Ethers and Epoxides
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
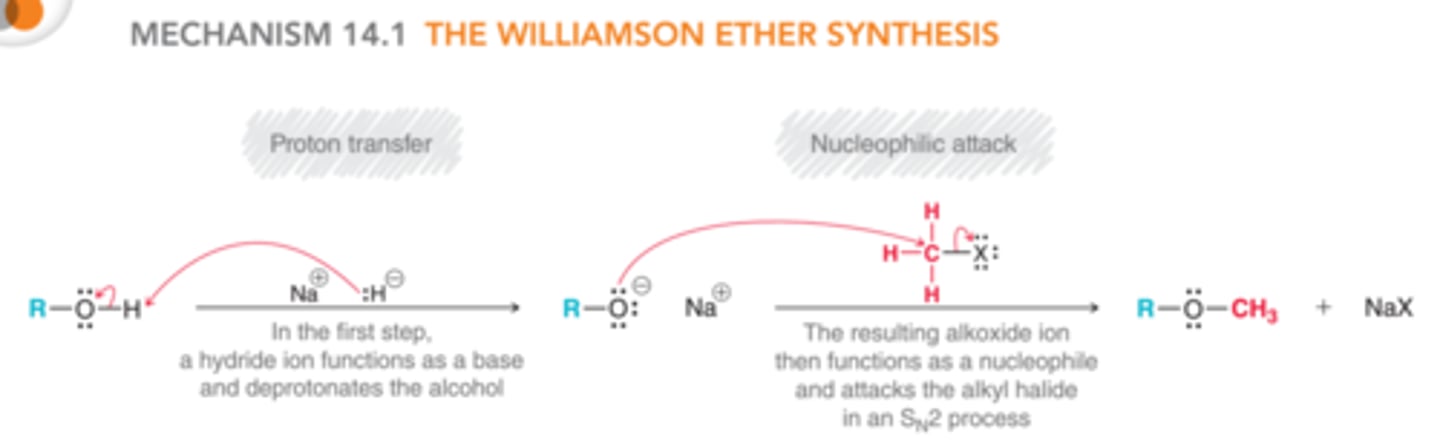
Williamson Ether Synthesis
SN2 reaction NaH: forms an ether by forming an alkoxide ion then SN2 with R-X
Ways to prepare ethers (R-O-R)
SN2, Williamson Ether synthesis from an alcohol: from a tertiary OH: NaH → alkoxide L.G. → CH3-X → ether
Alkoxymercuration from an alkene: 1. Hg(OAc)2, EtOH 2. NaBH4, OH- →
Alcohol dehydration: primary alcohol → H2SO4/heat → symmetrical ether (SN2)
tert- alcohol → H2SO4 → asymmetrical ether (SN1)
tert-butyl alcohol w/ Williamson method
when treated w/ a strong base (NaH) -> tert-butoxide which can undergo SN2 -> methyl ether
Can you form methyl-ether from methanol via Williamson method?
