PSC 101 Bio Psych Midterm 2
1/80
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
(5.2) Which ion has the greatest intracellular concentration?
Cl-
K+
Ca2+
K+
(5.3) When Cl- channels open, Cl- will flow ___________ the cell and cause the cell to ______________.
Into, Hyperpolarize
Out of, Depolarize
Into, Depolarize
Out of Hyperpolarize
Into, Hyperpolarize
(6.2) An AP will fire if the membrane potential becomes:
-74 mV
-84 mV
-64 mV
-54 mV
-54 mV
(6.3) Which channels are the most important for action potential firing?
Voltage-gated Na+ channel & Ligand-gated Cl- channels
Voltage-gated Na+ channel & Voltage-gated K+ channels
Voltage-gated Ca2+ channel & Voltage-gated Na+ channels
Ligand-gated Ca2+ channel & Ligand-gated Cl- channels
Voltage-gated Na+ channel & Voltage-gated K+ channels
(6.4) The refractory period is:
The period of time that it is impossible or very unlikely for an action potential to fire.
The time between action potential peaks.
The period of time it takes a neuron to reach action potential threshold.
Peak action potential membrane potential amplitude.
The period of time that it is impossible or very unlikely for an action potential to fire.
(6.5) Nodes of Ranvier are:
The site of NT release
Where the cell body meets the axon
Unmyelinated segments of axon between myelinated segments
Myelinated segments of an axon
Unmyelinated segments of axon between myelinated segments
(7.2) Which is not a method to clear neurotransmitters from the synaptic cleft?
Reuptake
Reduce
Diffusion
Degradation
Reduce
(7.2) SNARE complexes are triggered by:
ATP
Hyperpolarization
Ca2+
GPCRs
Ca2+
(7.3) GPCR are:
Voltage-gated channels responsible for depolarizing the cell during an action potential.
NT Receptors that activate other proteins causing long-term changes in the cell.
The fastest type of NT receptors.
Cause the vesicles to fuse with the membrane.
NT Receptors that activate other proteins causing long-term changes in the cell.
(7.3) D1 and D2 receptors in the basal ganglia demonstrate:
That the same NT can have inverse effects on different receptors.
DA is always excitatory.
GPCRs activates faster than ionotropic receptors.
DA is able to activate 5-HT receptors.
That the same NT can have inverse effects on different receptors.
(8.1) What will not make it through the blood-brain barrier?
Amino Acids
Small drugs and toxins
Oxygen
Large drugs and toxins
Large drugs and toxins
(8.1) Which is the slowest route of administration?
Ingestion
Intravenous injection
Inhalation
Absorption through the nose
Ingestion
(8.2) Exposure to high amounts of botulinum toxin through eating bad meat will result in:
Loss of wrinkles around the eyes.
Evening out muscle tension for eye movement.
Contracting botulism and possibly death.
Relief of tension headaches.
Contracting botulism and possibly death.
(8.3) Organophosphates interfere with synaptic signaling by:
Increasing the number of ACh receptors in the post synaptic cell
Breaking down SNARE complex in the presynaptic cell
Inhibiting ACh reuptake
Forming an unbreakable bond with ACh degradation proteins
Forming an unbreakable bond with ACh degradation proteins
(8.4) Reupdate inhibitors influence synaptic communication by increasing:
The number of postsynaptic receptors
The amount of time the NT is in the synaptic cleft
The amount of NT release per vesicle
Ca2+ influx into the cell
The amount of time the NT is in the synaptic cleft
(9.1) Opioids can influence pain perception by:
Inhibiting cells that carry pain information from the body to the brain.
Preventing the brain from remembering the painful stimuli.
Breaking the SNARE complex.
Activating the reward pathway.
Inhibiting cells that carry pain information from the body to the brain.
