Chapter 13 - Power & politics
A definition of power
- @@Power@@: capacity that A has to influence the behavior of B, so that B acts in B accordance with A’s wishes.
- @@Dependency@@: B’s relationship to A when A possesses something that requires.
Bases of power
- Formal power
- @@Coercive power@@: power base that is dependent on fear of the negative results from failing to comply.
- @@Reward power@@: compliance achieved based on the ability to distribute rewards that others view as valuable.
- @@Legitimate power@@: power a person receives as a result of his/her position in the formal hierarchy of an organization.
- Personal power
- @@Expert power@@: influence based on special skills or knowledge.
- @@Referent power@@: influence based on identification with a person who has desirable resources or personal traits.
Power tactics
- @@Power tactics@@: ways in which individuals translate power bases into specific actions.
- Nine influence tactics
- Legitimacy
- Rational persuasion
- Inspirational appeals
- Consultation
- Exchange
- Ingratiation
- Pressure
- Coalitions
- @@Political skill@@: ability to influence others in such a way as to enhance one’s objectives.
Politics: power in action
- @@Political behavior@@: activities that are not required as part of a person’s formal role in the organization but that influence or attempt to influence, the distribution of advantages and disadvantages within the organization.
Causes and consequences of political behavior
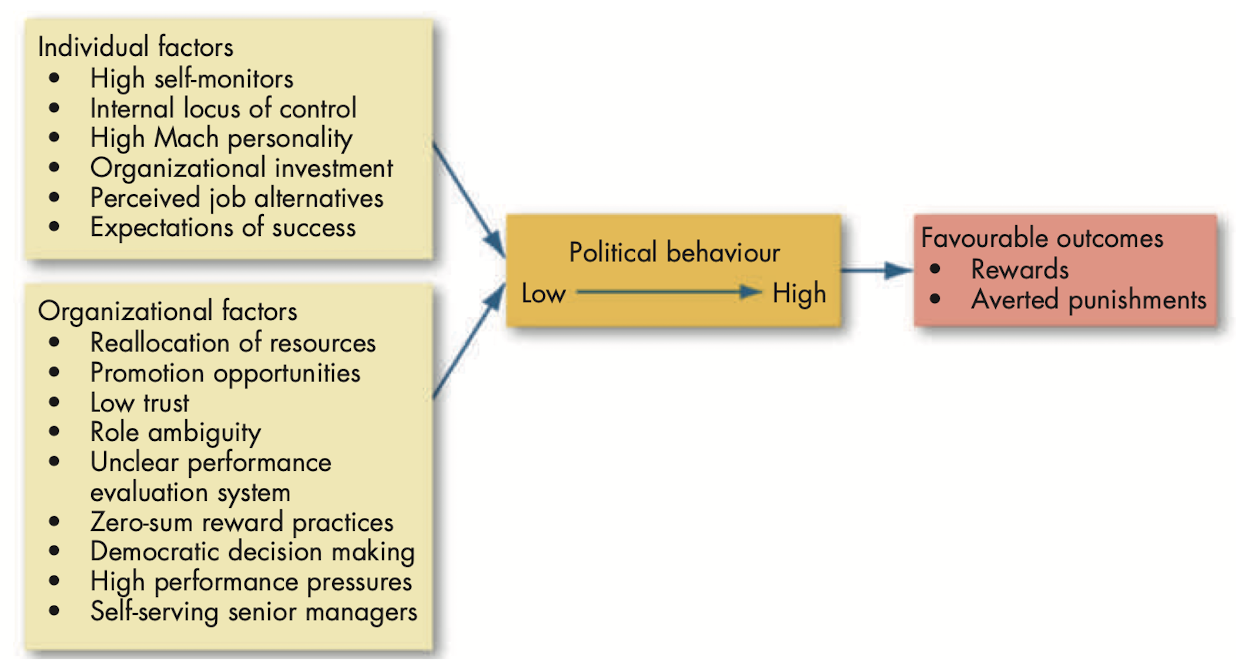
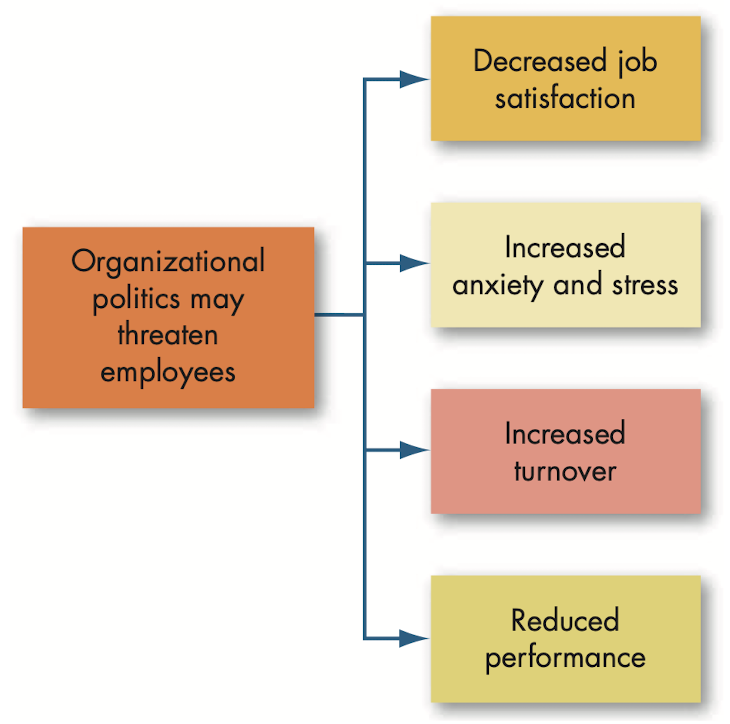
- @@Defensive behaviors@@: reactive and protective behaviors to avoid action, blame or change.
- @@Impression management (IM)@@: process by which individuals attempt to control the impression others form of them.