no because elimination would occur instead w/ bulky base
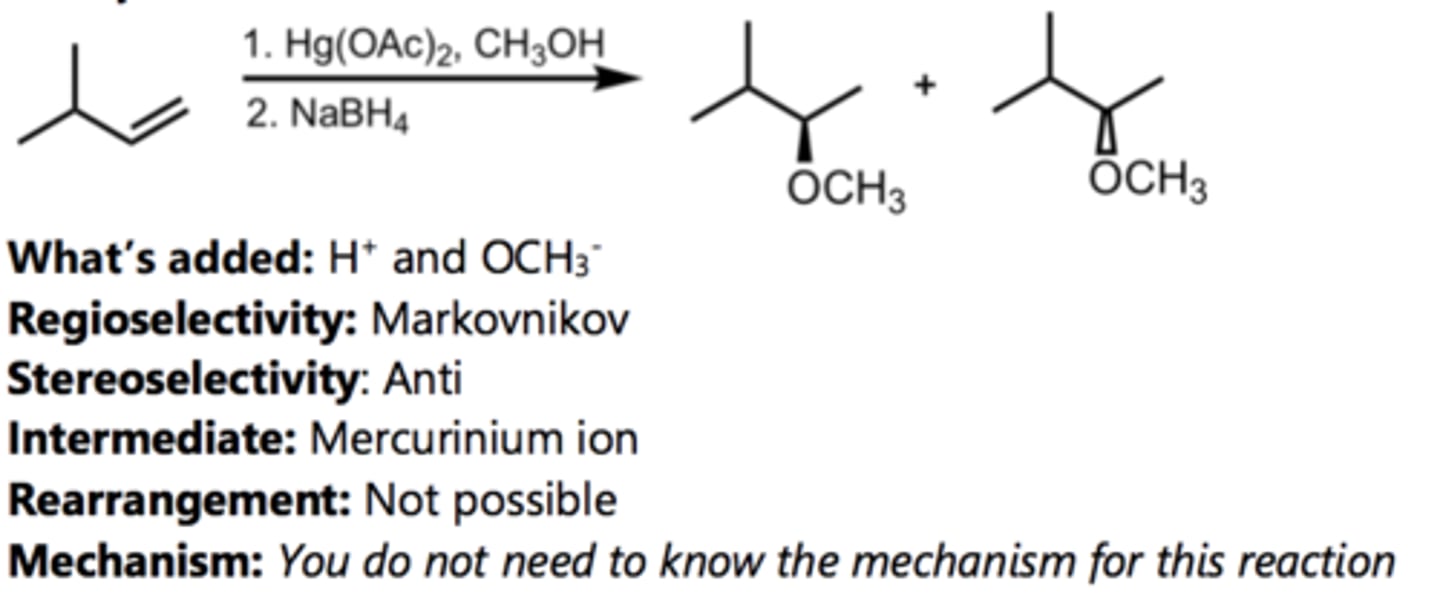
What does Alkoxymercuration- Reduction form?
1) Hg(OAc)2, CH3OH/ H2O Et2O
2) NaBH4
similar to oxymerc-red, but adds an ether from an alkene
-markovnikov product
How do you form symmetrical ethers from an alcohol?
Primary alcohol w/ H2SO4 + heat -> symmetrical ether (SN2 reaction)