(9.2) Long-term changes to the response to opioids due to high and/or chronic opioid drug dose(s) is called:
Gene Knockout
Tolerance
Amnesia
Depression
Tolerance
(9.3) Why do reward-seeking behaviors change following high and/or chronic dose(s) of opioid drugs?
Connections in the NA are rewired
Pain receptors are inhibited
Fewer DA reuptake proteins are in presynaptic cells
VTA cells produce more DA
Connections in the NA are rewired
(9.3) In the NA, you would expect to find opioid receptors on the:
Inhibitory interneuron
Postsynaptic neuron
DA neuron
NMJ
Inhibitory interneuron
(9.4) Naloxone is a(n):
Antagonist for ACh receptors
Agonists for DA receptors
Reuptake inhibitor for endogenous opioids
Antagonist for opioid receptors
Antagonist for opioid receptors
(5.1) Ca2+ has a greater __________ ionic concentration.
Intracellular
Extracellular
Extracellular
(5.1) Cl- has a greater __________ ionic concentration.
Intracellular
Extracellular
Extracellular
(5.1) K+ has a greater __________ ionic concentration.
Intracellular
Extracellular
Intracellular
(5.1) Na+ has a greater __________ ionic concentration.
Intracellular
Extracellular
Extracellular
(5.2) Ions are able to move in and out of the cell through:
The membrane
Vesicles
Ion channels
Gap junctions
Ion Channels
(5.2) Any positive ion can pass through a Na+ channel.
True
False
False
(5.2) ______ channels are always open and are important for maintaining the Em.
Leak
Voltage-Gated
Ligand-Gated
G-Protein Linked
Leak
(5.4) A single EPSP in enough to cause most neurons to fire an AP.
True
False
False
(5.4) Temporal summation is:
Rapid stimulations from an axon on the same dendrite
Multiple dendrites being activated at the same time
Slow stimulation to the same dendrite
A single EPSP traveling from a dendrite to the axon hillock
Rapid stimulations from an axon on the same dendrite
(5.4) Spatial summation is:
Rapid stimulations from an axon on the same dendrite
Multiple dendrites being activated at the same time
Slow stimulation to the same dendrite
A single EPSP traveling from a dendrite to the axon hillock
Multiple dendrites being activated at the same time
(6.1) Action potentials carry information from the:
Axon hillock to the synaptic terminal
Dendrites to the cell body
Synaptic terminal to the axon hillock
Cell body to the dendrites
Axon hillock to the synaptic terminal
(6.1) How do APs convey information?
Alternating between EPSPs and IPSPs.
Varying the AP amplitude.
Varying the number of APs fired per second.
Changing the AP threshold.
Varying the number of APs fired per second.
(6.2) What is an AP threshold?
The membrane potential needed to trigger an AP
The limit of APs that can be fired per second
The top amplitude an AP can reach
The number of IPSPs needed to fire an AP
The membrane potential needed to trigger an AP
(6.2) Em = _____, AP threshold = ______
-45 mV, -70 mV
-70 V, -55 V
-70 mV, -55 mV
-60 mV, -50 mV
-70 mV, -55 mV
(6.3) Which ions are essential for AP firing?
Na+, Ca2+
Na+, Cl -
Na+, K+
Ca2+ , Cl -
Na+, K+
(6.3) What is a difference between the Na+ and K+ channels that are important for AP firing?
