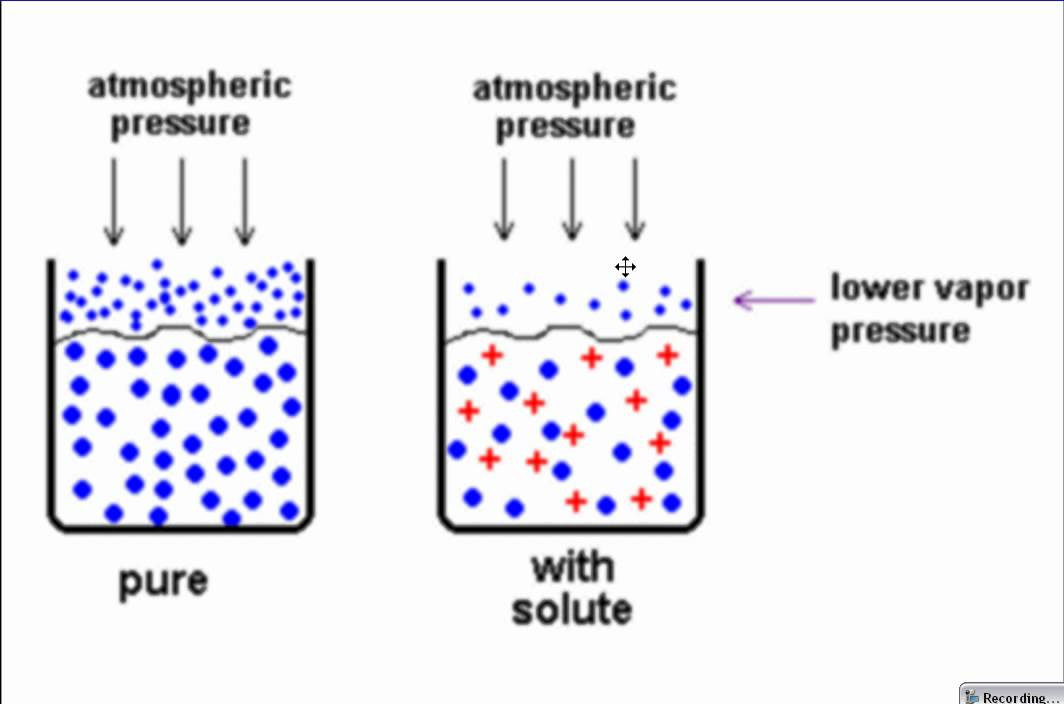
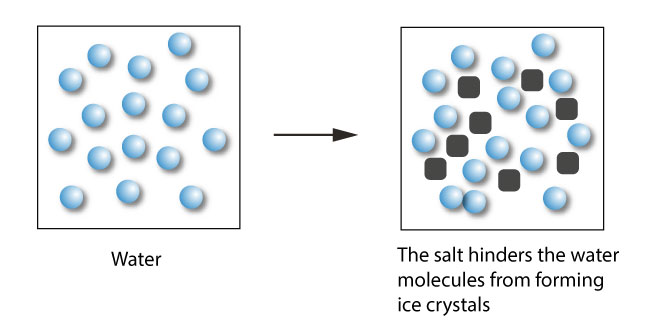
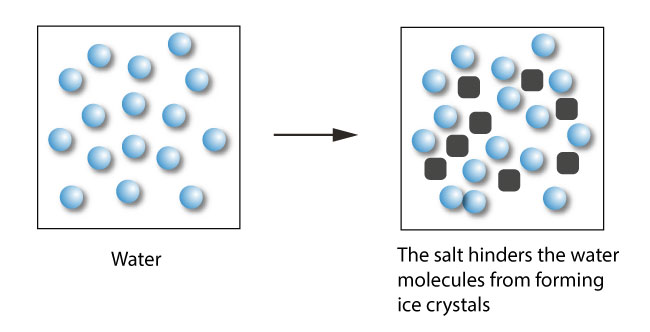
Describe the colligative property: Freezing point depression
∆Tf = i(Kbm)
solution freezes @ a lower temperature than the pure solvent
directly proportional to the MOLALITY of the solution
ex: industry salts (..NaCl)
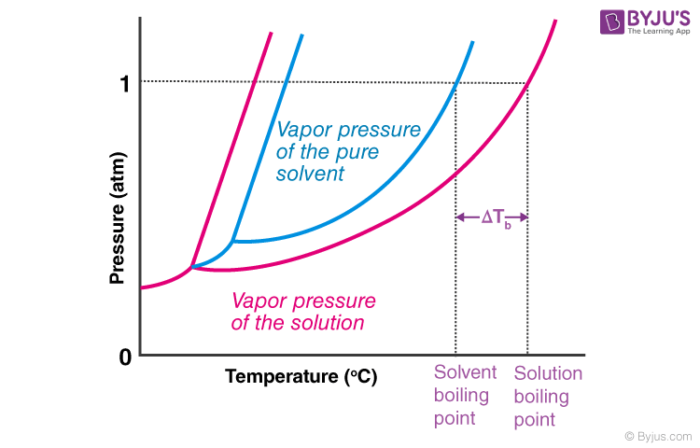
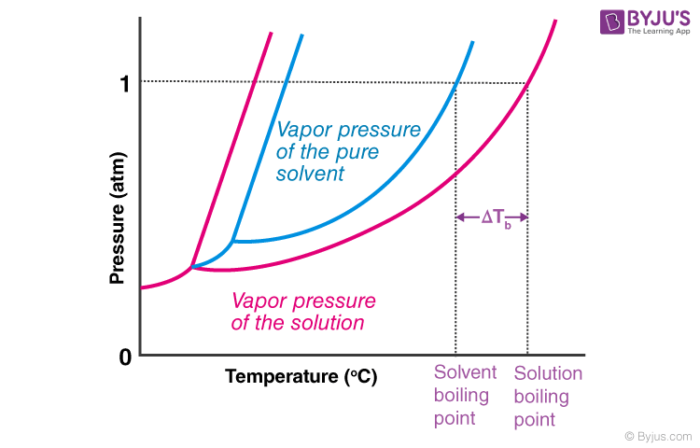
Describe the colligative property: Boiling point elevation
∆Tb = i(Kbm)
solution boils @ a higher temperature than the pure solvent (! result of vapor pressure lowering !)