How do you form asymmetrical ethers from an alcohol?
between tert- and primary alcohols w/ H2SO4 -> unsymmetrical ether (SN1 reaction)
How can ethers be cleaved?
with a strong acid under harsh conditions.
with primary alkyl groups -> SN2 mechanism
tert-alkyl groups -> SN1 mechanism

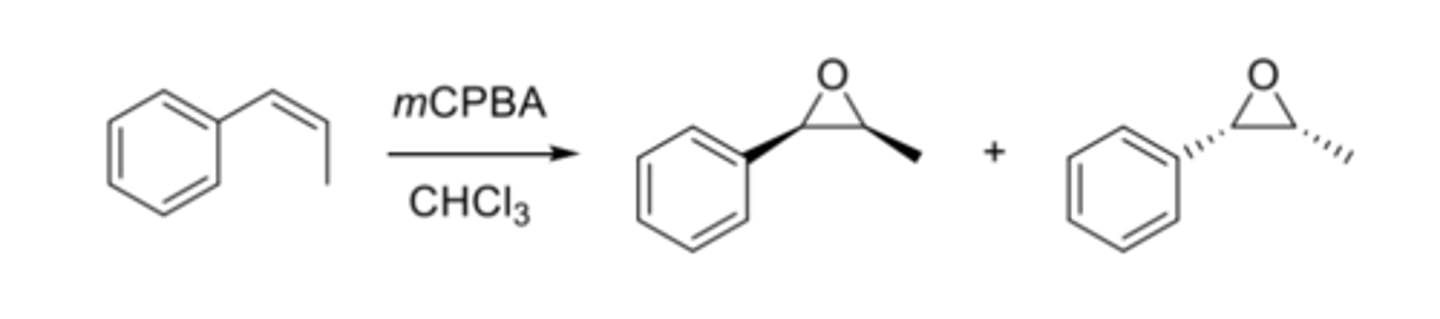
Preparation of Epoxides (Oxidation)
Oxidation: Alkene + Peroxy acid (mCPBA) --> stereospecific epoxide