Allow ions to flow across the membrane
Inactivation mechanisms
Ion selective
Voltage-gated
Inactivation mechanisms
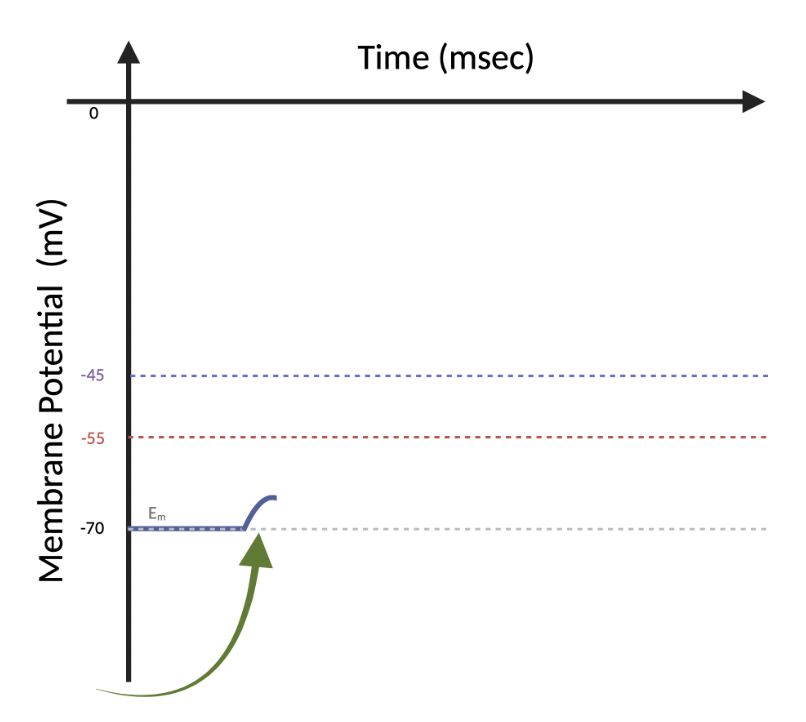
(6.4) Will this EPSP cause the neuron to fire an AP?
Yes
No
No
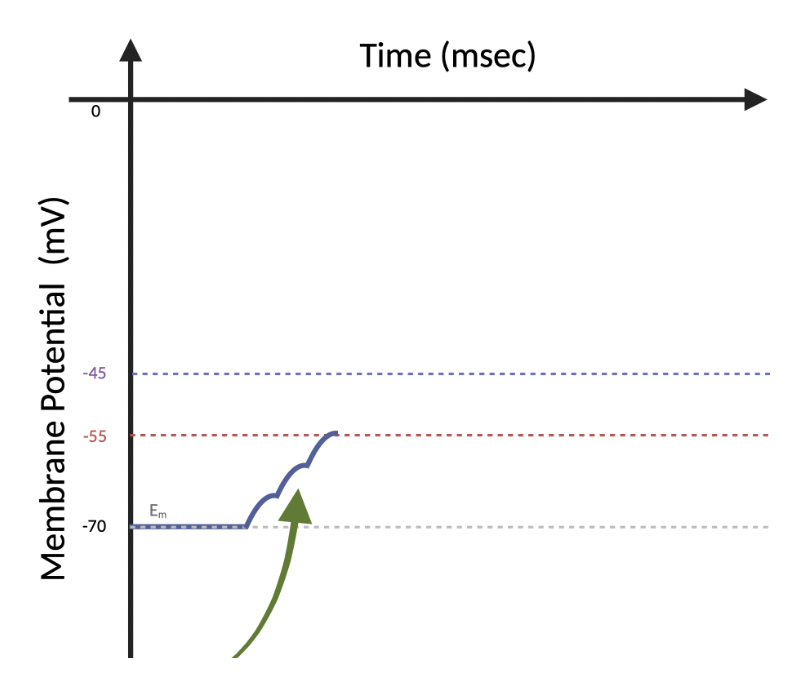
(6.4) Will these EPSPs cause the neuron to fire an AP?
