Bio lab- Plant Anatomy
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
123 Terms
cotyledons
first embryonic leaves present in seeds
cotyledons
the two major groups of flowering plants’ names are based on
shoot system
stem, leaves, flowers, and fruit
root system
roots make up the
primary growth
activity at terminal bud and tip of root causes a growth in length
meristem tissue
composed of meristem cells that divide and allow plants to grow their entire lives
apical meristem
located at the very tip and bottom of a plant
dermal, ground, and vascular
what are the three specialized tissues of the apical meristems
dermal tissue
outer protective covering
ground tissue
filler and carries out functions
vascular
transport
dermal tissue
covers the entire body of the plant, closely packed cells that act as a barrier, similar to skin
waxy cuticle
dermal tissue cells are covered with ______ to minimize water loss
ground tissue
what forms the bulk of leaves, stems, and roots
parenchyma, collenchyma, sclerenchyma
what are the three types of ground tissue cells

parenchyma
may contain chloroplast, carry on photosynthesis
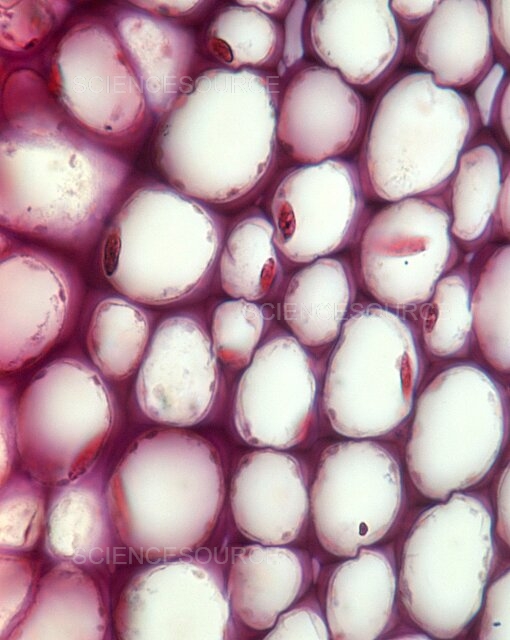
collenchyma
gives flexible support
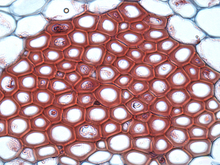
sclerenchyma
support for the mature regions of plants
vascular tissue
extends from the root through stem to leaves and vice versa
xylem
transports water and minerals from roots to leaves
vessel elements, tracheids
two types of conducting cells- both hollow, nonliving
vessel elements
what conducting cell is larger, continuous pipeline
tracheids
what conducting cell moves water from one to another
phloem
transports sugar and other organic compounds from leaves to roots
sieve-tube members, companion cells
what two cells are part of the phloem in vascular tissue
sieve-tube members
what cell in the phloem is a continuous tube, no nuclei
companion cell
what cell in the phloem is involved in transport function, has nuclei
stems
function
contain vascular bundles when xylem and phloem are found
transport materials between roots and leaves
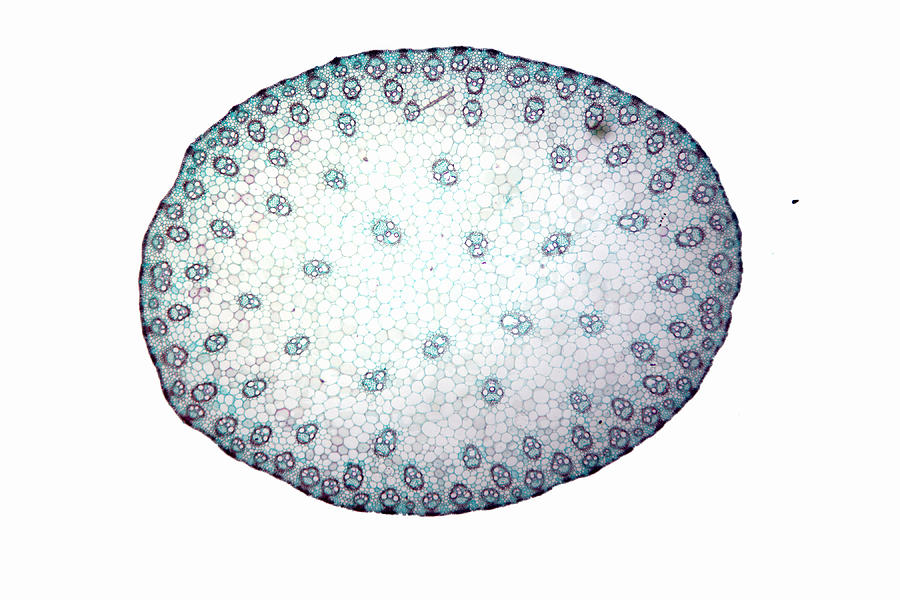
primary growth
nonwoody stems only experience _________ and occurs in herbaceous plants
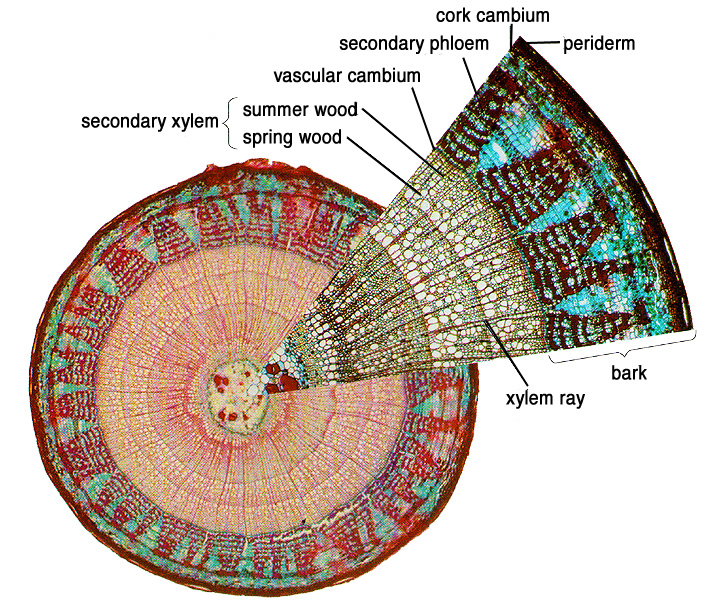
primary and secondary growth
woody stems (trees and shrubs) experience _______________
secondary growth
increases the girth of stems, branches, and roots
growth of shoot
vascular tissue supports _______
xylem and phloem
nonwoody stem vascular bundles
vascular cambium
forms a ring of meristem that divides parallel to plant surface (provides new xylem and phloem each year), occurs between bark and wood
bark, wood, pith
woody eudicot stem has three distinct areas
secondary growth
increases the girth of stems, branches, and roots
support and transport water and nutrients
what is the typical function of a stem
storage of water, nutrients, and support structure
what are the modified functions of the stem
rhizomes