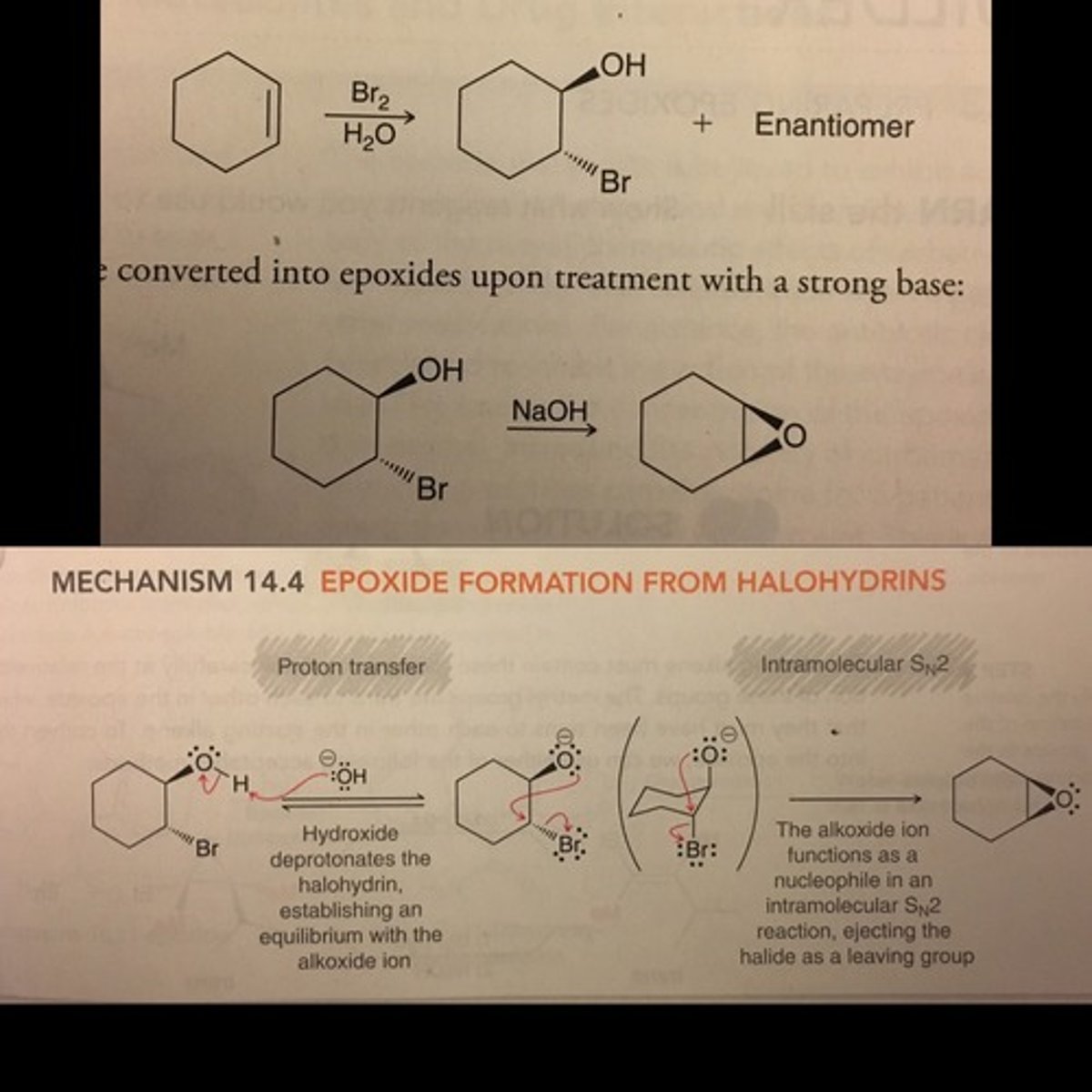
Preparation of Epoxides (halohydrins)
Cyclization (intramolecular): Cycloalkene + halohydrin X2/H2O -> Cyclo-halohydrin -> SN2 w/ NaOH -> cyclic epoxide
Ring opening of epoxides (primary and secondary carbon)
Epoxide -> SN2 w/ HX/ether (halogen attaches to primary C) trans and under mild acidity
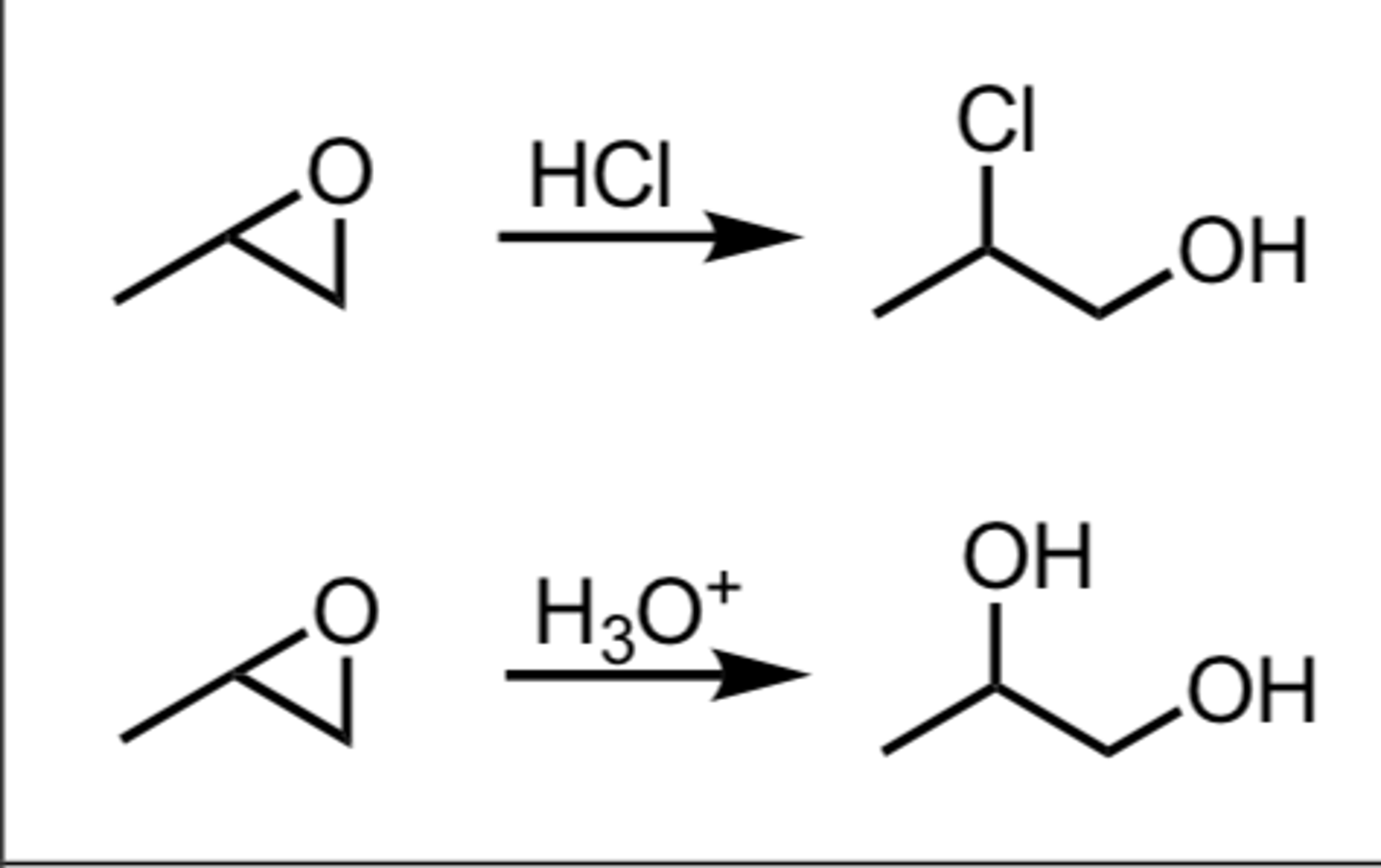
