reproductive hormones
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
male reproductive hormoone
testosterone
steroid hormone
secreted from testes
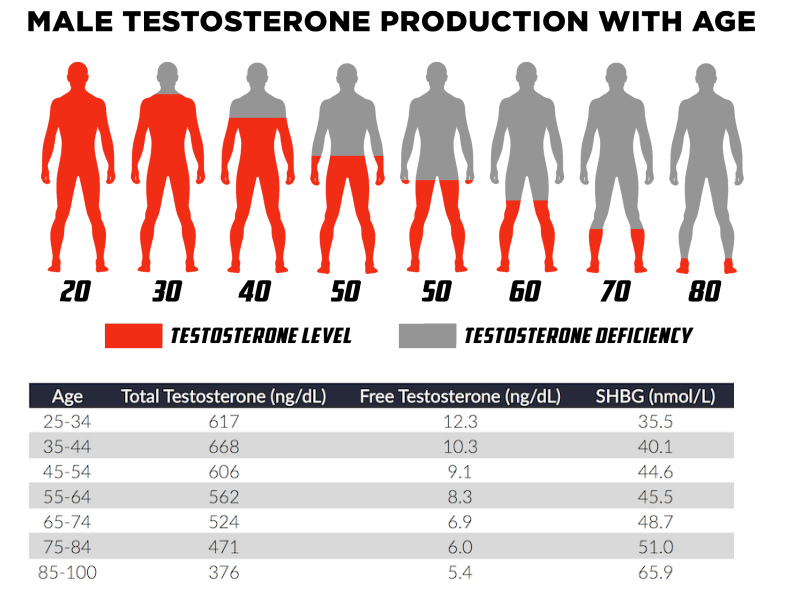
male testosterone age
levels decrease with age
peak is around 20s
release levels drops greatly 50s and after
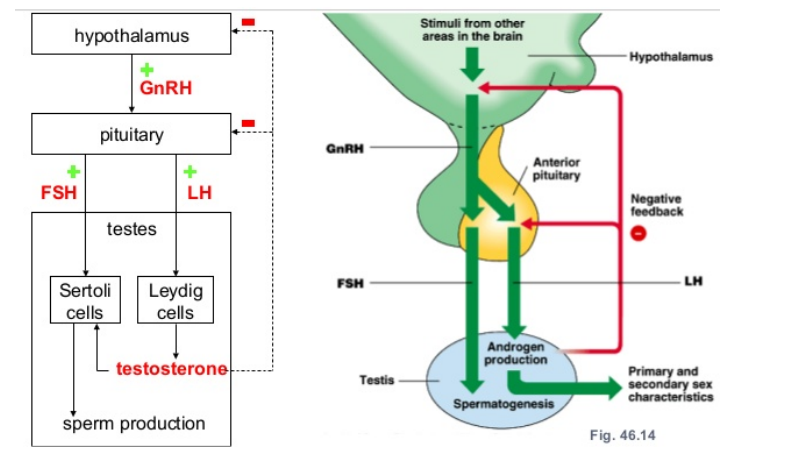
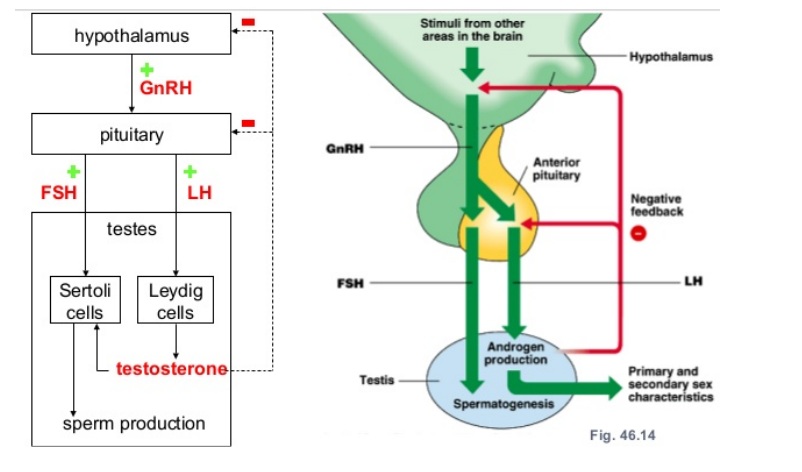
how is testosterone secreted?