rhizomes
horizontal underground stem
cladophyll

cladophyll
photosynthesis with reduced water loss
tubers

tubers
nutrient storage
bulb

bulb
short stem with fleshy leaves
tendril

tendril
what plant is used for support and attachment
thorn

thorn
defense
leaves
usually the chief organs of photosynthesis
deciduous plants
lose their leaves during a particular season (often for water conservation)
blade
wide portion of leaf (simple or compound)
petiole
stalk that attaches blade to stem
apex, margin, veins, midrib, and base
what makes up the blade of a leaf
pinnate

palmate

parallel

entire

undulate

lobed

serrate

leaf
main function is protection, water retention, nutrient collection, enhance pollination, shade, and reproduction
spines
protection
succulents
what plant is used for water retention
insectivorous
nutrient collection
bracts
enhance pollination
xeric
water retention
hydric
survive in water
spines (cactus)

succulents

venus fly trap

reproductive (bryophyllum)

bracts (poinsettia)

shade (elephants ear plant)

root
support plant by anchoring it in soil, absorb water and minerals
root hairs
found in root tip, increase absorptive capacity of root, constantly being replaced
fibrous, taproots, prop roots
root types
xylem, phloem
what makes up the vascular tissue in roots
endodermis
single layer of cells, regulates entrance into vascular tissues
petricycle
first layer of cells inside endodermic, can start development of branches or lateral roots
cortex
parenchyma cells, may function in food storage
epidermis
outer layer, root hairs in zone of maturation
root
what has the typical function of absorbing water and nutrients from the soil
support, gas exchange, reproduction
root modification
fibrous
monocots, anchor
taproot
dicots, storage
prop
what root gives support outside of the plant
buttressed
support
aerial
What type of root is used for support, gas exchange, reproduction
pneumatophores
support, gas exchange
adventitious
the type of root that gives support
prop root

buttressed

pneumatophores

adventitious

taproot
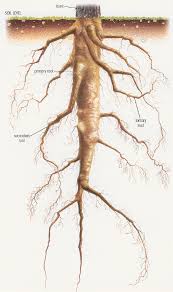
fibrous

secondary growth
bark, annual rings, woody picots/gymnosperms
primary growth
root and shoot apex