Ring opening of epoxides (tertiary carbon)
Epoxide -> SN1 w/ HX (halogen attaches to tertiary C)
trans
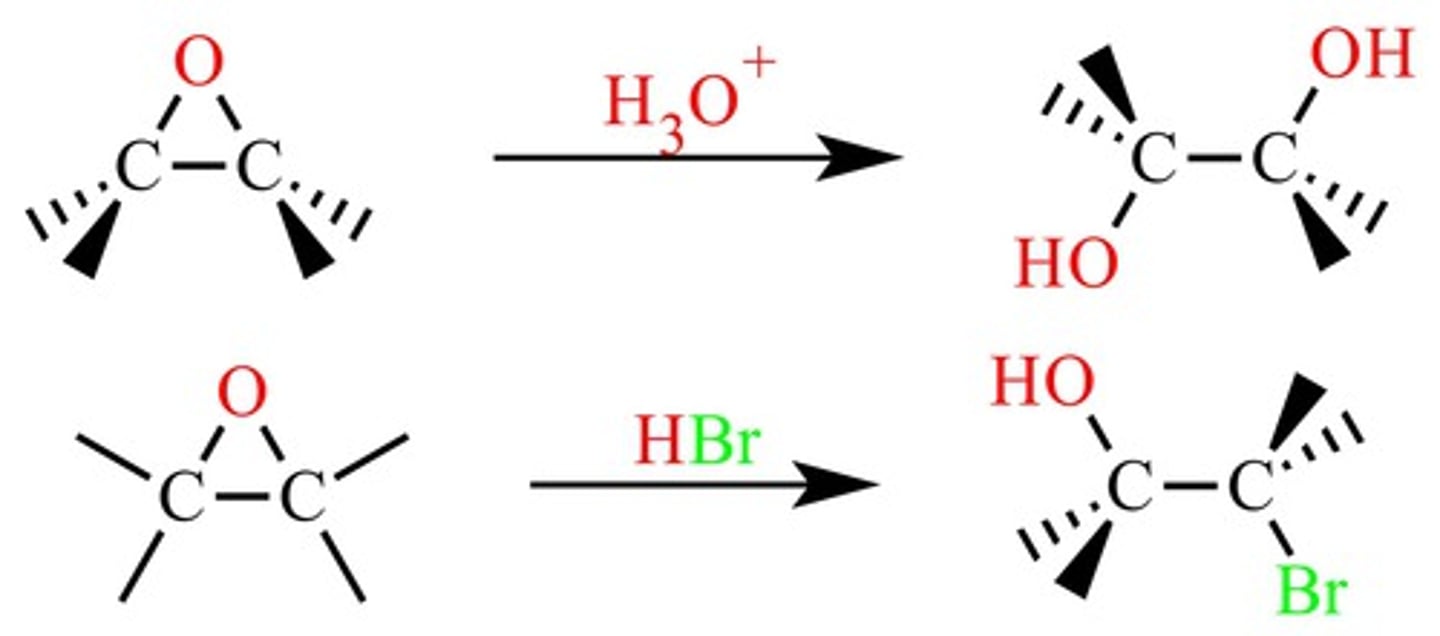
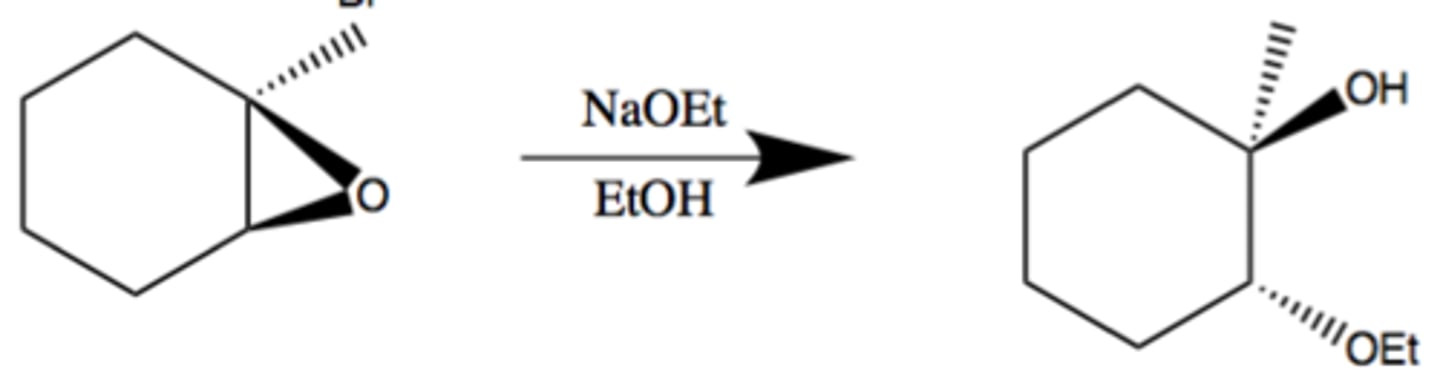
Ring opening of epoxides under basic conditions
Epoxide -> SN2 w/ NaEtO
or: R-MgBr, R-alkyne Na+, R2CuLi
regioselctive and stereoselective
nucleophile (OEt) reacts the less substituted carbon