hypothalamus releases GnRH into anterior pituitary
FSH and LH secreted by anterior pituitary
FSH and LH travel to gonads: ovaries/testes
LH stimulates leydig cells
leydig cells secrete androgen (testosterone) which causes primary and secondary sex characteristics
FSH and testosterone stimulates sertoli cells
sertoli cells cause spermatogenesis; sperm production
primary and secondary sex characteristics
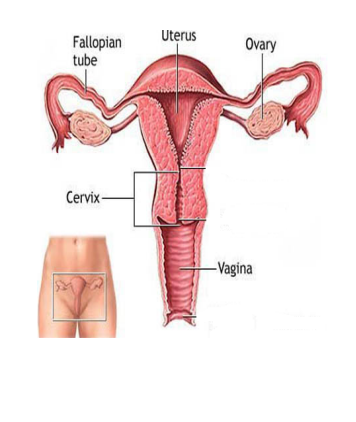
primary: reproductive organs; testes, penis, ovaries, uterus, vagina
secondary: during puberty; deeper voice, facial and body hair, increased muscle mass (men), breast development, hip widening, body fat redistribution (women)
androgen and negative feedback
high levels of androgens - testosterone
signal anterior pituitary to decrease production of LH and FSH
signal hypothalamus to decrease production of GnRH
androgens
class of hormones
present in men and women
testosterone
ovaries
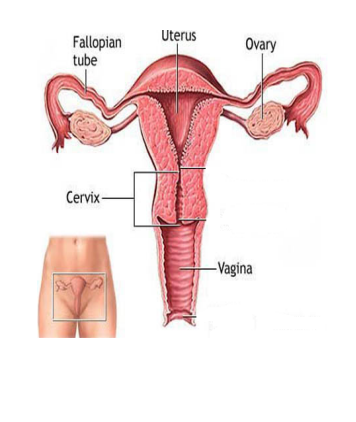
female reproductive system
produce gametes
produce estrogen
produce progesterone
estrogen
produced by ovaries
stimulates and controls reproductive system
prepares and maintains uterus for implantation
trouble getting pregnant/miscarragies linked to
low levels of progesterone
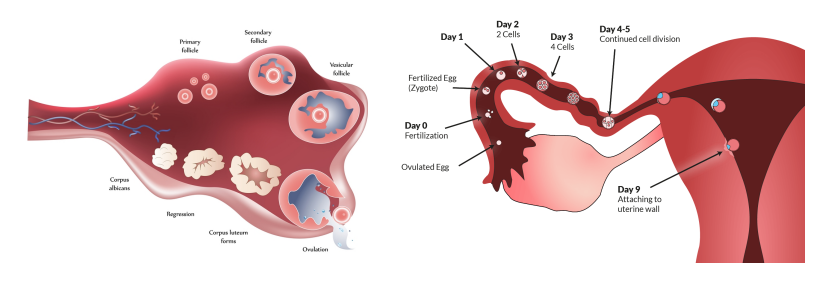
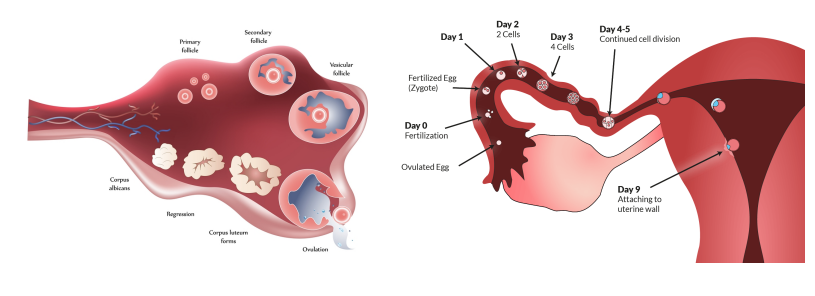
fertilization
after ovulation