Yes
No
Yes
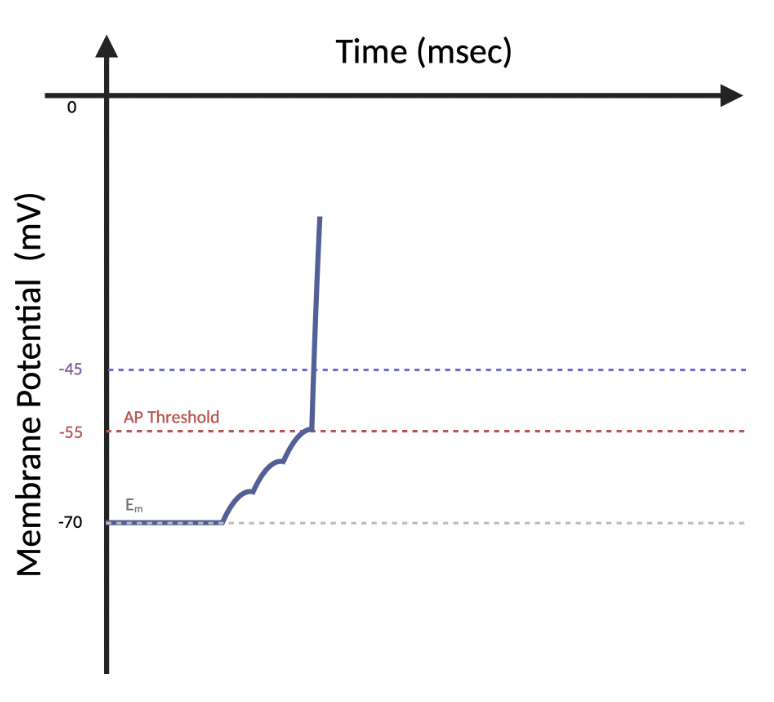
(6.4) At this timepoint, which ion has the greatest movement across the membrane?
Na+
K+
Na+
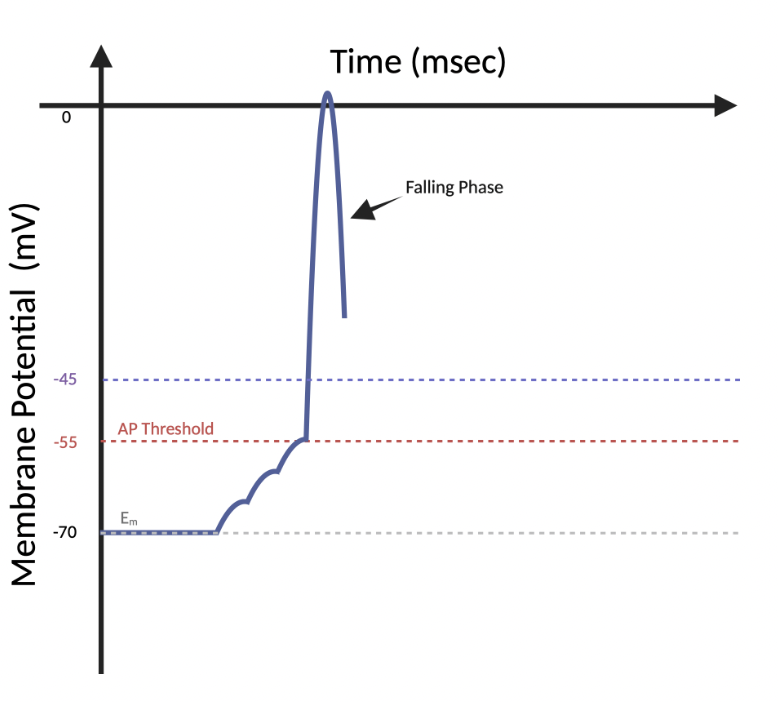
(6.4) At this timepoint, which ion has the greatest movement across the membrane?
Na+
K+
K+
(6.5) The relative refractory period is due to?
Na+ channels being inactivated
K+ channels being inactivated
Membrane potential being depolarized
Membrane potential being hyperpolarized
Membrane potential being hyperpolarized
(6.5) The absolute refractory period is due to?
Na+ channels being inactivated
K+ channels being inactivated
Membrane potential being depolarized
Membrane potential being hyperpolarized
Na+ channels being inactivated
(6.6) Where would you not expect to find Na+ or K+ voltage-gated channels?