Grignard reagent with epoxide
R-MgX + Epoxide w/ 1. ether, heat 2. H3O+ -> R-alcohol
good way to extend a carbon chain
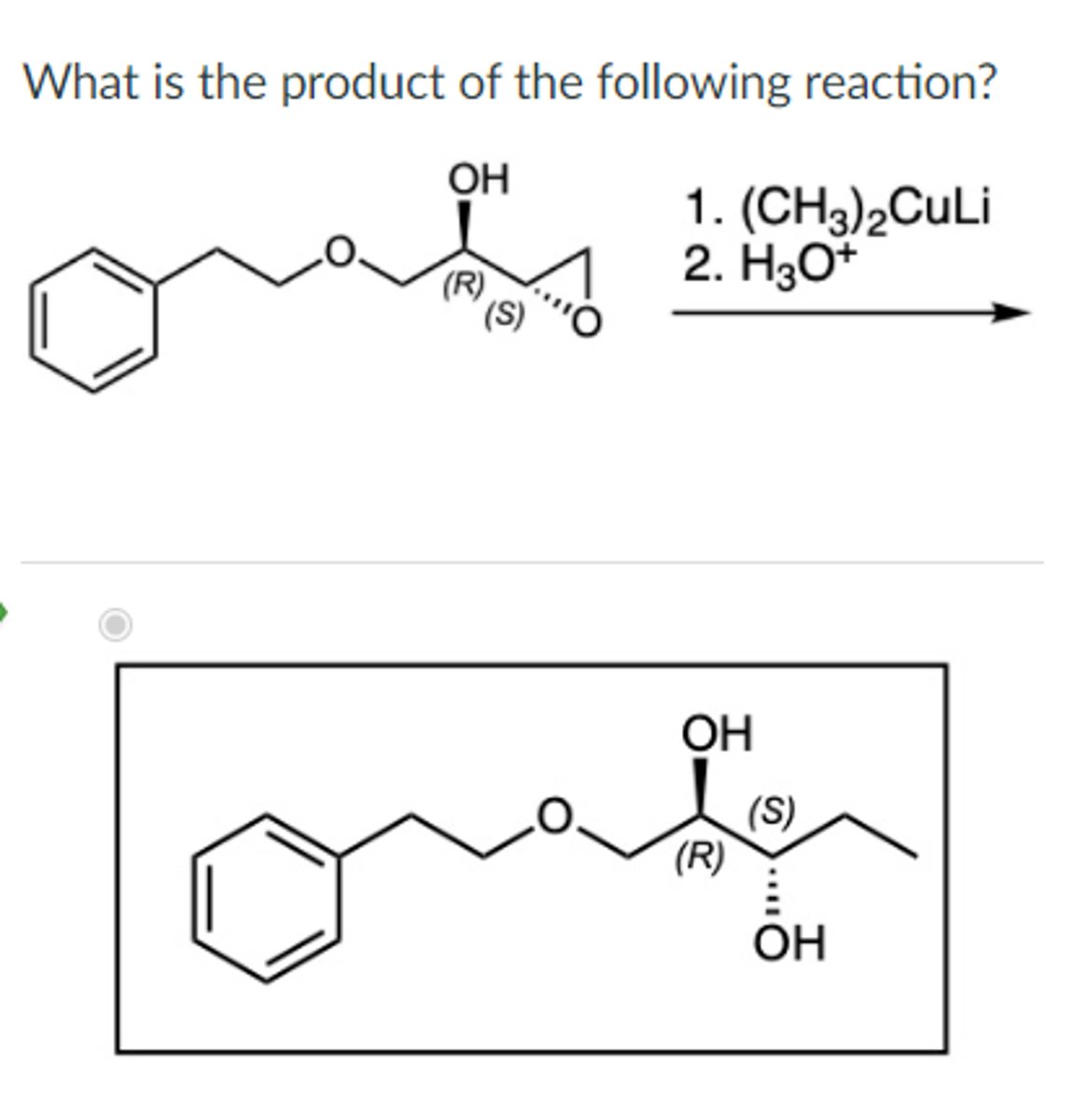
Gilman Reagent
R2CuLi + epoxide -> alcohol w/ carbon chain
acts as a mild nucleophile
attacks less substituted carbon
inversion stereochem
Alkynide as a nucleophile for epoxide ring opening
alkylnide when treated w/ strong base (NaNH2) creates strong nucleophile
