morphology of flowering plants
1/140
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
141 Terms
the direct elongation of radicle forms the
primary root
primary roots and its branches constitutes the
tap root system
ex of tap root system
mustard
primary root is short lived and replaced by large no of roots
fibrous root system
ex of fibrous root system
wheat
roots arises from parts other than the the radicle
adventitious root system
ex of adventitious root
grass, banyan, monstera
which plant organ stores reserve food materials
roots
which plant organ synthesizes plant growth regulators
roots

tap root system

fibrous root system

adventitious root system
The root is covered at the apex by a thimble-like structure called the
root cap
The cells of this region are very small, thin-walled and with dense protoplasm. They divide repeatedly.
meristematic region
A few millimetres above the root cap is the
meristematic region
The cells proximal to meristematic region undergo rapid elongation and enlargement and are responsible for the growth of the root.
elongation region
The cells of the this zone gradually differentiate and mature
elongation region
proximal to region of elongation, is called the
maturation region
root hair cells are formed from which type of cell
epidermal cell
which zone has root hair cells
maturation region
which plant organ bears nodes and internodes
stem
region on stem where leaves are borne
nodes
region between two successive points at which leaves are borne
internode
the ______ later develops into branch
axillary bud
which plant organ originates from shoot apical meristem
leaves
leaves arranged on stem in
acropetal order
the leaf is attached to the stem by
leaf base
leaf may bear two lateral small leaf like structures called
stipules
in which type of plants, tap root system is generally seen
dicots
in which type of plants, fibrous root system is seen
monocots
in which type of plants, the leaf base expands into a sheath covering the stem partially or wholly
monocots
the leafbase may become swollen, which is called the
pulvinus
which family of plants have pulvinus
legume
which part holds the leaf to light
petiole
Which part of the leaf has veins and veinlets
lamina
the arrangement of vein and veinlets in the lamina of leaf is termed as
venation
when the veinlets form a network is it called
reticulate venation
when the veins run parallel to each other
parallel venation
when lamina is entire or when incised, but incision do not touch the midrib
simple leaf
When the incisions of the lamina reach up to the midrib
compound leaf
____ is present on the axil of petiole in both leaves simple as well as compound but not in the axil of leaflet
bud
number of leaflets are present on a common axis, the rachis, which represents the midrib of the leaf
pinnately compound leaf
the leaflets are attached at a common point, i.e., at the tip of petiole
palmately compound leaf
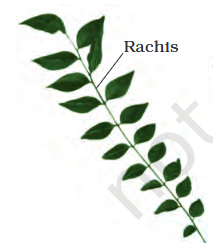
type of leaf
pinnately compound leaf

type of leaf
palmately compound leaf
ex of pinnately compound leaf
neem
ex of palmately compound leaf
silk cotton
pattern of arrangement of leaves on the stem or branch
phyllotaxy
ex of alternate phyllotaxy
china rose, mustard, sunflower
ex of opposite phyllotaxy
calotropis and guava
ex of whorled phyllotaxy
alstonia

which type of phyllotaxy is this
alternate

which type of phyllotaxy is this
opposite

which type of phyllotaxy is this
whorled
When a shoot tip transforms into a flower, it is always
solitary
the main axis continues to grow, the flowers are borne laterally in an acropetal succession
racemose
the main axis terminates in a flower, hence is limited in growth.The flowers are borne in a basipetal order
cymose

Type of inflorescence
racemose
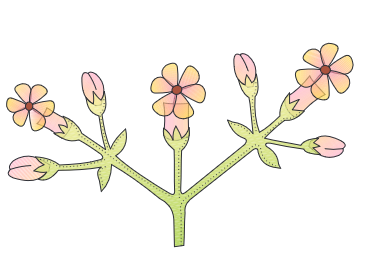
type of inflorescence
cymose
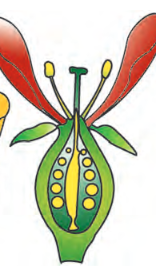
A typical flower has four different kinds of whorls arranged successively on the swollen end of the stalk or pedicel, called
thalamus
receptacle aka
thalamus
ex of perianth
lily
When a flower can be divided into two equal radial halves in any radial plane passing through the centre, it is said to be
actinomorphic
ex of actinomorphic
mustard, datura, chilli
When the flower can be divided into two similar halves only in one particular vertical plane, it is
zygomorphic
ex of zygomorphic
pea, gulmohur, bean, cassia
if the flower cannot be divided into two similar halves by any vertical plane passing through the centre
asymmetric
ex of asymmetric
canna
the gynoecium occupies the highest position while the other parts are situated below it.
hypogynous
ex of hypogyous
mustard, china rose, brinjal
If gynoecium is situated in the centre and other parts of the flower are located on the rim of the thalamus almost at the same level
perigynous
ex of perigynous
plum, rose, peach
the margin of thalamus grows upward enclosing the ovary completely and getting fused with it, the other parts of flower arise above the ovary
epigynous
ex of epigynous
guava, cucumber, ray floret sunflower
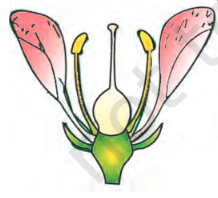
type of ovary
hypogynous

type of ovary
perigynous
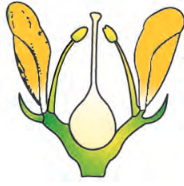
type of ovary
perigynous
type of ovary
epigynous
The mode of arrangement of sepals or petals in floral bud with respect to the other members of the same whorl is known as
aestivation
When sepals or petals in a whorl just touch one another at the margin, without overlapping
valvate
ex of valvate
calotropis
If one margin of the appendage overlaps that of the next one and so on
twisted
ex of twisted
china rose, lady finger, cotton
If the margins of sepals or petals overlap one another but not in any particular direction
imbricate
ex of imbricate
cassia, gulmohur
the largest (standard) overlaps the two lateral petals (wings) which in turn overlap the two smallest anterior petals (keel); this type of aestivation is known as
vexillary
ex of vexillary
pea, bean
in vexillary aestivation, the largest petal is known as
standard
in vexillary aestivation, the lateral petals are known as
wings
in vexillary aestivation, smallest anterior petal is known as
keel
A sterile stamen is called
staminode
When stamens are attached to the petals, they are
epipetalous
ex of epipetalous
brinjal
stamen attached to the perianth
epiphyllous
ex of epiphyllous
lily
stamen united in one bundle
monadelphous
ex of monadelphous
china rose
stamen united in two bundle
diadelphous
ex of diadelphous
pea
stamen united in many bundle
polyadelphous