Myelinated segments of the axon
The axon of an unmyelinated neuron
The axon hillock
The Nodes of Ranvier
Myelinated segments of the axon
(6.6) APs are passive processes where they are fired at the axon hillock and passively travel along the axon.
True
False
False
(7.1) Most synapses are formed between an axon and the______ for another neuron.
Axon Hillock
Cell Body
Dendrite
Synaptic Terminal
Dendrite
(7.1) What is not true about chemical synapses?
Release NTs
Uses gap junctions to communicate
Pre and postsynaptic cells do not touch
Are the majority of synapses in the nervous system
Uses gap junctions to communicate
(7.1) Electrical synapses are faster at signaling and more dynamic than chemical synapses.
True
False
False
(7.2) The protein complex used to fuse NT vesicles with the membrane are called:
SNARE
SNAPE
SNAP
SNAKE
SNARE
(7.2) Ca2+ ions flow into the presynaptic cell because:
NT bind to receptors
Voltage-gated channels are activated
Ion vesicles fuse with the membrane
The cell is hyperpolarized
Voltage-gated channels are activated
(7.2) How are NTs cleared from the synaptic cleft by degradation?
NTs are taken back into the cell
NTs drift out of the synaptic cleft
Receptors transport NTs into the postsynaptic cell
Enzymes break down free floating NTs in the synaptic cleft
Enzymes break down free floating NTs in the synaptic cleft
(7.3) NTs activate receptors by:
Binding to a ligand binding site
Depolarizing the membrane
Hyperpolarizing the membrane
Promoting gene expression
Binding to a ligand binding site
(7.3) What is different between ionotropic and GPCR receptors?
Respond to NTs
Have ligand binding sites
Can change membrane potential
Their signaling speeds are equal to each other
Their signaling speeds are equal to each other
(7.3) Why does GPCR activation have longer term effects on a cell?
They hyperpolarize the cell more than ionotropic receptors
They cannot change the membrane potential
They activate other proteins
They influence the cell more quickly than ionotropic receptors
They activate other proteins
(7.4) Inhibitory axons typically form synapses on the _______ of the postsynaptic neurons.
Axon
Cell Body
Dendrite
Synaptic Terminal
Cell Body
(7.4) _______ is the most common neurotransmitter in the brain and it is commonly associated with being an excitatory signal.
GABA
Glutamate
Dopamine
5-HT
Glutamate
(7.4) GABAA receptors are _______ receptors and they primarily ______.
Ionotropic, allow Cl- into the cell
GPCR, activate G proteins
Ionotropic, allow K+ out of the cell
GPCR, allow Na+ into the cell
Ionotropic, allow Cl- into the cell
(7.5) Which is not a reason why neuromodulator NTs are a major focus of research?
Their role in cognition
Association with neurological disorders
They are the most prevalent type of NT in the brain.
Their role in motor control
They are the most prevalent type of NT in the brain.
(7.5) Dopamine is produced:
All across the brain
In the cortex
In the thalamus
In the midbrain
In the midbrain
(8.1) Which of the following is the fastest route of administration?
Intravenous injection
Inhalation
Ingestion
Absorption
Intravenous injection
(8.1) Why do some drugs interact with the brain, while others do not?
If they are injected rather than ingested
If the veins are myelinated or not
If the substance is small enough
If it is a drug, rather than a medication
If the substance is small enough
(8.1) Antihistamines are a(n) _________ for histamine receptors.
Antagonist
Agonist
Protagonist
Opioid
Antagonist
(8.2) The primary NT used to communicate at the NMJ is:
Dopamine
Glutamate
GABA
Acetylcholine
Acetylcholine
(8.2) Botox influences NMJ signaling by:
Breaking down SNARE complex
Preventing NT vesicles from forming
Removing ACh receptors from the presynaptic cell
Blocking voltage-gated Ca2+ channels from opening
Breaking down SNARE complex
(8.2) Botulinum toxin is always toxic and has no clinical value.