Alkylnide Na+ -> 1. epoxide 2. H2O -> alcohol w/ alkyne
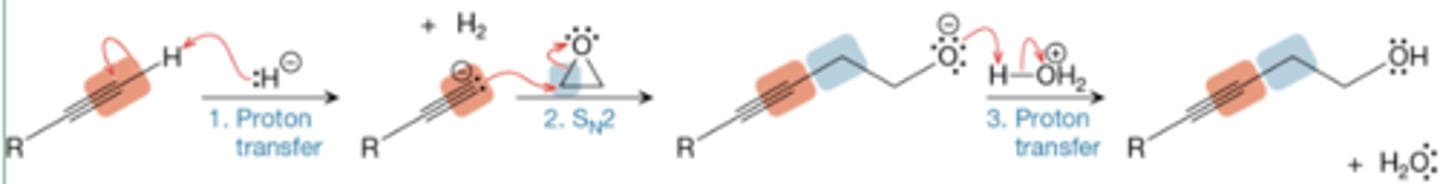
Synthesis of Thiols
Thiourea (S=NH2-NH2) reacts with alkyl halide (R-X) -> Thiol (R-SH)
thiolate is a weak base but strong nucleophile
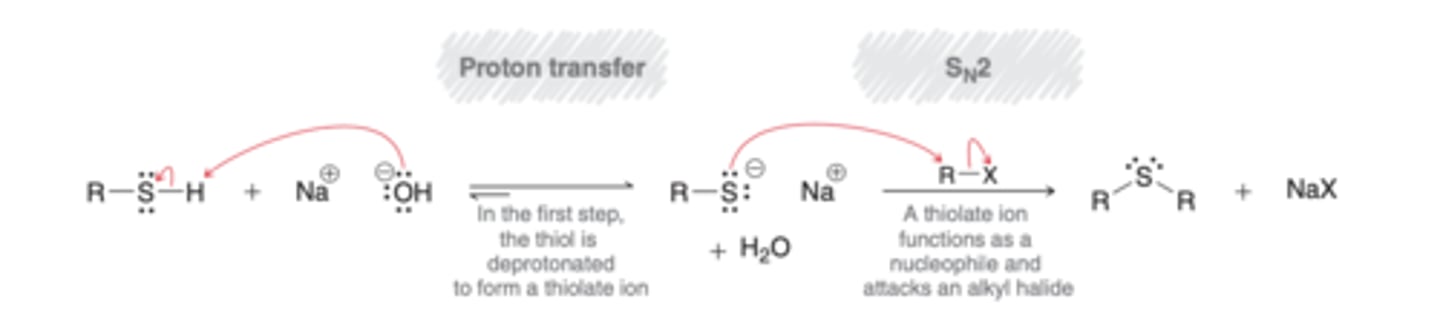
Oxidation of thiols
R-SH -> I2/Zn, H+ -> disulfide (R-S2-R) +HI
thiols can be oxidized to disulfides