directly proportional to the MOLALITY of the solution
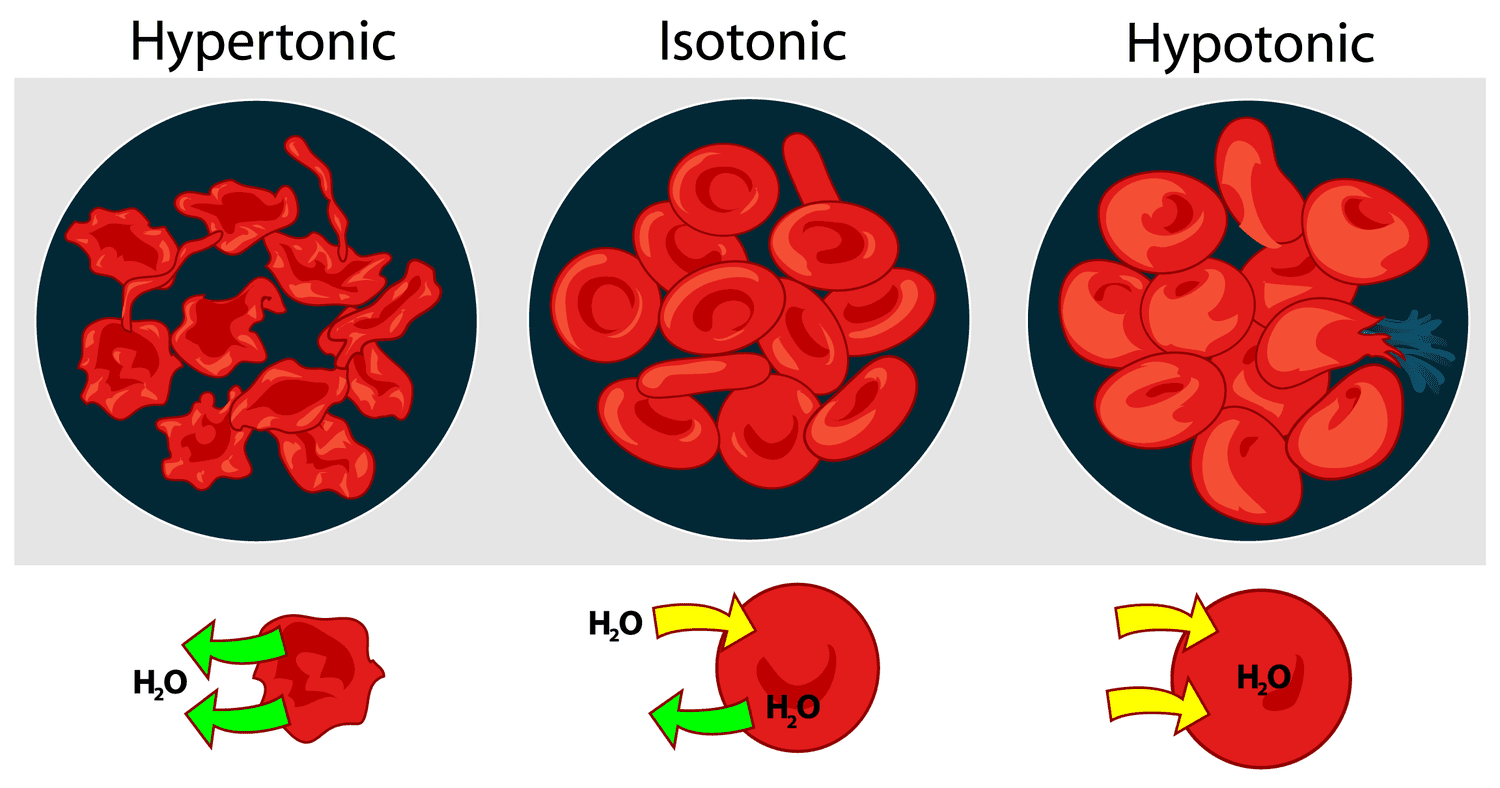
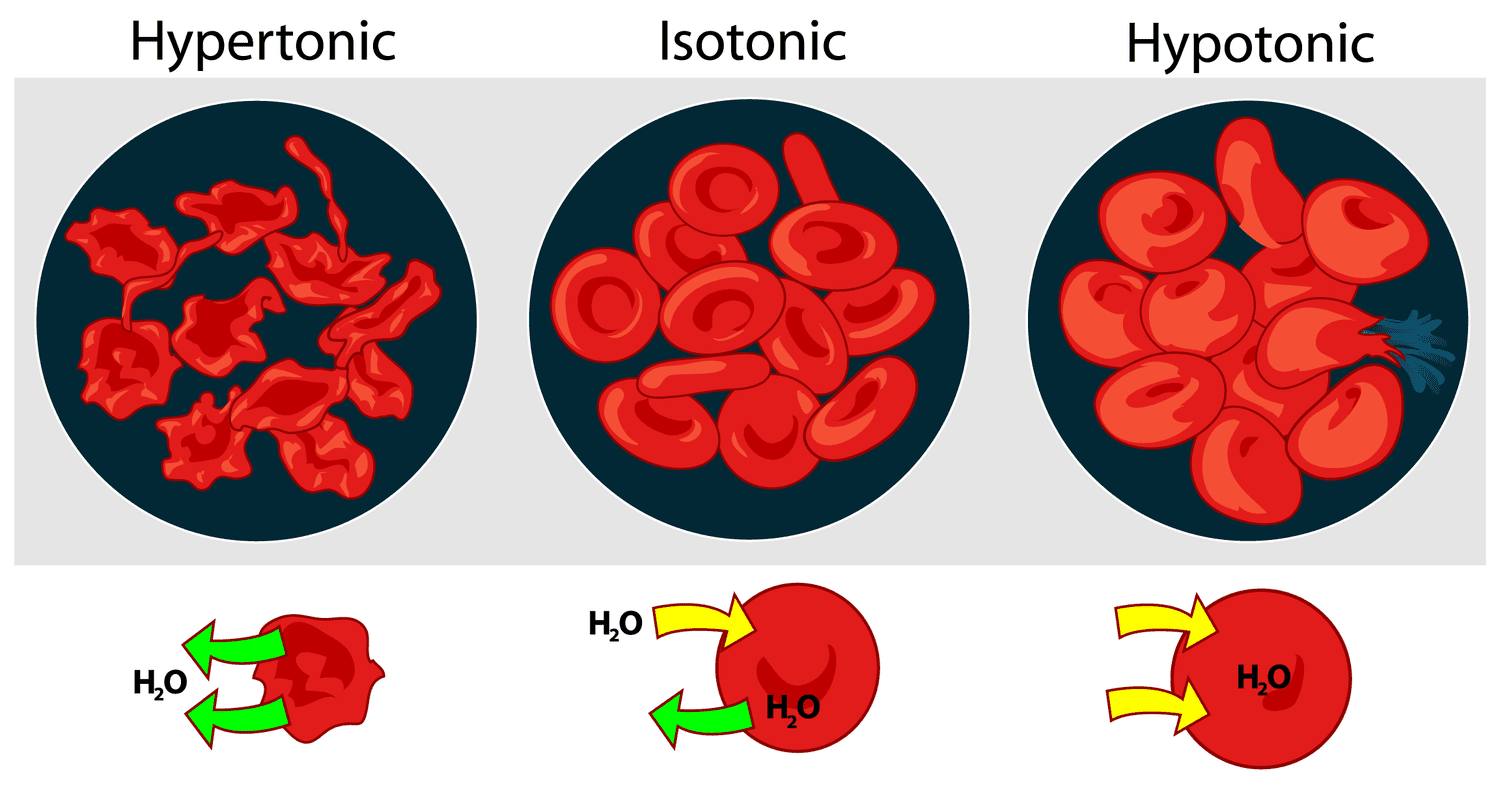
Describe the colligative property: Osmotic pressure
the pressure applied to prevent the net flow of solvent
π = MRT
M = molarity
R= 0.0821 (atm x L)/(mol x K)
T = kelvin temp.
osmosis → net flow of solvent to the more concentration solution
the higher the ***general solubility (molarity/molality, concentration)*** the..
___ the osmotic pressure
____ the boiling point
____ the freezing point
____ the vapor pressure
higher
higher
lower
lower
how many particles of this formula break into?
NH4Br
i = 2
which one has the highest freezing point & vapor pressure?
0.1m NaNO3
0.1m glucose
0.1m CaCl2
0.1m glucose
whiich one has the highest boiling point & osmotic pressure?
.1m NaNO3
0.1m glucose
0.1m CaCl2
0.1m CaCl2
which solution has the lowest freezing point?
0.1m CaCl2
0.1m (NH4)2SO4
0.1m Ca3(PO4)2
0.1m sucrose
Ca3(PO4)2