True
False
False
(8.3) Organophosphates interact with signaling at the NMJ by:
Destroying the SNARE complex
Blocking ACh reuptake
Preventing ACh degradation
Breaking down the blood-brain barrier
Preventing ACh degradation
(8.3) Blocking ACh degradation results in:
Increased AP firing in the presynaptic cell
Uncontrollable activation of the postsynaptic cell
Blocking Ca2+ influx in the presynaptic cell
Complete inhibition of postsynaptic cells
Uncontrollable activation of the postsynaptic cell
(8.3) Atropine can counteract the effects of organophosphates by:
Stopping the postsynaptic cell from responding
Reducing the amount of ACh in the synaptic cleft
Reducing the amount of ACh released by the presynaptic cell
Inhibiting APs in the presynaptic cell
Stopping the postsynaptic cell from responding
(8.4) SSRIs influence the:
Reuptake of DA
Degradation of ACh
Diffusion of 5-HT
Reuptake of 5-HT
Reuptake of 5-HT
(8.4) According to the Serotonin Hypothesis, SSRIs help people with depression and anxiety disorder because:
They increase the amount of time 5-HT remains in the synaptic cleft.
They remove the number of 5-HT receptors in the postsynaptic cell, reducing postsynaptic response.
They block 5-HT degradation proteins.
They increase the amount of 5-HT released per NT vesicle.
They increase the amount of time 5-HT remains in the synaptic cleft.
(8.4) Which is not a reason for why SSRIs are being researched for their effectiveness of treating depression and anxiety disorders?
SSRIs do not work for everyone with depression and anxiety disorders.
It is poorly understood how the long-term effects of the medication result in behavioral changes
The short-term mechanism of SSRIs are poorly understood.
The Serotonin Hypothesis of depression disorders is being reevaluated.
The short-term mechanism of SSRIs are poorly understood.
(9.1) Opioids suppress pain by:
Activating natural pain suppression mechanisms.
Killing the cells that perceive the pain.
Breaking down the SNARE complex of pain receptors.
Inhibiting all sensory perception.
Activating natural pain suppression mechanisms.
(9.1) Opioid receptors are:
Naturally occurring substances produced by opium poppies
Illegal recreational drugs
Type of protein produced by the body
Synthetic drugs used as pain killers
Type of protein produced by the body
(9.1) Opioid medications used for clinical pain management have no side effects, whereas recreationally used opioids do have side effects.
True
False
False
(9.2) Endogenous opioids are released into the cleft in equal concentrations as opioid drug saturation.
True
False
False
(9.2) Removal of opioid receptors will only influence signaling for opioid drugs.
True
False
False
(9.2) The reason opioid receptors are removed from the membrane is because:
DA neurons influence the activity of the endogenous opioid producing cells.
The reuptake proteins are inactivated.
The presynaptic cell runs out of endogenous opioids.
The postsynaptic cell detects the over activation due to the high concentration.
The postsynaptic cell detects the over activation due to the high concentration.
(9.3) You would expect VTA cells to increase their activity when:
Receiving an expected reward.
Receiving an unexpected reward.
Experiencing hedonic pleasure.
Not receiving an expected reward.
Receiving an unexpected reward.
(9.3) Reward seeking behaviors are mediated by which receptors?
DA & Opioid
5-HT & Opioid
ACh & Glu
Glu & GABA
DA & Opioid
(9.3) In the NA, you would expect to find opioid receptors on the:
DA neuron
Postsynaptic neuron
Inhibitory interneuron
NMJ
Inhibitory interneuron
(9.4) The majority of fatal opioid ODs are due to?
Stroke
Asphyxiation
Neurotoxicity
Paralysis
Asphyxiation
(9.4) Naloxone works by:
Blocking opioids from binding to receptors
Increasing opioid reuptake
Forming an unbreakable bond with opioid degradation proteins
Breaking down the SNARE complex
Blocking opioids from binding to receptors