fertilization occurs: zygote travels and implants in uterus
no fertilization: corpus luteum gradually shrinks, inhibits estrogen and progesterone secretion, egg degenerates → menstruation
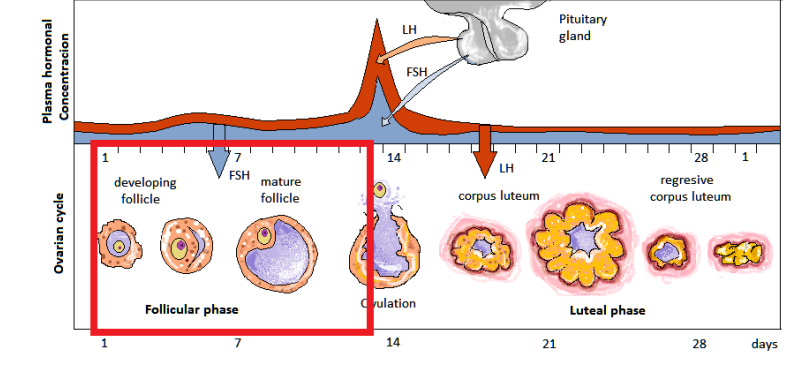
ovarian cycle: follicular phase
days 0-13
release of GnRH by hypothalamus
causes pituitary to release FSH and LH
stimulates release of estrogen
sperm can last in a womans body for
5 days
ovulation
day 14
LH, FSH, estrogen causes monthly release of one or few developing eggs/oocytes
24 hour period of fertility
LH and FSH peak
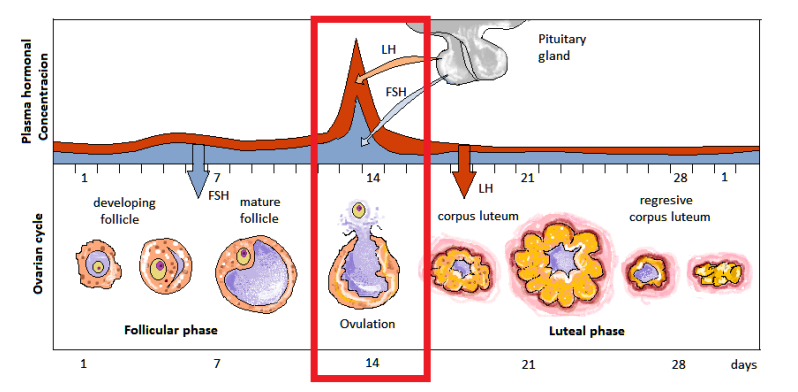
luteal phase
day 15-28
estrogen decreases, progesterone rises
LH causes follicle to form corpus luteum: mass of cells that secretes progesterone
progesterone causes lining of uterus to thicken for egg to implant and zygote to grow
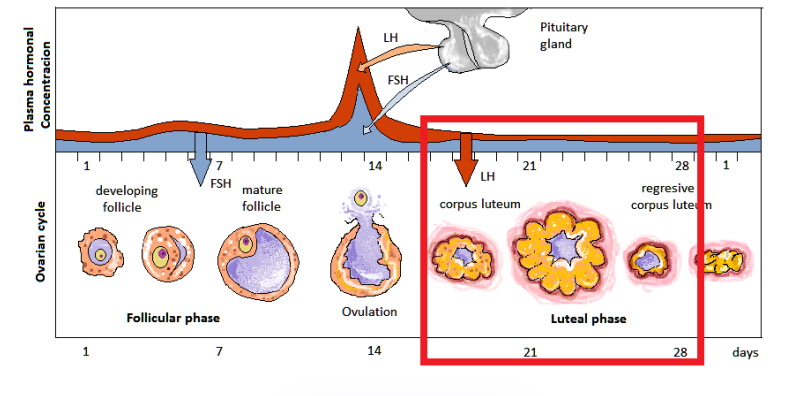
corpus luteum secretions
estrogen
progesterone
inhibin
follicular phase
begins with period
ends with ovulation
mature egg released
estrogen increases most
inhibin increases slightly
FSH and LH peak
lower body temp
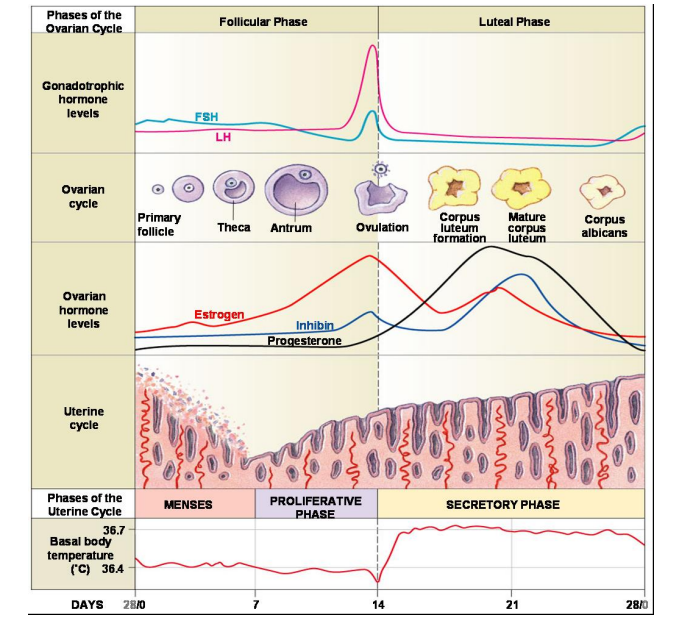
luteal phase characteristics
starts after ovulation
ends when period begins
corpus luteum forms
FSH and LH drop
estrogen drops
progesterone increases most
inhibin increases
higher body temp
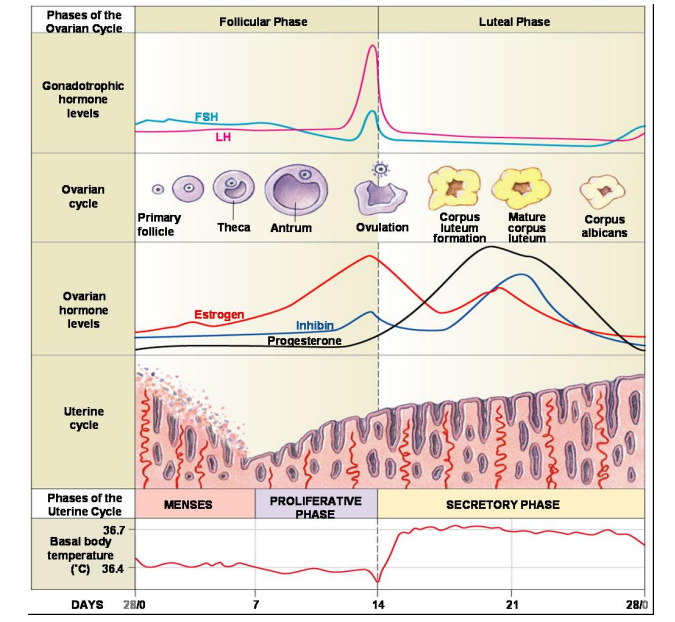
what hromone slows LH?
progesterone